Abstract
Background
Since July 2021, some countries and regions have initiated the vaccination of minors against coronavirus disease (COVID-19), and parental COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy will affect the vaccination of minors. We aimed to identify the level of parental hesitancy to vaccinate their children against COVID-19 in Taiwan and the factors associated with vaccine hesitancy.
Methods
We conducted a population-based, self-administered online questionnaire in Taiwan to assess parental hesitancy and the factors influencing their children’s vaccination against COVID-19.
Results
Among 384 respondents, 64.1% were hesitant to have their children vaccinated against COVID-19. Mothers were more likely to hesitate to vaccinate their teens than their fathers (67.5% vs. 50%, P < 0.005). Multiple regression results showed that parents who were hesitant to vaccinate themselves (OR = 3.81, 95% CI:2.07–7.02) and those who scored lower on their perception of their children’s vaccination (OR = 9.73, 95% CI:5.62–16.84) were more hesitant to vaccinate their children with COVID-19 vaccine.
Conclusions
According to the study findings, 64.1% of Taiwanese parents were hesitant to vaccinate their children against COVID-19. Parents who were hesitant to receive the COVID-19 vaccine for themselves and had negative views of the vaccine for their children were more likely to be hesitant to vaccinate their children. An in-depth discussion of the factors affecting vaccine hesitancy and targeted health education is conducive to promoting vaccination in children with COVID-19.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Since December 2019, COVID-19 has spread unexpectedly worldwide and has had a massive effect on people’s fitness and existence [1]. Since the outbreak of the pandemic, a collection of measures, including social distancing, sporting masks, and usual hand washing, have decreased the spreading and mortality of the virus. With the meaningful improvement and examination of a range of COVID-19 vaccines, governments around the world have taken COVID-19 vaccination as an essential approach to resolving the COVID-19 epidemic, so they pay specific attention to the COVID-19 vaccine vaccination work [2]. To contain the pandemic, immunizing the population is essential, and the most reliable way to do this is through mass vaccination [3]. To mitigate the transmission of the new coronavirus, it was estimated that 67% of the population wants to receive a vaccine to acquire the impact of herd immunity [4], and increasing vaccination rates in children is important for herd immunization. A survey conducted in Singapore [5] revealed that children received the COVID-19 vaccine at a substantially slower rate than adults and adolescents, highlighting the significance of raising childhood vaccination rates for herd immunization.
Although nations have had incredible achievements in creating vaccines, the hesitancy of people towards the COVID-19 vaccine is still an important factor that hinders its popularity and coverage of the COVID-19 vaccine [6]. The World Health Organization (WHO) Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) defines vaccine hesitancy as a “Delay in the acceptance or refusal of vaccination despite the availability of vaccination services” [7]. However, vaccine hesitancy remains widespread because of vaccine development. The hesitation toward vaccines can lead to a decline in vaccine coverage and is not conducive to controlling the spread of epidemics [8].
Children’s bodily features and immune structures have not yet fully developed, and the chance of contracting new coronary pneumonia is higher; therefore, it is necessary for youngsters to be vaccinated against COVID-19 [9]. However, it was discovered that many of the parents interviewed in a study of the factors influencing parental hesitancy to immunize children aged 5–11 in Quebec expressed less concern about the risk of children contracting COVID-19 because they believed there was a low risk of COVID-19 complications [10], which is obviously not conducive to protecting children’s health during a pandemic. The hesitancy of parents to get their young ones vaccinated against COVID-19 is one of the major factors hindering childhood vaccination. The existence of this phenomenon is no longer conducive to achieving herd immunity for the duration of the pandemic [11]. Therefore, it is of great importance to learn about the factors that influence parents’ hesitancy to vaccinate their children against COVID-19 to enhance the vaccination rate of COVID-19 and control the outbreak of COVID-19. The purpose of this study is to investigate the reasons why Taiwanese parents hesitate to vaccinate their children against the novel coronavirus.
Methods
Study design and population
We performed a cross-sectional online survey of parents in Taiwan from July 14, 2021, to September 23, 2021. Google was used as the survey platform, and the response rate was 100%. Our target population was parents of at least one child below the age of 18, and 384 questionnaires were collected. Parents who refused to participate in the survey and those without children under the age of 18 living at home were excluded from the study. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Taizhou Hospital, Zhejiang Province (approval number: K20210520). All strategies were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Institutional Ethics Committee and adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki, and all participant data were anonymized. Ethics Committee of Taizhou Hospital,Zhejiang Province waived informed consent from participants.
Structured questionnaire
A self-administered questionnaire was designed [12]. The contents of the questionnaire are as follows: (1) basic demographic information, such as gender, region of residence, education level, occupation, and number of minor children; (2) Knowledge about the COVID-19 vaccine: do you know about the COVID-19 vaccine? (Yes, No), do you think the COVID-19 vaccine is effective in preventing the COVID-19 outbreak? (effective, ineffective), how protective do you suppose the COVID-19 vaccine is? (safe, unsafe), and do you assume the COVID-19 vaccine has a preventive impact on COVID-19? How big is it? (Greater effect, lesser effect); (3) Hesitation regarding COVID-19 vaccination for children: Are you hesitant to have your children vaccinated? (Yes; No); (4) Willingness to have teenagers vaccinated against COVID-19?: Score of opinion on children’s vaccination against COVID-19 (Q1: < 30; Q2:≥30, the greater the score, the more advantageous the parents’ view of their child’s vaccination toward the COVID-19.)
Statistical analysis
The primary finding of the survey was the parental reluctance to vaccinate their children against COVID-19. General demographic features and vaccinations are described using component proportions [n(%)]. To identify the probable causes of parental hesitation to vaccinate their children with the COVID-19 vaccine, a chi-square test was used. The causes of vaccine reluctance were investigated using logistic regression analysis.
Variables significant at P < 0.2 level in chi-square or t-test were included in the binary logistic regression model. The factors associated with parental hesitation to vaccinate their children with COVID-19 were determined using binary logistic regression analysis, and the dominance ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated. Statistical significance was considered at P < 0.05, using the IBM SPSS statistical software.
Literature search strategy
We searched the PubMed database for relevant studies published from inception to July 1, 2022. Terms related to key concepts, include vaccine hesitancy, parents, children, and vaccines. Duplicates were removed by scanning the titles and abstracts, resulting in 20 relevant documents. We used a data extraction form to extract the following data from the included studies: first author, study design, study duration, and study duration.
Results
In this study, 384 participants completed the questionnaire. Table 1 shows that among the 384 parents, 19.8% (76/384) were male, 80.2% (308/384) were female, 15.4% (59/384) lived in township areas, 84.6% (325/294) lived in urban areas, 43.0% (165/384) were employed as medical workers, and 57.0% (219/384) were employed as nonmedical workers.
Among the 384 parents, 64.1% (246/384) expressed hesitance to have their children vaccinated against COVID-19, 67.5% (208/308) mothers were hesitant to vaccinate their children against COVID-19, and 50% (38/76) fathers were hesitant to vaccinate their children against COVID-19 (Table 2). Of the 247 parents who were themselves hesitant to take the COVID-19 vaccination, 83.8% (207/247) were also hesitant to have their children vaccinated against COVID-19; Of the 137 parents who were themselves not hesitant to take the COVID-19vaccination, 71.5% (98/137) parents did not hesitate to have their children vaccinated against COVID-19. In addition, of the 247 parents who were hesitant to be vaccinated, 81.8% (6/33) were fathers, and 84.1% (180/214) of mothers were hesitant to have their children vaccinated (Fig. 1).
Table 3 shows that parents’ hesitation to vaccinate their children with the COVID-19 vaccine was associated with gender (χ2 = 8.097,p = 0.004), knowledge of the COVID-19 vaccine (χ2 = 31.17,p < 0.001), perception of the safety of COVID-19 vaccine (χ2 = 27.041,p < 0.001), perception of the preventive effect of COVID-19 on COVID-19 preventive effect (χ2 = 5.395,p = 0.02), perceived effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccine (χ2 = 8.818, p = 0.093), and perception score of COVID-19 vaccination for children (t = − 4.081,p < 0,001) were related. Moreover, there was a correlation between parents’ hesitation to vaccinate themselves and their hesitation to vaccinate their children (χ2 = 117.217, P < 0.001).
Among them, perception of the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine, knowledge of the COVID-19 vaccine, and score of perception of children’s vaccination against new crowns were associated with fathers’ and mothers’ hesitation to vaccinate their children against the COVID-19 vaccine (P < 0.2). In addition, fathers’ hesitation to vaccinate their children with the COVID-19 vaccine was associated with whether their occupation was medical (χ2 = 1.774, P = 0.183) and their perception of the preventive effect of COVID-19 vaccine on COVID-19(χ2 = 10.483, P = 0.001), whereas mothers’ hesitation to vaccinate their children with COVID-19 vaccine was associated with the type of residence (χ2 = 2.366, P = 0.124).
The results of the regression model are presented in Table 4. Parents who were hesitant to vaccinate themselves with the new crown vaccine (OR = 3.81, 95% CI:2.07–7.02) and those who scored lower on their perceptions of their children’s COVID-19 vaccination (OR = 9.73, 95% CI:5.62–16.84) were more hesitant to vaccinate their children with the COVID-19 vaccine. Parents’ type of residence, education, whether they were an only child, and whether they were medical workers were not significant in the multiple regression model and thus can be considered confounding factors.
Both fathers’ and mothers’ hesitation to vaccinate their children with the COVID-19 vaccine were associated with scores on perceptions of their children’s vaccination and hesitation to vaccinate themselves with the COVID-19 vaccine. The type of residence was associated with mothers’ hesitation to vaccinate their children against COVID-19 (OR = 0.30,95% CI:2.07–7.02), whereas fathers were not affected by this factor.
Discussion
Impact of vaccine hesitancy
Vaccine hesitancy is a phenomenon that has always existed and has caused great harm to people’s health [ 13]. Although a COVID-19 vaccine has been developed, vaccine hesitancy is not conducive to the global control of the current COVID-19 pandemic, and the existence of this phenomenon will have adverse effects on people’s physical health, mental health, and social economy [6].
According to the results of this survey, 64.1% (246/384) of the parents were hesitant to have their children vaccinated against COVID-19. The hesitation of parents to vaccinate their children against COVID-19 in the various study populations is listed in Table 5. These studies emphasize the importance of community immunity as a means of containing the COVID-19 pandemic, and most of them have discovered that parents’ hesitation in having their children vaccinated against COVID-19 has a minimal bearing on vaccine safety [10, 11, 14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. Parents in various countries or areas are typically hesitant to have their children vaccinated against COVID-19. According to an analysis of the hesitancy of parents in those countries or regions to have their children vaccinated, hesitation rates range from 8 to 88%.
Influencing factors of vaccine hesitancy
Our study showed a correlation between parents’ hesitation to vaccinate themselves and their hesitation to vaccinate their children, with parents who were more hesitant to vaccinate themselves being more hesitant to vaccinate their children. A study of parental hesitancy to vaccinate children against COVID-19 in the United States [11] showed a significant correlation between parents’ intention to vaccinate against COVID-19 and their intention to vaccinate their children against COVID-19. This provides new ways to improve COVID-19 vaccine coverage in children. Studies have shown that promoting the health of children is an important reason why parents are willing to vaccinate their children against COVID-19 [33]. Therefore, there is a need to raise awareness among parents about the importance of COVID-19 vaccination, to understand the important role of the COVID-19 vaccine for children’s health during a pandemic, to give parents correct information about the COVID-19 vaccine, and to increase acceptance and trust of the vaccine among adults and, to some extent, children’s vaccination rates.
Vaccine hesitation is a complex social phenomenon influenced by environmental, social, cultural, and political factors in addition to individual attitudes and beliefs [34]. A study examining the growing trend of parental vaccine hesitancy suggested that many factors influence parental hesitancy about vaccines for their children, divided into parent-specific factors (race, income, education level, knowledge of vaccines, past experiences), vaccine-specific factors (perceived vaccine effectiveness, perceived vaccine safety, perceived disease susceptibility), and external factors (policy, media, social norms, school immunization requirements, etc.) [35]. Our survey results showed that the lower the perception score of their child’s COVID-19 vaccination, the more hesitant parents were to vaccinate their children. This is sufficient to show that parental attitudes regarding COVID-19 vaccination can, to some extent, influence their decisions to vaccinate their children against COVID-19. In a cross-sectional study [15] investigating the effects of vaccine literacy, vaccine perceptions, and vaccine hesitancy on Israeli parents’ willingness to get COVID-19 vaccine for their children, vaccine literacy, perceived vaccine hesitancy, and COVID-19 vaccine perceptions were found to be associated with parents’ willingness to vaccinate their children against COVID-19. This is similar to the results of our study, which demonstrated that parental attitudes, perceptions of the COVID-19 vaccine, and literacy are influential factors in parents’ willingness to vaccinate their children against COVID-19.
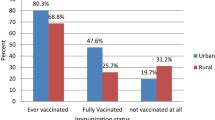
In line with the results of other studies [36,37,38], in the current study, we found that women living in rural areas were more hesitant to have their children vaccinated with COVID-19 than those living in urban areas. In a study on attitudes toward the COVID-19 vaccine and vaccine hesitancy among rural and urban communities in Tamil Nadu, India, it was found that residents living in urban areas had more trust in the effectiveness of the vaccine and that they did not prefer natural immunization, while women from rural areas had less trust in the health system, COVID-19 vaccine, and its effectiveness [39]. In addition, in a study of hesitant adults in Arkansas who had received the COVID- 19 vaccine, it was found that people living in rural areas were more hesitant to be vaccinated, possibly because of the high cost of vaccination and the low rates of influenza vaccination in the past few years [40]. These results suggest that we need to increase awareness of vaccines in rural areas, improve healthcare systems in rural areas, provide more medical resources in rural areas, and proactively address the health and social inequalities created during pandemics.
Concerns regarding vaccine safety have long been one of the most common reasons for vaccination. Multiple studies have found that those who are hesitant to get the COVID-19 vaccine or to vaccinate their children cite safety as a primary concern [28]. In mainland China, although the vaccination rate for the new crown vaccine is high, many respondents still expressed concerns about the safety and side effects of the vaccine [41]. Studies have shown that healthcare providers and the Internet are the most common sources of information on COVID-19 vaccines [15]. Therefore, government departments need to actively cooperate with the healthcare sector to take advantage of the rapidity and extensiveness of the Internet in information dissemination to convey information about the safety and efficacy of the COVID-19 vaccine to the general public and to enhance public understanding and information about the vaccine.
Limitations
Although a population-based study was conducted, this study has the following limitations. First, there were limitations in the selection of research objects. The samples in this survey were unevenly distributed in terms of sex and educational level. Second, this is a cross-sectional study, which can only reflect the situation at a specific point in time and cannot reflect the changes in people’s attitudes at different times. Finally, the questions on the questionnaire were limited and could not reflect other influencing factors such as differences in policies and cultures between Taiwan and other regions. These factors require further investigation.
Conclusion
Vaccine hesitancy is an important public health issue with multiple root causes. According to the study’s findings, 64.1% of Taiwanese parents were hesitant to vaccinate their children against COVID-19. Parents who were hesitant to get the COVID-19 vaccine for themselves and had negative views of the vaccine for their children were more likely to be hesitant to vaccinate their children. Promoting the vaccination of children with the COVID-19 vaccine requires a thorough examination of the variables that influence vaccine hesitancy, as well as focused health education. Taiwan’s culture, politics, and economics are special, necessitating thorough discussion.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Yuki K, Fujiogi M, Koutsogiannaki S. COVID-19 pathophysiology: a review. Clin Immunol. 2020;215:108427.
Mathieu E, Ritchie H, Ortiz-Ospina E, Roser M, Hasell J, Appel C, et al. A global database of COVID-19 vaccinations. Nat Hum Behav. 2021;5(7):947–53.
Rasmussen AL. Vaccination is the only acceptable path to herd immunity. Med. 2020;1(1):21–3.
Randolph HE, Barreiro LB. Herd immunity: understanding COVID-19. Immunity. 2020;52(5):737–41.
Low JM, et al. Predicting vaccine hesitancy among parents towards COVID-19 vaccination for their children in Singapore. Front Pediatr. 2022;10:994675.
Sallam M. COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy worldwide: a concise systematic review of vaccine acceptance rates. Vaccines. 2021;9(2):160.
MacDonald NE, SAGE Working Group on Vaccine Hesitancy. Vaccine hesitancy: definition, scope and determinants. Vaccine. 2015;33(34):4161–4.
Wang K, Wong ELY, Ho KF, Cheung AWL, Yau PSY, Dong D, et al. Change of willingness to accept COVID-19 vaccine and reasons of vaccine hesitancy of working people at different waves of local epidemic in Hong Kong, China: repeated cross-sectional surveys. Vaccines. 2021;9(1):62.
Du M, Tao L, Liu J. The association between risk perception and COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy for children among reproductive women in China: an online survey. Front Med. 2021;8:741298.
Dubé E, et al. COVID-19 vaccination in 5-11 years old children: drivers of vaccine hesitancy among parents in Quebec. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022;18(1):2028516.
Wong WHS, So HK, Rosa Duque JS, Tso WWY, Chong PCY, Kwan MYW, et al. Impact of a focus education in zoom on COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in Hong Kong parents of the preschoolers. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022;18:2081460.
Zhang MX, Lin XQ, Chen Y, Tung TH, Zhu JS. Determinants of parental hesitancy to vaccinate their children against COVID-19 in China. Expert Rev Vaccin. 2021;20(10):1339–49.
He K, Mack WJ, Neely M, Lewis L, Anand V. Parental perspectives on immunizations: impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on childhood vaccine hesitancy. J Community Health. 2022;47(1):39–52.
Bagateli LE, Saeki EY, Fadda M, Agostoni C, Marchisio P, Milani GP. COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of children and adolescents living in Brazil. Vaccines. 2021;9(10):1115.
Gendler Y, Ofri L. Investigating the influence of vaccine literacy, vaccine perception and vaccine hesitancy on Israeli parents' acceptance of the COVID-19 vaccine for their children: a cross-sectional study. Vaccines. 2021;9(12):1391.
Kitro A, Sirikul W, Dilokkhamaruk E, Sumitmoh G, Pasirayut S, Wongcharoen A, et al. COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy and influential factors among Thai parents and guardians to vaccinate their children. Vaccine. 2022;X:100182.
Miraglia del Giudice G, Napoli A, Corea F, Folcarelli L, Angelillo IF. Evaluating COVID-19 vaccine willingness and hesitancy among parents of children aged 5–11 years with chronic conditions in Italy. Vaccines. 2022;10(3):396.
Li T, Qiu X, Gong X, Zhan R, Zheng X. The cross-sectional survey on COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy and it predictors among Chinese parents of 3–17 years aged children in Shenzhen City. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2022;29(1):120–5.
Wang CS, Doma R, Westbrook AL, et al. Vaccine attitudes and COVID-19 vaccine intention among parents of children with kidney disease or primary hypertension. Am J Kidney Dis. 2023;81(1):25-35.e1.
Abuhammad S, Khader Y. Shaher Hamaideh, attitude of parents toward vaccination against COVID-19 for own children in Jordan: a cross-sectional study. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;31:101000.
Temsah MH, Alhuzaimi AN, Aljamaan F, Bahkali F, Al-Eyadhy A, Alrabiaah A, et al. Parental attitudes and hesitancy about COVID-19 vs. routine childhood vaccinations: a National Survey. Front Public Health. 2021;9:752323.
Al-Mohaithef M, Padhi BK, Ennaceur SA. Demographics of COVID19 vaccine hesitancy during the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional web-based survey in Saudi Arabia. medRxiv; 2021.
Wang Q, Xiu S, Zhao S, Wang J, Han Y, Dong S, et al. Vaccine hesitancy: COVID-19 and influenza vaccine willingness among parents in Wuxi, China-A Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines. 2021;9(4):342.
Alfieri NL, Kusma JD, Heard-Garris N, Davis MM, Golbeck E, Barrera L, et al. Parental COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy for children: vulnerability in an urban hotspot. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):1662.
Skeens MA, Hill K, Olsavsky A, Buff K, Stevens J, Akard TF, et al. Factors affecting COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in parents of children with cancer. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2022;69(6):e29707.
Teasdale CA, Ratzan S, Rauh L, Lathan HS, Kimball S, El-Mohandes A. COVID-19 vaccine coverage and hesitancy among new York City parents of children aged 5–11 years. Am J Public Health. 2022;0:e1–6.
Musa S, Dergaa I, Abdulmalik MA, Ammar A, Chamari K, Saad HB. BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents of 4023 young adolescents (12–15 years) in Qatar. Vaccines. 2021;9(9):981.
Middleman AB, Klein J, Quinn J. Vaccine hesitancy in the time of COVID-19: attitudes and intentions of teens and parents regarding the COVID-19 vaccine. Vaccines. 2021;10(1):4.
Huynh G, Nguyen HTN, Van Tran K, Le An P, Tran TD. Determinants of COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Postgrad Med. 2022;134(3):303–8.
Schilling S, Orr CJ, Delamater AM, Flower KB, Heerman WJ, Perrin EM, et al. COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among low-income, racially and ethnically diverse US parents. Patient Educ Couns. 2022;105:2771–7.
Montalti M, Rallo F, Guaraldi F, Bartoli L, Po G, Stillo M, et al. Would parents get their children vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2? Rate and predictors of vaccine hesitancy according to a survey over 5000 families from Bologna, Italy. Vaccines. 2021;9(4):366.
Xu Y, Xu D, Luo L, et al. A cross-sectional survey on COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among parents from Shandong vs. Zhejiang. Front Public Health. 2021;9:779720.
Ruiz JB, Bell RA. Parental COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in the United States. Public Health Rep. 2022;137(6):1162–9.
Dubé E, Laberge C, Guay M, et al. Vaccine hesitancy: an overview. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013;9(8):1763–73.
Gowda C, Dempsey AF. The rise (and fall?) of parental vaccine hesitancy. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013;9(8):1755–62. https://doi.org/10.4161/hv.25085.
Khubchandani J, Sharma S, Price JH, Wiblishauser MJ, Sharma M, Webb FJ. COVID-19 vaccination hesitancy in the United States: a rapid national assessment. J Community Health. 2021;46(2):270–327.
Kricorian K, Civen R, Equils O. COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy: misinformation and perceptions of vaccine safety. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022;18(1):1950504.
McElfish PA, Willis DE, Shah SK, Bryant-Moore K, Rojo MO, Selig JP. Sociodemographic determinants of COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy, fear of infection, and protection self-efficacy. J Prim Care Community Health. 2021;12:21501327211040746.
Danabal KGM, et al. Attitude towards COVID 19 vaccines and vaccine hesitancy in urban and rural communities in Tamil Nadu, India - a community based survey. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):994.
McElfish PA, et al. Hesitant adopters: an examination of hesitancy among adults in Arkansas who have taken the COVID-19 vaccine. Clin Transl Sci. 2022;15(10):2316–22.
Liu T, He Z, Huang J, Yan N, Chen Q, Huang F, et al. A comparison of vaccine hesitancy of COVID-19 vaccination in China and the United States. Vaccines. 2021;9(6):649.
Acknowledgments
We thank the participants for their cooperation and support and J.Y.C. collected the data in Taiwan.
Funding
This study was supported in part by the Medical and Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province (2020385612) and Science and Technology Administration Public Interest Technology Research Project of Zhejiang Province (LGF19H030013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JS.Z. and THT conceived the study and designed the questionnaire. J.Y.C collected the data. J.S.D. was responsible for analyzing and writing the first draft of the paper. C.L.H and X.Q L searched, sorted and interpreted the relevant literature. All authors edited and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Taizhou Hospital, Zhejiang Province (approval number: K20210520). All strategies were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Institutional Ethics Committee and adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki, and all participant data were anonymized. Ethics Committee of Taizhou Hospital, Zhejiang Province waived informed consent from participants.
Consent for publication
This section is not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, JS., Chen, JY., Lin, XQ. et al. Parental hesitancy against COVID-19 vaccination for children and associated factors in Taiwan. BMC Public Health 23, 571 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-15158-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-15158-0