Abstract
Background
Early sexual initiation is one of the risky sexual practices. Early sexual beginning is associated with an increased risk of HIV/AIDS, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), unexpected pregnancies, unsafe abortion, premature deliveries, and psychosocial issues. However, there is still a lack of evidence, particularly in East Africa, where community-level factors are not investigated. Therefore, this study aimed to estimate the pooled prevalence and to identify associated factors of early sexual initiation among female youth in Eastern Africa.
Methods
A total weighted sample of 49,716 female youth was included in this analysis. STATA version 14 software was used for data extraction, recoding, and analysis. A multilevel binary logistic regression model was fitted to identify determinants of early sexual initiation in the region. Finally, Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR) with a 95% Confidence Interval (CI) was reported to declare the factors that are significantly associated with early sexual initiation.
Result
The prevalence of early sexual initiation in East Africa was 21.14% [95% CI: 20.00%, 21.50%]. In the multivariable multilevel analysis; being age 20–24 years [AOR = 0.65: 95% CI; 0.61, 0.69], primary [AOR = 0.73: 95% CI; 0.67, 0.78], secondary &above education [AOR = 0.30: 95% CI; 0.27,0.33], married [AOR = 1.85: 95% CI; 1.73,1.97], middle wealth [AOR = 0.78: 95% CI; 0.72,0.84], richest [AOR = 0.74: 95% CI; 0.68,0.80], and reading newspaper [AOR 0.77: 95% CI;0.71,0.83] were significantly associated with early sexual initiation.
Conclusion
The study revealed that early sexual initiation among female youth was high in East Africa. Educational status, respondent age, marital status, wealth index, age at first cohabitation, contraceptive use, reading newspaper, and place of residence were associated with early sexual initiation. Therefore, the survey findings will help policymakers, as well as governmental and non-governmental organizations, design the most effective interventions. Moreover, strengthening information, education, and wealth status are important intervention areas to delay the age of early sexual debut.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Early sexual initiation is defined as an experience of first intercourse before 15 years of age [1,2,3]. According to evidence, youth who engage in early sexual intercourse, are exposed to multiple sexual partners, and use incorrect or irregular condoms are at risk of HIV/AIDS, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), unexpected pregnancies, unsafe abortion, early births, and psychosocial problems. [4,5,6].Early sexual initiation exposes young people to a variety of sexual and reproductive health issues [7, 8]. Female youth, in particular, are exposed to pregnancy and childbirth difficulties (such as fistula or even death), which are exacerbated by physiological immaturity to engage in sexual intercourse and give birth [9,10,11].
Early sexual activity is still a persistent issue with harmful psychological and health consequences. The age at sexual debut differs from country to country and individual, and is influenced by a variety of circumstances [12,13,14]. Early sexual debut among youths is influenced by a variety of factors, including:-Age, residence, religion, educational status, viewing pornographic, alcohol drinking, khat chewing, media content and social/religious ceremonies were the factors associated with early sexual initiation [15,16,17,18,19]. Furthermore, wealth index, media exposure, employment status, comprehensive HIV knowledge, and age at first marriage are all factors that contribute to an early sexual debut [2, 20,21,22].
According to data from developing-country demographic health surveys, approximately 10% of young girls became mothers at the age of 16, with the majority coming from Sub-Saharan Africa, South Central and South-Eastern Asia [2, 23]. According to studies conducted in various parts of the world, the prevalence of early sexual debut 9.8% in Malaysia [24], 18.1% in China [25], and 58.6% in Caribbean Countries [26]. Besides, early sexual debuts are common in African settings, ranging from 26.8% in Nigeria [27] to 55% in Ghana [28]. Despite studies on the prevalence and associated factors of early sexual initiation have been undertaken in various east African countries [1, 2, 29, 30], there is limited evidence on the region's pooled prevalence and associated factors of early sexual beginning. Although various studies on early sexual initiation have been conducted, the majority of them have failed to take into account community-level factors that may influence the possibility of early sexual initiation.
Therefore, this study aimed to estimate the pooled prevalence and to identify associated factors of early sexual initiation in East Africa based on the pooled nationally representative Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS). As a result, the findings of this study could assist policymakers, as well as governmental and non-governmental organizations, in developing programs and interventions addressing early sexual debut and related consequences.
Methods
Data source and participants
The Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) data were pooled from the 12 East African countries from 2008 to 2018 (Burundi, Ethiopia, Comoros, Uganda, Rwanda, Tanzania, Mozambique, Madagascar, Zimbabwe, Kenya, Zambia, and Malawi). Mayotte, Reunion, South Sudan, Djibouti, Seychelles, and Mauritius were removed due to a lack of DHS history. Furthermore, Eritrea and Sudan were not included due to the long period since their last DHS. It was carried out on the basis of a two-stage stratified sampling process. In the first stage, Enumeration Areas (EAs) were assigned at random to their respective clusters. In the second stage, households were selected. The source population were all-female youth (15–24 years old) irrespective of their sexual activity across the east African countries whereas the study populations were all-female youth (15–24 years old) irrespective of their sexual activity in the survey period in the selected Enumeration Areas (EA). The detailed sampling procedure was presented in the full DHS report. A total of 49,716 weighted female youth who have ever experienced sexual intercourse were considered for this analysis.
Variables of study
In this study, the outcome variable was (early sexual initiation) dichotomized as (Yes/No). Youth who initiated sexual intercourse before the age of 15 years were considered as those experienced an “early sexual initiation [31]. If youth were initiated sexual intercourse before the age of 15 years coded as “1”, otherwise coded as “0”.
Individual and community-level variables were considered as independent variables in this study. Individual-level factors include respondent age, marital status, literacy, contraceptive use, educational status, wealth index, media exposure, employment status, and age at first marriage. The community-level factors were residence and country.
Data management and statistical analysis
STATA version 14 software was used for data extraction, recoding, and analysis. To restore the data's representativeness and produce a reliable estimate and standard error, the data were weighted. A multilevel logistic regression analysis was employed since the hierarchical structure of the DHS data contradicts the independent assumptions of the ordinary logistic regression model. Whether there was clustering, the Interclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) and Median Odds Ratio (MOR) were calculated. The null model (without explanatory variables), model I (with individual-level factors), model II (with community-level factors), and model III (with both individual and community-level factors at same time) were used in this analysis. Models were compared using deviance (-2LL), and the best-fitted model was selected as the one with the lowest deviance. In the bi-variable analysis, variables having a p-value of 0.25 were considered for multivariable analysis. Finally, factors having a P-value of 0.05 were considered a significant factor associated with early sexual initiation in the multivariable analysis.
Results
Socio-demographic characteristics
A total of 49,716 female youth were included in this study. Among this, 38,273 (76.98%) were rural residents, and more than half (80.68%) were between the ages of 20–24 years. The majority of the study participants were from Kenya, Malawi, Burundi, and Uganda. About 57.86% had completed primary school, and 47.56% came from poor families. More than half of the youth (61.24%) were unmarried, and 59.00% did not use any form of contraception (Table 1).
Prevalence of early sexual initiation in East Africa
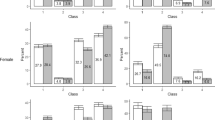
The pooled prevalence of early sexual initiation in East Africa was 21.14% [95% CI: 20.00%, 21.50%] with the highest early sexual initiation in Mozambique (35.72%) and the lowest early sexual initiation in Rwanda (3.53%) (Fig. 1).
Factors associated with early sexual initiation in East Africa
Random effect (measures of variations) results
The ICC value in the null model was 0.18, implying that about 18% of the total variation in female youth sexual initiation was due to the clustering effect, while the remaining 82% variation in sexual initiation was due to between-individual variability. Besides that, the MOR value was 2.25 (95% CI: 2.17, 2.36), indicating that early sexual initiation varied significantly between clusters. The final model (Model III) suited the best in terms of model fitness because it had the highest log likelihood and lowest deviance.
Multi-level fixed effects (measures of associations) analysis
In the multivariable multilevel binary logistic regression analysis age of respondent, educational status, marital status, wealth status, age at first cohabitation, contraceptive use, reading newspaper, residence, and country were found to be statistically associated with early sexual initiation.
In this study, the odds of early sexual initiation were 35% less likely among youth aged 20–24 years (AOR = 0.65, 95% CI: 0.61, 0.69) than among youth aged 15–19 years. Youth who attained primary and secondary &above education had decreased the odds of early sexual initiation by 27% (AOR = 0.73, 95% CI: 0.67, 0.78) and 70% (AOR = 0.30, 95% CI: 0.27, 0.33) than youth who had no formal education respectively. Married youth had 85% (AOR = 1.85, 95% CI: 1.73, 1.97) higher odds of early sexual initiation as compared with unmarried youth. The odds of early sexual initiation among youth in the middle and richest households were reduced by 22% (AOR = 0.78, 95% CI: 0.72–0.84) and 26% (AOR = 0.74, 95% CI: 0.68–0.80), respectively, compared to youth in the poorest household. When compared to those who did not read the newspaper, youth who read the newspaper were 23% less likely to have early sexual initiation (AOR 0.77, 95% CI 0.71–0.83).Youth who used contraceptives had 1.19 times [AOR = 1.19; 95% CI: 1.28, 1.55] higher odds of early sexual initiation as compared to their counterparts. Youth who began first cohabitation at the ages of less than 15 years and 15–19 years were 13 times (AOR = 13; 95% CI: 11.94 -15) and 1.37 times (AOR = 1.37; 95% CI: 1.23–1.53) more likely to experience early sexual initiation than those who began cohabitation at the ages of 20–24 years, respectively.
Regarding to place of residence youth from urban resident had 16% more likely (AOR = 1.16, 95% CI: 1.07, 1.26) early sexual initiation than rural resident. Furthermore, youth who live in Kenya, Comoros, Madagascar, Malawi, Mozambique, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia were 7.6 (AOR = 7.6; 95% CI: 5.66–10.14), 7.5(AOR = 7.5; 95% CI: 5.45–10.44), 9.9 (AOR = 9.9; 95% CI: 7.40–13.29), 6.3 (AOR = 6.4; 95% CI: 4.66–8.37), 17 (AOR = 17; 95% CI: 12.78–22.96), 7.7 (AOR = 7.7; 95% CI: 5.67–10.31), 9.4 (AOR = 9.4; 95% CI: 6.99–12.49), 7.3 (AOR = 9.4; 95% CI: 5.43–9.83), and 7.3 (AOR = 9.4; 95% CI: 5.43–9.83), times higher odds of early sexual initiation than Rwanda respectively (Table 2).
Discussion
This study aimed to assess the pooled prevalence and associated factors of early sexual debut in east Africa using the recent demographic and health survey data. The pooled prevalence of female youth East African countries was 21.14% [95% CI: 20.00%, 21.50%] with the highest prevalence in Mozambique (35.72%) and the lowest prevalence in Rwanda (3.53%). The finding was higher than previous studies conducted in South Africa (8.9%) [32], Peru (17.1%) [33] sub-Saharan Africa [1], Ethiopia (17.9%) [34], Caribbean countries [35]. This could be the period when trends in globalization and new technologies are having a growing impact on young female sexual health. Furthermore, we used a large sample size and included people from a wide range of sociocultural and socioeconomic backgrounds.
In the multilevel multivariable logistic regression analysis age, educational level, marital status, wealth status, age at first cohabitation, contraceptive use, newspaper reading, residence, and living countries were determinants of early sexual initiation in the East Africa Countries.
The odds of early sexual initiation were less likely among female aged 20–24 years than among female aged 15–19 years, which consistent with study in Africa [12, 36,37,38]. This could be due to cultural behaviors such as early marriage and abduction, which were popular at the time. Furthermore, the disparity between the two age-group cohorts may be attributed to the demise of youth-friendly health services.
As the level of education increases, the likelihood of experiencing early sexual initiation decreases. The result was supported by previous studies [39,40,41]. The possible explanation is that when youth have a better educational level, they are more aware of the potential problems associated with early sexual intercourse and may prevent themselves from involvement. Besides that, education may result in changes in behaviors that reduce possible risks such as substance use, which may expose them to early sexual initiation.
Being married had higher odds of early sexual initiation than youth who were not in a union. This finding was supported by a studies done in Africa [39, 42, 43]. This could be engaged in early marriage before the age of 15 years, which is a potential situation for female to experience sexual activity at an early age.
Female youth from middle and high-income households were less likely to participate in early sex than youth from lower-income households. This is consistent with the study conducted in Africa [28, 39, 44]. This might be females from low-income families may participate in earlier sexual relations to obtain money and other benefits, whereas rich people have good health-seeking behavior, awareness of lifestyle determinants, and family traits.
Youth who started their first cohabitation at the ages of less than 15 years and 15–19 years were more likely to have early sexual initiation than those who started cohabitation at the ages of 20–24 years, respectively this finding was supported by study in Ghana [38].This study found that youth females who used contraception had a higher risk of early sexual debut than their counterparts, which is consistent with other studies in Africa [2]. This could be because young people who take contraception are less likely to become pregnant and have more confidence to begin sexual activity at a young age.
Young girls who read newspapers or magazines are less likely to engage in sexual intercourse at a young age, which is in line with previous findings [2, 45,46,47]. This could be because participants who read newspapers are more likely to be aware of the risks of early sexual initiation.
Furthermore, youth from rural areas had a lower likelihood of early sexual initiation compared to urban youth; this finding was consistent with previous studies [48,49,50]. This could be attributed to urban females being exposed to alcohol, substances, and pornographic materials, which leads to an early sexual debut. Pornographic media can arouse emotional and physiological desire for sex, pushing the girl to put what she has seen to the test, leading to early sexual practice [47, 51].
In East African countries, country residency has a significant impact on early sexual initiation. Rwanda was selected as a reference for its low percentage of early sexual beginning. This could be ascribed to altering conventional norms as a result of globalization, which causes changes in socio-demographic characteristics such as religion, media exposure, education, and youths people's socioeconomic situation [52,53,54]. This difference could be the reason why young females' sexual debuts differ across the country.
Strength and limitation of the study
As strength, weighted nationally representative data from 12 eastern African countries with a substantial sample size were used in the study. Besides, the study was based on an advanced (multilevel) model, by taking into account the clustering effect, to get reliable standard error and estimate. However, this study had certain limitations. First, because the data came from a cross-sectional survey, no causal conclusions regarding whether characteristics connected with early sexual initiation could be drawn. Second, because females tend to under-report sexual behavior, data obtained from self-reported sexual behaviors may be skewed or misleading.
Conclusion
This study showed that early sexual initiation was high among female youth in East Africa. Country, urban residence, age at first cohabitation, married marital status, and contraceptive use was positively associated with early sexual initiation. Whereas, educational status, age group 20–24 years, newspaper reading, middle and rich wealth status was negatively associated with early sexual initiation. Therefore, the survey findings will help policymakers, as well as governmental and non-governmental organizations, design the most effective interventions. Moreover, strengthening information, education, and wealth status are important intervention areas to delay the age of early sexual debut. Besides, African countries should develop an integrated strategy for improving preventing early sexual initiation among youth with low socioeconomic level.
Availability of data and materials
Data we used for this study are publicly available in the MEASURE DHS program and you can access it from www.measuredhs.com after explaining the objectives of the study. Then after receiving the authorization letter, the data is accessible and freely downloaded.
Abbreviations
- AOR:
-
Adjusted odds ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- DHS:
-
Demographic and health survey
- ICC:
-
Intra class correlation coefficient
- LLR:
-
Log-likelihood ratio
- MOR:
-
Median odds ratio
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- PVC:
-
Proportional change in variance
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Seff I, Steiner JJ, Stark L. Early sexual debut: a multi-country, sex-stratified analysis in sub-Saharan Africa. Glob Public Health. 2021;16(7):1046–56.
Abate BB, Kassie AM, Kassaw MW. Prevalence and determinants of early initiation of sexual intercourse among youth girls in Ethiopia. J Pediatr Nurs. 2020;55(20):e305–12.
Berhan Y, Hailu D, Alano A. Predictors of sexual-risk behaviour and HIV-preventive practices among university students in Ethiopia. Afr J AIDS Res. 2011;10(3):225–34.
Muchiri E, Odimegwu C. Trends and gender differences in age at sex debut among adolescents and young adults in urban cape area, South Africa. Afr Health Sci. 2019;19(4):2964–72.
Seff I, Steiner JJ, Stark L. Early sexual debut: a multi-country, sex-stratified analysis in sub-Saharan Africa. Glob Public Health. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1080/17441692.2020.1814833.
Bearinger LH, Sieving RE, Ferguson J, Sharma V. Global perspectives on the sexual and reproductive health of adolescents: patterns, prevention, and potential. Lancet. 2007;369(9568):1220–31.
Yosef T, Nigussie T, Getachew D, Tesfaye M. Prevalence and factors associated with early sexual initiation among college students in Southwest Ethiopia. Angelillo IF, editor. Biomed Res Int. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8855276
Kassahun EA, Gelagay AA, Muche AA, Dessie AA, Kassie BA. Factors associated with early sexual initiation among preparatory and high school youths in Woldia town, northeast Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):378. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-6682-8.
Temmerman M, Khosla R, Say L. Sexual and reproductive health and rights: a global development, health, and human rights priority. Lancet. 2014;384(9941):30–1.
WHO. Sexual and Reproductive Health |WHO| Regional Office for Africa.
Mekonnen BD. Early sexual debut and associated factors among students in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Public health Res. 2020;9(3):1795.
Desalegn Z, Id W. Sexual behaviors and associated factors among youths in Nekemte town , East Wollega , Oromia , Ethiopia : A cross-sectional study. 2019;1–10.
Shayo FK, Kalomo MH. Prevalence and correlates of sexual intercourse among sexually active in-school adolescents: An analysis of five sub-Sahara African countries for the adolescent’s sexual health policy implications. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):1–8.
Zoakah AI. Exploring the factors influencing adolescent sexual behavior in plateau state Nigeria. Am J Med Med Sci. 2017;2017(1):1–6.
Adongo BW. Assessing factors influencing early sexual initiation among adolescents (13 to 19 Years) in Ghana: a qualitative study. Int J Caring Sci. 2018;11(1):53–60.
Arega WL, Zewale TA, Bogale KA. Premarital sexual practice and associated factors among high school youths in Debretabor town, South Gondar zone, North West Ethiopia, 2017. BMC Res Notes. 2019;12(1):314. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-019-4348-3.
Bizuneh H. Correlates of sexual initiation among adolescent and youth in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia : a community based cross sectional study. 2019.
Yibrehu MS, Mbwele B. Parent - adolescent communication on sexual and reproductive health: the qualitative evidences from parents and students of Addis Ababa Ethiopia. Reprod Health. 2020;17(1):78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-020-00927-6.
Tuoyire DA. Timing of sexual debut among unmarried youths aged 15–24 years in sub-Saharan Africa. J Biosoc Sci. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021932017000098.
Ayalew A, Abreha K. Magnitude and predictors of early sexual debut among high and preparatory school students in Northern Ethiopia: a school-based crosssectional study. J Heal Educ Res Dev. 2015. https://doi.org/10.4172/2380-5439.1000151.
Molla M, Berhane Y, Lindtjørn B. Traditional values of virginity and sexual behaviour in rural Ethiopian youth: Results from a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2008;8:1–10.
Umutesi J, Ntaganira J, Birungi F. Early sexual debut and subsequent risk factors among youth in Rwanda : A secondary data analysis of Rwanda Demographic and Health Survey 2015 [unpublished masters’s dissertation]. University of Rwanda. 2016.
Christiansen CS, Gibbs S, Chandra-Mouli V. Preventing Early Pregnancy and Pregnancy-Related Mortality and Morbidity in Adolescents in Developing Countries: The Place of Interventions in the Prepregnancy Period. Bhutta ZA, editor. J Pregnancy. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/257546
Abdul Samad S, Hairi NN, Ismail M. Role of individual, family, and peers in sexual initiation among late adolescents attending institutions of higher learning in Malaysia. Asia Pacific J Public Heal. 2016;28(4):313–24. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010539516645158.
Li J, Li S, Yan H, Xu D, Xiao H, Cao Y, et al. Early sex initiation and subsequent unsafe sexual behaviors and sex-related risks among female undergraduates in Wuhan China. Asia Pacific J Public Heal. 2015;27(2):21S-29S.
Pengpid S, Peltzer K. Prevalence and correlates of sexual risk behavior among school-going adolescents in four Caribbean Countries. Behav Sci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10110166.
Funmito Omolola F, Akintunde Olusegun F, Olumuyiwa AO, Samuel Ebun A, Timothy Olufemi A, Idowu Paulin O, et al. Prevalence and predictors of early sexual debut among adolescents in ogbomoso, Nigeria. Am J Public Heal Res. 2018;6(3):148–54.
Asante KO, Nketiah-amponsah E, Andoh-arthur J, Boafo IM, Ampaw S. Correlates of early sexual debut among sexually active Youth in Ghana. 2018.
Howard AL, Pals S, Walker B, Benevides R, Massetti GM, Oluoch RP, et al. Forced sexual initiation and early sexual debut and associated risk factors and health problems among adolescent girls and young women—violence against children and youth surveys, nine PEPFAR countries, 2007–2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(47):1629–34.
Durowade KA, Babatunde OA, Omokanye LO, Elegbede OE, Ayodele LM, Adewoye KR, et al. Early sexual debut: prevalence and risk factors among secondary school students in Ido-Ekiti, Ekiti state, South-West Nigeria. Afr Health Sci. 2017;17(3):614–22.
Sidibé S, Delamou A, Kaba ML, Magassouba AS, Samake AT, Serge Y, et al. The effects of nutritional supplementation on body mass index and CD4 count among AIDS on antiretroviral treat-ment in Conakry, Guinea. J Public Health Africa. 2018;9:9–12.
McClinton Appollis T, Jonas K, Beauclair R, Lombard C, Duby Z, Cheyip M, et al. Early sexual debut and the effects on well-being among South African adolescent girls and young women aged 15 to 24 years. Int J Sex Heal. 2022;34(2):242–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/19317611.2021.1979162.
Cueto S, Leon J. Early sexual initiation among adolescents: a longitudinal analysis for 15-year-olds in Peru. Interam J Psychol. 2016;50(2):186–203.
Yosef T, Nigussie T, Getachew D, Tesfaye M. Prevalence and factors associated with early sexual initiation among college students in southwest Ethiopia. Biomed Res Int. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8855276.
Peltzer K, Pengpid S. Early sexual debut and associated factors among in-school adolescents in six Caribbean Countries. West Indian Med J. 2015;64(4):351–6.
Son DT, Oh J, Heo J, Van HN, Van MH, Choi S, et al. Early sexual initiation and multiple sexual partners among Vietnamese women: analysis from the multiple indicator cluster survey, 2011. Glob Health Action. 2016;9(1):29575. https://doi.org/10.3402/gha.v9.29575.
McClinton Appollis T, Jonas K, Beauclair R, Lombard C, Duby Z, Cheyip M, et al. Early sexual debut and the effects on well-being among south african adolescent girls and young women aged 15 to 24 years. Int J Sex Heal. 2022;34(2):242–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/19317611.2021.1979162.
Alhassan AR, Abdulai K, Alhassan MA. Early sexual debut among ghanaian women : correlates and psychological effect. BioMed Res Int. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5838510.
Nigatu AM, Birhanu AY, Endehabtu BF. Geographical variations of early age sexual initiation among reproductive-age women in Ethiopia: evidence from EDHS 2016. Arch Public Health. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-020-00411-4.
Hee J, Hyunjeong Y, Eun P, Kim Y. Predictors of the timing of sexual intercourse initiation among adolescents in South Korea. J Community Health. 2019;44(3):580–6.
Lubis R, Hinduan ZR, Jatnika R, Agustiani H. Predictors of early sexual intercourse on middle adolescents in Medan. Humanit Indones Psychol J. 2021;18(2):112.
Region A, Tadesse G, Yakob B. Risky sexual behaviors among female youth in tiss abay, a semi-urban area of the Amhara region, Ethiopia. PLoS One. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119050.
Lydia Watsi et al. Demographic determinants of risky sexual behaviours among senior high school students in the Hohoe municipality, Ghana. PAMJ Clin Med. 2020;2:81. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj-cm.2020.2.81.21304.
Turi E, Merga BT, Fekadu G, Abajobir AA. Why too soon? Early initiation of sexual intercourse among adolescent females in Ethiopia: evidence from 2016 Ethiopian demographic and health survey. Int J Women’s Health. 2020;12:269–75.
Mulu W, Yimer M, Abera B. Sexual behaviours and associated factors among students at Bahir Dar University: a cross sectional study. Reprod Health. 2014;11(1):84. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4755-11-84.
Collins RL, Martino SC, Shaw R. Influence of new media on adolescent sexual health : evidence and opportunities. 2011.
Mahapatra B, Saggurti N. Exposure to pornographic videos and its effect on HIV-related sexual risk behaviours among male migrant workers in Southern India. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(11):1–14.
Mellie BH. Assessment of time of sexual initiation and its associated factors among students in Northwest Ethiopia. Sci J Public Heal. 2015;3(1):10.
Tekletsadik EA, Ayisa AA, Mekonen EG, Workneh BS, Ali MS. Determinants of risky sexual behaviour among undergraduate students at the University of Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia. Epidemiol Infect. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268821002661.
Girmay A, Mariye T, Gerensea H. Early sexual debut and associated factors among secondary school students of central zone of Tigray, Northern Ethiopia, 2018. Pan Afr Med J. 2019. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2019.34.1.17139.
Carroll JA, Kirkpatrick RL. Impact of social media on adolescent behavioral health. Calif Adolesc Heal Collab. 2011;510:6.
Melesse DY, Cane RM, Mangombe A, Ijadunola MY, Manu A, Bamgboye E, et al. Inequalities in early marriage, childbearing and sexual debut among adolescents in sub-Saharan Africa. Reprod Health. 2021;18(Suppl 1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-021-01125-8.
Doyle AM, Mavedzenge SN, Plummer ML, Ross DA. The sexual behaviour of adolescents in sub-Saharan Africa: patterns and trends from national surveys. Trop Med Int Heal. 2012;17(7):796–807.
Odimegwu C, Somefun OD, Chisumpa VH. Regional differences in positive sexual behaviour among youth in sub-Saharan Africa. J Biosoc Sci. 2019;51(2):254–72.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the DHS program, for providing the dataset used in this study.
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Proposal preparation, acquisition of data, analysis, and interpretation of data was done by SH, GG, BT, SM, YH, AE, and FH which guided the study design data extraction and analysis. SH drafted the manuscript and all authors have a substantial contribution in revising and finalizing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical clearance for the current study was obtained from the International Review Board (IRB) of the Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) Program. Data are available to the general public by request in different formats from the Measure DHS website (www.measuredhsprogram.com). We used Measure DHS by briefly outlining the study's aims and obtaining permission to download the dataset. The Measure DHS program provided a permission letter for access to the database. The Helsinki declaration is followed by the DHS research process.
Consent for publication
Not applicable for this section.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Hailegebreal, S., Gilano, G., Seboka, B.T. et al. Prevalence and associated factors of early sexual initiation among female youth in East Africa: further analysis of recent demographic and health survey. BMC Women's Health 22, 304 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-022-01895-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-022-01895-8