Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the prevalence and risk factors of wrist pain.
Methods
Systematic review. Data sources: The MEDLINE and EMBASE via OVID, CINAHL and SPORTDiscus via EBSCO databases were searched from database inception to 9th March 2018. Specific criteria were used to define inclusion and exclusion. Data was extracted independently by a pair of reviewers.
Results
In total 32 cross sectional studies were identified for inclusion (1 with a longitudinal component). The median prevalence of wrist pain in the general population and non-manual workers within the short term (within last week) was 6 and 4.2% within the medium term (> 1 week and within a year). The median prevalence of wrist pain in physically demanding occupations and sports people was 10% within the short term and 24% within the medium term. Non-modifiable factors associated with wrist pain included increased age (1 study in adults and 3 studies in children/adolescents) and female sex (2 studies). Modifiable risk factors included high job physical strain (2 studies), high job psychological strain (1 study), abnormal physeal morphology in children/adolescents (2 studies), high frequency impact tool use (1 study) and effort reward imbalance (1 study).
Conclusions
Wrist pain is highly prevalent in groups who partake in physically demanding activities from day to day such as manual labourers and sportspeople. It is less prevalent in the general population and non-manual workers, although there is a relative lack of research in the general population.
Trial registration
The review protocol was registered with PROSPERO under the registration number CRD42018090834.
Level of Evidence
1 (Prognostic study).
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Musculoskeletal pain is a highly prevalent and costly health care problem globally [1]. Wrist pain accounts for an annual consultation prevalence rate of 58 in 10,000 patients in the UK [2], and is the fourth most common site of musculoskeletal pain in the upper limb after the shoulder, hand and elbow. While Walker-Bone et al. have demonstrated that non specific hand and wrist pain has a prevalence of around 10% in the general population [3]. Wrist pain is seen by a wide variety of clinicians in the United Kingdon including general practitioners, physiotherapists, occuptational therapists, sports doctors, orthopaedic surgeons, plastic surgeons and rheumatologists. Generally the management depends upon diagnosis reached, certain traumatic conditions are managed very differently to inflammatory conditions.
The factors associated with pain in the hand and the distal upper limb in general have been reviewed by other authors [4, 5], while other studies have reported on the prevalence of specific musculoskeletal problems in specific professions such as physicians and golfers [6, 7]. Other reviews have summarised the evidence relating to the whole upper limb [8], or have results which do not separate the wrist from the hand [9]. However we are unaware of any previous systematic review related to the epidemiological evidence relating to wrist pain as a specific entity. From a clinical perspective wrist pain and hand pain are very different entities, not only in terms of diagnosis but also in terms of management.
In this context our aim was to summarise the epidemiological evidence relating specifically to wrist pain. Specifically our aim was to perform a systematic review of the prevalence and risk factors of outcome of wrist pain in adults and children. All risk factors were sub grouped into the modifiable and non-modifiable categories.
Methods
The systematic review was developed in accordance with the PRISMA statement, using the methods decribed in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions and modified as described here. The protocol was developed and peer reviewed locally before registration on the PROSPERO database (CRD42018090834).
Data sources and searches
A comprehensive search strategy was created in collaboration with a research librarian (NT) and was designed to capture all relevant articles pertaining to observational studies relating to wrist pain (Additional file 1:). The full search strategy is detailed on the PROSPERO website. The search strategy was applied to the following bibliographic databases from database inception until 9th March 2018: MEDLINE and EMBASE via OVID, CINAHL and SPORTDiscus via EBSCO from database inception until 9th March 2018.
Inclusion/exclusion criteria
The inclusion and exclusion criteria were defined prospectively during the protocol stage. Inclusion criteria included any cross sectional study or longitudinal study with a study population of any age and any setting with signs and/or symptoms of wrist pain reported within this group. There was no restriction on the type of setting for potential included papers. Included studies were required to report prevalence data, and had to be published in English or where an English translation was available. Exclusion criteria included: if the study population was defined on the basis of wrist pain (e.g.a solely asymptomatic and/or symptomatic group); if the study population was selected from a specific disease area (e.g. diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis); if patients with acute traumatic wrist pathology were deliberately included as new ‘incident’ cases (e.g. scaphoid fracture, distal radius fracture, scapholunate ligament rupture). Only studies which had asked participants specifically about wrist pain were included, studies which had amalgamated hand and wrist pain together in their questioning were excluded. Therefore wrist pain was defined as any pain attributed to the wrist by the patient or an observer/assessor, and pain attributed non-specifically to the wrist (for example to both the wrist and hand in a question or diagram) was not included within this definition. Studies in which the data had not been broken down to exclusively relate to wrist pain (for example by combining hand and wrist pain) were excluded. This underpinned the stated aim of the review which was to summarise information relating to wrist pain, not hand and wrist pain. Case reports and systematic reviews were excluded. A paediatric/adolescent population was defined as a population containing entirely members under the age of 18 years.
Selection of studies
Duplicates were removed and relevant studies identified from the search were imported into Covidence for screening. Studies were independently screened by title and abstract by two authors (BD and RF). The references of all included studies and all relevant review articles on the topic were also reviewed to identify other potential studies for inclusion. This was followed by a full-text evaluation of the selected studies. Disagreement between the two reviewers was solved by consensus involving a third author (NR).
Data extraction
Two reviewers (BD and RF) independently extracted data. Data was extracted using a custom data extraction sheet in Covidence (http://www.covidence.org). The data extracted included the author name, year of publication, journal, setting of study, type of study, population type and demographics, type of measurement used, prevalence of wrist pain, risk factors and predictive risk factors. Risk factors were defined as factors associated with wrist pain at one time point; while a predictive risk factor was defined as a factor which was assessed for predicting the development of wrist pain, meaning that a minimum of two time points would need to be studied. Risk factors were divided into the non-modifiable and modifiable groups. Any inconsistencies between the two reviewers’ forms were resolved by consensus discussion. A third review (NR) was available for any disagreement that could not be resolved by this initial discussion.
If data was not available from full-text articles or trial registrations, authors were contacted to provide this information. If authors were not contactable as regards additional data, then this aspect of the study was excluded from the data synthesis. If contactable authors did not respond to initial requests, they were sent two subsequent reminders over a minimum of 6 weeks. If there was still no response for the additional data, then this aspect of the study could not be included in the data synthesis.
Outcomes
The prevalence and risk factors of wrist pain were of primary interest. The time frame over which incident wrist pain was reported was grouped as short term (current or up to and including past 7 days) and medium term (beyond 1 week and up to and including 1 year).
Risk of bias assessment
Included studies were assessed for risk of bias by two independent raters (BD and NR) using a custom checklist based on that used by Lewis et al. [10]. It included six sections that assessed the study population, participant attrition, prognostic factor measurement, outcome measurement, confounding measurement, and statistical analysis. Each section had from 3 to 6 questions that were rated as high, low or unclear risk of bias (Additional File 4). Where appropriate, separate questions were used to evaluate studies which investigated risk factors and predictive risk factors. Any disagreements between ratings were resolved by discussion between the raters. A third party (NR) was available in any case where disagreements persisted after discussion. The checklist is attached a Additional file 2.
Data analysis
Descriptive analysis was performed for all data to facilitate narrative interpretation and comparison across studies. We analysed the prevalence data by dividing it into six groups based upon the time period over which the wrist pain was assessed and the type of participant group (general population and non-manual workers, higher risk groups (physically demanding occupations and sportspeople) and children/adolescents. We excluded the data from studies which did not state the time period over which the prevalence of wrist pain was assessed over.
Results
Study selection
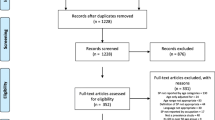
A total of 1342 studies were identified by the search, after duplicates were removed. Following initial screening 82 studies remained for screening by full-text, 32 studies were then identified as eligible for inclusion (Fig. 1). The number of studies identified and excluded at each stage is detailed in Fig. 1.
Study characteristics, results of individual studies and synthesis of results
Study characteristics of the included studies including the demographics, study design and wrist pain measurement method are provided in Table 1. The results are summarised in Tables 1 and 2. Table 1 details the prevalence of wrist pain. Table 2 details any extra information, as well as the associated factors and risk factors for wrist pain.
Study characteristics
Of the 32 included studies, all of which were cross sectional studies (1 with a longitudinal component); seven of these studies compared two distinct populations while the remainder analysed only one population. Seven studies related to solely children and adolescents, while the remaining 25 studies related solely to adult populations. The studies by Davatchi et al. and Fiori et al. do have overlap in terms of the population group studied, although they have described different results relating to these populations. The method of assessing the prevalence of wrist pain was highly variable. The CMDQ (Cornell Musculoskeletal Disorder Questionnaire) was used by three studies, the COPCORD Core Questionnaire (CCQ) by two studies and a version of the NMDQ (Nordic Musculoskeletal Disorder Questionnaire) by three studies. The other methods for assessing wrist pain are summarised in Table 1. The time frame over which wrist pain was assessesed was also highly variable, varying from ‘current’ to pain within the last year as is detailed in Table 1.
Results – prevalence
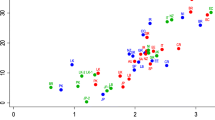
These results are detailed in Table 1 and shown in Fig. 2. The median prevalence of wrist pain in all populations combined within the short term (within last week) was 10% (IQR 3.3 to 15.6) and 19.1% (IQR 8.5 to 40.5) within the medium term (> 1 week and within a year).
The median prevalence of wrist pain in the general population and non-manual workers within the short term (within last week) was 6% (IQR 0.5 to 10.3) and 4.2% (IQR 43.75 to 5.6) within the medium term (> 1 week and within a year). The median prevalence of wrist pain in physically demanding occupations and in sportspeople was 10% (IQR 5.6 to 17.8) within the short term and 24% (IQR 12.7 to 38.6) within the medium term. The median prevalence of wrist pain in the medium term in female child/adolescent gymnasts was 57% (IQR 56 to 73). Figure 2 represent a scatter plot of the prevalence of wrist pain in the different groups, we wish to make it clear this is not a form of meta-analysis. The prevalence of wrist pain was much lower in the non-gymnastic general paediatric population as reported by Kirby et al., however no time frame was reported for the wrist pain so this was not included within the scatter plot [11].
Results – risk factors
These results are detailed in Table 2, while Fig. 2 shows the prevalence of wrist pain in the different groups.
Non-modifiable risk factors
The non-modifiable factors associated with wrist pain included increased age (1 study in adults [12] and 2 studies in children/adolescents [13,14,15]), and female sex [16, 17]. Kihlberg et al. demonstrated an odds ratio of 1.4 (95% CI 1.1–1.7) with increased age [12], while the studies by Di Fiori et al. did not provided an odds or risk ratio, Davatchi et al. showed that the frequency of wrist pain was 14.7% (CI 13.6–15.8) in women, higher than in men 5.6% (CI 4.9–6.3), however no odds or risk ratio was provided [16]. Harutunian et al. found a higher prevalence of wrist pain in women but provided no further data relating to the strength of this association [17].
Modifiable risk actors
The impact of occupation was investigated by several studies. The prevalence of wrist pain was in higher in brick field (85%) vs officer workers (3%) [18], brass metal (62%) vs officer workers (4%) [19], athletes vs university staff [20], gymnasts (33%) versus non gymnasts (2%) [11], endoscopists versus non endoscopists [21], garment workers vs hospital employees (RR 3.9 (95% CI 1.4–10.9) [22], and sewing machine operators versus controls [23].
The modifiable factors associated with wrist pain included high job physical strain ( [24, 25], 2 studies), high job psychological strain [25], abnormal physeal morphology in children/adolescents (2 studies [13, 26]), high frequency impact tool use [12] and effort reward umbalance [25]. Yu et al. demonstrated that wrist pain was more common in men and women with high job strain (psychological demands) (men OR 1.4 (95%CI 1.02–1.91) and women OR 2.20 (95%CI 1.31–3.69)) and high job strain (physical demands) (men OR 1.37 (95%CI 1.05–1.80) and women OR 1.56 (95%CI 1.02–2.40)); wrist pain was also more common in men and women with a effort reward imbalance (ERI) (men OR 1.29 (95% CI 1.02–1.23) and women OR 1.56 (95% CI 1.00–2.42, 25). Celik et al. nurses who often lifted/carried heavy materials felt significantly more pain in the wrist (37.8%; OR, 0.17; 95% CI, 0.05–0.49). Chang et al. found that 24.6% of the 171 painful wrists had abnormal growth plate morphology compared to 19 (10.5%) of the 181 asymptomatic wrists (RR 2.3, 26). While Kihlberg et al. found a higher risk of wrist pain with high frequency impact tool use (OR 1.5 (95% CI 1.0–2.3)) [12].
Predictive risk factors
Only one study assessed predictive risk factors and this was observed at a follow up time of five years, demonstrating that in workers who use power tools a higher rate of wrist pain at 5 years associated with high frequency impact tool use (RR 1.6 (95%CI 0.8–3.4)) and number of years in occupation (RR 1.5 (95% CI 0.9–2.5)) [12].
Risk of bias within studies and across studies
The risk of bias summary is shown in Fig. 3 and the risk of bias graph in the Additional file 3. The risk of bias was generally low for the study population domains (description of sampling, inclusion/exclusion criteria and reporting of basic participant characteristics). In terms of response rate and wrist pain measurement the risk of bias was higher on average, with a majority of studies judged to be at high risk of bias in these domains. Again the results were mixed in the confounding and statistics domains for studies which investigated associated factors. A significant proportion of studies investigating the associated factors did not report odds ratios or risk ratios with their 95% confidence intervals, as well as those adjusted for confounding. Only one study assessed the risk factors of wrist pain and was scored against the relevant domains for prognostic studies.
Discussion
The key finding of this systematic review is that wrist pain is highly prevalent in groups who partake in physically demanding activities from day to day such as manual labourers and sportspeople. It is less prevalent in the general population and non-manual workers, although there is a relative lack of research in this area. It is also pertinent that there is a lack of epidemiological research investigating the relationship between structural abnormalities and pain in adults.
There is a significant body of evidence which demonstrates that modifiable risk factors such as occupation, workplace demands and sporting activity are associated with wrist pain [11, 12, 18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. This is consistent with the evidence relating to other sites of chronic musculoskeletal pain such as the shoulder and spine [27,28,29,30]. While Da Costa et al. have shown that heavy physical work, smoking, high body mass index, high psychosocial work demands increase the risk of work related musculoskeletal disorders [31]. In this review only one study assessed predictive risk factors, demonstrating that workers who use power tools have a higher rate of wrist pain at 5 years, this is associated with high frequency impact tool use and the number of years in occupation. This points to the importance of the holistic approach in assessing and managing patients with wrist pain, as it may be useful to detect specific modifiable risk factors which can be incorporated into any potential treatment plan.
Although wrist pain is not as common as back, shoulder, hip and knee pain, it nonetheless represents a significant proportion of the overall musculoskeletal burden [2]. While there is epidemiological evidence to demonstrate a relationship between structural abnormalities in hip and shoulder pain for example [32, 33], this review has found no epidemiological evidence that demonstrates a clear relationship between structural change and wrist pain in adults. This is problematic as in the absence of the epidemiological evidence to demonstrate that specific structural abnormalities are associated with pain and dysfunction, there should be significant uncertainty regarding the treatment of any form of chronic wrist pain with a surgical intervention in order to address structure. The studies by DiFiori et al. in young gymasts are the only ones within this review which have shown that a structural abnormality, abnormal physeal morphology, is associated with wrist pain [13, 26].
The prevalence of radiographic wrist osteoarthritis varies within the scientific literature. Studies by Kellgren and Van Saase both demonstrated a prevalence of radiographic wrist osteoarthritis of around 5 to 10% in men women, [34, 35]. A lower prevalence was reported in the Framingham study of less than 2% [36]. These differences may well relate to different radiographic thresholds used for determining the presence of radiographic osteoarthritis. While other structural abnormalities around the wrist have been shown to be highly prevalent in asymptomatic patients such as those relating to the TFCC [37], extensor carpi ulnaris tendon [38] and ganglia [39, 40]. In this context it is unsurprising that the results of surgery can be unpredictable when treating structural abnormalities which are highly prevalent in the asymptomatic general population. Generally degenerative structural change is far more common with increasing age and it is salient in this review that only one study demonstrated that age was an associated factor for wrist pain [12]. This means that highly prevalent structural abnormalities are unlikely to be a significant explanatory factor for wrist pain in general adult populations.
Limitations
The main limitations of this systematic review relate to the included studies’ limitations. There are significant methodological flaws present within the included studies. These include the use of unvalidated methods of assessing wrist pain, the low response rates and the lack of adjustment for confounding factors in some studies. Another significant limitation is the number of studies (n = 41) which had to be excluded due to study design (Fig. 1), this was largely down to the way in which wrist pain had not been specifically investigated. As previously stated our specific aim was to assess wrist pain as a distinct entity and this underlies the exclusion of studies which did not separate hand and wrist pain.
Conclusions
Overall there is a lack of high quality research investigating the epidemiology of wrist pain. The existing evidence demonstrates that wrist pain is highly prevalent in groups who partake in physically demanding activities from day to day such as manual labourers and sportspeople, while it is less prevalent in the general population and non-manual workers.. There is also a lack of research investigating the relationship between structural abnormalities and pain in adults which would be a sensible target for future research.
Availability of data and materials
All data underlying the results are available as part of the article and no additional source data are required.
Abbreviations
- CCQ:
-
COPCORD Core Questionnaire
- CMDQ:
-
Cornell Musculoskeletal Disorder Questionnaire
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- NMDQ:
-
Nordic Musculoskeletal Disorder Questionnaire
- TFCC:
-
Triangular fibrocartilage complex
- UK:
-
United Kingdom
References
Urwin M, Symmons D, Allison T, Brammah T, Busby H, Roxby M, et al. Estimating the burden of musculoskeletal disorders in the community: the comparative prevalence of symptoms at different anatomical sites, and the relation to social deprivation. Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57(11):649–655. PubMed PMID: 9924205. Pubmed Central PMCID: 1752494. Epub 1999/01/30. eng.
Jordan KP, Kadam UT, Hayward R, Porcheret M, Young C, Croft P. Annual consultation prevalence of regional musculoskeletal problems in primary care: an observational study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2010;11:144. PubMed PMID: 20598124. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC2903510. Epub 2010/07/06. eng.
Walker-Bone K, Palmer KT, Reading I, Coggon D, Cooper C. Prevalence and impact of musculoskeletal disorders of the upper limb in the general population. Arthritis Rheum 2004;51(4):642–651. PubMed PMID: 15334439. Epub 2004/08/31. eng.
Nicholls EE, van der Windt DA, Jordan JL, Dziedzic KS, Thomas E. Factors associated with the severity and progression of self-reported hand pain and functional difficulty in community-dwelling older adults: a systematic review. Musculoskeletal care 2012;10(1):51–62. PubMed PMID: 22290761. Epub 2012/02/01. eng.
Whibley D, Martin KR, Lovell K, Jones GT.A systematic review of prognostic factors for distal upper limb pain. British Journal of Pain. 2015 ;9(4):241–255. PubMed PMID: 607791477.
Oude Hengel KM, Visser B, Sluiter JK. The prevalence and incidence of musculoskeletal symptoms among hospital physicians: a systematic review. International archives of occupational and environmental health. 2011;84(2):115–119. PubMed PMID: 20686782. Epub 08/05. eng.
Robinson PG, Murray IR, Duckworth AD, Hawkes R, Glover D, Tilley NR, et al. Systematic review of musculoskeletal injuries in professional golfers. Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(1):13.
Huisstede BMA, Bierma-Zeinstra SMA, Koes BW, Verhaar JAN. Incidence and prevalence of upper-extremity musculoskeletal disorders. A systematic appraisal of the literature. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2006;7:7-. PubMed PMID: 16448572. eng.
Fuglkjær S, Dissing KB, Hestbæk L. Prevalence and incidence of musculoskeletal extremity complaints in children and adolescents. A systematic reviewBMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2017 2017/10/18;18(1):418.
Lewis GN, Rice DA, McNair PJ, Kluger M. Predictors of persistent pain after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth 2015;114(4):551–561. PubMed PMID: 25542191. Epub 2014/12/30. eng.
Kirby RL, Simms FC, Symington VJ, Garner JB. Flexibility and musculoskeletal symptomatology in female gymnasts and age-matched controls. Am J Sports Med 1981;9(3):160–164. PubMed PMID: 7235112. Epub 1981/05/01. eng.
Kihlberg S, Hagberg M. Hand-arm symptoms related to impact and nonimpact hand-held power tools. International Archives of Occupational & Environmental Health 1997;69(4):282–288. PubMed PMID: 9138003.
DiFiori JP, Puffer JC, Aish B, Dorey F. Wrist pain, distal radial physeal injury, and ulnar variance in young gymnasts: does a relationship exist? Am J Sports Med 2002;30(6):879–885. PubMed PMID: 12435656. Epub 2002/11/19. eng.
DiFiori JP, Puffer JC, Aish B, Dorey F. Wrist pain in young gymnasts: frequency and effects upon training over 1 year. Clin J Sport Med 2002;12(6):348–353. PubMed PMID: 12466689.
DiFiori JP, Puffer JC, Mandelbaum BR, Mar S. Factors associated with wrist pain in the young gymnast. Am J Sports Med 1996;24(1):9–14. PubMed PMID: 8638761.
Davatchi F, Jamshidi AR, Banihashemi AT, Gholami J, Forouzanfar MH, Akhlaghi M, et al. WHO-ILAR COPCORD study (stage 1, urban study) in Iran. J Rheumatol 2008;35(7):1384. PubMed PMID: 18464299. Epub 2008/05/09. eng.
Harutunian K, Gargallo-Albiol J, Figueiredo R, Gay-Escoda C. Ergonomics and musculoskeletal pain among postgraduate students and faculty members of the School of Dentistry of the University of Barcelona (Spain). A cross-sectional study. Medicina oral, patologia oral y cirugia bucal 2011;16(3):e425–e429. PubMed PMID: 20711125.
Das B. Assessment of occupational health problems and physiological stress among the brick field workers of West Bengal, India. International Journal of Occupational Medicine & Environmental Health 2014;27(3):413–425. PubMed PMID: 24952141.
Gangopadhyay S, Ghosh T, Das T, Ghoshal G, Das BB. Prevalence of upper limb musculo skeletal disorders among brass metal workers in West Bengal, India Industrial Health 2007;45(2):365–370. PubMed PMID: 17485885.
Jonasson P, Halldin K, Karlsson J, Thoreson O, Hvannberg J, Sward L, et al. Prevalence of joint-related pain in the extremities and spine in five groups of top athletes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2011;19(9):1540–1546. PubMed PMID: 21559845.
Kuwabara T, Urabe Y, Hiyama T, Tanaka S, Shimomura T, Oko S, et al. Prevalence and impact of musculoskeletal pain in Japanese gastrointestinal endoscopists: a controlled study. World J Gastroenterol 2011;17(11):1488–1493. PubMed PMID: 21472109.
Punnett L, Robins JM, Wegman DH, Keyserling WM. Soft tissue disorders in the upper limbs of female garment workers. Scand J Work Environ Health 1985;11(6):417–425. PubMed PMID: 4095519.
Sokas RK, Spiegelman D, Wegman DH. Self-reported musculoskeletal complaints among garment workers. Am J Ind Med 1989;15(2):197–206. PubMed PMID: 2786337.
Celik S, Tasdemir N, Oksuzoglu A, Dirimese E, Kocasli S. Critical-care Nurses' pain experiences and the prognostic factors. DCCN - Dimensions of Critical Care Nursing 2018;37(1):3–11. PubMed PMID: 29194167.
Yu S, Nakata A, Gu G, Swanson NG, He L, Zhou W, et al. Job strain, effort-reward imbalance and neck, shoulder and wrist symptoms among Chinese workers. Ind Health 2013;51(2):180–192. PubMed PMID: 23268836.
Chang CY, Shih C, Penn IW, Tiu CM, Chang T, Wu JJ. Wrist injuries in adolescent gymnasts of a Chinese opera school: radiographic survey. Radiology. 1995 Jun;195(3):861–864. PubMed PMID: 7754022. Epub 1995/06/01. eng.
Sommerich CM, McGlothlin JD, Marras WS. Occupational risk factors associated with soft tissue disorders of the shoulder: a review of recent investigations in the literature. Ergonomics. 1993 Jun;36(6):697–717. PubMed PMID: 8513776. Epub 1993/06/01. eng.
Wang ZX, Qin RL, Li YZ, Zhang XY, Jia N, Zhang QL, et al. [The epidemiological study of work-related musculoskeletal disorders and related factors among automobile assembly workers]. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi/Zhonghua Laodong Weisheng Zhiyebing Zazhi/Chinese Journal of Industrial Hygiene & Occupational Diseases 2011;29(8):572–578. PubMed PMID: 22335153.
Chaman R, Aliyari R, Sadeghian F, Vatani Shoaa J, Masoudi M, Zahedi S, et al. Psychosocial Factors and Musculoskeletal Pain Among Rural Hand-woven Carpet Weavers in Iran. Safety and Health at Work. 2015;6(2):120–127. PubMed PMID: 603273461.
Moussavi-Najarkola SAMN. Ergonomic risk factor assessment of Upper Extremities Musculoskeletal Disorders (UEMSDs) by Comprehensive Exposure Index (CEI) in textile industry. Occupational and Environmental Medicine Conference: 23rd Conference on Epidemiology in Occupational Health, EPICOH. 2013;70(SUPPL. 1). PubMed PMID: 71745480.
da Costa BR, Vieira ER. Risk factors for work-related musculoskeletal disorders: a systematic review of recent longitudinal studies. American journal of industrial medicine. 2010 2010/03/01;53(3):285–323.
Kim C, Nevitt MC, Niu J, Clancy MM, Lane NE, Link TM, et al. Association of hip pain with radiographic evidence of hip osteoarthritis: diagnostic test study. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2015;351.
Hinsley H, Nicholls A, Daines M, Wallace G, Arden N, Carr A. Classification of rotator cuff tendinopathy using high definition ultrasound. Muscles, ligaments and tendons journal 2014;4(3):391–397. PubMed PMID: 25489559. Pubmed Central PMCID: 4241433. Epub 2014/12/10. eng.
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 1957;16(4):494–502. PubMed PMID: 13498604. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC1006995. Epub 1957/12/01. eng.
van Saase JL, van Romunde LK, Cats A, Vandenbroucke JP, Valkenburg HA. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: Zoetermeer survey. Comparison of radiological osteoarthritis in a Dutch population with that in 10 other populations. Ann Rheum Dis 1989;48(4):271–280. PubMed PMID: 2712610. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC1003741. Epub 1989/04/01. eng.
Haugen IK, Englund M, Aliabadi P, Niu J, Clancy M, Kvien TK, et al. Prevalence, incidence and progression of hand osteoarthritis in the general population: the Framingham osteoarthritis study. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;70(9):1581–1586. PubMed PMID: 21622766. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC3867970. Epub 2011/05/31. eng.
Iordache SD, Rowan R, Garvin GJ, Osman S, Grewal R, Faber KJ. Prevalence of triangular fibrocartilage complex abnormalities on MRI scans of asymptomatic wrists. Journal of Hand Surgery - American Volume 2012;37(1):98–103. PubMed PMID: 22129657.
Thornton AL, McCarty CW, Burgess MJ. Effectiveness of low-level laser therapy combined with an exercise program to reduce pain and increase function in adults with shoulder pain: a critically appraised topic. J Sport Rehabil 2013;22(1):72–78. PubMed PMID: 23069702. Epub 2012/10/17. eng.
Lowden CM, Attiah M, Garvin G, Macdermid JC, Osman S, Faber KJ. The prevalence of wrist ganglia in an asymptomatic population: magnetic resonance evaluation. Journal of hand surgery (Edinburgh, Scotland). 2005 30(3):302–306. PubMed PMID: 15862373. Epub 2005/05/03. eng.
Burgess RA, Pavlosky WF, Thompson RT. MRI-identified abnormalities and wrist range of motion in asymptomatic versus symptomatic computer users. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2010;11:273-. PubMed PMID: PMC2998464.
Carnes D, Ashby D, Parsons S, Underwood M. Chronic forearm pain presents as a transient and indistinct pain site in a community setting: results from a UK population survey. Family practice. 2008;25(3):197–201.
Davatchi F, Jamshidi A, Tehrani Banihashemi A, Sandoughi M, Moghimi N, Gholami J. Epidemiology of rheumatic diseases in Iran; Adjusted analysis of 4 copcord studies. International journal of rheumatic diseases. 2015;1):14.
Hawkes R, O'Connor P, Campbell D. The prevalence, variety and impact of wrist problems in elite professional golfers on the European Tour. British journal of sports medicine. 2013;47(17):1075–9.
Hou JY, Shiao JS. Risk factors for musculoskeletal discomfort in nurses. Journal of Nursing Research. 2006;14(3):228–36.
Inaba R, Okumura M, Mirbod SM. Subjective symptoms of female workers sorting goods in summer. Industrial Health. 2011;49(4):464–74.
MacDonald K, King D. Work-related musculoskeletal disorders in veterinary echocardiographers: a cross-sectional study on prevalence and risk factors. Journal of Veterinary Cardiology. 2014;16(1):27–37.
McCue TJ, Guse CE, Dempsey RL. Upper extremity pain seen with fly-casting technique: a survey of fly-casting instructors. Wilderness & environmental medicine. 2004;15(4):267–73.
Menzel NN, Brooks SM, Bernard TE, Nelson A. The physical workload of nursing personnel: association with musculoskeletal discomfort. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2004;41(8):859–67.
O'Kane JW, Levy MR, Pietila KE, Caine DJ, Schiff MA. Survey of injuries in Seattle area levels 4 to 10 female club gymnasts. Clinical journal of sport medicine : official journal of the Canadian Academy of Sport Medicine. 2011;21(6):486–92.
Purnell M, Shirley D, Nicholson L, Adams R. Acrobatic gymnastics injury: occurrence, site and training risk factors. Physical therapy in sport : official journal of the Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Sports Medicine. 2010;11(2):40–6.
Saxena P, Gupta SK, Jain S, Jain D. Work-related musculoskeletal pain among dentists in Madhya Pradesh, India: prevalence, associated risk factors, and preventive measures. Asia-Pacific Journal of Public Health. 2014;26(3):304–9.
Smith DR, Leggat PA. Musculoskeletal disorders among rural Australian nursing students. Australian Journal of Rural Health. 2004;12(6):241–5.
Viljamaa K, Liira J, Kaakkola S, Savolainen A. Musculoskeletal Symptoms Among Finnish Professional Orchestra Musicians. Medical problems of performing artists. 2017;32(4):195–200.
Waikakul S, Waikakul W. Chronic upper extremity pain in rubber tree plantation workers. Pain Clinic. 1999;11(4):339–43.
White SC. Prevalence and Risk Factors Associated with Musculoskeletal Discomfort in Spay and Neuter Veterinarians. Animals [Electronic Resource]. 2013;3(1):85–108.
Woldendorp KH, Boonstra AM, Arendzen JH, Reneman MF. Variation in occupational exposure associated with musculoskeletal complaints: a crosssectional study among professional bassists. International Archives of Occupational & Environmental Health. 2018;91(2):215–23.
Funding
BJFD is supported by the BMA’s Doris Hillier Arthritis and Rheumatism Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BD has contributed in terms of study design, acquisition, analysis, interpretation, drafting, revision and final approval. NR and AW have contributed in terms of design, interpretation, drafting, revision and approval. RF has contributed in terms of acquisition, analysis, interpretation, drafting, revision and final approval. NT has contributed in terms of design, acquisition, drafting, revision and approval. AC has contributed in terms of study design, interpretation, drafting, revision and final approval. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1.
Full search histories.
Additional file 2.
PRISMA checklist.
Additional file 3.
Risk of bias graph. Review authors’ judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
Additional file 4.
Details of the risk of bias domains against which studies were deemed at ‘high’, ‘low’ or ‘unclear’ risk of bias.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Ferguson, R., Riley, N.D., Wijendra, A. et al. Wrist pain: a systematic review of prevalence and risk factors– what is the role of occupation and activity?. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 20, 542 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2902-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2902-8