Abstract
Background
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) reportedly participate in the mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) chondrogenic differentiation regulation. We objected to examine how miR-218 regulate chondrogenic differentiation of synovium-derived MSCs (SDSCs) and the maturation of RCJ3.1C5.1 chondrocytes. SDSCs were sourced from the knee joint synovium of New Zealand white rabbits, and their multilineage differentiation potentials were examined. The level of miR-218 was measured during SDSC chondrogenic differentiation, together with determination of SDSCs chondrogenic markers and RCJ3.1C5.1 chondrocytes maturation markers expression level after transfection of miR-218 mimics/inhibitor.
Results
miR-218 expression was notably upregulated in early chondrogenesis but mostly ceased during the maturation phases of chondrogenic differentiation in SDSCs. The transfection of miR-218 mimics notably enhanced SDSCs chondrocytes differentiation, as evidenced by augmented expressions of chondrogenic markers (SOX9, COL2A1, ACAN, GAG, and COMP) in terms of mRNA and protein level, and the inhibition of miR-218 yielded opposite resutls. Additionally, miR-218 overexpression substantially suppressed the expression of osteogenic markers (ALP, BSP, COL1A1, OCN and OPN) during the early stage of chondrogenesis while increasing that of chondrogenic markers (SOX9, COL2A1, ACAN, GAG and COMP). However, miR-218 mimics notably suppressed maturation markers (CMP, COL10A1, MMP-13 and VEGF) expression in RCJ3.1C5.18 chondrocytes, and the miR-218 inhibitor promoted the expression of these maturation markers. We proposed miR-218 plays a regulatory role on 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (HPGD), which plays a key role in chondrogenic differentiation, and this finding indicates that miR-218 directly regulates HPGD expression in SDSCs.
Conclusion
Our study suggests that miR-218 contributes to early chondrogenesis while suppressing later chondrocyte maturation. The miR-218-HPGD pathway offers us a perspective into how SDSCs differentiate into chondrogenic cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Articular cartilage (AC) is an avascular tissue, and thus is characterised with restricted ability to repair itself after trauma or degenerative disease [1]. Various methods are attempted to treat AC injuries, including abrasion under arthroscope, transplantations with mature chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), or grafted with tissues like periosteum. Autologous chondrocyte transplantation (ACT), which delivers autologous chondrocytes into the area of defect [2], has been proposed by most clinicians as an feasible approach for cartilage repair, though randomized trials have reported little clinical benefit with this procedure compared with subchondral bone microfracture [3]. An apparent drawback with ACT is it involved morbidity to the donor-site and therefore resultant osteoarthritic changes in the donor joint [4], emphasizing the need for alternative sources of chondrocyte cells. Adult stem cells have been proposed as an excellent cell candidate for cartilage repair due to their proliferation and multilineage differentiation capacity. Especially, synovium-derived MSCs (SDSCs) are unique because of their tissue specificity for cartilage regeneration [5], and these cells have been shown to have great potential in cartilage regeneration research.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) is a class of small, noncoding, single-stranded RNAs that regulate at posttranscriptional level through either mRNA translation inhibition or mRNA degradation promotion. There are many reports on critical roles miRNAs play in biology, such as differentiation, development, proliferation, and tumorigenesis. Moreover, several miRNAs have been identified to modulate cartilage differentiation and degradation [6,7,8]. For example, miR-365 targets histone deacetylase 4 and enhances chondrogenesis [9], and miR-145 inhibits early chondrogenesis by targeting Sox9 [10]. Recent reports have found that miR-218 targets the transcription factor Runx2 to control development pathway in osteogenic lineage [11]. It also activates WNT signaling, which play a role in the MSCs chondrogenic differentiation [12, 13]. However, the paticipation of miR-218 in SDSC chondrogenic differentiation and maturation stays unclear.
As an important regulator, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) significantly promotes chondrogenic markers (SOX9, ACAN, COMP and COL2A1) expression in the early stage of chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits chondrocyte maturation in the late stage. HPGD is a known effecter that regulates PGE2 by converting it to its biologically inactive metabolite. Taken together, Runx2 and HPGD (dehydrogenase of PGE2) play key roles in chondrogenic differentiation and chondrocyte maturation during chondrogenic differentiation.
Methods
Isolation and culture of SDSCs
Synovial tissue was harvested from the knees of New Zealand White rabbits which were obtained from the Animal Center of Second Military Medical University. Surgeries were approved by Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of Second Military Medical University. The rabbits were anaesthetized through the intravenous injection of 0.6% pentobarbital sodium; the injection dosages were 22–26 mg/kg, and the injection rates were 10–20 ml/5–10 min. At a respiratory rate of 46–68/min, the heart rate was 180–210/min, and the corneal reflex was weakened, indicating that the rabbit was under anesthesia. After the isolation of synovial tissue, all the rabbits were alive and fed at the Animal Center of Second Military Medical University. The synovial tissue was finely minced and digested with 0.1% trypsin (Roche DiACANostics, Mannheim, Germany) at 37 °C for 30 min and then with 0.1% collagenase D (Roche) for 2 h. Cells were collected after filtering and plated at clonal density in 60-cm2 culture dishes (Nalge Nunc International, Rochester, N.Y., USA) in complete medium (α-minimum essential medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 mg/mL streptomycin, and 0.25 mg/mL fungizone [Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA]) and incubated at 37 °C with 5% humidified CO2. Non-adherent cells were removed when the medium was changed every two days. SDSCs were harvested when adherent cells reached ~ 80% confluence.
Detection of SDSC surface markers
A flow cytometry analysis was performed to confirm isolated SDSCs surface markers as previously described [14]. Anti-rabbit CD44-PE, CD90-FITC (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA), CD105-FITC, CD14-FITC, CD34-FITC, and CD45-FITC (eBioscience, San Diego, CA, USA) were employed as monoclonal antibodies. Flow cytometry was conducted with a FACSCalibur cytometer (BD Biosciences), and data analyses were performed using BD FAC Suite software (BD Biosciences).
Adipogenic, osteogenic and SDSCs chondrogenic differentiation
SDSCs at passage 3 were collected and seeded in a six-well plate at a density of 1 × 105/well. When they reached ~ 80% confluence, the SDSCs were incubated in either adipogenic differentiation medium, osteogenic differentiation medium, or chondrogenic differentiation medium supplemented with 10 ng/mL transforming growth factor beta 3 (TGF-β3). All three types of differentiation media were purchased from BD Biosciences (Bedford, MA, USA), and the culture medium was changed every 3 days. Staining for adipogenic, osteogenic, or chondrogenic differentiation was performed with fresh Oil Red O solution (Sigma-Aldrich, MO, USA) for 2 h, 0.1% Alizarin Red (Sigma-Aldrich, MO, USA) solution for 40 min, or 1% Alcian Blue solution (Sigma-Aldrich) for 30 min at room temperature, respectively.
Lentivirus-mediated cell transfection
Recombinant lentivirus miR-218-mimics and miR-218-inhibitor were purchased from GeneChem (Shanghai, China). For the lentivirus infection, differentiated SDSCs and RCJ3.1C5.18 chondrocytes were seeded in a 12-well plate and cultured overnight to 70% confluence according to the manufacturers’ instructions. The cells were then transfected with different lentiviruses for 24 h.
Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Life Technologies Inc., Grand Island, NY) and RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Approximately 1 μg of mRNA was used for reverse transcriptase with a High-Capacity cDNA Archive Kit (Applied Biosystems) at 37 °C for 2 h. For miRNA detection, reverse transcription was performed using miRNA-specific stem-loop primers, and real-time PCR was performed using SYBR green Master Mix. Chondrogenic marker genes SOX9, COL2A1, ACAN, GAG and COMP, osteogenic marker genes ALP, BSP, Col1a1, OCN and OPN, and maturation markers CMP, Col10a1, MMP-13, and VEGF were customized by Applied Biosystems as part of Custom TaqMan Gene Expression Assays (Table 1). β-Actin and U6 were employed as internal controls to determine mRNA and miRNA expression levels. The RT-PCR conditions were as follows: an initial 10-min incubation at 95 °C, 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, 60 °C for 20 s and 72 °C for 30 s, and 5 min at 4 °C. Relative quantification analysis was conducted using the 2−△△CT method. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate, and all experiments were carried out three times independently.
Western blot analysis
For total protein extraction, cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (GuHCl, Sigma-Aldrich) supplemented with phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) and centrifuged at 12,000×g and 4 °C for 10 min. The supernatant was collected, and total protein was quantified using a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Sigma-Aldrich) according to the manufacturer’s protocols. Equal amounts (40 μg) of protein samples were separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). After blocking with 5% nonfat milk in TBST (100 mM Tris-HCl, 0.9% NaCl, 1% Tween 20, pH 7.5) for 1 h, membranes were individually incubated with primary monoclonal antibodies against chondrogenic markers SOX9, COL2A1, ACAN, GAG and COMP, osteogenic markers ALP, BPS, COL1A1, OCN and OPN, and maturation markers CMP, COL10A1, MMP-13 and VEGF in 1% nonfat milk in TBST for 3 h at room temperature. Membranes were then incubated with a secondary horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody (dilution factor of 1:5000) for 40 min at room temperature, followed by exposure in SuperSignal West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate using CL-XPosure Film.
Immunocytochemistry
A total of 2.5 × 105 passage-3 SDSCs were seeded into 15-mL centrifuge tubes and cultured in 0.5 mL of chondrogenic differentiation medium for 21 days. The pellets (n = 2) were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at 4 °C overnight, followed by dehydration in a gradient ethanol series, clearing with xylene, and embedding in paraffin blocks. Sections with a thickness of approximately 5 mm were stained with Alcian Blue (Sigma; counterstained with Fast Red) and Safranin O (Sigma; counterstained with hematoxylin) for sulfated glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). For immunohistochemistry analysis, sections were probed with primary antibodies against collagen II (II-II6B3; DSHB, Iowa City, IA, USA), followed by the secondary antibody biotinylated horse anti-rabbit IgG (Vector, Burlingame, CA, USA). Immunoactivity was detected using Vectastain ABC reagent (Vector) with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) as a substrate. Hematoxylin (Vector) served as a counterstain.
Luciferase reporter assay
pMiR-REPORT-mut-HPGD 3’UTR constructs containing the HPGD 3′ untranslated region (UTR) with three point mutations in the seed sequence were produced using a QuikChange II Site-Directed Mutagenesis kit (Stratagene). HEK293 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate for 24 h and then cotransfected with pMIR-REPORT-HPGD 3’UTR plasmid or pMIR-REPORT-mut-HPGD 3’UTR plasmid, internal control pRL-TK-Renilla-luciferase plasmid and the indicated RNAs. In contrast, the pMIR-REPORT-HPGD 3’UTR plasmid or pMIR-REPORT-mut-HPGD 3’UTR plasmid and pRL-TK plasmid were transfected into SDSCs in 24-well plates. After the induction of chondrogenic differentiation for 14 days, luciferase activities were determined using a Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay Kit (Promega). All transfection experiments were conducted in triplicate and repeated three times independently.
Statistical analysis
The experimental values are presented as the means ± standard deviations (SDs). The statistical analyses were conducted with GraphPad Prism Software Version 6.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). Significant differences between groups were evaluated by one-way ANOVA. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Identificaiton and determination of multilineage differentiation capacity of SDSCs
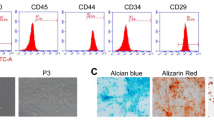
To confirm whether our cultured SDSCs exhibit the characteristics of MSCs, passage-3 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Rabbit SDSCs were positive for CD44, CD90, and CD105 but negative for CD14, CD34 and CD45 (Fig. 1). To further identify the multilineage differentiation potentials of SDSCs, adipogenic, osteogenic or chondrogenic differentiation was induced in the third-passage cells. Following induction for 21 days, SDSCs were positive for Oil Red O staining, alkaline phosphatase or Alcian Blue staining (Fig. 1).
Characterization of MSC properties (a-f) and multilineage differentiation capacity (g-i) of SDSCs. Flow cytometry was used to characterize MSC surface phenotypic markers CD44 (a), CD90 (b), CD105 (c), CD14 (d), CD34 (e), and CD45 (f) in SDSCs. Adipogenic, osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation were assessed using Oil Red O staining (g), alkaline phosphatase positivity (h) and Alcian Blue staining (i), respectively. Bar 100 μm
miR-218 is upregulated in early chondrogenesis but downregulated in late chondrogenesis in SDSCs
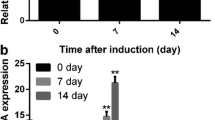
Expression of 6 miRNAs implicated in chondrogenesis was evaluated by RT-qPCR at 0, 7, 14, 21 and 28 days of chondrogenic differentiation [6,7,8,9,10]. Our results showed that expression of chondrogenesis-related miRNAs miR-140, miR-199a, miR-365, and miR-675 increased gradually during the entire chondrogenesis process, whereas miR-145 levels gradually decreased. Of note, miR-218 increased significantly in a time-dependent manner during early chondrogenesis and peaked at 14 days, though expression of miR-218 was downregulated in late stages of SDSC chondrogenesis (Fig. 2).
miR-218 was upregulated in SDSCs early in chondrogenesis but downregulated in later chondrogenesis. Expression of 6 miRNAs, miR-140, miR-199a, miR-365, miR-675, miR-145 and miR-218, was determined using quantitative real-time PCR on days 0, 7, 14, 21 and 28 of chondrogenic differentiation. The expression levels of miRNA were normalized to those of U6. The data are presented as the means ± SDs (n = 3). *P < 0.05 vs. Day 0, **P < 00.01 vs. Day 0
miR-218 enhances SDSCs chondrogenic differentiation during the early stage
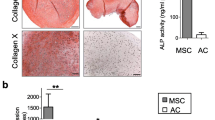
Twenty-one days after induction of chondrogenic differentiation, immunohistochemistry staining was employed to detect type II collagen (Col II); Alcian Blue and Safranin O were used to stain sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) and aggrecan (ACAN). The mRNA and protein levels of SOX9, COL2A1, ACAN and COMP in SDSCs were measured at 0, 7, 14 or 21 days of chondrogenic differentiation. As shown in Fig. 3a, the size of the cell pellet increased with miR-218 mimic transfection but decreased following miR-218 inhibitor transfection. Additionally, RT-qPCR results showed that miR-218 mimic transfection led to a significant increase in chondrogenic marker mRNA (Fig. 3b) and protein expression levels (Fig. 3c), whereas these chondrogenic markers were markedly downregulated in miR-218 inhibitor-transfected SDSCs.
miR-218 promotes SDSC chondrogenesis. SDSCs were transfected with either miR-218 mimics or miR-218 inhibitor. After induction of chondrogenic differentiation for 21 days, (a) immunohistochemistry was used to detect Col II, and Alcian Blue and Safranin O were utilized to stain sulfated GAG or ACAN, respectively. b RT-PCR was used to measure expression of chondrogenic marker genes, including SOX9, COL2A1, Aggrecan, and COMP, in miR-218-overexpressing and miR-218-inhibited SDSCs. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate, and the data are presented as the means ± SDs. * P < 0.05 vs. the control group, ** P < 0.01 vs. the control group. c miR-218 mimics were transfected into SDSCs, and SOX9, COL2A1, Aggrecan and COMP protein levels were assessed by western blot analysis
miR-218 represses early osteogenesis of SDSCs
Twenty-one days after induction of chondrogenic differentiation, the mRNA and protein levels of osteogenic markers ALP, BSP, Col1a1, OCN, and OPN were examined at days 0, 7, 14 and 21. As shown in Fig. 4a, RT-qPCR results showed that miR-218 mimic transfection led to a significant decrease in osteogenic marker mRNA expression levels; in contrast, these osteogenic markers were markedly upregulated in miR-218 inhibitor-transfected SDSCs, and western blotting results were consistent with the results of RT-qPCR (Fig. 4b).
miR-218 represses SDSC osteogenesis. SDSCs were transfected with either miR-218 mimics or miR-218 inhibitor. a After induction of chondrogenic differentiation for 21 days, expression of osteogenic marker genes, including ALP, BPS, Col1a, OCN, and OPN, was measured by RT-PCR in miR-218-overexpressing SDSCs. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate, and the data are presented as the means ± SDs. * P < 0.05 vs. the control group, ** P < 0.01 vs. the control group. P (b) miR-218 inhibitor was transfected into SDSCs, and ALP, BPS, COL1A1, OCN and OPN protein levels were measured by western blot analysis. * P < 0.05 vs. the control group, ** P < 0.01 vs. the control group
miR-218 inhibits chondrocyte maturation
Twenty-eight days after induction of chondrogenic differentiation, the mRNA and protein levels of the maturation markers CMP, COL10A1, MMP-13, and VEGF were examined at days 0, 21 and 28. RT-qPCR revealed that miR-218 mimic transfection led to a significant decrease in mRNA expression of maturation marker, whereas levels of these markers were markedly increased in miR-218 inhibitor-transfected C5.18 chondrocytes (Fig. 5a). Western blotting results were consistent with the RT-qPCR results (Fig. 5b).
miR-218 inhibits chondrocyte maturation. C5.18 chondrocyte cells were transfected with either miR-218 mimics or miR-218 inhibitor. a After induction of chondrogenic differentiation for 28 days, expression of mature marker genes, including CMP, Col10a1, MMP-13 and VEGF, was measured by RT-PCR in miR-218-overexpressing C5.18 chondrocyte cells. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate, and the data are presented as the means ± SDs. ** P < 0.01 vs. the control group. b miR-218 inhibitor was transfected into C5.18 chondrocyte cells, and CMP, COL10A1, MMP-13 and VEGF protein levels were measured by western blot analysis. ** P < 0.01 vs. the control group
miR-218 directly regulates HPGD expression in SDSCs
The TargetScan bioinformatics tool was used to search for miRNAs targeting the HPGD 3’UTR, and only miR-218-5p and miR-26-5p were predicted as candidate miRNAs. Moreover, miR-218-5p was predicted to target two conserved regions of HPGD. Luciferase reporters carrying either the wild-type 3’UTR of HPGD or a mutant 3’UTR with three point mutations in the target site (as a negative control) were engineered to investigate whether HPGD is directly targeted by miR-218 (Fig. 6a) and were then cotransfected with miR-218 mimics into HEK293 cells. Compared with the negative control, the luciferase activity of the wild-type HPGD reporter were significantly reduced by miR-218 mimics. miR-199 was also cotransfected with reporters as a negative RNA control. In contrast, the mimics of miR-218 did not repress the expression of mutant reporters (Fig. 6b). To examine the role of endogenous miR-218 in inhibiting the HPGD 3’UTR reporter in chondrogenic differentiation, SDSCs were cotransfected with the wild-type 3’UTR luciferase reporter and the luciferase reporter with the mutant UTR as a negative control at 14 days after chondrogenic differentiation, and significant inhibition of the wild-type HPGD 3’UTR luciferase reporter activity was observed in the differentiated compared with undifferentiated SDSCs (Fig. 6c). Taken together, these results show that miR-218 directly regulates HPGD by targeting its 3’UTR and that miR-218 might play a prominent role during chondrogenic differentiation.
miR-218 directly regulates HPGD expression in SDSCs. The predicted pairing of miRNAs and their target regions in the wild-type HPGD 3’UTR or the mutant (mut) HPGD 3’UTR are shown (a). HEK293 cells were cotransfected with the firefly luciferase-expressing vector pMIR-REPORT containing the wild-type HPGD 3’UTR, the mut HPGD 3’UTR or the control insert as well as the internal control Renilla-luciferase-expressing vector pRL-TK and the indicated RNAs. miR-199 was cotransfected with reporters as a negative RNA control. Luciferase activities were measured after 48 h. The data were normalized by dividing firefly luciferase activity with that of Renilla luciferase; **, P < 0.01 (b). Luciferase activities were measured in SDSCs cotransfected with the pMIR-REPORT plasmid containing wild-type HPGD 3’UTR, mut HPGD 3’UTR or control insert and the internal control pRL-TK. All samples were assayed in duplicate (n = 3). **, P < 0.01 (c)
Discussion
Because miRNAs are central to the regulations of self-renewal and differentiation of stem cells [15, 16], stem cells represent novel targets for regulating their behavior and differentiation. In this study, we have examined how miR-218 regulates SDSCs chondrogenic differentiation and RCJ3.1C5.1 chondrocytes maturation. miR-218 was found to be dramatically upregulated in SDSC early chondrogenesis but was downregulated in late stages. Moreover, miR-218 mimics strongly promoted the differentiation of SDSCs into chondrocytes. In contrast, miR-218 inhibition suppressed SDSC differentiation into chondrocytes. In addition, the level of osteogenic marker expression was found to significantly decrease in the early stage of chondrogenesis, and miR-218 overexpression might negatively regulate this process. Chondrogenic markers were dramatically increased by overexpression of miR-218. Furthermore, transfection of miR-218 mimics markedly suppressed expression of maturation markers in RCJ3.1C5.18 chondrocytes, but miR-218 inhibitor notably promoted expression of these maturation markers. miR-218 might directly regulate HPGD expression in SDSCs. These findings indicate that miR-218 possibly regulates SDSC chondrogenesis via the miR-218-HPGD pathway.
Articular cartilage is a unique tissue characterized by low cellular density and a lack of vascular components. The major composition of articular cartilage is proteoglycans and extracellular collagens and it has a very limited self-healing capacity in pathological conditions such as injury and degeneration [1]. Moreover, treatment options for cartilage trauma have dramatic differences in terms of effectiveness. Although early clinical studies indicated the effectiveness of ACT [17], randomized studies have reported little value of this ACT procedure in terms of effectiveness when compared with inducing subchondral bone microfracture [3]. ACT also involves donor-site morbidity and joint osteoarthritic alterations [4]. Therefore, alternative cell sources are required. MSCs have been recommended as candidates because they are capable of differentiating into chondrocytes with biological functions. Additionally, the similarity between differentiated MSCs and host cells render them ideal for cartilage replacement therapy [18]. Accordingly, transplantation of MSCs possessing chronic differentiation capacity might be an effective treatment strategy for articular cartilage injury. However, despite successful reports, MSC transplantation has also been associated with drawbacks; for example, transplantation of MSCs may lead to heterogeneous undifferentiated and differentiated populations [19]. Thus, new strategies are needed to enhance dedicated chondrocytes differentiation from MSCs.
There are abundant experimental findings pointing at the critical regulatory role that miRNAs play in MSC chondrogenic differentiation. By suppression of certain genes, several miRNAs have been shown to regulate chondrocytes differentiation from MSCs. For instance, miR-140 [20], miR-23b [21], miR-455 [20], and miR-335 [22] were found to boost chondrogenic differentiation by suppressing ADAMTS5, PRKACB, Smad2/3, and ROCK1. On the other hand, miR-574 [23], miR-29a [24], and miR-495 [25] were found to downregulate chondrogenesis by inhibiting RXRα, FOXO3A, and SOX9. WNT signaling plays an important role in the MSCs chondrogenic differentiation [13], and miR-218 activates WNT signaling pathway by targeting its negative regulatory factors [12]. Based on these results, we hypothesized that miR-218 might positively regulate MSC chondrogenic differentiation as well as maturation of RCJ3.1C5.1 chondrocytes. Our findings clarified that miR-218 acts as a promoter during early chondrogenic differentiation of SDSCs and as a silencer during later chondrocyte maturation.
Chondrogenesis has been divided into two phases: early chondrogenesis and hypertrophy. The former stage is featured by upregulated COL2A1 and SOX9, and the latter stage is evidenced by upregulated Col10a1 and Runx2 [26]. Both phases are inter-regulated via interactions among several signaling pathways [27], and they antagonize each other [28,29,30,31]. Runx2, a key regulatory gene in osteogenic differentiation, mediates many osteogenic-related genes. However, Runx2 suppresses MSCs chondrogenic differentiation in the early stage and promotes later chondrocyte maturation [32]. PGE2 may promote cell proliferation and increase SOX9, COL2A1, and aggrecan expression in the early phase of MSCs chondrogenic differentiation while restraining later chondrocyte maturation. These findings reveal that Runx2 and PGE2 may play critical roles in early chondrogenic differentiation and later chondrocyte maturation.
In conclusion, our results showed significant upregulation of miR-218 early in SDSC chondrogenic differentiation and downregulation later during chondrocyte maturation. miR-218 overexpression enhances expression of chondrogenic markers, promoting early SDSC chondrogenic differentiation and suppressing later chondrocyte maturation. Moreover, miR-218 may regulate SDSC chondrogenesis via the miR-218-HPGD pathway. Therefore, miR-218 mimics may constitute a therapeutic strategy when applying SDSC-based therapy for the treatment of cartilage-related disorders.
Conclusion
Our study suggests that miR-218 contributes to early chondrogenesis while suppressing later chondrocyte maturation. The miR-218-HPGD pathway offers us a perspective into how SDSCs differentiate into chondrogenic cells and constitute a therapeutic strategy when applying SDSC-based therapy for the treatment of cartilage-related disorders.
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Articular cartilage
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- COMP:
-
Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein
- GAGs:
-
Glycosaminoglycans
- HPGD:
-
15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase
- MMP-13:
-
Metal matrix proteinase 13
- MSC:
-
Mesenchymal stem cell.
- OCN:
-
Osteocalcin
- OPN:
-
Osteopontin
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PGE2:
-
Prostaglandin E2
- Runx2:
-
Runt-related transcription factor 2
- SDs:
-
Standard deviations
- SDSCs:
-
Synovium-derived MSCs
- SOX9:
-
SRY-related gene 9
- TGF-β3:
-
Transforming growth factor beta 3
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Redman SN, Oldfield SF, Archer CW. Current strategies for articular cartilage repair. European cells & materials. 2005;9:23–32 discussion 23-32.
Peterson L, Minas T, Brittberg M, Nilsson A, Sjogren-Jansson E, Lindahl A. Two- to 9-year outcome after autologous chondrocyte transplantation of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;374:212–34.
Knutsen G, Engebretsen L, Ludvigsen TC, Drogset JO, Grontvedt T, Solheim E, Strand T, Roberts S, Isaksen V, Johansen O. Autologous chondrocyte implantation compared with microfracture in the knee. A randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(3):455–64.
Lee CR, Grodzinsky AJ, Hsu HP, Martin SD, Spector M. Effects of harvest and selected cartilage repair procedures on the physical and biochemical properties of articular cartilage in the canine knee. J Orthop Res. 2000;18(5):790–9.
Jones BA, Pei M. Synovium-derived stem cells: a tissue-specific stem cell for cartilage engineering and regeneration. Tissue Eng B Rev. 2012;18(4):301–11.
Kobayashi T, Lu J, Cobb BS, Rodda SJ, McMahon AP, Schipani E, Merkenschlager M, Kronenberg HM. Dicer-dependent pathways regulate chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(6):1949–54.
Dong S, Yang B, Guo H, Kang F. MicroRNAs regulate osteogenesis and chondrogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;418(4):587–91.
Hong E, Reddi AH. MicroRNAs in chondrogenesis, articular cartilage, and osteoarthritis: implications for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng B Rev. 2012;18(6):445–53.
Guan YJ, Yang X, Wei L, Chen Q. MiR-365: a mechanosensitive microRNA stimulates chondrocyte differentiation through targeting histone deacetylase 4. FASEB J. 2011;25(12):4457–66.
Yang B, Guo H, Zhang Y, Chen L, Ying D, Dong S. MicroRNA-145 regulates chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by targeting Sox9. PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21679.
Zhang Y, Xie RL, Croce CM, Stein JL, Lian JB, van Wijnen AJ, Stein GS. A program of microRNAs controls osteogenic lineage progression by targeting transcription factor Runx2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(24):9863–8.
Hassan MQ, Maeda Y, Taipaleenmaki H, Zhang W, Jafferji M, Gordon JA, Li Z, Croce CM, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, et al. miR-218 directs a Wnt signaling circuit to promote differentiation of osteoblasts and osteomimicry of metastatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(50):42084–92.
Akiyama H, Lyons JP, Mori-Akiyama Y, Yang X, Zhang R, Zhang Z, Deng JM, Taketo MM, Nakamura T, Behringer RR, et al. Interactions between Sox9 and beta-catenin control chondrocyte differentiation. Genes Dev. 2004;18(9):1072–87.
Pei M, He F, Vunjak-Novakovic G. Synovium-derived stem cell-based chondrogenesis. Differentiation; research in biological diversity. 2008;76(10):1044–56.
Gangaraju VK, Lin H. MicroRNAs: key regulators of stem cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(2):116–25.
Lakshmipathy U, Hart RP. Concise review: MicroRNA expression in multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26(2):356–63.
Brittberg M, Lindahl A, Nilsson A, Ohlsson C, Isaksson O, Peterson L. Treatment of deep cartilage defects in the knee with autologous chondrocyte transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1994;331(14):889–95.
Oreffo RO, Cooper C, Mason C, Clements M. Mesenchymal stem cells: lineage, plasticity, and skeletal therapeutic potential. Stem cell reviews. 2005;1(2):169–78.
Ham O, Lee CY, Kim R, Lee J, Oh S, Lee MY, Kim J, Hwang KC, Maeng LS, Chang W. Therapeutic potential of differentiated mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(7):14961–78.
Swingler TE, Wheeler G, Carmont V, Elliott HR, Barter MJ, Abu-Elmagd M, Donell ST, Boot-Handford RP, Hajihosseini MK, Munsterberg A, et al. The expression and function of microRNAs in chondrogenesis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1909–19.
Ham O, Song BW, Lee SY, Choi E, Cha MJ, Lee CY, Park JH, Kim IK, Chang W, Lim S, et al. The role of microRNA-23b in the differentiation of MSC into chondrocyte by targeting protein kinase a signaling. Biomaterials. 2012;33(18):4500–7.
Lin X, Wu L, Zhang Z, Yang R, Guan Q, Hou X, Wu Q. MiR-335-5p promotes chondrogenesis in mouse mesenchymal stem cells and is regulated through two positive feedback loops. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(7):1575–85.
Guerit D, Philipot D, Chuchana P, Toupet K, Brondello JM, Mathieu M, Jorgensen C, Noel D. Sox9-regulated miRNA-574-3p inhibits chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e62582.
Guerit D, Brondello JM, Chuchana P, Philipot D, Toupet K, Bony C, Jorgensen C, Noel D. FOXO3A regulation by miRNA-29a controls chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and cartilage formation. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(11):1195–205.
Lee S, Yoon DS, Paik S, Lee KM, Jang Y, Lee JW. microRNA-495 inhibits chondrogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells by targeting Sox9. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(15):1798–808.
Hou C, Yang Z, Kang Y, Zhang Z, Fu M, He A, Zhang Z, Liao W. MiR-193b regulates early chondrogenesis by inhibiting the TGF-beta2 signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(9):1040–7.
Shimizu H, Yokoyama S, Asahara H. Growth and differentiation of the developing limb bud from the perspective of chondrogenesis. Develop Growth Differ. 2007;49(6):449–54.
Cheng A, Genever PG. SOX9 determines RUNX2 transactivity by directing intracellular degradation. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(12):2680–9.
Yamashita S, Andoh M, Ueno-Kudoh H, Sato T, Miyaki S, Asahara H. Sox9 directly promotes Bapx1 gene expression to repress Runx2 in chondrocytes. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(13):2231–40.
Chen H, Ghori-Javed FY, Rashid H, Adhami MD, Serra R, Gutierrez SE, Javed A. Runx2 regulates endochondral ossification through control of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(12):2653–65.
Ulrich C, Rolauffs B, Abele H, Bonin M, Nieselt K, Hart ML, Aicher WK. Low osteogenic differentiation potential of placenta-derived mesenchymal stromal cells correlates with low expression of the transcription factors Runx2 and Twist2. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(21):2859–72.
Komori T. Regulation of bone development and extracellular matrix protein genes by RUNX2. Cell Tissue Res. 2010;339(1):189–95.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This project was partially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai City, China (Grant No. 15ZR1414000, to PLF), and the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81601889, to SC).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Author disclosure statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: SC, ZYX, JHS, PLF, HSW. Performed the experiments: SC, ZYX, JHS. Analyzed the data: SC, ZYX, JHS. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: HSW. Wrote the paper: SC, ZYX, JHS. All the authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Care and Protection Committee of Second Military Medical University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Xu, Z., Shao, J. et al. MicroRNA-218 promotes early chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells and inhibits later chondrocyte maturation. BMC Biotechnol 19, 6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-018-0496-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-018-0496-0