Abstract
Background
Health systems need constant changes and reforms in their structure to adapt to changing conditions and meet the needs of society. One of the fundamental changes in the health system of Iran is the health transformation plan (HTP), the effects of which must be examined from different aspects. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of HTP on the performance indicators of public hospitals in Yazd city, Iran.
Methods
This cross-sectional study was carried out in all public hospitals in city of Yazd. Six performance indicators were examined monthly and in two time periods of 12 months before and 12 months after the implementation of Health Transformation Plan (HTP). The data was analyzed by SPSS software program version 22, using the paired T-test, and the Interrupted Time Series (ITS) model.
Findings
Findings showed that the performance indicators of the studied hospitals have improved after the implementation of the HTP. According to the ITS model, the implementation of HTP did not have a significant effect on the level and trend of the bed rotation distance, average length of stay and the ratio of surgical operations to bed indicators. However, it had a statistically significant effect on the level and trend of mortality and hospitalization rates. Moreover, the implementation of HTP had a significant effect on the level of the bed occupancy rate, but did not have a significant effect on the trend of this indicator.
Conclusion
Based on the research findings, all the selected indicators changed to some extent after the implementation of HTP, which showed the effect of this plan on the performance of hospitals. However, not all indicators were statistically significant as the findings sub-section revealed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Over the past decades, several countries including Turkey, Thailand, China, South Korea, Ghana and Mexico have introduced reforms aimed at improving financial access to medical services and increasing quality and equity in the health system[1,2,3,4,5]. For example, in 2003, major reforms were implemented in the health system in Turkey, aiming to boost primary health care services, integrate health financing and reorganize the health system which were successful in improving health equity and access to health services for the underprivileged populations[6].
In Iran, several major health reforms have been implemented over the last four decades aiming to improve the health system performance[7,8,9,10,11,12]. These reforms include the formation of the Ministry of Health and Medical Education in 1985 to solve problems related to training and supplying of health workforces; establishment of vast District Health Network in 1985 to provide affordable primary health care services for the whole population especially in deprived regions and rural areas; establishment of Universal health Insurance Organization in 1994 to achieve universal health insurance coverage; and implementation of Family Physician Program in the rural areas in 2005 to organize health system [10,11,12,13,14,15,16].
Although these reforms made considerable achievements in the health system including improvement in public health indicators and increase in human resources and physical and financial resources, there were still several main problems such as high out-of-pocket payments, inequity in access to and utilization of health care services among different groups of the insured population, low quality of health services in the public health sector, and no health insurance coverage for a part of the population [10, 11, 17]. To address these chronic problems, in line with the changes implemented in other countries, the Ministry of Health and Medical Education of Iran, in order to achieve the vision of 2025, has designed a comprehensive transformation plan in the health system, so-called Health Transformation Plan (HTP), which has been implemented since May 5, 2014, and is now ongoing[18]. The HTP began with three approaches (financial protection for the patients, improving equity in access to health services, and improving the quality of services) consisting of seven programs[11, 19]. As a result of HTP, several main changes occurred in Iran, for instance, government spending on health increased unprecedentedly, health insurance coverage extended to all populations and about 11 million people were covered, medical tariffs were revised and about 1700 medical services were added into the basic benefit package, new hospitals and public health facilities were created in deprived regions, many hospitals and public health facilities were renovated, hospital beds increased, and more physicians and health workers, such as nurses and midwives were recruited in remote areas[11, 20]. Table 1 shows some the main demographic and health system indicators in Iran[10].
Table 2 also presents the number of hospitals in Iran affiliated with different organizations in 2018[10].
As a result of the above initiatives introduced in the health system, it is not surprising to see an increase in access and utilization of health care services soon after the implementation of HTP. The impact of HTP on different aspects of the Iranian health system has been studied by different studies over the last years. For instance, according to official statistics, the cost of out-of-pocket payments in Iran has been declining since the beginning of the health system transformation plan, from 58 % to 2011 to 49 % in 2013, 40 % in 2014, and finally 32.46 % in 2017[17, 21]. As such, the purpose of the HTP is to improve people’s health, reduce out-of-pocket payments and develop health indicators[22]. HTP increased access to outpatient and inpatient health care services, for instance in 2015 and for patients covered by the Iran Health Insurance Organization (one of the three main social health insurance funds in Iran) alone, utilization of inpatient services and average hospitalization costs increased by 6 % and by more than 73 % respectively during the years 2012-2016[17]. Several studies in Iran have been conducted to investigate whether the HTP has improved the hospital performance indicators especially in terms of using medical resources efficiently[23,24,25]. The most important functional indicators to measure the efficiency of hospitals are Bed Occupancy Rate (BOR), Bed Rotation Distance (BRD), Average Length of Stay (ALS), the ratio of surgeries to the bed, the rate of hospitalization per bed, and the mortality rate [26, 27].
Studies by Dadgar, Rezaei, Mousavi Rigi, Ghazizadeh, Yusefi, and Hashemian separately examined the effect of health transformation plan on performance indicators in different hospitals in Iran and concluded that the implementation of HTP has led to a significant increase in inpatient health services utilization and in turn in the performance indicators of hospitals[22, 26, 28,29,30,31]. Although several studies have been conducted in different parts of Iran regarding the impact of the implementation of HTP on the performance indicators of hospitals, so far no study has been done in this regard in public hospitals of Yazd Province. As a result of high-quality health services in Yazd city, Yazd health centers are considered as referral centers for patients from other provinces needing outpatient and inpatient health services. Many people from the southern and southeastern regions of Iran come to these hospitals for their health needs.
Yazd Province is located in the center of Iran. At the 2016 census, its population was about 1.138.000. Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences administers 13 public hospitals and over 90 clinics throughout the city and province of Yazd. There are also 8 other kinds of hospitals including private hospitals and hospitals affiliated with Social Security Organization, Islamic Azad University etc. There were 292 general physicians, 843 specialists, 1000 dentists, 130 pharmacists, and 680 nurses in Yazd province in 2017. The number of active hospital beds in the Yazd province in 2017 was 2664, of which 1671 beds were public. According to the report by the treatment deputy of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, more than 50 % of hospitalizations in Yazd province are from other provinces[32, 33]. So this study was conducted to investigate the effect of HTP on the level and trend of performance indicators of the public hospitals in Yazd city.
Methods
Selection of hospitals and performance indicators
The present study is analytical research using the interrupted time series method to investigate the impact of the implementation of HTP on the trend of changes in the performance indicators of public hospitals in the city of Yazd. There are ten hospitals in Yazd city, including four public hospitals, four private hospitals, one hospital affiliated with Social Security Organization as one of the main social basic health insurance schemes, and one hospital for Islamic Azad University. Three of these public hospitals are general (named Shahid Sadoughi, Rahnamoun, and Afshar) and one of them is a specialized hospital. These general hospitals are big and generally similar to each other. So we expected to see similar changes in these hospitals in the selected indicators. As HTP was implemented in the public health sector only, we chose these three hospitals for the purpose of the study. We focused on the hospital performance indicators especially in terms of efficiency including BOR, BRD, ALS, the ratio of surgeries to the bed, the rate of hospitalization per bed, and the mortality rate. We chose these indicators as they are collected routinely by the medical statistics units in the hospitals as the main indicators to measure efficiency in hospitals and we expected to see rapid changes in these indicators as a result of HTP implementation.
Data collection and duration of the study
Data related to hospital performance indicators were collected in the form of Excel sheets and on a monthly basis for the two periods of 12 months before (from April 21, 2013, to April 20, 2014) and 12 months after (from May 22, 2014, to May 21, 2015) the implementation of HTP. The process of data collection was done in 2019. Data were provided by the medical statistics and nursing units of studied hospitals and also by the deputy of treatment of the Yazd University of Medical Sciences. Data were analyzed by SPSS software version 22. We combined the data from the three hospitals for all the analyses.
Statistical methods
To check the difference in the annual average of each indicator for the year before and after the HTP, the paired t-test was applied. Then, using the interrupted time series analysis method, the data in the two periods before and after HTP were considered as an interrupted time series and the effects of the transformation plan on both the level of indicators and the trend of changes of the indicators after the plan were examined. In the interrupted time series model (ITS), two variables show the effect of a policy or intervention; the first one is the level which determines the immediate effect of the intervention and the second is the trend variable that indicates the long-term effect of the intervention. The passage of time in the present study refers to the months that have passed since the implementation of the HTP, in which we considered 12 months after the transformation plan in addition to 12 months before the plan (although May is not included in the analysis). ITS can reveal the probable changes (immediate and short-term changes) in the level of indicators at the beginning of the project, i.e. in the 13th month and also how the trend of each indicator has changed over time (month by month). To estimate the ITS model, according to the use of time-series data, first to prevent the false regression estimation of static data, the data of the indicators were examined using the root test of the Dickey-Fuller unit. Accordingly, the null hypothesis stating that there is a single root for all indicators is rejected (p <0.05) and the time series is static for all indicators. Then, for each of the indicators, the following regression pattern is estimated:
Y = β0 + β1T + β2X + β3XT + ε.
Y represents the value of each indicator per month. T, X, XT and ε indicate time, interference, the interaction of time and interference, and part of the error, respectively. Since the month of the intervention (here HTP), X1, is an imaginary variable, takes the value of 1 and before that the value of zero. β0, β1, β2, and β3 indicate a constant value, time trend without considering an intervention, immediate effects of the intervention on the level of selected indicators and continuous effect of the intervention on the trend of indicators, respectively.
Results
Here we present the findings of the study and the effect of HTP on the selected indicators according to the paired t-tests and ITS analysis. Table 3 shows that the total number of active beds for one of the hospitals, and the total number of hospitalizations, has increased during the first year after the implementation of the HTP.
Table 4 shows the results of running paired t-tests for comparing the mean of performance indicators in 12 months before and after the implementation of the HTP. According to the findings, the mean of “bed occupancy rate”, “hospitalization rate” and “the ratio of surgical operations to bed” has increased significantly (see p-values in Table 4) and at the same time “bed rotation distance”, “average patient stay” and “mortality rate” has decreased after the implementation of the transformation plan. All of these changes show that efficiency in using the beds has increased after the HTP.
Table 5 shows the results of the interrupted time series analysis for the performance indicators of the studied hospitals. According to Table 5, the coefficient of the level indicates the immediate effect of the HTP on each indicator, and the coefficient of the trend indicates the continuous effect of the HTP on the trend of each of the indicators. According to the ITS test, the HTP had an immediate effect on increasing the level of the number of hospitalizations and bed occupancy rate but the trend of bed occupancy rate had a declining slope (β3= - 0.006) over time. According to the ITS analysis, mortality rate decreased after the HTP but experienced an increasing slope over time. ITS did not show significant difference for the level and trend of other indicators including bed rotation distance, average length of stay at hospital, and the ratio of surgical operations to bed. The trend of changes in the all indicators over time is shown in Fig. 1.
Discussion
The findings showed that the number of hospitalizations increased after the implementation of the HTP, although this was not statistically significant. Another study by Ghazizadeh also confirmed the positive nature of the HTP and the increase in the number of hospitalizations in East Azerbaijan, Iran[26]. The reason for this increase can be attributed to the goals of the HTP, including reducing patients’ out-of-pocket payments and financially protecting patients against expensive and hard-to-cure diseases and also extending the free health insurance coverage for groups of population without coverage[29]. According to the Ministry of Health and Medical Education, just within the first year after the implementation of the HTP, patients coinsurance rates decreased from 37 to 4.5 % on average for the inpatient health services in the public health sector, which in turn increases people’s access to health services, especially for the poor. This led to an increase in hospital admissions[26]. Shen et al. examined the effects of the health transformation plan on the performance of hospitals in China from 2001 to 2005 and concluded that the new health reform policy had positive effects on reducing patients’ economic burden [34].
Study showed the bed rotation distance after the implementation of the transformation plan has been decreasing. In a study by Faridfar and et al., they concluded that HTP had a growing positive impact on hospital productivity [35]. The reason can be attributed to the increase of hospitalizations and also bed occupancy rate after the implementation of the HTP (46). Additionally, according to Hashemian’s study, the average of this indicator in university centers of Isfahan province has increased from 70.2 times in 2012 to 71.2 in 2013, 73.9 in 2014 and 76.4 times in 2015[31].
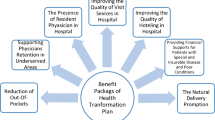
ITS analysis also showed that as a result of HTP, the bed occupancy rate increased, but the trend or slope of the indicator has decreased over time. Rezaei also confirmed the positive implementation of the HTP and the increase of this indicator in Hamedan’s hospitals, Iran [22]. Yasar also showed that the implementation of the transformation plan in the Turkish health system has increased hospital bed occupancy rate [22]. The following reasons could have been influencing in increasing the bed occupancy indicator including: reducing patient payments, retaining physicians in disadvantaged areas, the presence of specialist physicians in public hospitals, improving the quality of hospital services, improving hospital hoteling services, and financial protection against high health care expenditures[36] (49). According to Yusefi’s study, the average of this indicator in public hospitals in Shiraz, Iran, has increased by 8 % and increased from 72.7 % (2013) to 80.55 % (2015) [30]. Similar studies by Rezaei, Dadgar, Zarei, and Yusefi also revealed the same results [22, 23, 29, 30].
The ratio of surgeries to bed has increased significantly after the implementation of the HTP. This increase indicates that the treatment of patients who needed surgery was performed on time by specialist physicians present at the hospitals. Moreover, increasing the quality of hospital visits and hoteling services after the implementation of HTP can justify this increase[22]. In a study that examined the program of the HTP in Turkey, the effect of the plan on increasing the number of surgeries was significant[37]. Additionally, according to Yusefi’s study, the average monthly number of emergency surgeries in public hospitals in Shiraz has reached from 189.18 (2013) to 208.43 (2015) and at the same time the average of elective surgeries increased from 517.95 to 637.71 [30].
According to the findings, the HTP increased the average length of stay of the patients in hospitals, although it was not statistically significant. This finding is inconsistent with the results of Rezaei’s study carried out in Hamadan hospitals [22]. Numerous studies in Isfahan hospitals have shown that this plan has increased the length of stay of patients. This led to a lack of beds for other patients. One of the reasons for the increase in the length of stay in Lorestan hospitals after the HTP was the increase in the number of expensive and more complicated surgeries, which required longer stay in hospital [29]. Moreover, according to Hashemian’s study, the average patient stay for all hospitals studied between 2012 and 2015 was 2.8, 3, 2.8 and 2.9, respectively [31].
In the present study, the mortality rate has significantly decreased after the implementation of the health transformation plan. Of course, it should be noted that various factors such as time, place, the number and experience of health workers, the sufficiency and quality of medical equipment and supplies and etc. can affect the mortality rate and one cannot judge the performance of hospitals just base on the number of deaths [38].
Limitations of the study
We just investigated the effect of HTP as the main intervention on the hospital performance indicators, while there may be other factors affecting the trend of hospital indicators which have not been taken into account in this research. Another limitation was that we just focused on data from three public hospitals in Yazd city and excluded other public and private hospitals in the whole of Yazd province which limits comparing the changes of studied indicators in these hospitals. We also combined the data for all three hospitals for analysis which ignores the probable heterogeneity among the studied hospitals which can limit the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusions
Based on the research findings, all the selected indicators changed to some extent after the implementation of HTP, which showed the effect of this plan on the performance of the hospitals. However, not all indicators were statistically significant as the findings sub-section revealed. Improvement of the hospitals’ performance indicators as a result of HTP’ initiatives indicates indirectly that HTP has increased the access of people to the health care services. This might have increased equity in health services utilization by improving the access of those people who suffered from lack of health insurance coverage or had to face high coinsurance and copayment rates for using health services in hospitals. It is necessary to investigate the effects of HTP on the performance of other kinds of hospitals such as private hospitals and also the utilization of health care services by different groups of population. Such investigations can help policy makers to make necessary modifications in the programs in order to make them more accessible.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are not publicly available as it is not allowed by the Research Deputy of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- HTP:
-
health transformation plan
- BOR:
-
Bed Occupancy Rate
- BRD:
-
Bed Rotation Distance
- ALS:
-
Average Length of Stay
References
Yildirim HH. 15 years of AK Party rule: An evaluation in terms of health and health policies. Insight Turkey. 2017;19(2):167–88.
Tangcharoensathien V, Suphanchaimat R, Thammatacharee N, Patcharanarumol W. Thailand’s universal health coverage scheme. Economic and Political Weekly. 2012:53–7.
Pannarunothai S, Patmasiriwat D, Srithamrongsawat S. Universal health coverage in Thailand: ideas for reform and policy struggling. Health Policy. 2004;68(1):17–30.
Tangcharoensathien V, Limwattananon S, Patcharanarumol W, Thammatacharee J. Monitoring and evaluating progress towards universal health coverage in Thailand. PLoS Medicine. 2014;11(9):e1001726.
Na S, Kwon S. Building systems for universal health coverage in South Korea. 2015.
Atun R, Aydın S, Chakraborty S, Sümer S, Aran M, Gürol I, et al. Universal health coverage in Turkey: enhancement of equity. The Lancet. 2013;382(9886):65–99.
MAJDZADEH R, Delavari A, Rajabi F, Khatibzadeh S, Esmailzadeh H, BAGHERI LK. Iran’s health innovation and science development plan by 2025. Iranian Journal Of Public Health. 2009;38(1):13–6.
Zare H, Trujillo AJ, Driessen J, Ghasemi M, Gallego G. Health inequalities and development plans in Iran; an analysis of the past three decades (1984–2010). Int J Equity Health. 2014;13(1):1–12.
Mehrdad R. Health system in Iran. JMAJ. 2009;52(1):69–73.
Doshmangir L, Bazyar M, Majdzadeh R, Takian A. So near, so far: four decades of health policy reforms in Iran, achievements and challenges. Arch Iran Med. 2019;22(10):592–605.
Doshmangir L, Bazyar M, Rashidian A, Gordeev VS. Iran health insurance system in transition: equity concerns and steps to achieve universal health coverage. Int J Equity Health. 2021;20(1):1–14.
Shadpour K. Primary health care networks in the Islamic Republic of Iran. EMHJ-Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, 6 (4), 822-825, 2000. 2000:822-5.
Malekafzali H. Primary health care in the rural area of the Islamic Republic of Iran. Iran J Public Health. 2009;38(Suppl 1):69–70.
Gooshki ES, Pourabbasi A, Akbari H, Rezaei N, Kheradmand AA, Kheiry Z, et al. Internationalization of medical education in Iran: A way towards implementation of the plans of development and innovation in medical education. Journal of Advances in Medical Education Professionalism. 2018;6(1):43–8.
Dehnavieh R, Rahimi H. Basic health insurance package in Iran: revision challenges. Iranian journal of public health. 2017;46(5):719–20.
Ibrahimipour H, Maleki M-R, Brown R, Gohari M, Karimi I, Dehnavieh R. A qualitative study of the difficulties in reaching sustainable universal health insurance coverage in Iran. Health policy planning. 2011;26(6):485–95.
Doshmangir L, Bazyar M, Najafi B, Haghparast-Bidgoli H. Health financing consequences of implementing health transformation plan in Iran: achievements and challenges. International journal of health policy management. 2019;8(6):384.
Emamgholipour S, Jaafaripooyan E, Mohammadshahi M, Mohammadi Yazani E. The effect of Health Sector Evolution Plan on the performance indices of emergency department in hospitals of Tehran & Iran universities of medical sciences: interrupted time series analysis. Iran J Emerg Med. 2018;5(9):1–8.
Harirchi I, Hajiaghajani M, Sayari A, Dinarvand R, Sajadi HS, Mahdavi M, et al. How health transformation plan was designed and implemented in the Islamic Republic of Iran? International journal of preventive medicine. 2020;11.
Moradi-Lakeh M, Vosoogh-Moghaddam A. Health sector evolution plan in Iran; equity and sustainability concerns. International journal of health policy management. 2015;4(10):637.
Piroozi B, Rashidian A, Moradi G, Takian A, Ghasri H, Ghadimi T. Out-of-pocket and informal payment before and after the health transformation plan in Iran: evidence from hospitals located in Kurdistan. Iran International journal of health policy management. 2017;6(10):573.
Rezaei S, RAHIMI FA, Arab M, Jaafaripooyan E. Effects of the new health reform plan on the performance indicators of Hamedan university hospitals. Journal of School of Public Health Institute of Public Health Research. 2016;14(2):51–60.
Zarei E, Anisi S. Hospital performance indicators: before and after of implementing health sector evolution plan in Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences. Pajoohandeh Journal. 2016;21(5):263–71.
Hosseini SE, Ebrahimipour H, Badiee S, Haghighi H, Mahmoudian P, Vafaee-Najar A. Performance evaluation of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences’ hospitals during 2006-2011: Application of pabon lasso model. Jentashapir Journal of Health Research. 2016;7(4).
Mosavirigi S, Mahrami M, Montazerolfarag R, Dehghanitafti A, Dorahaki M, Barati O. Reviews and comparisons of hospital performance indicators before and after the implementation of the healthcare reform package design therapeutic hospitals of Bushehr University of Medical Sciences. Tolooebehdasht. 2017;15(6):107–19.
Ghazizadeh J, Partovi Y, Alidoost S, Kavakebi N. Performance indicators of hospitals affiliated to Health Network in East Azerbaijan before and after health reform. Payesh. 2018;17(3):217–26.
Pabon Lasso H. Evaluating hospital performance through simultaneous application of several indicators. Bulletin of the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO); 20 (4), 1986. 1986;20(4):341-57.
Mousavi Sj, Mohadesi H, Farhad N, Fathi A. Evaluating satisfaction level among in-patientsabout the health system evolution program in affiliated hospitals of urmia university of medical sciences. Journal Of Urmia Nursing Midwifery Faculty. 2016;14(7):601–10.
Dadgar R, Mahmoudi G. The impact of health system reform plan on the hospital’s performance indicators of Lorestan University of Medical Sciences. Yafte. 2017;19(2):93–102.
Yusefi AR, Bastani P, Bordbar S, Sadeghi A, Hesami SZ. The effects of health transformation plan implementation on the performance indicators of public hospitals. Health Scope. 2018;7(S).
Hashemian M, Ferdosi M. Efficiency evaluation and comparison of Isfahan provinces hospitals before and after the reform in health system using the Pabon Lasso Model (1391-1394). scientific journal of ilam university of medical sciences. 2017;25(3):186–200.
Www.ssu.ac.ir.
Shen JJ, Zhou S, Xu L, Chen J, Cochran CR, Fisher ER. Effects of the new health care reform on hospital performance in china: A seven-year Trend from 2005 to 2011. Journal of Health Care Finance. 2014;41(1).
Faridfar N, Alimohammadzadeh K, Seyedin SH. The impact of health system reform on clinical, paraclinical and surgical indicators as well as patients’satisfaction in rasoul-e-akram hospital in 2013 to 2014. Razi Journal Of Medical Sciences (Journal Of Iran University Of Medical Sciences). 016;22(140):92-9.
Heydarian N. The Impact of Healthcare Reform Plan to Pay Out of Pocket Patients in Public Hospitals of Isfahan. journal of medical council of islamic republic of iran. 2015;33(3):187–94.
Sahin I, Ozcan YA, Ozgen H. Assessment of hospital efficiency under health transformation program in Turkey. CEJOR. 2011;19(1):19–37.
Sadeghifar J, Ashrafrezaee N, Hamouzadeh P, Taghavi Shahri M, Shams L. Relationship between performance indicators and hospital evaluation score at hospitals affiliated to Urmia University of Medical Sciences. Nursing Midwifery Journal. 2011;9(4):270–6.
Acknowledgements
This paper has been extracted from the MSc research thesis of Shahid Sadoughi University of medical sciences.
Funding
We are grateful to Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences that supported the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MR, HJ, MB, MP and VP designed the research; MR and VP conducted it; VP and MB extracted the data; MP and MB analyzed data: MR, HJ, MB, MP and VP prepared the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This research was approved by the ethics committee of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences in Yazd based on the approval of IR.SSU.SPH.REC.1397.136 on 2/2/2019. Administrative permissions to access to the hospital databases for the purposes of the study were required by the formal request from the Research Deputy of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjbar, M., Bazyar, M., Jafari, H. et al. Investigating the effect of health transformation plan on the public hospitals performance indicators; a case study from Iran. BMC Health Serv Res 21, 1133 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-07164-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-07164-y