Abstract
Background
Routine clinical management of breast cancer (BC) currently depends on surrogate subtypes according to estrogen- (ER) and progesterone (PR) receptor, Ki-67, and HER2-status. However, there has been growing demand for reduced immunohistochemistry (IHC) turnaround times. The Xpert® Breast Cancer STRAT4* Assay (STRAT4)*, a standardized test for ESR1/PGR/MKi67/ERBB2 mRNA biomarker assessment, takes less than 2 hours. Here, we compared the concordance between the STRAT4 and IHC/SISH, thereby evaluating the effect of method choice on surrogate subtype assessment and adjuvant treatment decisions.
Methods
In total, 100 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded core needle biopsy (CNB) samples and matching surgical specimens for 98 patients with primary invasive BC were evaluated using the STRAT4 assay. The concordance between STRAT4 and IHC was calculated for individual markers for the CNB and surgical specimens. In addition, we investigated whether changes in surrogate BC subtyping based on the STRAT4 results would change adjuvant treatment recommendations.
Results
The overall percent agreement (OPA) between STRAT4 and IHC/SISH ranged between 76 and 99% for the different biomarkers. Concordance for all four biomarkers in the surgical specimens and CNBs was only 66 and 57%, respectively. In total, 74% of surgical specimens were concordant for subtype, regardless of the method used. IHC- and STRAT4-based subtyping for the surgical specimen were shown to be discordant for 25/98 patients and 18/25 patients would theoretically have been recommended a different adjuvant treatment, primarily receiving more chemotherapy and trastuzumab.
Conclusions
A comparison of data from IHC/in situ hybridization and STRAT4 demonstrated that subsequent changes in surrogate subtyping for the surgical specimen may theoretically result in more adjuvant treatment given, primarily with chemotherapy and trastuzumab.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
To provide the best pre- and postoperative treatment for a patient with early breast cancer, reliable pathology data about the biology of the tumor is needed [1,2,3,4,5]. Biomarker assessment of estrogen receptor (ER)-, progesterone receptor (PR)-, Ki-67, and HER2 status with immunohistochemistry (IHC) is used to classify breast cancer by intrinsic/surrogate subtypes according to international WHO guidelines: Luminal A-like, Luminal B-like (HER2- or HER2+), HER2+ (non-luminal) and Triple-negative [6]. Additional clinicopathological features (tumor grade and size, patient’s age and co-morbidities and axillary lymph node status) are then used for pre- or postoperative adjuvant treatment decisions.
Core needle biopsy (CNB) has become a well-established preoperative diagnostic method for breast lesions [6,7,8,9], especially for breast cancer patients being considered for neoadjuvant treatment [3]. International and national guidelines recommend the pathology-based assessment of ER, PR, HER2, Ki-67 [9] using immunohistochemistry, and good concordance has been shown for these biomarkers in matched CNB and surgical specimens [8, 10, 11]. However, IHC is frequently associated with interlaboratory variability due to differences in the choice of antibodies, manual or computer-assisted imaging scoring methods, as well as subjective interpretations by different pathologists [12,13,14]. Moreover, there is still considerable debate over optimal Ki-67 cutoffs to distinguish Luminal-like breast cancers [1, 15]. Subsequent in situ hybridization for HER2 testing (e.g. FISH, SISH) could take an additional 5 days before necessary information is obtained and optimal therapy planning can be conducted. Thus, there is a need to develop a fast, reliable, and reproducible method to standardize the assessment of ER, PR, HER2, and Ki-67.
A number of commercial gene signature assays (e.g. PAM50/Prosigna, Mammaprint/BluePrint) have been developed to classify breast cancer, thereby improving prognostication and treatment decision-making [16,17,18]. However, each molecular assay uses different technological platforms, gene signatures comprised of various numbers of transcripts with distinct biological functions, and benefits specific patient groups. The Xpert® Breast Cancer STRAT4 Assay (STRAT4)* is a cartridge-based, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) assay with qualitative cut-off values for ESR1-, PGR -, ERBB2-, and MKi67- mRNA expression normalized to a reference gene (CYFIP1) using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) invasive breast cancer tissue. RNA is automatically extracted, purified, and detected inside the cartridge using a tissue lysate prepared from a tumor-enriched region in the FFPE section, as identified by a pathologist. In comparison with traditional IHC, the total turnaround time for the STRAT4 assay is under 2 hours, including hands-on time. Previous studies have shown reproducible results and high concordance with IHC [19, 20].
The aim of the present study was to a) evaluate the concordance of the STRAT4 assay relative to standard-of-care IHC and SISH-test in matched breast cancer CNBs and surgical specimens, and b) investigate whether changes in STRAT4-based surrogate breast cancer subtyping of the surgical specimen would have had a theoretical effect on adjuvant treatment recommendations.
Methods
Patient samples
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples (i.e. preoperative CNBs and surgical tumor specimens) were retrieved from the Department of Clinical Pathology at Sahlgrenska University Hospital (Gothenburg, Sweden) for 98 consecutive patients with primary breast cancer diagnosed between January and May 2017. Two patients had bilateral breast cancer. In total, 100 matching samples were examined. The age of the FFPE samples was 18–22 months. Clinical data on adjuvant treatment based on IHC, axillary node status, tumor size, tumor grade, patient age at the time of diagnosis and co-morbidities were retrieved from electronic medical records. Patients with neoadjuvant treatment, tumor size less than 5 mm, multifocal/multicentric breast cancer, bifocal breast cancer and previous surgery for breast cancer were not included. Patients treated with neoadjuvant treatment were excluded to avoid the possible loss of available matching surgical samples for assessment due to partial or complete reduction of the tumor area following therapy response. Another exclusion criteria was FFPE specimens that were fixed in fixatives other than 10% Neutral Buffered Formalin (NBF), fixed in NBF for < 6 or > 72 h, or aged more than 4 weeks since initial preparation/fixation, but this was not relevant in this study. The clinicopathologic features of the 100 specimens are shown in Table 1.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and cutoffs for biomarker analysis in CNB and surgical specimen
ER, PR, HER2 and Ki-67 protein expression data (IHC) were retrospectively collected for both the CNB and surgical specimens from the Sympathy database (Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Department of Clinical Pathology) and no re-assessments were conducted. As the CNB sample is only a random sampling of the tumor, IHC assessment is routinely performed on both the CNB and the matching surgical specimen at our institution. Routine IHC staining protocols at the Department of Clinical Pathology used the following antibodies to assess ER, PR, HER2 and Ki-67 expression: rabbit anti-ERα (Agilent Dako IR084, clone EP1), mouse anti-PR (Agilent Dako IR068, clone 636), mouse anti-KI-67 (Agilent Dako IR626, clone MIB-1), and HercepTest (Agilent Dako SK001, clone poly), respectively. In brief, FFPE sections were pretreated using the Dako PTLink system (Agilent Dako) and processed on an automated Dako Autostainer platform, as previously described [21]. The Ventana dual SISH test was also performed, if necessary to resolve final HER2 status. International guidelines were used to determine biomarker status, where ER, PR, and Ki-67 were considered to be positive with ≥1%, ≥1%, and ≥ 20% immunostaining in neoplastic cells, respectively [1, 6]. HercepTest scored 2+ and 3+ was followed by SISH testing, and considered positive with confirmed HER2 amplification. SISH testing was not performed on the surgical specimen, if the matching CNB was HER2-amplified. New SISH tests were performed on the surgical specimen, for non HER2-amplified CNBs with HercepTest scored as 2+.
STRAT4 analysis
STRAT4 analysis was performed in November 2018 and was limited to two operators (S.J. and S.D.L.), each blinded to the IHC status of individual biomarkers. For each patient, a single 4 μm or 5 μm FFPE section (adjacent to the section used for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, determined by a board-certified pathologist (A.K.)) was prepared for both the CNB and the matching surgical specimen. For some surgical specimens, macrodissection (tumor area outlined by the pathologist) was required to remove non-neoplastic tissue. The FFPE sections were first placed in a water bath at 40 °C, mounted onto positively charged FLEX IHC microscope slides (Agilent Dako) and dried overnight at room temperature. The FFPE section was then scraped from the slide and transferred to a 1.5 ml lysis tube. FFPE samples containing CNBs were sectioned and transferred directly to lysis tubes.
Tissue lysis was prepared by adding 1.2 ml Xpert® FFPE lysis kit reagent and 20 μl proteinase K (PK) to each sample, followed by incubation at 80 °C for 30 min. The tissue lysate was then transferred to a provided 5 ml sample vial and precipitated with 1.2 ml 95% ethanol. An aliquot containing 520 μl tissue lysate was transferred to the Xpert Breast Cancer STRAT4 cartridge, the cartridge lid was closed, and then the closed cartridge was placed into the GeneXpert instrument. Furthermore, nucleic acid purification, and RT-qPCR amplification and detection are fully automated in the GeneXpert instrument, with all the reagents required for the different stages preloaded in the cartridge. The GeneXpert instrument system simultaneously measured the cycle threshold (Ct) values in multiplex for the reference gene (CYFIP1) and target genes (ESR1, PGR, MKi67, and ERBB2), and then calculated the delta cycle threshold (dCt) values (dCt = reference gene Ct minus target gene Ct) for each marker. The CYFIP1 Ct and individual dCt values for each marker were then compared to pre-specified Ct and dCt cutoffs to classify ESR1, PGR, MKi67, and ERBB2 mRNA expression as POSITIVE, NEGATIVE, INDETERMINATE, INVALID, or ERROR. Samples classified as INDETERMINATE (only applicable for PGR and/or MKi67 results, where the dCt value is below the specified cutoff value and the CYFIP1 reference gene Ct is greater than 31) or INVALID (CYFIP1 Ct > 35) were repeated using a more concentrated lysate (i.e. 260 μl FFPE lysis reagent, 5 μl PK, and 260 μl ethanol), whereas samples classified as ERROR were repeated using the remaining sample lysate.
Clinical evaluation of surrogate subtyping
For each surgical specimen, the IHC and STRAT4 analyses were then used to determine the surrogate breast cancer subtype (i.e. Luminal A-like, Luminal B-like (HER2- or HER2+), HER2+ (non-luminal), and Triple-negative) and recommended treatment for breast cancer patients according to national guidelines [22]. In brief, the Ki-67 cut-off was set to 20% to differentiate Luminal A-like breast cancer (Ki-67 < 20%) from Luminal B-like HER2- (Ki-67 ≥ 20%) and Luminal B-like HER2+ tumors (any Ki-67) [1]. Patients with subsequent changes in surrogate subtyping according to the STRAT4 assay results for ESR1, PGR, ERBB2, and MKi67 gene expression were further evaluated by the medical and surgical oncologists (K.L. and S.J.), whom were blinded to the administered treatment for each patient.
Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using a 0.05 p-value cutoff for statistical significance in MedCalc Statistical Software (version 18.10.2) or R/Bioconductor (version 3.6.0). To assess the concordance between STRAT4 and the reference method(s) (IHC or SISH, as applicable), standard 2 × 2 cross-tables were utilized along with calculation of the overall percent agreement (OPA), positive percent agreement (PPA) negative percent agreement (NPA) positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV). A kappa statistic with 95% two-sided confidence intervals (CI) was calculated to estimate the overall agreement between the compared methods, with k-values > 0.8, between 0.6 and 0.8, 0.4 and 0.6, < 0.4, and < 0.2 classified as very good, good, moderate, fair, and poor agreement, respectively [23]. Scatterplots were constructed using the ggplot2 package (version 3.3.0) in R [24].
Results
In total, the STRAT4 assay was performed twice for 12/200 samples due to INDETERMINATE Ki-67 results for four CNBs and three surgical specimens, ERROR for one CNB sample and three surgical specimens, as well as, INVALID for one surgical specimen. After repeating the STRAT4 protocol with the remaining tissue lysate or a more concentrated sample, the 12 samples yielded valid test results, i.e. POSITIVE or NEGATIVE.
Good agreement between STRAT4 and IHC when each biomarker is investigated separately
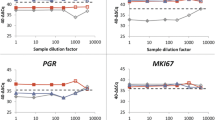
The Cohen’s kappa value and the overall percent agreement (OPA) were calculated to determine the concordance between the STRAT4 and IHC results (i.e. STRAT4 vs STRAT4, and STRAT4 vs IHC) for both sample types (i.e. CNB and surgical specimen; Table 2). In general, agreement between ER status was very good (k-values > 0.8) for all comparisons, while PR had good agreement (k-values between 0.6 and 0.8), HER2 ranged from good to very good agreement, and Ki-67 had moderate agreement (k-values between 0.4 and 0.6). These findings were in line with the OPA rates, which showed the highest OPAs for ER (range, 96–99%), PR (range, 89–94%), and HER2 status (range, 86–91%). Compared to IHC, STRAT4 detected a high number of false positives for Ki-67 and HER2 in the CNB samples. ER status was found to be most consistent between the two analytical methods, while Ki-67 status was least consistent when determined using Xpert MKi67 dCt values (Figs. 1 and 2).
Comparison of ER, PR, Ki-67, and HER2 status according to IHC (ER, PR and Ki-67 considered to be positive with ≥1%, ≥1, and 20% immunostaining respectively, HercepTest scored 2+ (with confirmed HER2 amplification using SISH testing) or 3+ considered to be HER2-positive) and STRAT4 (ER, PR, Ki-67, and HER2 considered to be positive with dCt cut offs ≥ − 1.0, ≥ − 3.5, ≥ − 4.0 and ≥ −1.0 respectively) in the surgical specimens
Comparison of ER, PR, Ki-67, and HER2 status according to IHC (ER, PR and Ki-67 considered to be positive with ≥1%, ≥1, and 20% immunostaining respectively, HercepTest scored 2+ (with confirmed HER2 amplification using SISH testing) or 3+ considered to be HER2-positive) and STRAT4 (ER, PR, Ki-67, and HER2 considered to be positive with dCt cut offs ≥ − 1.0, ≥ − 3.5, ≥ − 4.0 and ≥ − 1.0 respectively) in the core biopsies
Differences in concordance between two or more biomarkers assessed simultaneously
We then assessed whether two or more of the biomarkers (ER, PR, Ki-67, and HER2) were concordant for both IHC and STRAT4 (Table 3). Agreement between the biomarkers was generally lower in CNBs than surgical specimens, in particular for the four biomarkers (ER, PR, Ki-67, and HER2; 57%) and three biomarkers (ER, Ki-67, and HER2; 64%). In surgical specimens, the lowest concordance between IHC and STRAT4 was also found for the four biomarkers (ER, PR, Ki-67, and HER2; 66%). In contrast, the highest concordance between the two analytical methods were observed for ER and HER2 in surgical specimens (87%) and CNB (84%).
STRAT4-based subtyping may potentially result in more treatment of breast cancer patients
To evaluate the clinical utility of the STRAT4 assay, STRAT4 based biomarker assessment was first used to stratify the 100 surgical specimens into the surrogate breast cancer subtypes (Table 4). Subtyping was then used to compare administered treatment (according to IHC-based subtyping) to theoretical treatment decisions based on STRAT4 subtyping. In total, 74 (74%) specimens were concordant for the breast cancer subtypes, regardless of the method used (IHC or STRAT4). However, discordant subtyping was found to be due to changes in ER- (n = 5), Ki-67- (n = 12), and HER2-status (n = 9). Reevaluation of the IHC slides (by A.K. and S.J.) for the 26 discordant cases demonstrated the presence of DCIS in 4/26 cases and peritumoral normal tissue in all samples.
We then conducted a review of the medical records for the 25 discordant patients (one with bilateral breast cancer) to evaluate whether changes in subtype according to STRAT4 would have resulted in changed treatment decisions (Fig. 3). For 18 of the 25 patients with subtype changes, recommendations for adjuvant treatment would have changed with additional endocrine therapy for three patients, chemotherapy for six patients, trastuzumab for three patients, and combination therapy with chemotherapy and trastuzumab for four patients. Two patients would have been recommended less treatment: one patient would have not been recommended endocrine therapy, while the other patient would have not been recommended combination therapy with chemotherapy and trastuzumab.
Discussion
Here, we show that the concordance between STRAT4 and IHC is relatively good for ER, PR, Ki-67, and HER2, if each variable is investigated separately, which is in line with previous findings from Wu et al. [20] and Wasserman et al. [19]. However, surrogate subtype stratification (based on STRAT4 or IHC) in the surgical specimen differed for 26 cases (26%), which would potentially have changed the treatment recommendations for 18 patients (18%). The discrepancies between the STRAT4 and IHC results for the 26 cases may have, in part, been due to the presence of DCIS in four samples and peritumoral normal tissue in all the samples.
The tumor intrinsic/surrogate subtype is one of the most important factors for therapy planning, together with tumor size, grade, nodal status, age and co-morbidities that aids in choice of neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatment. To be able to provide the best individually tailored pre- and postoperative care for a breast cancer patient, the treating physician is dependent on reliable information regarding tumor biomarkers in CNBs and surgical specimens. These biomarkers need to be taken into account as a panel. The present study demonstrated fair to good concordance between STRAT4 and IHC for individual variables (ER, PR, Ki-67, and HER2), but concordance for all four variables together was less favorable.
While the pathologist solely examines neoplastic cells in IHC slides, gene assays frequently analyze RNA levels in the whole tumor mass (containing both neoplastic and non-neoplastic cells). As surrogate subtyping and, thus, treatment planning are dependent on the accurate assessment of ER, PR, Ki-67, and HER2 expression [3, 25, 26], routine diagnostic tools should be robust, reliable and reproducible. Gupta et al. suggested that macrodissection is sufficient [27], but we suggest that microdissection could potentially be useful to further improve OPA between these analytical methods. As long as an H&E slide is available, manual microdissection would require approximately 5 min of the pathologist’s time to mark the unnecessary, non-invasive areas and an additional 5–10 min for the histotechnician to perform the microdissection. The discordant cases for ER and HER2 status may have depended on the presence of adjacent ER/PR-positive normal breast tissue and/or HER2-positive ductal cancer in situ components. Reevaluation of the eight HER2 discordant cases (HER2 negative according to IHC, but HER2 positive according to STRAT4) revealed the presence of DCIS in four cases and peritumoral normal tissue in all eight cases. However, DCIS could also have been present in the corresponding FFPE section in which the STRAT4 analysis was performed. Of the eight discordant cases, seven were ductal carcinoma (including the four cases where DCIS was present) and one was mucinous cancer. Therefore, reevaluation of the IHC slides could resolve the discrepant cases and highlighted potential pitfalls with the STRAT4 assay.
In the present study, we revealed a number of Xpert ERBB2 false positive cases, with dCt values just over the current ERBB2 dCt cutoff (dCt = − 1.0). The current ERBB2 cutoff was initially developed and prospectively validated in retrospective FFPE samples, some of which had aged > 10 years from the time of initial collection and block preparation. These samples may have experienced RNA degradation over time, which would have underestimated a more optimal concordance cutoff had prospectively collected samples, such as the samples used in the present study, been used in the original validation studies. Therefore, further studies are recommended to reevaluate an appropriate ERBB2 dCt cutoff in prospectively collected specimens and using WHO guidelines (including The European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO), American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), St. Gallen International Breast Cancer Expert Panel and the National Comprehensive Cancer network (NCCN)) for defining HER2-positivity.
From a clinical point of view, use of STRAT4 instead of IHC to approximate the surrogate subtypes would theoretically have resulted in a high number patients receiving more treatment, primarily chemotherapy and trastuzumab. In patients correctly identified as HER2+, there is an overall survival benefit when given a combination of chemotherapy and HER2-targeted treatment [3]. However, chemotherapy has side effects and the administration of adjuvant chemotherapy involves careful consideration. Overtreatment with chemotherapy and trastuzumab will lead to unnecessary suffering with potentially irreversible side effects and no additional benefit [28, 29]. For a large group of ER-positive breast cancer patients, endocrine treatment can also be difficult to tolerate. Recent studies have shown that side effects can have an impact on decisions to discontinue therapy early [30, 31]. Furthermore, the significant financial burden of cancer care can also be a driving factor for therapy choice, particularly in countries that in part or fully subsidize treatment costs. It is, therefore, important that the most suitable treatment is recommended [32,33,34]. Further validation studies, ideally conducted using prospectively collected specimens and potentially alternate dCt cutoffs (particularly for ERBB2 and MKi67 given the lack of consensus on the IHC cutoffs for Ki-67), are warranted to demonstrate improved STRAT4 accuracy and ensure a correct and robust assessment of all biomarkers. In addition, the clinical utility of STRAT4 should be compared with established multigene prognostic tests for breast cancer (e.g. PAM50/Prosigna, Mammaprint/BluePrint).
Conclusions
In summary, use of other diagnostic methods to assess surrogate BC subtyping in the surgical specimen (e.g. STRAT4) may theoretically result in patients receiving more adjuvant treatment, primarily with chemotherapy and trastuzumab. It is imperative that ER, PR, Ki67, and HER2 biomarker assessment in CNBs and surgical specimens is accurate when new diagnostic methods are tested, as the results may have an impact on treatment decisions. Inadequate treatment can have serious consequences for the patient with regards to side effects and survival. Furthermore, comparison with established multigene prognostic tests for breast cancer should also be assessed so that the accuracy of the biomarkers is more precise.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from Cepheid but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of Cepheid.
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
23 April 2021
The family name of author Roger Olofsson Bagge has been corrected.
Abbreviations
- BC:
-
Breast cancer
- ER:
-
Estrogen
- PR:
-
Progesterone
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- CNB:
-
Core needle biopsy
- STRAT4:
-
Xpert® Breast Cancer STRAT4 Assay
- FFPE:
-
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded
- NBF:
-
Neutral Buffered Formalin
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- Ct:
-
Cycle threshold
- dCt:
-
Delta cycle threshold
References
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B, et al. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast Cancer 2013. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(9):2206–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt303.
Coates AS, Winer EP, Goldhirsch A, Gelber RD, Gnant M, Piccart-Gebhart M, et al. Tailoring therapies--improving the management of early breast cancer: St Gallen international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast Cancer 2015. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(8):1533–46. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv221.
Wang X, He Y, Fan Z, Wang T, Xie Y, Li J, et al. Effect of Trastuzumab among HER2-positive breast Cancer patients that achieved pathologic complete response after Neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Care. 2019;14(6):388–93. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495186.
Francis PA, Pagani O, Fleming GF, Walley BA, Colleoni M, Láng I, et al. Tailoring adjuvant endocrine therapy for premenopausal breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(2):122–37. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1803164.
Criscitiello C, Disalvatore D, De Laurentiis M, et al. High Ki-67 score is indicative of a greater benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy when added to endocrine therapy in luminal B HER2 negative and node-positive breast cancer. Breast. 2014;23(1):69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2013.11.007.
AJCC. Cancer Staging Manual. 8th Edtion ed. Chicago: Springer; 2017.
Tamaki K, Sasano H, Ishida T, Miyashita M, Takeda M, Amari M, et al. Comparison of core needle biopsy (CNB) and surgical specimens for accurate preoperative evaluation of ER, PgR and HER2 status of breast cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 2010;101(9):2074–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01630.x.
You K, Park S, Ryu JM, Kim I, Lee SK, Yu J, et al. Comparison of Core needle biopsy and surgical specimens in determining intrinsic biological subtypes of breast Cancer with immunohistochemistry. J Breast Cancer. 2017;20(3):297–303. https://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2017.20.3.297.
Breast Tumours. WHO classification of Tumours. 5th ed; 2019.
Park YJ, Youk JH, Son EJ, Gweon HM, Kim JA. Comparison of hormonal receptor and HER2 status between ultrasound-guided 14-gauge core needle biopsy and surgery in breast cancer patients. Ultrasonography. 2014;33(3):206–15. https://doi.org/10.14366/usg.14014.
Dekker TJ, Smit VT, Hooijer GK, et al. Reliability of core needle biopsy for determining ER and HER2 status in breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(4):931–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mds599.
Chebil G, Bendahl PO, Ferno M, South Sweden Breast Cancer G, North Sweden Breast Cancer G. Estrogen and progesterone receptor assay in paraffin-embedded breast cancer--reproducibility of assessment. Acta Oncol. 2003;42(1):43–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/02841860300672.
Rhodes A, Jasani B, Barnes DM, Bobrow LG, Miller KD. Reliability of immunohistochemical demonstration of oestrogen receptors in routine practice: interlaboratory variance in the sensitivity of detection and evaluation of scoring systems. J Clin Pathol. 2000;53(2):125–30. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.53.2.125.
Roepman P, Horlings HM, Krijgsman O, Kok M, Bueno-de-Mesquita JM, Bender R, et al. Microarray-based determination of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2 receptor status in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(22):7003–11. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0449.
Noske A, Anders SI, Ettl J, Hapfelmeier A, Steiger K, Specht K, et al. Risk stratification in luminal-type breast cancer: comparison of Ki-67 with EndoPredict test results. Breast. 2020;49:101–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2019.11.004.
Paik S, Shak S, Tang G, Kim C, Baker J, Cronin M, et al. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(27):2817–26. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa041588.
van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van't Veer LJ, et al. A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(25):1999–2009. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa021967.
Parker JS, Mullins M, Cheang MC, et al. Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(8):1160–7. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.18.1370.
Wasserman BE, Carvajal-Hausdorf DE, Ho K, Wong W, Wu N, Chu VC, et al. High concordance of a closed-system, RT-qPCR breast cancer assay for HER2 mRNA, compared to clinically determined immunohistochemistry, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and quantitative immunofluorescence. Lab Investig. 2017;97(12):1521–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2017.93.
Wu NC, Wong W, Ho KE, Chu VC, Rizo A, Davenport S, et al. Comparison of central laboratory assessments of ER, PR, HER2, and Ki67 by IHC/FISH and the corresponding mRNAs (ESR1, PGR, ERBB2, and MKi67) by RT-qPCR on an automated, broadly deployed diagnostic platform. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018;172(2):327–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-018-4889-5.
Parris TZ, Aziz L, Kovacs A, et al. Clinical relevance of breast cancer-related genes as potential biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2014;14(1):324. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-324.
The Swedish National Registry for Breast Cancer (NKBC). http://statistik.incanet.se/brostcancer/. p. Accessed online 15 Dec 2017.
Landis J, Koch G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159–74. https://doi.org/10.2307/2529310.
Wickham H. R package “ggplot2”: elegant graphics for data analysis; 2016.
Stierer M, Rosen H, Weber R, Hanak H, Spona J, Tuchler H. Immunohistochemical and biochemical measurement of estrogen and progesterone receptors in primary breast cancer. Correlation of histopathology and prognostic factors. Ann Surg. 1993;218(1):13–21. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-199307000-00004.
Denkert C, Loibl S, Muller BM, et al. Ki67 levels as predictive and prognostic parameters in pretherapeutic breast cancer core biopsies: a translational investigation in the neoadjuvant GeparTrio trial. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(11):2786–93. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt350.
Gupta S, Mani NR, Carvajal-Hausdorf DE, Bossuyt V, Ho K, Weidler J, et al. Macrodissection prior to closed system RT-qPCR is not necessary for estrogen receptor and HER2 concordance with IHC/FISH in breast cancer. Lab Investig. 2018;98(8):1076–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41374-018-0064-1.
Moilanen T, Jokimaki A, Tenhunen O, Koivunen JP. Trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity and its risk factors in real-world setting of breast cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018;144(8):1613–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2682-9.
Zhi WI, Chen P, Kwon A, Chen C, Harte SE, Piulson L, et al. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) in breast cancer survivors: a comparison of patient-reported outcomes and quantitative sensory testing. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;178(3):587–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05416-4.
Yin Z, Harrell M, Warner JL, Chen Q, Fabbri D, Malin BA. The therapy is making me sick: how online portal communications between breast cancer patients and physicians indicate medication discontinuation. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2018;25(11):1444–51. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocy118.
Skrabal Ross X, Gunn KM, Suppiah V, Patterson P, Olver I. Support Care Cancer. 2020;28(9):4043-50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-020-05469-y.
Monnier AM. The breast international group 1-98 trial: big results for women with hormone-sensitive early breast cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2007;7(5):627–34. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737140.7.5.627.
Carpenter R. Choosing early adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal women with hormone-sensitive breast cancer: aromatase inhibitors versus tamoxifen. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008;34(7):746–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2008.01.011.
Cameron D, Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Gelber RD, Procter M, Goldhirsch A, de Azambuja E, et al. 11 years' follow-up of trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive early breast cancer: final analysis of the HERceptin adjuvant (HERA) trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10075):1195–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32616-2.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Cepheid for providing material support for this study and the fruitful collaboration.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Assar Gabrielsson’s Foundation (FB18–92). Cepheid provided material support for this study. None of the funders had any role in the conduct of this study; collection, management, analysis and interpretation of the data nor decision to submit this manuscript. Open Access funding provided by University of Gothenburg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept and design: SJ, AK, TZP, SDL. Acquisition of data: SJ, AK, TZP, SDL. Statistical analysis: SN. Analysis and interpretation of data: SJ, AK, TZP, SN, SDL, KL, RAA, ROB. Drafting of the manuscript: SJ, AK, TZP, SN, SDL, RAA, ROB. All authors reviewed, edited and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All procedures were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Regional Ethical Review Board (Gothenburg, Sweden: 678–18).
The requirement for informed consent was waived by the Regional Ethical Review Board (Gothenburg, Sweden: 678–18) due to the retrospective nature of the study not changing any treatment decisions for the included patients. The authors did not need administrative permission to access the raw data.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Janeva, S., Parris, T.Z., Nasic, S. et al. Comparison of breast cancer surrogate subtyping using a closed-system RT-qPCR breast cancer assay and immunohistochemistry on 100 core needle biopsies with matching surgical specimens. BMC Cancer 21, 439 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-021-08171-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-021-08171-2