Abstract
Background
Caregiver self-efficacy is crucial in improving patient outcomes and caregiver well-being, but there is a lack of suitable scales to assess this concept within the context of Chinese culture. This study aimed to cross-culturally translate the Caregiver Self-Efficacy in Contributing to Patient Self-Care (CSE-CSC) Scale and evaluate its psychometric properties using classical test theory and item response theory.
Methods
The CSE-CSC scale was adapted using Brislin’s translation model after obtaining authorization from the original author. A multicenter, cross-sectional study was conducted to assess the psychometric properties of this scale. Classical test theory was used to evaluate reliability (internal consistency, test-retest reliability), validity (content validity, structural validity, convergent validity), and floor and ceiling effects. Item response theory was employed to assess the fit of the rating scale model, reliability, item difficulties, and measurement invariance.
Results
The translation and cultural adaptation process was completed. Classical test theory demonstrated good internal consistency (Cronbach’s α = 0.935) and test-retest reliability (ICC from 0.784 to 0.829, p<0.001). The I-CVI and K* of each item ranged from 0.875 to 1.00 and 0.871 to 1.00. The first-order 2-factor model fit well (χ2/df = 3.71, RMSEA = 0.082, SRMR = 0.032, CFI = 0.973, TLI = 0.60). Convergent validity showed that the CSE-CSC scores had a strong positive correlation with three separate scales of the CC-SC-CII. There was no floor and ceiling effect in this scale. Rasch analysis showed that the CSE-CSC scale demonstrated a good fit to the rating scale model and exhibited excellent reliability (person/item separation index>2, person/item reliability coefficients>0.8). The Wright map showed that item difficulty matched the respondents’ measured abilities. The analysis of differential item functioning (DIF) showed that all items were comparable in gender.
Conclusions
This study indicated that the CSE-CSC scale had good reliability, validity, difficulty degree, and measurement invariance. The CSE-CSC scale can be used to measure caregiver self-efficacy of Chinese patients with multiple chronic conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Background
Individuals with multiple chronic conditions (MCCs) are defined as patients with two or more concurrent chronic behavioral or physical conditions [1]. It has been estimated that more than 20% of adults globally suffer from MCCs [2]. MCCs are more common in the older population compared with the general population. The prevalence of MCCs in older people over 65 years reported by different studies ranged from 55 to 98% [2]. In China, the prevalence of MCCs reached 49% in community-dwelling older adults [3]. MCCs affect each other synergistically, leading to a more pronounced impact on patients’ health-related quality of life, physical limitations, and mortality [4, 5]. Additionally, chronic conditions usually require ongoing medical attention and support, resulting in a greater utilization of medical resources by individuals with MCCs. About 31% of the population with 1 or 2 conditions drove 23% of overall healthcare spending, while about 12% of the population with 5 or more chronic conditions was responsible for 41% of spending [1]. Self-care, defined as the process of maintaining one’s health through health-promoting behaviors and disease management [6], has been proven to be critical for improving clinical outcomes and reducing financial burden in MCCs [7]. Self-care in patients with MCCs includes prioritizing ever-changing needs, conditions, and goals, which defined as a dyadic phenomenon [8, 9]. Patients with MCCs are often older and have difficulty in integrating self-care across conditions, so a qualified caregiver is crucial to support patient self-care [10, 11].
Caregiver self-efficacy has been defined as the belief of caregivers in their ability to assist patients with self-care, including helping patients maintain disease stability, promoting symptom monitoring and perception, and responding to elevated physical conditions [12]. The caregiver self-efficacy can enhance patient adherence to disease management and subsequently have a positive impact on patient outcomes [13]. The evidence suggests that high levels of self-efficacy among caregivers could improve the functional and physical well-being of lung cancer patients and alleviate the severity of depression symptom [14]. Moreover, a survey conducted on stroke patients revealed that the self-efficacy level of partner who served as informal caregiver was significantly associated with the patient’s depression level and life satisfaction [15]. Besides, caregiver self-efficacy plays an important role in improving caregiver well-being. A previous study indicated that caregiver self-efficacy was associated with caregiver depression and burden [16].
Although caregiver self-efficacy has been associated with positive health outcomes for patients with MCCs and their caregivers, there are challenges in measuring caregiver self-efficacy for this specific population. The General Self-Efficacy Scale is usually used to evaluate belief in one’s competence to cope with a broad range of stressful or challenging demands, which may not fully capture the specific challenges faced by caregivers of patients with MCCs [17]. In addition, some tools for measuring caregiver self-efficacy have only been explored in the context of single chronic conditions, such as the Caregiver Caregiving Self-Efficacy Scale-Oral Cancer [18], and the Caregiver Confidence in Sign/Symptom Management scale [19]. The 10-item CSE-CSC scale was proposed based on the theory of Self-Care of Chronic Illness to measure caregiver self-efficacy in contributing to patient self-care maintenance, monitoring, and management of multiple chronic illnesses [20]. However, the CSE-CSC scale has not been translated into Chinese and validated.
There are two primary methodologies for evaluating the psychometric properties of a scale: classical test theory (CTT) and item response theory (IRT). While CTT has been extensively utilized for assessing instrument psychometric properties, it is important to acknowledge its limitations, such as its reliance on the sample and the assumption that each item contributes equally to the total scores [21]. IRT offers solutions to these limitations by considering the probability of a correct response based on individual abilities and item characteristics, enabling a more nuanced examination of item properties like difficulty and discrimination [22]. Integrating CTT and IRT can provide a comprehensive assessment of a scale’s properties, addressing the limitations of each approach [23]. Therefore, our study aimed to translate the CSE-CSC into Chinese and evaluate its psychometric properties based on CTT and IRT.
Methods
Participants and settings
From July 2022 to July 2023, the recruitment of caregivers was completed in the cardiology departments of 4 third-class hospitals in Tianjin, China. The inclusion criteria of caregivers were: (a) aged 18 years or older; (b) family members or close relatives of the patients, providing majority informal care tasks (e.g., help in daily activities); (c) provided care for patients who were aged 18 years or older, diagnosed with multiple chronic conditions according to Charlson Comorbidity Index [24]; (d) had clear awareness, reading and language expression ability, independent response and accessible communication; and (e) informed consent for both caregiver and patients. In our study, we excluded caregivers who were paid and had participated in the intervention trial for nearly three months.
The sample size was determined based on a subject-to-item ratio of 10:1 by assuming a non-response rate of 15% [25]. Thus, the sample size was at least 118. Additionally, large samples, usually 300 participants, are necessary for a Rasch model to obtain robust parameter estimates [26]. Finally, we enrolled 406 participants to support stable analysis.
Design and procedures
The translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the English CSE-CSC scale were conducted after obtaining written permission from Professor Maddalena De Maria, the developer of the original scale. The translation was based on Brislin’s translation model and included four steps: forward-translation, target harmonization, blind back-translation, and reconciliation [27]. These steps were repeated in cycles. If ambiguities and discrepancies could not be resolved, the process was repeated as necessary. Cross-cultural debugging was carried out through expert consultation and pilot testing to form the final version (Fig. 1).
Data collection
One data collector was selected from each of the four hospitals and received uniform training to minimize survey and measurement bias. The study purpose and data collection procedure were explained by the data collectors before the survey began. Under the uniform guidance of trained data collectors, 406 participants who provided informed consent were surveyed. Specifically, 61 participants were recruited from the first hospital, 115 from the second hospital, 179 from the third hospital, and 51 from the last hospital. A total of 30 participants who voluntarily left contact information underwent a remeasurement after a 2-week interval. Participants were given the choice to complete the questionnaires online or on paper. The effective recovery rate of the questionnaire was 100%.
Measures
-
(1)
Sociodemographic questionnaire: This part was self-designed and included sociodemographic characteristics of the caregivers and their patients, such as age, gender, education, work status, years of caregiving.
-
(2)
The Caregiver Self-Efficacy in Contributing to Patient Self-Care (CSE-CSC) Scale: The CSE-CSC scale is a 10-item scale produced by Maddalena De Maria et al. [20] and includes two subscales: Self-efficacy in self-care maintenance and monitoring, Self-efficacy in self-care management. The CSE-CSC scale uses a 5-point Likert format (1 = “not confident” to 5 = “very confident”), and the total score is standardized on a scale of 0 to 100, where higher scores mean higher caregiver self-efficacy in contributing to the self-care of patients with MCCs. The Cronbach’s alpha value of the original version was 0.942 for the whole scale [20].
-
(3)
The Caregiver Contribution to Self-Care of Chronic Illness Inventory (CC-SC-CII): The CC-SC-CII is a 19-item tool that measures informal caregiver contribution to self-care behaviors in patients with chronic illness. It consists of three separate scales: the caregiver contribution to self-care maintenance scale, the caregiver contribution to self-care monitoring scale, and the caregiver contribution to self-care management scale [28]. Each scale has a score range of 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating better caregiver contribution. The Chinese version of CC-SC-CII was translated by Dandan Chen, and the Cronbach’s alpha values of three scales were 0.792, 0.880, and 0.870 [29].
Data analysis
Data analysis was conducted using SPSS 24.0, Mplus 8.3, and WINSTEPS 3.6.6, and a p-value < 0.05 was considered significant.
Validity and reliability testing using CTT
-
(1)
Content validity: Content validity index (CVI) and Kappa value (K*) were used to evaluate content validity. Experts were asked to fill out a 4-level content equivalence scale (1 = “not relevant” to 4 = “very relevant and succinct”). The inclusion criteria for experts were as follows: (1) having rich experience in chronic disease management; (2) having been working at least for ten years; (3) being willing to participate in this research. I-CVI was calculated by dividing the number of experts with a relevance rating of 3 or 4 by the total number of experts. S-CVI was calculated by the averaging method, which is the mean value of I-CVI for each item [30]. To avoid the randomness of expert opinion, each item’s Kappa value (K*) was calculated by SPSS 24.0. Quality criteria of good content validity: I-CVI ≥ 0.78, S-CVI/Ave ≥ 0.90, and K*≥ 0.60 [31].
-
(2)
Structural validity: Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was performed to assess the structural validity. The internal structure of the CSE-CSC scale was evaluated using the maximum likelihood estimation method. Overall fit indexes were employed to identify the model’s goodness: normed χ2/df < 3.0, the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) < 0.08, the standardized root mean square residual (SRMR)<0.08, the Comparative Fit Index (CFI) and Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) > 0.9 [32]. The model’s misfit was improved by considering the eventual residual covariances justified to theoretical and methodological reasons.
-
(3)
Convergent validity: Convergent validity was tested by examining the correlation between the CSE-CSC scale and CC-SC-CII scale scores. The hypothesis was that the CSE-CSC scale would have a large positive correlation (Pearson correlation coefficient r ≥ 0.50) with the CC-SC-CII, as reported in the theory [12] and previous study [20].
-
(4)
Reliability: Reliability was evaluated using internal consistency and test-retest reliability. A Cronbach’s α of ≥ 0.70 indicated high internal consistency for the scale. Test-retest reliability means stability, reliability, or reproducibility among the same group of respondents between two time points. In the study, 30 participants were remeasured after two weeks [33]. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were used to identify test-retest reliability, with quality criteria of ICC ≥ 0.70 for good test-retest reliability [34].
-
(5)
Floor/ceiling effect: Floor effects were evaluated by examining the percentage of the respondents who achieved the lowest possible scores, while ceiling effects were assessed by looking at the percentage of respondents who reached the highest possible score. If more than 15% of respondents achieved the highest or lowest possible score, it indicates a ceiling or floor effect [34].
Validity and reliability testing using IRT
-
(1)
Structural validity: The structural validity using Rasch analysis can be rated as sufficient when assumptions on monotonicity, unidimensionality, and local independence are not violated and when there is an adequate model fit [35]. Monotonicity means that the probability of a “correct” response cannot fluctuate, which can be determined based on the item characteristic curves [36]. Principal component analysis was used to test unidimensionality. If the Rasch model explains at least 40% of the variance and the eigenvalue of “Unexplained variance in 1st contrast” does not exceed 3, the scale meets the assumption of unidimensionality [37]. Local independence means that responses to an item should not be dependent on responses to other items. After controlling for the dominant factor, this is violated when residual correlations among the items were greater than 0.3 [38]. The overall fit degree to the Rasch model was estimated by Infit MNSQ and Outfit MNSQ, where a range of 0.5 to 1.5 means fit to the Rasch model [35]. If the result is beyond this range, consideration should be given to whether to carry out item censoring or refinement. Positive and high values (> 0.3) of point-measure correlation indicated that the items were working in the same direction to measure a single basic construct [39].
-
(2)
Reliability analysis: The indicators used to assess reliability were the Person/Item separation index and Person/Item reliability coefficients. Separation indices were employed to assess the difficulty of a project or the continuous distribution of an individual’s ability, and scores exceeding 2.0 indicated a good separation level. Reliability coefficients gauged the replicability of the measurement results, and scores surpassing 0.8 signified good reliability [39].
-
(3)
Item difficulties: Item measure meant the difficulty level of the item for the subjects, with higher values indicating greater difficulty for the item. Besides, a Wright map was used to visually compare the difficulty of the scale items with the participants’ abilities. The Wright map directly compared item difficulty and respondents’ measured abilities in one logit Rasch “bar”.
-
(4)
Measurement invariance: To examine whether the scale items were used in the same way by all groups, a differential item functioning (DIF) was conducted. Logit scores were compared for each item between different genders using the Welch t-test to assess DIF. DIF should be noticed when item DIF Prob. < 0.05 logits [40].
Ethical considerations
The research was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University (Grant number: TMuhMEC2022021). Both caregivers and patients provided written informed consent for participating in the study.
Results
Translation and cultural adaptation
The CSE-CSC scale was translated strictly following the Brislin’s translation model. In order to make the scale easier to accept and understand by the caregivers in the Chinese cultural context and also identify the clarity of the instructions, conceptual and content equivalence, a two-round expert consultation was conducted. The scale was modified in three aspects: (1) The “the person you care for” of the original scale was changed to “patient” to enhance clarity for caregivers, which will improve caregivers’ response speed. (2) Item 2 in the original scale, “Follow the treatment plan that has been given to the person you care for?” did not specify the treatment makers, leading to confusion among caregivers. Experts observed that within the Chinese cultural context, caregivers may sometimes adopt health management methods from unofficial healthcare organizations. Therefore, it is necessary to clarify that the treatment plan refers specifically to those prescribed by medical professionals. (3) The “conditions” was changed to “health conditions” in items 4 and 5. During the plot testing, all 10 participants thought all the items were well-articulated, and the meaning was easily understood. The revised scale used for the final population validation was consistent with the original intention of the scale developers and the Chinese culture. The original CSE-CSC scale and its translated Chinese version are presented in Table 1.
Participants characteristics
Table 2 presents the demographic characteristics of the 406 caregivers and their patients. The caregivers had an average age of 56.35 ± 14.265 years, with 252 (62.1%) female. Care tasks were predominantly undertaken by spouses/partners or children, covering 95.3% of the patients. Half of the caregivers provided care to patients for more than six years. About 58.9% of the patients were male, and 52.2% had 2–4 chronic diseases.
Validity and reliability testing using CTT
Content validity
The results of expert consultation, consisting of eight experts, showed that the I-CVI of the CSE-CSC scale ranged from 0.875 to 1.00, with an overall S-CVI of 0.95. K* values for each item ranged from 0.871 to 1.00. These findings indicated that the content validity of the CSE-CSC was good.
Structural validity
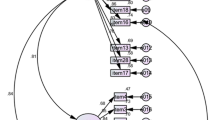
The results of CFA showed that the second-order 2-factor structure supported by the original scale did not exhibit a good fit in this study (see row 1 of Table 3). Based on the original structure, the first-order 2-factor and first-order 1-factor models were verified using the same samples. The first-order 2-factor model demonstrated the best overall fit indexes, with RMSEA = 0.082, SRMR = 0.032, CFI = 0.973, and TLI = 0.60. The χ2/df more than 3 may be due to the lack of a sufficiently large sample size [41]. Factor loading of each item ranged from 0.511 to 0.853, as illustrated in Fig. 2. The model fit was improved by estimating residual covariances between three pairs of items: item 2 and item 5, item 8 and item 9, item 9 and item 10. Item 2 and item 5 were the self-efficacy in self-care maintenance and monitoring dimension. Item 8, 9, and 10 focused on symptom management. The covariances between item residuals were allowed because they followed principles of reasonable methodology or theory [20].
Convergent validity
The results of Pearson’s correlation analysis showed that the CSE-CSC scores had strong positive correlations with three separate scales of the CC-SC-CII: r = 0.605 (P<0.001), r = 0.541 (P<0.001), and r = 0.563(P<0.001), respectively.
Reliability
The Cronbach’s alpha coefficients of the total scale and two factors were 0.935, 0.863, and 0.963, respectively. Although Cronbach’s alpha of total scale and factor 2 were both greater than 0.9, indicating a potential issue of item redundancy, considering the clinical significance of the scale items and the theory of self-efficacy, the internal consistency of the scale was still recognized in this study. The CSE-CSC and two factors had good test-retest reliability, and the ICCs were 0.810 (P<0.001), 0.784 (P<0.001), and 0.829 (P<0.001), respectively.
Floor/ceiling effect
The theoretical and practical score ranges of the CSE-CSC scale were presented in Table 4. The biggest percentage of the occurrences of the lowest/highest possible was 5.17%, so there was no floor and ceiling effect in this scale and two dimensions, which indicated that the Chinese version scale can adequately reflect the actual level of caregiver self-efficacy in contributing to patient self-care.
Rasch analysis of the CSE-CSC
Unidimensionality, local dependency, and monotonicity
Item characteristic curves were shown in Fig. 3, which exhibit the ideal shape, with consistent and distinct peak ordering and appropriate separation of the curves. The assumption of monotonicity was supported. The PCA of the standardized residuals showed that the dimension extracted by the Rasch model accounted for 65.1% of the variance in the data, and the eigenvalue of the unexplained variance in the first extracted component was 2.3. The CSE-CSC scale with ten items satisfied the assumption of unidimensionality. Indication of local dependency between 5 item-pairs (Item 1&7, 5&9, 5&10, 8&9, 9&10) was detected with residual correlations > 0.30 in all 45 item-pairs. In terms of content, the observed local dependency within the scale made sense since these item pairs focused on caregiver confidence in patient symptom management or monitoring.
The response characteristic curves of items. The different colors represent the response options. The x axis represented the range of latent trait of item, the y axis “Category Probability” indicated the probability of endorsing a response option (Orange: response category 1, blue: response category 2, rose: response category 3, brown: response category 4, green: response category 5)
Rasch model fit
The rating scale model showed a good fit to the data. Only one item deviated from the model with both infit and outfit MNSQ were greater than 1.50 (Table 5). All the items produced acceptable point-measure correlations greater than 0.3.
Reliability analysis
The person reliability index (0.93) represented strong consistency among individuals, while the item reliability index (0.99) showed an excellent score. The separation index for individuals in our analysis was 3.51, demonstrating that the scale distinguished the subject population into at least three different ability levels. The separation index of items was 8.36, indicating a clear hierarchy of difficulty among scale items.
Item measure and the wright map
In this study, participants’ abilities ranged from − 8.41 to 7.50 logits, and the difficulty of items ranged from − 1.02 to 1.91 logits. As illustrated in Table 4, item 1 (‘Keep the illness of the person you care for stable and free of symptoms?’) was identified as the most challenging item (1.96 logits) for all respondents. In contrast, item 6 (‘Recognize symptoms in the person you care for if they occur?’) had the lowest difficulty (-1.02 logits). The Wright map visualization for the CSE-CSC scale was presented in Fig. 4. In this study, the average person’s ability was slightly greater than the average item difficulty, indicating a generally good level of caregiver self-efficacy in contributing to patients’ self-care. The figure also showed that a small subset of individuals had high self-efficacy ability with no corresponding questions to match them. This observation could potentially indicate a ceiling effect in the scale’s IRT analysis [39].
Wright person-item Rasch map for the CSE-CSC scale (n = 406). The right side of the figure showed the distribution of items, with the most difficult items at the top to the least difficult at the bottom. On the left side, the distribution represented respondents’ measured abilities, from the most capable at the top to the least capable at the bottom. The symbol of “#” represented 4 persons, and “.” represents 1–3 persons
Measurement invariance
As shown in Table 6, no items exhibited DIF (prob > 0.05) for the male and female subgroups of respondents. The non-significant result revealed a similar level of self-efficiency in contributing to patient self-care among participants in different genders.
Discussion
In this study, the CSE-CSC scale was translated and adapted to the Chinese version, following a clear and user-friendly cultural adaptation guideline to ensure cultural appropriateness [42]. From data collected across multiple research centers, CTT and IRT analyses revealed favorable psychometric characteristics, including reliability, validity, difficulty degree, and measurement invariance. The reliable and valid CSE-CSC scale will contribute to a more accurate evaluation and in-depth understanding of caregiver self-efficacy levels among patients with MCCs. Clinical nurses in China can utilize this scale to gain insights into the role of caregiver self-efficacy in patient and caregiver outcomes. Furthermore, the scale provides a new perspective for evaluating intervention programs targeting patients with MCCs, which can help us select more effective health management strategies to address the unique needs of patients with MCCs and improve the overall quality of care.
The reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the CSE-CSC were unquestionable. In CTT, Cronbach’s alpha reflected the intrinsic reliability, and ICC reflected extrinsic reliability. Our study demonstrated that the Chinese version of the CSE-CSC scale exhibited high internal consistency and temporal stability. In Rasch analysis, the ideal person/item reliability and separation index indicated the scale’s ability to distinguish different potential characteristic populations and achieve good measurement precision. In CTT, this study conducted CFA based on the scale structure summarized by the developer and its possible factor structure. As a result, the overall fit index of the first-order 2-factor model surpassed that of the first-order 1-factor and second-order 2-factor models. In IRT, the total scale was evaluated unidimensionally first. Interestingly, the total scale met the assumption of unidimensionality. Although CTT and IRT supported different factor structures, we did not deny the scale’s structural validity and stability due to the different theoretical and hypothesis bases of the two methods. We need more ground to support the existence of two dimensions or to encourage users to use the two dimensions as separate subscales.
Overall, the scale had moderate difficulty and a good differentiating degree, allowing for an accurate reflection of the actual level of caregiver self-efficacy in Chinese patients with MCCs. As observed in the Wright map, individual ability was greater than the difficulty of the scale. However, the overall level of caregiver self-efficacy in China appeared to be lower than that in Italy [20]. Individuals exhibited unstable responses to item 1, which owned the highest difficulty level among all the items. The instability in response may be attributed to the Rasch model’s expectation of high scores while participants performed poorly on this particular item. MCCs mean patients suffer a higher symptom burden and an increased risk of unplanned readmission [43, 44]. In a Canadian qualitative study, caregivers described their experience of caring for a person with MCCs as overwhelming, stressful, and challenging [45]. Caregivers of patients with MCCs may feel isolated and lack confidence in managing complex care tasks and maintaining the stable condition of patients. In our study, items 3, 5, and 7–10 were moderately difficult, while items 2, 4, and 6 were the simplest. Most caregivers lived in urban areas and had experienced secondary school education or higher. Furthermore, 85% of the caregivers had undertaken care tasks for over three years. Their extensive care experience allowed them to be familiar with the patient’s situation and their responsibilities in performing care tasks, such as following the treatment plan, monitoring health conditions, and recognizing changes in health conditions [46]. Furthermore, caregiver self-efficacy had a strong positive correlation with their contribution to self-care maintenance, monitoring, and management. This finding provided an effective breakthrough to promote the caregiver’s contribution to the patient’s self-care.
Strength and limitation
The psychometric characteristics of the CSE-CSC scale measured in this study were sufficient, and this scale provided a tool with statistical sufficiency and objectivity to measure caregiver self-efficacy in contributing to patient self-care in China. Although conducting a multiple center research trying to balance bias in sample selection, it was essential to acknowledge and consider some limitations. Firstly, the recruitment and testing of subjects were completed in hospital settings in our study. Caregivers in community settings were not considered due to limited energy and resources. Secondly, this study was conducted in four hospitals in Tianjin, China. Since most patients received treatment at nearby hospitals, the sample was geographically limited. The results also confirmed that the proportion of residences in our study subjects was uneven, with only 22.7% of caregivers living in town or the countryside. As a result, a larger survey was recommended to validate the scale in a broader and more representative sample, paying more attention to caregivers in community settings or those in town or countryside.
Conclusions
The Chinese version of the CSE-CSC scale owned sufficient criterion-related validity, reliability, and objectivity. The CSE-CSC scale could accurately measure the self-efficacy of caregivers who care for patients with MCCs in China. With the increasing prevalence of chronic comorbidity, this scale has become essential for enhancing the well-being of both caregivers and patients with MCCs.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- The CSE-CSC scale:
-
The Caregiver Self-Efficacy in Contributing to Patient Self-Care Scale
- MCCs:
-
Multiple chronic conditions
- CTT:
-
Classical test theory
- IRT:
-
Item response theory
- CC-SC-CII:
-
The Caregiver Contribution to Self-Care of Chronic Illness Inventory
- CVI:
-
Content validity index
- I-CVI:
-
Content validity index at the item level
- S-CVI:
-
Content validity index at the scale level
- CFA:
-
Confirmatory factor analysis
- RMSEA:
-
The root mean square error of approximation
- SRMR:
-
The standardized root mean square residual
- CFI:
-
Comparative Fit Index
- TLI:
-
Tucker-Lewis Index
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficients
- DIF:
-
Differential item functioning
References
Sherman BW. Management of individuals with multiple chronic conditions: a continuing challenge. Am J Manag Care. 2021;27(6):256–60.
Cheng C, Inder K, Chan SW. Coping with multiple chronic conditions: an integrative review. Nurs Health Sci. 2020;22(3):486–97.
Gu J, Chao J, Chen W, Xu H, Wu Z, Chen H, He T, Deng L, Zhang R. Multimorbidity in the community-dwelling elderly in urban China. Arch Gerontol Geriat. 2017;68:62–7.
Van Wilder L, Devleesschauwer B, Clays E, De Buyser S, Van der Heyden J, Charafeddine R, Boeckxstaens P, De Bacquer D, Vandepitte S, De Smedt D. The impact of multimorbidity patterns on health-related quality of life in the general population: results of the Belgian health interview survey. Qual Life Res. 2022;31(2):551–65.
Calderón-Larrañaga A, Vetrano DL, Ferrucci L, Mercer SW, Marengoni A, Onder G, Eriksdotter M, Fratiglioni L. Multimorbidity and functional impairment-bidirectional interplay, synergistic effects and common pathways. J Intern Med. 2019;285(3):255–71.
Riegel B, Jaarsma T, Stromberg A. A middle-range theory of self-care of chronic illness. Adv Nurs Sci. 2012;35(3):194–204.
De Maria M, Ferro F, Vellone E, Ausili D, Luciani M, Matarese M. Self-care of patients with multiple chronic conditions and their caregivers during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative descriptive study. J Adv Nurs. 2022;78(5):1431–47.
De Maria M, Ausili D, Lorini S, Vellone E, Riegel B, Matarese M. Patient self-care and caregiver contribution to patient self-care of chronic conditions: what is dyadic and what it is not. Value Health. 2022;25(7):1165–73.
Ko D, Bratzke LC, Roberts T. Self-management assessment in multiple chronic conditions: a narrative review of literature. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;83:83–90.
Cocchieri A, Riegel B, D’Agostino F, Rocco G, Fida R, Alvaro R, Vellone E. Describing self-care in Italian adults with heart failure and identifying determinants of poor self-care. Eur J Cardiovasc Nur. 2015;14(2):126–36.
Riegel B, Dunbar SB, Fitzsimons D, Freedland KE, Lee CS, Middleton S, Stromberg A, Vellone E, Webber DE, Jaarsma T. Self-care research: where are we now? Where are we going? Int J Nurs Stud. 2021;116:103402.
Vellone E, Riegel B, Alvaro R. A Situation-Specific Theory of Caregiver contributions to Heart failure self-care. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2019;34(2):166–73.
Young L, D’Aoust RF, Budhathoki C, Casida JM. Proposed mechanism of adherence in caregivers providing care to adults living with a left ventricular assist device. PROG Transpl. 2022;32(3):219–25.
Porter LS, Keefe FJ, Garst J, McBride CM, Baucom D. Self-efficacy for managing pain, symptoms, and function in patients with lung cancer and their informal caregivers: associations with symptoms and distress. Pain. 2008;137(2):306–15.
Welten J, Cox V, Kruithof WJ, Visser-Meily J, Post M, van Heugten CM, Schepers V. Intra- and interpersonal effects of coping style and self-efficacy on anxiety, depression and life satisfaction in patient-partner couples after stroke. Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2023;33(5):849–70.
Phongtankuel V, Moxley J, Reid MC, Adelman RD, Czaja SJ. The relationship of caregiver self-efficacy to caregiver outcomes: a correlation and mediation analysis. Aging Ment Health 2022:1–7.
Luszczynska A, Scholz U, Schwarzer R. The general self-efficacy scale: multicultural validation studies. J Psychol. 2005;139(5):439–57.
Cheng JC, Chang TT, Wang LW, Liang SY, Hsu SC, Wu SF, Wang TJ, Liu CY. Development and psychometric evaluation of the Caregiver Caregiving Self-Efficacy Scale for family members with oral cancer. Int J Nurs Pract. 2022;28(6):e12957.
Piggott CA, Zimmerman S, Reed D, Sloane PD. Development and testing of a measure of Caregiver confidence in Medical Sign/Symptom Management. Am J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;32(7):373–81.
De Maria M, Iovino P, Lorini S, Ausili D, Matarese M, Vellone E. Development and psychometric testing of the Caregiver Self-Efficacy in contributing to patient self-care scale. Value Health. 2021;24(10):1407–15.
Streiner DL. Measure for measure: New Developments in Measurement and Item Response Theory. Can J Psychiat. 2010;55(3):180–6.
Cai L, Choi K, Hansen M, Harrell L. Item Response Theory.|.*3*3. Edited by Fienberg SE, Stigler SM; 2016:297–321.
Pang N, Tseu M, Gupta P, Dhaarshini J, Kamu A, Ho CM, Ahmed O, Chung S. Adaptation and validation of the malay version of the stress and anxiety to viral Epidemics-6 items Scale among the General Population. Front Psychiatry. 2022;13:908825.
Dattalo M, DuGoff E, Ronk K, Kennelty K, Gilmore-Bykovskyi A, Kind AJ. Apples and oranges: four definitions of multiple chronic conditions and their relationship to 30-Day hospital readmission. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(4):712–20.
Lewis V. Health measurement scales: a practical guide to their development and use, 5th edition. Aust Nz J Publ Heal 2016, 40(3):294–295.
Chen WH, Lenderking W, Jin Y, Wyrwich KW, Gelhorn H, Revicki DA. Is Rasch model analysis applicable in small sample size pilot studies for assessing item characteristics? An example using PROMIS pain behavior item bank data. Qual Life Res. 2014;23(2):485–93.
Jones PS, Lee JW, Phillips LR, Zhang XE, Jaceldo KB. An adaptation of Brislin’s translation model for cross-cultural research. Nurs Res. 2001;50(5):300–4.
Vellone E, Lorini S, Ausili D, Alvaro R, Di Mauro S, De Marinis MG, Matarese M, De Maria M. Psychometric characteristics of the caregiver contribution to self-care of chronic illness inventory. J Adv Nurs. 2020;76(9):2434–45.
Chen DD, Zhang H, Cui N, Tang L, Shao J, Wang X, Wang D, Liu N, Ye Z. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the caregiver contribution to self-care of chronic illness inventory in China: a cross-sectional study. Bmj Open. 2021;11(9):e48875.
Yang Z, Sun Y, Wang H, Zhang C, Wang A. A scale for measuring home-based cardiac rehabilitation exercise adherence: a development and validation study. Bmc Nurs. 2023;22(1):259.
Polit DF, Beck CT. The content validity index: are you sure you know what’s being reported? Critique and recommendations. Res Nurs Health. 2006;29(5):489–97.
Hu LT, Bentler PM. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in Covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria Versus New Alternatives. Struct Equ Model. 1999;6(1):1–55.
Park MS, Kang KJ, Jang SJ, Lee JY, Chang SJ. Evaluating test-retest reliability in patient-reported outcome measures for older people: a systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;79:58–69.
Terwee CB, Bot SD, de Boer MR, van der Windt DA, Knol DL, Dekker J, Bouter LM, de Vet HC. Quality criteria were proposed for measurement properties of health status questionnaires. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60(1):34–42.
Prinsen C, Mokkink LB, Bouter LM, Alonso J, Patrick DL, de Vet H, Terwee CB. COSMIN guideline for systematic reviews of patient-reported outcome measures. Qual Life Res. 2018;27(5):1147–57.
Stover AM, McLeod LD, Langer MM, Chen WH, Reeve BB. State of the psychometric methods: patient-reported outcome measure development and refinement using item response theory. J Patient-Rep Outcom. 2019;3(1):50.
Cho SK, Kim H, Song YJ, Nam E, Jones B, Ndosi M, Sung YK. Validation of the Korean Leeds satisfaction questionnaire in rheumatoid arthritis with Rasch models. Int J Rheum Dis. 2022;25(11):1270–8.
Franchignoni F, Giordano A, Marcantonio L, Coccetta CA, Ferriero G. Current issues in psychometric assessment of outcome measures. Medicina-Buenos Aire. 2012;48:463–70.
A user’s guide to WINSTEP®MINISTEP. Rasch-Model Computer Programs.; 2020.
Rangka IB, Hidayah N, Hanurawan F, Eva N. A rasch-based validation of the Indonesian version of the food neophobia scale. Food Qual Prefer 2023, 109.
Shi D, Lee T, Maydeu-Olivares A. Understanding the model size effect on SEM fit indices. Educ Psychol Meas. 2019;79(2):310–34.
Sousa VD, Rojjanasrirat W. Translation, adaptation and validation of instruments or scales for use in cross-cultural health care research: a clear and user-friendly guideline. J Eval Clin Pract. 2011;17(2):268–74.
Coatsworth-Puspoky R, Dahlke S, Duggleby W, Hunter KF. Safeguarding survival: Older persons with multiple chronic conditions’ unplanned readmission experiences: A mixed methods systematic review. J Clin Nurs 2023.
Portz JD, Kutner JS, Blatchford PJ, Ritchie CS. High Symptom Burden and Low Functional Status in the setting of Multimorbidity. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(10):2285–9.
Ploeg J, Matthew-Maich N, Fraser K, Dufour S, McAiney C, Kaasalainen S, Markle-Reid M, Upshur R, Cleghorn L, Emili A. Managing multiple chronic conditions in the community: a Canadian qualitative study of the experiences of older adults, family caregivers and healthcare providers. Bmc Geriatr 2017, 17.
Iovino P, Lyons KS, De Maria M, Vellone E, Ausili D, Lee CS, Riegel B, Matarese M. Patient and caregiver contributions to self-care in multiple chronic conditions: a multilevel modelling analysis. Int J Nurs Stud 2021, 116.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 72304206, 71974142, 72274134); Humanities and Social Science Found of Ministry of Education of China (grant number: 23YJAZH189); Nursing Special Development Fund of Tianjin Medical University (grant number: 2022XKZX-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaoying Zang, the correspondence author of this study, was responsible for designing, guiding, organizing, and planning this study. Qingyun Lv and Xiaonan Zhang were responsible for the scale translation and manuscript preparation. Yaqi Wang and Xueying Xu were responsible for data collection and data analysis. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The research was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University (Grant number: TMuhMEC2022021) and written informed consents were obtained from all participants. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations (declaration of Helsinki).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Q., Zhang, X., Wang, Y. et al. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the caregiver self-efficacy in contributing to patient self-care scale in China. BMC Public Health 24, 1977 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-19534-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-19534-2