Abstract
Background
Total tooth loss (edentulism) can be a debilitating condition, impacting on ability to chew, speak and interact with others. The most common treatment is with complete removable dentures, which may be successful, but in the lower jaw, bone resorption that worsens over time makes denture-wearing difficult. Two dental implants in the mandible to retain the lower denture has been advocated as the gold standard of treatment, but has not been universally provided due largely to financial constraints and also patient fear. Mini implants (MI) are cheaper and less invasive than conventional implants (CI), but may not have equivalent longevity. Therefore, it is unknown whether they represent a cost-effective treatment modality over time. The aim of this pilot randomised controlled trial was to assess the feasibility of carrying out a trial on this cohort of patients, and to inform the study design of a large multicentre trial.
Methods
Forty-six patients were randomly allocated to receive either two mini implants or two conventional implants in the mandible to retain their lower dentures. Quality of life (QoL) questionnaires, pain and anxiety scores, and an objective “gummy jelly” chewing test were carried out at multiple timepoints, along with detailed health economics information. Implants were placed one-stage, and an early loading protocol was utilised. Patients were reviewed 8 weeks post-placement, and finally at 6 months. Implant failure, recruitment and retention rates were recorded and analysed.
Results
The pilot study demonstrated that it is possible to recruit, randomise and retain edentulous (mainly elderly) patients for an implant trial. We recruited to target and retention rates were acceptable. The large number of questionnaires was onerous for participants to complete, but the distribution of scores and feedback from participants helped inform the choice of primary and secondary outcomes in a full trial. The chewing test was time-consuming and inconsistent. Implant failure rate was low (1/46). The data on indirect costs gathered at every visit was viewed as repetitive and unnecessary, as there was little or no change between visits.
Conclusions
The pilot study has shown that acceptable recruitment and retention rates are achievable in this population of patients for this intervention. The results provide valuable information for selection of outcome variables and sample size calculations for future trials.
Trial registration
(ISRCTN): 87342238 Trial registration date: 05/07/2013.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The World Health Organisation (WHO) considers edentulism (total tooth loss) a physical disability [1, 2]. The majority of edentulous patients are able to chew their food with complete dentures but over time, the lower jaw becomes resorbed and there is less bone to retain the lower denture. This makes it more difficult to retain the denture which causes problems for the denture-wearer, such as difficulties in eating and speaking, which may lead to a change in lifestyle, as those affected become embarrassed to socialise and eat with friends [3]. Furthermore, their inability to chew results in poorer food choices [4, 5] with many opting for highly calorific softer foods that are easier to eat. This undoubtedly affects their nutrition and thus general health. All of these factors have been shown to impact greatly on a patient’s quality of life [6].
The dental literature is awash with papers showing significant improvements in quality of life in edentulous patients who have two dental implants placed in their lower jaw to secure their lower dentures [6–15]. Indeed there are national and international consensus statements that this treatment modality should be the first line of treatment for patients with an edentulous mandible [16, 17]. However, this treatment is costly for both individual patients and health services around the world to provide. Furthermore, surgery to place implants is invasive [18], and this can pose a barrier to treatment even when provided free of charge [19, 20]. Edentulous patients are often older people (over 65 years) and may have significant bone resorption in their lower jaw and complex medical histories, which may affect their suitability for implant treatment.
Mini dental implants have been in use for the last 12 years [21–36] and offer a number of advantages over conventional implants: they have a smaller diameter (<2.4 mm) and are often made of a titanium alloy (Ti 6Al-4 V ELI) as opposed to commercially pure titanium (type 4) used in conventional dental implants. They are often placed using a minimally invasive technique, resulting in less post-operative pain [37]; and are therefore approximately a quarter of the cost of current conventional alternatives [21, 22]. These advantages need to be considered against a potentially higher failure rate [38] when compared to conventional implants, which have an impressively high survival rate over 10 years [15], and possibly a need for more intensive on-going maintenance [39].
There is a lack of high quality evidence of the effects of mini implants compared to conventional implants in retaining mandibular complete dentures [39, 40]. The primary aim of this study was to assess the feasibility of conducting a large surgical randomized controlled trial of mini versus conventional implants in a population of patients who can benefit from an implant- retained lower denture. The identified key areas of uncertainty to be explored in this trial focused upon the processes of recruitment and retention of participants, choice of clinical, quality of life and cost outcome measures and their method of capture. The objectives were specifically to determine:
-
The proportion of referred patients that were eligible to participate, consented to the trial and provided data at all time-points;
-
Whether masticatory functional ability could be measured using a validated ‘gummy jelly’ chewing test;
-
The completeness and variability of using different instruments to collect data on pain, QoL, implant failure; and
-
How to collect and measure costs
Methods
Design and eligibility criteria
The pilot trial was a two-arm parallel group randomised controlled pilot trial. Full ethical approval was obtained from the National Health Service Health Research Authority, National Research Ethics Service, Research Ethics Committee (ref: REC 13/NW/0384), and the study clinicians collected informed consent. All edentulous patients experiencing difficulties with their lower dentures, referred to the University Dental Hospital of Manchester or from internal referrals from hospital consultants, were initially screened for eligibility from the referral letters. Potentially eligible participants were booked onto consultation clinics for full medical history and clinical examination. Patients with an edentulous mandible, with residual mandibular ridge Cawood and Howell Class V or VI [41] with continued difficulties eating, even after the provision of new dentures, were eligible to participate. Patients with a history of bisphosphonate therapy or implant treatment, requiring sedation or general anaesthetic for implant placement, smokers, or patients unable to maintain adequate levels of oral hygiene were excluded.
Randomisation
The Clinical Trials Unit centrally randomised patients to one of two treatment groups with a 1:1 allocation ratio using random permuted blocks. A study clinician enrolled participants onto the trial and assigned participants to interventions according to the randomisation. The clinician performing the implant placement and health economist could not be blinded to treatment allocation; the research nurse (who collected masticatory efficiency and patient rated outcome data) and the trial statistician were blinded.
Treatment procedures
All patients were given an oral loading dose of 2 mg Amoxicillin (or 600 mg Clindamycin if allergic to penicillin) as per best current evidence [42]. All patients were asked to rinse for 60 s with Chlorhexidine (0.2%) mouthwash (with both dentures removed) and given local anaesthetic using 2% lignocaine + 1:80,000 adrenaline infiltrated into the anterior mandible.
Mini-implant (MI)
Two mini implants (3 M® 2.1 mm diameter, 10 mm length one-piece implant with a square collar and ball abutment) were placed transmucosally (flapless) in the interforamina region of the edentulous mandible.
Conventional implant (CI)
Two conventional (ASTRA TECH® Osseospeed 3 mm diameter, 11 mm length) implants were placed in the interforamina region of the edentulous mandible. These were placed after raising soft tissue flaps and drilling directly into bone. Ball abutments were placed on the conventional implants in a one-stage surgery approach to mimic the mini-implant attachment system.
Following surgery, all patients were given oral and written post-operative instructions and advised not to wear their lower dentures for 1 week. All patients were given 24 × 500 mg Paracetamol tablets to take as required. At 1 week postoperatively participants’ lower dentures were hollowed out chair-side so they could fit over the exposed ball abutments. Therefore, lower dentures could be worn but the implants were not directly loaded. At the 2-month review appointment an impression was taken of the implant ball abutments using a polyether impression material (Impregum™ Penta™ 3 M ESPE) in the patient’s lower complete denture. The denture was retrofitted with stud attachments on the same day by dental laboratory technicians using heat-cured acrylic.
Outcomes
Multiple outcome measures were assessed in accordance with the objectives of the study and as per the schedule below (Table 1). The primary outcomes of this study were feasibility outcomes. The feasibility of a main trial using the same study design and protocol was assessed according to the objectives of the pilot trial: recruitment and retention of trial participants; use of outcome measures and collection of cost data.
-
The feasibility of recruitment was measured in terms of eligibility (the proportion of eligible patients from the number of screened patients), recruitment (the proportion of recruited patients from the number of eligible patients), and whether the required sample size could be met within the designated 12-month recruitment period. The success of patient retention was measured in terms of compliance with randomisation (the proportion of participants receiving their allocated treatment) completeness of follow-up (the proportion of patients providing 6 month follow up data). The denominator was the number of patients randomised.
-
The feasibility of using masticatory efficiency as an effectiveness outcome was assessed as the number of ‘gummy jelly’ samples that were provided, and were able to be analysed.
-
The appropriateness of the different outcome measures was assessed quantitatively in terms of proportion of completed questionnaires, and qualitatively in variation, absence of floor or ceiling effects and variability of responses over time.
-
The feasibility and appropriateness of collecting cost information was assessed based on the proportions of completed patient questionnaires (patient costs) and completed health care costs, and the recording of unanticipated resource use.
Formal hypothesis testing for effectiveness was not be undertaken as the aim of a pilot trial is not to assess effectiveness and as such the study is underpowered for this purpose.
Sample size
As this was a pilot trial a formal sample size calculation was not appropriate. We estimated that of those patients screened and meeting the inclusion criteria, 50% would agree to participate. A total of 44 patients (22 in each arm) would have a 95% confidence interval ranging from 35% to 65% of patients who will agree to participate. A recruitment target was set at 44 patients or 1 year of recruitment, whichever endpoint was reached soonest.
Statistical analysis
It was not our intention to compare treatment groups and we did not test hypotheses. Cumulative and monthly (to assess season variation) recruitment figures were calculated, as were loss to follow up at 2 and 6 months post-surgery. Descriptive analyses were undertaken for a 12 month period (covering the period 6 months prior to the study start and the 6 months follow up) to identify the total number of referrals, the number and proportion of participants who attended for assessment, and the number and proportion of patients who required implants after fitting a new set of conventional complete dentures. Simple descriptive statistics involving calculation of ranges, frequency distributions and measures of central tendency and dispersion were used to assess the completeness and variability of clinical, quality of life and cost outcome measures collected at each time point.
The health economics analysis presents the resources recorded and their respective unit costs. Costs were calculated from the National Health Service (NHS) and social care provider perspective, secondary analysis includes costs from the patient perspective, and this approach approximates a societal perspective. The time trade-off (TTO) measurement for weighting the EQ-5D was used, as this is the recommended utility weight advocated by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence NICE [43]. The TTO weights are obtained from Dolan (1997) [44]. The SF-12 was mapped onto the SF-6D (since the SF-6D has Health-Related QoL weights). SF-6D weights were obtained from Brazier and Roberts (2004) [45].
Results
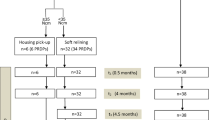
The recruitment and retention of participants from screening through to 6-month follow-up is shown in Fig. 1. Of note is that only 81/181 of those referred were eligible for the study, and of the 73 patients for whom new complete dentures were made, 12 were relatively satisfied with their new lower denture and declined further treatment. Furthermore, only four patients who were dissatisfied with their new denture did not want to be randomised, having a preference for mini-implants (three patients) or conventional implants (one patient). Of the 46 patients randomized 43 (93.5%) completed the trial.
Although the initial plan was to recruit a maximum of 44 participants or as many participants as possible in the planned 1-year recruitment period, in total 46 patients were recruited and randomised (further ethical approval was provided to recruit the additional participants). The median number of patients recruited per month was three and the monthly and cumulative recruitment figures are summarised in Fig. 2. The maximum number of patients recruited in a single month was six patients (June 2014); the minimum number of patients recruited was one (February 2014 and September 2014).
During the trial there was one protocol violation. During analysis it transpired that one patient was taking bisphosphonates a concomitant medication that that was not fully disclosed at recruitment. This patient was not included in the analyses. Table 2 shows the baseline characteristics of the trial participants.
Table 3 presents the clinical and patient rates of oral health quality of life outcomes. No participants refused to take the ‘gummy jelly’ test and we were able to measure the glucose released from all samples. The pattern of results for the ‘gummy jelly’ test did not reflect those of the OHIP-20 or subjective assessment of chewing ability (see Fig. 5.) However, due to differences in batch composition the glucose released at 6 months was not comparable to baseline or 2 month measures.
Pain VAS scores recorded immediately post-op and after 1 week post-op are presented in Fig. 3. The range of scores was wider in the conventional implant group compared to the mini implant group; this difference in distribution was most notable 1 week post-operatively.
Clinician and patient reported analgesic consumption, at face value, was also higher in the CI group compared to the MI group during the surgical procedure and at 1 week post-surgery.
The results of the OHIP-20 scores are presented in Fig. 4. There was downward trend in OHIP QoL scores in both groups at 6-month follow up compared to baseline suggesting an improvement in oral health related quality of life.
The denture satisfaction questionnaire records different aspects of patient satisfaction with their prosthesis using a 100 mm VAS. The scales are anchored by the extremes of potential responses (e.g., not at all satisfied to extremely satisfied). Higher values indicate a positive response and improvement. The distributions of responses for each domain of the prosthesis assessment questionnaire are shown in Fig. 5.
There were no adverse events reported in the MI group. CI group had 4 adverse events (8.9%). One was due to pain, and three due to infection. All were treated medically with painkillers and antibiotics as appropriate. One patient died during the follow-up period, from a condition unrelated to treatment. No other Serious Adverse Events were recorded.
There was a total of 74 unscheduled visits in 45 patients (mean 1.7, range 0 to 6): In the MI group there were 23 implant-related visits, due primarily to problems with O-ring attachments, and 18 prosthesis-related visits; in the CI group there were 13 implant-related visits, 17 prosthesis related visits and 3 visits for other reasons.
The costs of the MI and C- groups are presented in Table 4. Mean NHS costs observed over the trial for MIs were lower than that for CIs (column 1 of Table 4, £296 vs. £688). The MI group had lower observed mean staff costs (£37 vs. £88), equipment and consumable costs (£181 vs. £532), and medication costs (£0.23 vs. £4.24). The MI group had higher observed mean unscheduled visits costs (£78 vs. £63) (a detailed analysis of all costs recorded and methods used to generate costs are contained in the Additional file 1).
There was a higher mean patient cost observed for the MI group (£193 vs. £156) (column 2 of Table 4). Missing data was evident in most patient costs; most patients reported the same costs at each visit and were perplexed that the same questions were asked at each visit. The compounding nature of missing data (since there are three instances of follow ups and numerous unscheduled visits) resulted in a final complete cost sample of 15 patients. Of these, the mean observed costs of MI were lower than that for CI (£481 vs. £814).
Table 5 presents the results of EQ-5D and SF-6D questionnaires at baseline and at 2 and 6 months assessment. A higher score represents higher health-related QoL (HRQoL). Data was complete in the sense that no missing data was apparent aside from those patients who did not complete the trial. At face value mean baseline EQ-5D and SF-6D scores were lower for the CI group compared to the MI group. Mean EQ-5D and SF-6D scores for both groups showed little variation at 6 months follow-up compared to baseline. Comparisons of changes in EQ-5D and SF-6D scores from baseline to 6 months assessment for those completing the trial suggest reductions in EQ-5D score for both implant groups. For SF-6D scores there appears to be higher mean SF-6D scores at 6 months compared to baseline for the CI group and a reduction in mean scores for the MI group.
Discussion
Overview of the findings
This paper reports the findings of a National Institute for Health Research (NIHR)-funded pilot trial, the main purpose of which was to inform the design and conduct of future trials. Conventional implants have a long history and their clinical outcomes have been well documented [46–50]. Over the last 30 years, successive Adult Dental Health Surveys [51] have shown that the number of edentulous patients has fallen dramatically. The inability to retain a mandibular denture is debilitating, with dental need falling across the whole population a case could be made in the UK for NHS resources to be redirected to address the significant needs of this patient group. Mini implants could offer the NHS an effective and affordable means of providing care for this group of patients as a first line course of treatment. But to make a convincing case a high-quality, large, multi-centre trial with adequate follow up is required.
The primary aim of this study was to assess the feasibility of a conducting a large surgical randomised controlled trial as proposed in a population of patients who can benefit from an implant retained lower denture. The identified key areas of uncertainty to be explored in this trial focused upon the processes of recruitment and retention of participants, choice of clinical, QoL and cost outcome measures and their method of capture.
Our concerns over the willingness of this cohort to be randomized to different surgical options proved to be unfounded. We reached our required sample size within the pre-specified recruitment period, and very few eligible patients declined to take part in the trial because of a strong patient preference or unwillingness to be randomised. These results suggest that recruitment of participants through a major, secondary referral centre is feasible. Moreover, attrition over the 6 months duration was minimal (43 out of 46 patients (93.5%) completed the trial) with only four adverse events reported, all minor in nature and related to the surgery. However, follow up in this pilot study was limited to 6-months; in trials with a predominantly elderly sample some attrition from mortality unrelated to the intervention can be expected.
Trial participants were accepting of the test of masticatory function (‘gummy jelly’ test [52]) as evidenced by the number of samples provided, but the lack of consistency in measurement over time suggests that this measure is underdeveloped. Further development and evidence of repeatability and reliability is needed before the test could be used with confidence in a clinical trial.
All participants provided responses to pain outcome at all time-points. The data suggests we could expect to find a large difference in short-term post-operative pain scores between the groups in a definitive trial. Descriptively, the pain scores of participants in the CI group were substantially higher than participants in the MI group at 24 h and 7 days post-surgery. It would seem that 7 days post-surgery would be the optimal time for measurement and little is to be gained from measuring at both 24 h and 7 days.
Our Public Patient Involvement (PPI) group strongly recommended QoL as a primary outcome measure for any future trials in this area. Adherence to the NICE guidance for health technology appraisal requires health effects to be expressed in Quality Adjusted Life Years [43]. A key finding from our research is that the components of the generic EQ-5D and SF-6D HRQoL measures seem to show poor responsiveness to oral health-related changes in quality of life and many participants queried the relevance of the questions in these measures to an oral health intervention. A full trial may wish to utilise only one of the HRQoL measures, our data suggests SF-6D may provide some variability in the different implant groups but the EQ-5D is the preferred measure of HRQoL to aid in consistency when comparing the health effects across appraisals and so should be the measure of choice to use in future trials [43].
Data indicated that the OHIP-20 measure [3, 53, 54] and the individual items of the Assessment of Prosthesis scale [7] were sensitive to changes before and after placement of implants. The Assessment of Prosthesis scale performed as expected, with improvements between pre and post implant placement in both groups, but no apparent distinction between the two groups regarding ease of general satisfaction, cleaning, aesthetic and oral conditions. Satisfaction level was high in both groups after fitting the implants. Ability to speak, the level of comfort, stability of the dentures, perception of the chewing ability and function showed similar improvement in both groups pre and post implant placement. From a trials design perspective the lack of a single summary statistic to summarise each individual’s response means that this instrument in its entirety cannot be used to calculate a trial sample size but the individual items of this measure particularly, subjective assessment of chewing ability, can provide valuable information as a secondary outcome measure in the absence of well-validated objective measures.
Responses to the OHIP questionnaire illustrated the expected improvement in oral health-related QoL and the pattern of responses in each group was very similar. This could indicate either that the effects of the interventions are indeed very similar, or that the instrument is insufficiently sensitive to detect any differences between the groups. Our view is that survival should be the primary outcome measure of a future multi-centre trial. This is the primary outcome measure of the majority of implants trials reported in Cochrane systematic reviews [42, 55–59] and will be the key determinant of clinical and economic outcomes. The literature suggests that mini implants have a lower survival rate than conventional implants [29, 34, 38, 40, 60, 61] but from the data we present seem less expensive to place and also to replace if they fail. Studies [34, 60, 61] also suggest that if an implant is going to fail it is likely to happen in the first 2–3 years, suggesting that follow up period for future trials could be confined to 3 years, which would help contain costs. Although in this pilot trial follow-up was limited to 6 months, implant failure was rare, with only one failure of a single implant in the mini implant group and no failures in the conventional implant group. A subsequent audit of longevity of mini implants placed, involving all cases completed in University Dental Hospital of Manchester Restorative Department over a 92-month period, indicates that most failures occur in the first 2–3 years following placement. A low event rate would mean that a substantial number of participants would be required to achieve adequate power for a Randomised Controlled Trial (RCT) if implant failure is the primary outcome.
The pilot trial provided important information with regard to the health economics of implant-retained dentures. Any difference in costs appears to be driven by the differences in implant (materials) costs and staff costs (reflected in staff time). Large differences in staff costs, equipment and consumable costs were evident between the groups but little difference in medication costs. The number of unscheduled visits amount to 41 for the mini implant group and 33 for the conventional implant group. Our PPI group recommended a shorter, single measure of indirect (patient-borne) costs should be used in a full trial. Unscheduled visit costs to the NHS and medication costs did not substantially differ between groups and neither did patient costs (travel, time off work etc.). This strongly suggests that in future studies measurement of costs should be mainly restricted to direct costs of treatment, whether that is borne by the state, insurance companies or individual patients. One issue that our PPI group raised, which is important for future trials to consider, is the costs of ongoing maintenance of implants in primary care. Patients reported difficulty in finding providers of ongoing care and also the high costs of maintenance both of which need to be measured and factored into health economic analyses of future trials.
Strengths and limitations
This trial had narrow inclusion criteria; only patients with the most atrophic mandibles were invited to participate (Cawood and Howell Class V or VI [41]). However, in the screening process summarised in the CONSORT flow diagram (Fig. 1.) of the 99 patients who were ineligible for inclusion 48 were excluded because their mandibular ridge was Class IV or better, but these patients still had problems retaining their lower denture. Also there is evidence [62] to demonstrate that placement of implants slows down bone resorption and so reduces the clinical problems faced by surgeons and prosthodontists. These findings strongly suggests that many more patients could benefit from implants than patients with Class V or VI ridges and points to the need for widening inclusion criteria in future large, multi-centre pragmatic trials. Broadening inclusion criteria exclusion criteria could result in a higher recruitment rate and increase applicability of findings.
Other than implant failure and chewing ability, we limited our measurements to patient reported outcomes. The rationale behind this choice was that we wanted to ensure that in addition to clinically important outcomes, we captured outcomes that were important to patients. There was uncertainty as to what patient reported outcomes would be acceptable and useable with elderly people in a secondary care setting. Conversely, there is a consensus on clinically important outcomes such as failure of the denture superstructure retained by the implants (total replacement or refurbishment needed), quality and quantity of peri-implant bone. Such measurements are routinely taken in secondary care (where the full trial would be undertaken) and so uncertainty surrounding the use of these outcome measures within an RCT is minimal.
Although the standard practice is the placement of four or more mini implants in the interforaminal region [26, 28–30, 32, 36], this study trialled the use of two, which has been shown in clinical case studies and in previous studies [25, 31] to provide equivalent retention to the recommended four. A recent RCT compared 4 mini implants with 2 mini implants with 2 conventional [63]. Further trials are required to assess the costs effectiveness of 2 versus 4 implant retained lower dentures. Although it could be argued that if mini implants fail they can be readily and cheaply replaced, however this assumption needs to be robustly evaluated in future trials.
This was a pilot trial; its purpose was to ascertain whether a full trial would be feasible and justified and to collect information to inform the design and conduct of subsequent trials. Our trial has shown that a full evaluation of ‘which is more cost-effective, mini implants or conventional implants to retain a lower denture?’ using the proposed design and methods we employed is feasible. The data suggest that mini implants are cheaper, have less post-operative pain and less complications than conventional implants whilst producing similar QoL improvements. However, the follow up period was too short to assess implant survival and long term cost effectiveness. The study was also restricted to one site and to have greater external validity, multi-centre trials are required in different populations with different care providers.
Conclusions
Recruitment and retention of sufficient, eligible patients to a trial within a realistic timescale is possible. There are limitations in using generic and ‘disease-specific’ QoL measures to evaluate effectiveness in this context. Implant survival is important for patients and has a major impact on clinical effectiveness and costs and should therefore be considered as a primary outcome measure. Outcomes should be assessed at 7 days post operatively (pain) and 6 monthly intervals (implant survival) following implant placement.
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Conventional Implants
- EQ-5D:
-
Euroqol-5D questionnaire
- HRQoL:
-
Health-Related Quality of Life
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- MI:
-
Mini implants
- NHS:
-
National Health Service
- NICE:
-
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
- NIHR:
-
National Institute for Health Research
- OHIP:
-
Oral Health Impact Profile
- OHRQoL:
-
Oral health-Related Quality of Life
- PPI:
-
Public Patient Involvement
- QoL:
-
Quality of Life
- RCT:
-
Randomised Controlled Trial
- RfPB:
-
Research for Patient Benefit
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SF:
-
Short Form
- TTO:
-
Time Trade-Off
- VAS:
-
Visual Analogue Scale
- VRS:
-
Verbal Rating Scale
- WHO:
-
World Health Organisation
References
Organization WH. International classification of functioning, disability and health: ICF: World Health Organization. 2001.
Petersen PE, Bourgeois D, Ogawa H, Estupinan-Day S, Ndiaye C. The global burden of oral diseases and risks to oral health. Bull World Health Org Suppl. 2005;83(9):661–9.
Heydecke G, Locker D, Awad MA, Lund JP, Feine JS. Oral and general health-related quality of life with conventional and implant dentures. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2003;31(3):161–8. Epub 2003/05/20. eng.
De Marchi RJ, Hugo FN, Padilha DM, Hilgert JB, Machado DB, Durgante PC, et al. Edentulism, use of dentures and consumption of fruit and vegetables in south Brazilian community-dwelling elderly. J Oral Rehabil. 2011;38(7):533–40. Epub 2011/01/05. eng.
Gunne H-SJ, Wall A-K. The effect of new complete dentures on mastication and dietary intake. Acta Odontol. 1985;43(5):257–68.
Emami E, Heydecke G, Rompre PH, de Grandmont P, Feine JS. Impact of implant support for mandibular dentures on satisfaction, oral and general health-related quality of life: a meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(6):533–44. Epub 2009/06/12. eng.
Allen PF, Thomason JM, Jepson NJ, Nohl F, Smith DG, Ellis J. A randomized controlled trial of implant-retained mandibular overdentures. J Dent Res. 2006;85(6):547–51. Epub 2006/05/26. eng.
Awad MA, Lund JP, Dufresne E, Feine JS. Comparing the efficacy of mandibular implant-retained overdentures and conventional dentures among middle-aged edentulous patients: satisfaction and functional assessment. Int J Prosthodont. 2003;16(2):117–22. Epub 2003/05/10. eng.
Kapur KK, Garrett NR, Hamada MO, Roumanas ED, Freymiller E, Han T, et al. Randomized clinical trial comparing the efficacy of mandibular implant-supported overdentures and conventional dentures in diabetic patients. Part III: comparisons of patient satisfaction. J Prosthet Dent. 1999;82(4):416–27. Epub 1999/10/08. eng.
Fueki K, Kimoto K, Ogawa T, Garrett NR. Effect of implant-supported or retained dentures on masticatory performance: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2007;98(6):470–7. Epub 2007/12/07. eng.
Rashid F, Awad MA, Thomason JM, Piovano A, Spielberg GP, Scilingo E, et al. The effectiveness of 2-implant overdentures - a pragmatic international multicentre study. J Oral Rehabil. 2011;38(3):176–84. Epub 2010/08/14. eng.
Boerrigter EM, Geertman ME, Van Oort RP, Bouma J, Raghoebar GM, van Waas MA, et al. Patient satisfaction with implant-retained mandibular overdentures. A comparison with new complete dentures not retained by implants-a multicentre randomized clinical trial. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995;33(5):282–8. Epub 1995/10/01. eng.
Meijer HJ, Raghoebar GM, Van’t Hof MA, Visser A, Geertman ME, Van Oort RP. A controlled clinical trial of implant-retained mandibular overdentures; five-years’ results of clinical aspects and aftercare of IMZ implants and Branemark implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000;11(5):441–7. Epub 2001/02/13. eng.
Meijer HJ, Geertman ME, Raghoebar GM, Kwakman JM. Implant-retained mandibular overdentures: 6-year results of a multicenter clinical trial on 3 different implant systems. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001;59(11):1260–8. discussion 9–70. Epub 2001/11/01. eng.
Meijer HJ, Raghoebar GM, Batenburg RH, Visser A, Vissink A. Mandibular overdentures supported by two or four endosseous implants: a 10-year clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(7):722–8. Epub 2009/06/06. eng.
Thomason JM, Feine J, Exley C, Moynihan P, Muller F, Naert I, et al. Mandibular two implant-supported overdentures as the first choice standard of care for edentulous patients-the York Consensus Statement. Br Dent J. 2009;207(4):185–6. Epub 2009/08/22. eng.
Feine JS, Carlsson GE, Awad MA, Chehade A, Duncan WJ, Gizani S, et al. The McGill consensus statement on overdentures. Mandibular two-implant overdentures as first choice standard of care for edentulous patients. Gerodontology. 2002;19(1):3–4. Epub 2002/08/08. eng.
Fortin T, Bosson JL, Isidori M, Blanchet E. Effect of flapless surgery on pain experienced in implant placement using an image-guided system. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005;21(2):298–304.
Walton JN, MacEntee MI. Choosing or refusing oral implants: a prospective study of edentulous volunteers for a clinical trial. Int J Prosthodont. 2005;18(6):483–8. Epub 2005/12/13. eng.
Pommer B, Mailath-Pokorny G, Haas R, Busenlechner D, Fürhauser R, Watzek G. Patients’ preferences towards minimally invasive treatment alternatives for implant rehabilitation of edentulous jaws. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2014;7:91–109.
Christensen GJ. The ‘mini’-implant has arrived. J Am Dent Assoc. 2006;137(3):387–90. Epub 2006/03/31. eng.
Sendax V. Mini implant strategy offers a broad range of uses. Dent today. 1995;14(1):227–32.
Vigolo P, Givani A. Clinical evaluation of single-tooth mini-implant restorations: a five-year retrospective study. J Prosthet Dent. 2000;84(1):50–4.
Vigolo P, Givani A, Majzoub Z, Cordioli G. Clinical evaluation of small-diameter implants in single-tooth and multiple-implant restorations: a 7-year retrospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003;19(5):703–9.
Morneburg TR, Proschel P. Success rates of microimplants in edentulous patients with residual ridge resorption. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008;23(2):270.
Griffitts TM, Collins CP, Collins PC. Mini dental implants: an adjunct for retention, stability, and comfort for the edentulous patient. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;100(5):e81–4.
Ahn M-R, An K-M, Choi J-H, Sohn D-S. Immediate loading with mini dental implants in the fully edentulous mandible. Implant Dent. 2004;13(4):367–72.
Lerner H. Minimal invasive implantology with small diameter implants. Implant Pract. 2009;2(1):30–5.
Scepanovic M, Calvo-Guirado JL, Markovic A, Delgardo-Ruiz R, Todorovic A, Milicic B, et al. A 1-year prospective cohort study on mandibular overdentures retained by mini dental implants. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2011;5(4):367–79.
Mundt T, Schwahn C, Stark T, Biffar R. Clinical response of edentulous people treated with mini dental implants in nine dental practices. Gerodontology. 2013;32(3):179–87.
Jofre J, Hamada T, Nishimura M, Klattenhoff C. The effect of maximum bite force on marginal bone loss of mini-implants supporting a mandibular overdenture: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(2):243–9. Epub 2010/01/15. eng.
Preoteasa E, Meleşcanu-Imre M, Preoteasa CT, Marin M, Lerner H. Aspects of oral morphology as decision factors in mini-implant supported overdenture. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2010;51(2):309–14.
Preoteasa E, Marin M, Imre M, Lerner H, Preoteasa CT. Patients’ satisfaction with conventional dentures and mini implant anchored overdentures. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2012;116(1):310–6. Epub 2012/10/20. eng.
Preoteasa E, Imre M, Preoteasa CT. A 3-Year Follow-up Study of Overdentures Retained by Mini-Dental Implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;29(5):1170–6.
Melescanu Imre M, Preoteasa E, Tancu A, Preoteasa CT. Imaging technique for the complete edentulous patient treated conventionally or with mini implant overdenture. J Med Life. 2013;6(1):86–92. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3624656, Epub 2013/04/20. eng.
Tomasi C, Idmyr BO, Wennstrom JL. Patient satisfaction with mini-implant stabilised full dentures. A 1-year prospective study. J Oral Rehabil. 2013;40(7):526–34. Epub 2013/04/05. eng.
Ribeiro A, Della Vecchia M, Cunha T, Sorgini D, Reis A, Muglia V, et al. Short‐term post‐operative pain and discomfort following insertion of mini‐implants for retaining mandibular overdentures: a randomized controlled trial. J Oral Rehabil. 2015;42(8):605–14.
Bidra AS, Almas K. Mini implants for definitive prosthodontic treatment: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2013;109(3):156–64. Epub 2013/03/26. eng.
Elsyad MA. Patient satisfaction and prosthetic aspects with mini‐implants retained mandibular overdentures. A 5‐year prospective study. Clin Oral Implant Res. 2015;27(7):926–33.
Bulard RA, Vance JB. Multi-clinic evaluation using mini-dental implants for long-term denture stabilization: a preliminary biometric evaluation. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2005;26(12):892–7. Epub 2006/01/05. eng.
Cawood JI, Howell RA. A classification of the edentulous jaws. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1988;17(4):232–6. Epub 1988/08/01. eng.
Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Worthington HV. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: antibiotics at dental implant placement to prevent complications. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;7:CD004152. Epub 2013/08/02. eng.
NICE. Process and methods guide: Guide to the methods of technology appraisal. 2013. https://www.nice.org.uk/process/pmg9/chapter/foreword. Accessed 19 Jan 2017.
Dolan P. Modeling valuations for EuroQol health states. Med Care. 1997;35(11):1095–108.
Brazier JE, Roberts J. The estimation of a preference-based measure of health from the SF-12. Med Care. 2004;42(9):851–9.
Meijer HJ, Raghoebar GM, Batenburg RH, Vissink A. Mandibular overdentures supported by two Branemark, IMZ or ITI implants: a ten-year prospective randomized study. J Clin Periodontol. 2009;36(9):799–806. Epub 2009/07/01. eng.
Branemark PI, Adell R, Albrektsson T, Lekholm U, Lundkvist S, Rockler B. Osseointegrated titanium fixtures in the treatment of edentulousness. Biomaterials. 1983;4(1):25–8. Epub 1983/01/01. eng.
Branemark PI, Hansson BO, Adell R, Breine U, Lindstrom J, Hallen O, et al. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Experience from a 10-year period. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Suppl. 1977;16:1–132. Epub 1977/01/01. eng.
Curtis DA, Sharma AB, Finzen FC. The use of dental implants to improve quality of life for edentulous patients. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2008;36(4):275–80. Epub 2008/05/17. eng.
Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, Brånemark P-I. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int J Oral Surg. 1981;10(6):387–416.
Office for National Statistics. Social Survey Division and Information Centre for Health and Social Care ADHS. 2009 [computer file]. 2nd Edition. Colchester, Essex: UK Data Archive [distributor], August 2012. SN: 6884, http://dx.doi.org/10.5255/UKDA-SN-6884-2.
Ikebe K, Morii K, Matsuda K-i, Hazeyama T, Nokubi T. Reproducibility and accuracy in measuring masticatory performance using test gummy jelly. Prosthodont Res Pract. 2005;4(1):9–15.
Allen PF, McMillan AS, Locker D. An assessment of sensitivity to change of the Oral Health Impact Profile in a clinical trial. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2001;29(3):175–82. Epub 2001/06/21. eng.
Allen F, Locker D. A modified short version of the oral health impact profile for assessing health-related quality of life in edentulous adults. Int J Prosthodont. 2002;15(5):446–50.
Esposito M, Ardebili Y, Worthington HV. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: different types of dental implants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;7:CD003815. Epub 2014/07/23. eng.
Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Chew YS, Coulthard P, Worthington HV. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: 1- versus 2-stage implant placement. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;3:CD006698. Epub 2009/07/10. eng.
Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Maghaireh H, Worthington HV. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: different times for loading dental implants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;3:CD003878. Epub 2013/04/02. eng.
Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Polyzos IP, Felice P, Worthington HV. Timing of implant placement after tooth extraction: immediate, immediate-delayed or delayed implants? A Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2010;3(3):189–205. Epub 2010/09/18. eng.
Esposito M, Maghaireh H, Grusovin MG, Ziounas I, Worthington HV. Soft tissue management for dental implants: what are the most effective techniques? A Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2012;5(3):221–38. Epub 2012/09/25. eng.
Shatkin T, Petrotto C. Mini dental implants: a retrospective analysis of 5640 implants placed over a 12-year period. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2011;33:2–9.
Shatkin TE, Shatkin S, Oppenheimer BD, Oppenheimer AJ. Mini dental implants for long-term fixed and removable prosthetics: a retrospective analysis of 2514 implants placed over a five-year period. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2007;28(2):92–9. quiz 100–1.
Jemt T, Lekholm U. Implant treatment in edentulous maxillae: a 5-year follow-up report on patients with different degrees of jaw resorption. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995;10(3):303–11.
de Souza R, Ribeiro A, Della Vecchia M, Costa L, Cunha T, Reis A, et al. Mini vs. Standard Implants for Mandibular Overdentures A Randomized Trial. J Dent Res. 2015;94(10):1376–84.
Humphris G, Morrison T, Lindsay S. The Modified Dental Anxiety Scale: UK norms and evidence for validity. Community Dent Health. 1995;12(3):143–50.
Allen F, Locker D. A modified short version of the oral health impact profile for assessing health-related quality of life in edentulous adults. Int J Prosthodont. 2001;15(5):446–50.
Group TE. EuroQol-a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy. 1990;16(3):199–208.
Ware Jr J, Kosinski M, Turner-Bowker D, Gandek B. How to score version 2 of the SF-12 Health Survey (with a supplement documenting version 1). Lincoln: QualityMetric. Inc; 2002.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Dr Mark Harrison, Health Economist, for his contribution to the rationale for health economics analysis and for devising the health economics questionnaires. We would also like to acknowledge Ronnie Polak as our PPI lead. We would also like to thank members of our PPI group made up of previous implant patients who provided advice and opinions on the proposed research. We would also like to acknowledge Takahiro Ono who kindly provided the gummy jelly for the masticatory test.
Funding
The study was funded by the (NIHR) Research for Patient Benefit (RfPB) stream (£250,000) Competition 18 in May 2012 (ref: PBPG021227050). The funding body peer reviewed the study prior to its commence and made comments that contributed to its design. It had no role, however in data collection, analysis or interpretation nor in the writing of this manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors’ contributions
All authors contributed substantially to the design and execution of the pilot study. The manuscript was prepared, revised, edited and approved by SJ, TW, MT, WW and CB. All authors are accountable for the information contained herein. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors all declare no competing interests in relation to this research.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Full ethical approval was obtained from the National Health Service Health Research Authority, National Research Ethics Service, Research Ethics Committee (ref: REC 13/NW/0384), and the study clinicians collected informed consent from all participants in writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Additional file 1:
CIMIDENT HE Report BMC Oral Health Appendix. Health Economics Analysis. Methods and analysis of costs for the two implant procedures and subsequent comparison. (DOCX 83 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Jawad, S., Barclay, C., Whittaker, W. et al. A pilot randomised controlled trial evaluating mini and conventional implant retained dentures on the function and quality of life of patients with an edentulous mandible. BMC Oral Health 17, 53 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-017-0333-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-017-0333-1