Abstract
Background
BRAF mutations are present in 40 % of human skin melanomas. Mutated tumors with an increased percentage of BRAF mutant alleles (BRAF-M%) may have a better response to RAF/MEK inhibitors. We evaluated the BRAF-M% in melanomas, and the genetic causes of its variation.
Methods
BRAF-M% was quantified by pyrosequencing, real-time PCR (rtPCR) and/or picoliter-droplet PCR (dPCR). BRAF mutant expression was detected by immunohistochemistry. Chromosomal alterations were analyzed with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays.
Results
BRAF-M% quantification obtained with pyrosequencing was highly correlated (R = 0.94) with rtPCR, and with dPCR. BRAF-M% quantified from DNA and RNA were also highly correlated (R = 0.98). Among 368 samples with >80 % tumor cells, 38.6 % had a BRAFV600E mutation. Only 66.2 % cases were heterozygous (BRAF-M% 30 to 60 %). Increased BRAF-M% (>60 %) was observed in 19 % of cases. FISH showed a polysomy of chromosome 7 in 13.6 %, 35.3 % and 54.5 % of BRAF wild-type, heterozygous and non-heterozygous BRAF-mutated samples, respectively (P < 0.005). Amplification (5.6 %) and loss (3.2 %) of BRAF locus were rare. By contrast, chromosome 7 was disomic in 27/27 BRAF-mutated nevi.
Conclusions
BRAF-M% is heterogeneous and frequently increased in BRAF-mutant melanomas. Aneuploidy of chromosome 7 is more frequent in BRAF mutant melanomas, specifically in those with high BRAF-M%.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Since the discovery of gain of function mutations in the proto-oncogenes NRAS [1] and BRAF [2], thousands of human skin melanoma samples have been analyzed, and the estimated incidence of NRAS and BRAF mutations are 18 % and 41 %, respectively [3]. These mutations are often mutually exclusive [4, 5]. The BRAF locus is localized on chromosome 7q, and most BRAF mutations involve the kinase activation loop at the p.V600 position. The most common BRAF mutation is a substitution of a valine to a glutamic acid (c.1799 T > A, p.V600E). BRAF V600E accounts for 85 % of exon 15 mutations in the most recent studies [6, 7]. Another mutation, V600K is present in 9 % of melanomas. These BRAF mutations constitutively activate the MAPK signaling pathway [8].
Two BRAF inhibitors, vemurafenib and dabrafenib, targeting the BRAF p.V600 mutated protein, have recently been shown to prolong the progression-free and/or the overall survival of BRAF V600-mutated advanced melanoma, as compared to dacarbazine [9–11]. However, both are limited by the development of acquired resistance in many patients, with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 6.9 and 6.7 months for vemurafenib and dabrafenib, respectively [10, 12].
Mechanisms underlying acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors have been extensively studied, and most of them involve acquired mutations within the same RAS-RAF-ERK pathway [13]. By contrast, only little data is available concerning biomarkers of good/prolonged response to BRAF inhibitors. Recently, a high ratio of mutant/wild-type alleles of BRAF was reported to be associated with a good response to BRAF inhibitors [14].
Like most oncogenes, somatic mutations of BRAF are thought to be heterozygous in tumors. Some studies reported that BRAF mutations are not heterozygous in some cases [15]. Additionally, in contrast to wild-type BRAF, which is only active as a dimer, products of alleles with gain of function mutations are also active as monomers [16].
We present herein a validated quantification of mutated BRAF in a large series of human skin melanoma samples, and demonstrate that several cases are not heterozygous. We also present the results of a genetic study on mechanisms of the BRAF mutant allele increase in melanoma.
Methods
Samples and nucleic acid extraction
All samples were obtained from the bank of biological resources of Ambroise Paré Hospital. All surgical or fine needle biopsies were performed for routine diagnosis or evaluation of disease progression. The research was performed in compliance with the ethical principles of the Helsinki Declaration (1964). In accordance with French ethics laws, all patients were informed that part of their samples could also be used for research purposes, and that they could refuse this. None of patients refused the use of samples for research. Tumor sample collection was declared to the French Ministry of Research (DC 2009-933) and CPP IDF 8 ethics committee approved the MelanCohort study (030209), which is registered with Clinicaltrials.gov (NCT00839410). Signed informed consent for translational research was obtained from patients still alive. All diagnoses were confirmed by pathology review.
For most of the nucleic acid quantification studies, the tumor DNA was extracted from formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissue. However, for mRNA extraction and high density SNP analysis, frozen samples were used. In all cases, a 4 micrometers-thick section was stained with hematoxylin & eosin and reviewed by a pathologist before extraction, to confirm the presence of melanoma and to select areas with the highest density of tumor cells for macrodissection. For all samples, tumors cell content was estimated in the percentage of tumor cells and the data was noted. To evaluate the accuracy of tumor cell content assessment, a series of 41 randomly selected samples was assessed by three independent pathologists.
For each sample, serial sections or punch sampling were then used for nucleic acid extraction. For DNA extraction, samples were digested by an overnight incubation in the presence of proteinase K, followed by the application of the QIAamp DNA mini kit (Qiagen, Courtaboeuf, France) as previously described [17]. The RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen) was applied for RNA extraction. DNA and RNA were controlled with a spectrophotometer (ND-100, Nanodrop®).
Real-time PCR
Real-time PCR (rtPCR) was performed as previously described [18]. 1 μL of DNA brought to 25 ng/μL was applied to each reaction mixture. The amplification reaction was performed in Applied Prism 7900 HT (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Illkirch, France). Each sample was analyzed in two different reaction mixes: in the first one, all BRAF alleles present in the tumors were amplified; in the second one, only the mutated allele was detected by peptide nucleic acids (PNAs)-specific inhibition of wild-type (WT) allele amplification. Each PCR reaction was carried out in duplicate. The primers and probe sequences were published previously [17]. The relative quantification method was used to compare expression levels of wild type allele and BRAF V600E mutated allele using comparative Ct method as described by Livak et al. [19].
Picoliter-droplet digital PCR
Picoliter-droplet digital PCR (dPCR) testing was performed using previously described protocols [20, 21] with the Raindrop Instrument (RainDance Technologies, Billerica, MA). Shortly, in a pre-PCR environment, 12.5 μL Taqman Genotyping Master Mix (Life Technologies, Saint Aubin, France) was mixed with the assay solution. The assay solution contained: 0.75 μL of 40 mM dNTP Mix (New England BioLabs, Evry, France), 0.5 μL of 25 mM MgCl2, 2.5 μL of 10x Droplet Stabilizer (RainDance Technologies), 1.25 μL of 20x Taqman® Assay Mix containing 8 μM of forward and reverse primers, 200 nM of 6-FAM and 200 nM of VIC Taqman® labelled-probes (Additional file 1) and target DNA template to a final reaction volume of 25 μL. A minimum of 280 ng of DNA was used in each assay. 5 millions highly monodispersed droplets were generated using the Raindrop source instrument following manufacturer’s instructions. The emulsions were submitted to thermocycling, starting with 2 min at 50 °C, 10 min at 95 °C, followed by 45 cycles of: 95 °C, 15 s and 60 °C, 1 min (using a 0.6 °C/min ramp rate). After completion, the end-point fluorescence signals from each droplet were measured using the Raindrop Sense instrument. Analyses of the data were performed using the Raindrop analyst software as previously described [20, 21]. The reference sequence was B-RAF cDNA sequence (GenBank NM_00433.4).
Pyrosequencing
Pyrosequencing was performed as previously described [22]. It is a method of DNA sequencing based on the "sequencing by synthesis" principle. The results are displayed in the form of peaks corresponding to the detection of pyrophosphate release after nucleotides incorporation (pyrogram). Peak area is proportional to the number of individual nucleotide incorporated to the sequence; thus allowing the relative quantifications of mutated and WT alleles. RNA was transcribed to cDNA and FFPE tumor DNA concentrations were brought to 10 and 20-25 ng/μL prior to PCR amplification. Primers used for FFPE tumor DNA amplification and pyrosequencing were published previously [17]. Biotinylated amplicon was verified on agarose gel and analyzed with PyroMark 24 (Qiagen) according to manufacturer recommendations. Primers used for frozen tumor DNA/RNA amplification and pyrosequencing are presented in Additional file 1.
FISH and Immunohistochemistry
Tissue microarray (TMA) was performed for 141 samples of melanomas (140 patients) and 42 samples of melanocytic nevi (junctional, intradermal and compound) of more than 4 mm long axis. For each tumor, three cores of 0.6 mm diameter from distinct tumor regions were spotted onto the slides.
For immunohistochemistry, the VE1 antibody was used as previously described [17, 23]. Detection of BRAF p.V600E mutated protein with VE1 has been shown to have a high sensitivity, specificity and reproducibility. Intensity of staining was evaluated by two independent observers on a semi-quantitative scale of 0–3. The VE1 antibody was scored as negative (0) when there was no staining, weak staining of single interspersed cells, or staining of monocytes/macrophages. Positive staining was scored as: weakly positive staining (1), moderately positive staining (2) and strongly positive staining (3) of melanoma cells. Cases were considered not interpretable when nuclear staining was present. Cases were scored as ambiguous if immunostaining could not be scored as positive or negative.
For FISH analysis, TMA section slides of 4 micrometers were stored at -20 °C and hybridization was performed within 2 weeks of cutting. All samples were analyzed with the RP11-121G9 BAC probe covering the BRAF gene. The chromosome 7 centromere probe was used as reference probe (Agilent Technologies, Les Ulis, France). A total of 53 tumor samples were also analyzed with the commercially available BRAF probe, SureFISH 7q34 BRAF (Agilent Technologies), together with the chromosome 7 centromere probe. For home-made probes, bacteria carrying a BAC vector were grown overnight onto solid agar medium, followed by an overnight proliferation in a LB medium. BAC DNA was extracted using NucleoBond PC 500 or NucleoBand Xtra BAC Kits (Macherey-Nagel, Hoerdt, France) as recommended by supplier. 1 μg of DNA was labeled by nick-translation reaction according to manufacturer’s instructions (Abbott Molecular Inc., Rungis, France). After overnight precipitation at -20 °C in the presence of human cot DNA, sodium acetate and ethanol, the probe was resuspended in the hybridization buffer (LSI/WCP Hybridization Buffer)(Abbott Molecular Inc). They were used at a final concentration of 40-50 ng/μL. FFPE slides were prepared for hybridization using Histology FISH accessory KIT (DAKO, Les Ulis, France). Commercial probes were applied according to the manufacturer’s recommendations (Agilent Technologies) and a co-denaturation of the probes and the tumor section were performed to create single-stranded DNA. The probes and the slides were denaturated separately when BRAF BAC probes were used together with commercial chromosome 7 centromere probe. Before an overnight incubation in a humidified chamber, a suppression of the repetitive sequences was performed for DNA BRAF BAC (45 min at 37 °C). After post-hybridization wash, and DAPI staining in the Vectashield® Mounting Media (Vector Laboratories, Les Ulis, France), fluorescence signals were analyzed using a Leica DM4000B microscope equipped with appropriate filters and a DFC300FX camera under the control of LAS V4.0 software (Leica). Two independent analyses were performed.
SNP analysis
DNA was extracted from frozen melanoma samples and hybridized on HumanCore BeadChip (Infinium Ilumina®, Evry, France) according to the manufacturer’s instructions by IntegraGen. This array contains more than 240,000 highly-informative genome-wide tag SNP and over 20,000 high-value markers. Chromosome 13p, 14p, 15p, 21p and 22p markers are not represented in this array. Chromosome Y and X were only used to control the gender of the patient. All genome positions were based upon NCBIGRCh37/hg19 from UCSC Genome Bioinformatics. The genotyping data were normalized by the IntegraGen commercial platform and analyzed (copy number aberrations (CNA) and allele disequilibrium (AD)) using GenomeStudio software (version 1) (Illumina Inc).
The Cancer Genome Atlas Dataset
For external validation of our results on an independent cohort, the skin melanoma dataset of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)(Provisional) was downloaded through the cBioPortal for Cancer Genomics website (http://www.cbioportal.org/ date March 13th 2015). We selected “All Complete Tumors (278)” of the patient/case set and entered the BRAF gene in the TCGA (Provisional) dataset. The cBioPortal website provided the data about mutation type, amino acid change and variant allele frequency. Analysis was performed as published [24].
Statistic analyses
The correlations between the percentage of mutated BRAF in cDNA/gDNA and in rtPCR/pyrosequencing analysis were tested by estimating the coefficient of correlation. The chi2 test supplemented when necessary in Yates correction was used to analyze the differences between different BRAF-M% groups and chromosome 7 status. The t-test was used to compare tumors with less or more than 80 % of tumor cells. The results were considered significant when P < 0.05.
Results
Validation of BRAF mutated allele quantification
The percentage of BRAF mutant alleles (BRAF-M%) in patients with melanoma was evaluated with two quantitative methods. Both pyrosequencing and real-time PCR allowed quantification of the relative amount of c.1799 T > A substitution. However these methods are only used qualitatively in determining BRAF status in clinical practice. We analyzed DNA extracted from 77 FFPE melanoma samples with both methods, and found a high positive correlation (R = 0.94) of BRAF-M% (Additional file 2A). For 7 samples, BRAF-M% obtained by pyrosequencing was compared with the absolute number of both alleles assessed by picoliter-droplet digital PCR in limiting dilution conditions and obtained similar results (Additional file 3A, B). We thus decided to use pyrosequencing for the subsequent quantitative analysis of BRAF V600E mutation.
As quantification of genomic DNA obtained from FFPE samples may not be representative of BRAF mutated messenger RNA (mRNA), we extracted both mRNA and genomic DNA (gDNA) from 27 frozen melanoma samples. Each sample was then analyzed with pyrosequencing assays designed to be specific for either cDNA or gDNA. A high correlation (R = 0.98) of BRAF-M% between BRAF V600E cDNA and gDNA was observed (Additional file 2B). Thus, the BRAF-M% assessed in genomic DNA from FFPE samples by pyrosequencing may be considered representative of the relative quantities of mutated/WT BRAF in mRNA.
Quantification of BRAF mutation
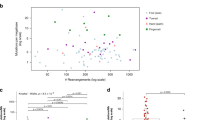
Pyrosequencing quantification was obtained in 475 FFPE melanoma samples from 428 patients with AJCC stage III or IV melanoma with either V600E or WT BRAF, after histological evaluation of the percentage of tumor cells (flow chart in Additional file 4). No discordance concerning BRAF mutational status was observed among the 46 patients with at least two distinct melanoma samples, and the median BRAF-M% variation was 2.5 %. As expected, according to the percentage of tumor cells in mutated BRAF melanomas, we observed a distinct distribution of the percentage of mutated allele (Fig. 1a). The inter-pathologist reproducibility for the evaluation of tumor cell content was substantial for the 80 % cut-off (κ = 0.79), and was only moderate for the 70 % cut-off (κ = 0.49). Thus, we decided to use the cut-off of 80 % of tumor cells. The distribution of mutated BRAF amounts in samples with less (n = 107) or more (n = 368) than 80 % of tumor cells were significantly different (P < 0.05). Therefore, we thus excluded samples with less than 80 % of melanoma cells from further analysis.
Variations in the percentage of BRAF V600E mutation in melanomas. a Scatter plot representation of the amounts of wild-type and V600E BRAF allele distribution in relation to the percentage of tumor cells in 475 FFPE melanoma samples. b Histogram representation of the percentage of BRAF V600E mutated allele in 368 melanomas obtained by pyrosequencing analysis. The Y axis corresponding to the number of cases is broken between 50 and 200
Among the 368 remaining samples, 142 were considered BRAF mutated (38.6 %); however BRAF-M% was highly heterogeneous (Fig. 1b), ranging from 10 % to 90 %. The majority of BRAF mutant cases (66.2 %, n = 94) had 30 % to 60 % of BRAF-M%, and were therefore considered heterozygous. By contrast, 48 cases were considered non-heterozygous for the BRAF mutation with BRAF-M% >60 % (n = 27) or <30 % (n = 21). Most BRAF mutated cases with BRAF-M% from 10 % to 30 % have been confirmed with another method and/or on another sample of the same patient. Immunohistochemistry with VE1 was performed on whole slides in cases with BRAF-M% <30 % when available (n = 14/21), and none of these cases contained any tumor area with loss of BRAF mutant expression.
In order to validate our results showing heterogeneous distribution of BRAF-M% in mutated melanoma tumors, we investigated the next-generation sequenced DNA mutation data of the 104 mutated skin melanomas in the TCGA database. The BRAF-M% from TCGA database ranged from 8 to 97 %, and the distribution was in keeping with our observation (Table 1).
Genetic causes of BRAF-M% heterogeneity
To elucidate mechanisms leading to BRAF-M% variation, we analyzed copy number alterations of chromosome 7 and BRAF locus. FISH was performed on TMA with two probes specific for the BRAF locus and for the chromosome 7 centromere. Among 125 samples, four types of chromosome 7 alterations were observed with BRAF probe RP11-121G9/centromere 7 (Fig. 2): no alteration (disomy), disomy but rare cells with polysomy, polysomy, and monosomy, which were respectively detected in 18.4 % (n = 23), 43.2 % (n = 54), 29.6 % (n = 37) and 3.2 % (n = 4) of cases. BRAF locus was amplified (6 to numerous BRAF copies) in 5.6 % of cases (n = 7).
Chromosome 7 alterations in human melanomas by FISH. Representative images of FISH with BRAF/chromosome 7 centromere probes in melanomas with different chromosome 7 alterations. a no alteration (disomy) but rare cells with chromosome 7 polysomy; b chromosome 7 polysomy; c BRAF amplification; d) chromosome 7 monosomy. White bar = 10 μm
FISH was also performed on 44 samples with another probe for the BRAF locus (SureFISH 7q34 BRAF) and similar results were obtained in all cases. To further confirm FISH results, we analyzed single nucleotide polymorphisms on chromosome 7 in 18 samples, and again all genomic results obtained were concordant with FISH (Table 2 and Additional file 5).
We then compared BRAF mutation allele quantity and chromosome 7 copy number changes (Additional file 6). Disomy of chromosome 7 - or only few cells with polysomy - were detected in 78 % (n = 46/59) of BRAF wild-type samples, but in only 47 % (n = 31/66) of BRAF mutants; however the difference didn’t reached statistical significance (P = 0.08). Quantification of BRAF-M% was not validated in samples with mutations other than V600E (n = 10/66). Correlation with FISH showed a polysomy of chromosome 7 in 13.6 % (n = 8/59), 35.3 % (n = 12/34) and 54.5 % (n = 12/22) of wild-type, heterozygous and non-heterozygous samples, respectively (P < 0.05) (Fig. 3). Furthermore, none of the 22 non-heterozygous cases, versus 33.9 % (n = 20/59) of the BRAF WT group, were diploid (P < 0.05). Among the 22 non-heterozygous samples, six had low BRAF-M% (Additional file 6). Six of the 10 samples with other BRAF mutations had a polysomy of chromosome 7.
Frequency of chromosome 7 aberrations in BRAF mutant melanoma (n = 125) and melanocytic nevi groups (n = 33).Histogram representation of prevalence of chromosome 7 abnormalities evaluated by FISH in 115 melanomas depending on the amounts of V600E mutation, in 10 melanomas with BRAF exon 15 mutations different from V600E and in 33 melanocytic nevi. WT – wild-type, HETR – heterozygous, MUT – mutation
BRAF copy number and BRAF expression
We also investigated the VE1 data for 114 samples from TMA slides. Both VE1 and FISH data were available for 45 BRAF V600E mutated melanomas. The VE1 staining were stronger in mutated cases showing hyperploidy or amplification for chromosome 7 (74 %, 17/23) than in tumors with only one chromosome 7 or with no (disomy) or minor (rare cells with polysomy) alterations (32 %, 7/22) (P < 0.05). Interestingly, the VE1 staining was stronger in melanomas with BRAF-M% >60 % than in those <60 %, but this was not statistically significant.
BRAF and chromosome 7 statuses in melanocytic nevi
The frequent chromosome 7 aneuploidy may be the cause or the consequence of BRAF mutations in melanomas. Alternatively, it may occur in melanocyte proliferations regardless of BRAF mutations. To address this question we analyzed 42 dermic and/or junctional melanocytic nevi. BRAF p.V600E mutation were detected by immunohistochemistry with VE1 on tissue arrays in 78.6 % (n = 33) of nevi. In situ hybridization with probes corresponding to the BRAF locus and the chromosome 7 centromere was interpretable in 27 of these 33 BRAF mutant benign tumors (81.2 %), and chromosome 7 was diploid in all cases (Fig. 3).
Discussion
The primary objective of this study was to assess the percentage of BRAF mutated allele (BRAF-M%) in a large series of human melanoma samples. For this purpose, we first validated quantification by pyrosequencing by comparing it with 2 other methods: real-time PCR and picoliter-droplet digital PCR. We also demonstrated a close correlation of BRAF-M% quantifications in genomic DNA and messenger RNA. The best inter-pathologist reproducibility of the estimation of the percentage of tumor cells in mutated melanoma was obtained with a cut-off at 80 %. Furthermore, the mean BRAF-M% was significantly lower for cases with <80 % of tumor cells, probably due to the presence of the wild type non-tumor cells. We therefore limited the analysis to samples containing at least 80 % of tumor cells.
Using this validated quantitative method, we analyzed BRAF-M% in a series of 368 melanoma samples and found that it was very heterogeneous. We then investigated the genetic cause of this high heterogeneity by FISH and high density SNP array, and demonstrated that chromosome 7 aneuploidy was the main mechanism of unbalanced BRAF allelic ratio. Finally we showed that, as opposed to melanomas, benign melanocytic tumors with BRAF mutations did not have any chromosome 7 instability.
Although oncogenic mutations are expected to occur in only one of the two parental alleles, we found that only two thirds of BRAF mutated melanomas were heterozygous. Decreased (<30 %) and increased (>60 %) levels of V600E mutations were detected in 14.8 % and 19 % of mutated BRAF p.V600E melanomas, respectively. Unbalanced BRAF mutations have been previously reported to be frequent in smaller series of melanoma [14, 16, 25]; however quantitative methods were not clearly validated, and correlation with mRNA levels was not established. Our results were further confirmed by analysis of the TCGA database. These results raise important questions concerning BRAF targeted therapies. Indeed, ATP-competitive RAF inhibitors have different effects in cells expressing wild-type or mutant BRAF forms, with up- or down-regulation of the ERK signaling pathway in certain in vitro conditions [26]. Furthermore, activation of the wild-type form depends on dimerization, while monomeric mutant forms have been shown to be active [16]. As BRAF-M% appears to be highly heterogeneous in melanomas, one could expect differences in response to ATP-competitive RAF inhibitors between tumors. Data from a recent clinical study support this hypothesis, showing that the BRAF V600 mutation level was significantly associated with a better response rate to vemurafenib during the first 10 months of treatment [14]. In our series, two patients with increased BRAF V600E levels (86.6 % and 86.7 %) had a prolonged disease-free survival during respectively 25 and 39 months of BRAF p.V600 inhibitors therapy. These results emphasize the appeal of mutant BRAF quantification assessment prior to BRAF inhibitor treatment, to correlate with clinical response rate and survival. In clinical practice, the quantification of BRAF mutations deserves to be considered as a standard item in reporting the mutational status of BRAF. Furthermore, in vitro screening of new drugs should include cell lines with different BRAF mutant levels, thus more closely representative of BRAF-M% in patients’ melanomas. Of note, an in vitro study showed that 4/4 melanoma cell lines with homozygous BRAFV600E mutations were sensible to vemurafenib, while 3/6 with heterozygous BRAFV600E mutations were resistant [27].
Our initial hypothesis was that amplification of the BRAF locus is responsible for high BRAF-M%. However, BRAF amplification was observed in only 5.6 % of samples (n = 7), including 5 BRAF mutated cases. By contrast, we detected a polysomy of chromosome 7 in the majority of cases with high BRAF-M%. A second FISH analysis with another probe specific for the BRAF locus and SNP analysis on chromosome 7 confirmed the quality of our FISH data.
The low BRAF-M% may be related to the presence of non-tumor cells. Indeed, we observed a relationship between percentage of tumor cells and BRAF-M%. However cases with low BRAF-M% were also detected when including only samples with >80 % of tumor cells. Tumor heterogeneity of BRAF mutated melanomas, including some areas without BRAF mutations, have been reported by a few groups [28, 29], and could also be responsible for low BRAF-M%. Therefore, we performed an in situ analysis of cases with <30 % of mutant allele by immunohistochemistry with the BRAF p.V600E-specific VE1 antibody on whole slide sections. In all cases available for analysis, no negative areas were detected. Thus the main cause of low BRAF-M% is probably similar to high BRAF-M%. Unfortunately, we cannot confirm this in the present study, because only 6 cases were analyzed by FISH. Interestingly, BRAF mutated tumors with numerous copies of chromosome 7 displayed stronger VE1 staining, suggesting a higher expression of the BRAF mutant allele.
We report herein that only 18.4 % of melanomas had no alterations of chromosome 7. Other groups have already shown that chromosome instability is not restricted to chromosome 7. Indeed DNA copy number alterations were widely studied in both primary melanomas [30, 31] and melanoma cell lines [31–34] and frequent gains of 6p, 7, 8, 17q and 20q and losses of 9p, 10, 21q were reported. However, these studies did not quantify the amounts of the mutated BRAF allele. Two groups correlated chromosome 7 copy numbers with BRAF mutational status [15, 35]; however BRAF-M% was evaluated on sequence electropherogram peaks. Willmore-Payne et al. detected seven cases with chromosome 7 polysomy and two with BRAF amplification [15]. The percentage of BRAF-mutated and WT alleles were compared with 100 K SNP chip data for chromosome 7 by Spittle and colleagues [25]. However, this analysis, carried out in eight melanoma cell lines, showed the preferential amplification of mutant BRAF as a mechanism of an increased ratio of mutant/WT BRAF.
We detected the BRAF p.V600E mutation in 78.6 % of dermal and/or junctional melanocytic naevi. These results were obtained through immunohistochemistry with the VE1 antibody, whose specificity, sensitivity and reproducibility were demonstrated in melanomas [17, 22, 36]. A similar frequency of BRAF mutations in the same types of nevi has already been reported [37]. We then analyzed chromosome 7 aneuploidy in BRAF mutated nevi with FISH of chromosome 7. As opposed to the results obtained in melanoma, no alterations were detected in the 27 cases of nevi available, thus excluding a causal link between BRAF mutations and chromosomal instability in melanocytic tumors. These results are in keeping with previously published data [38]. BRAF was previously proposed to be the driver of copy number increase in melanoma [35]. The present data do not support this hypothesis. However, association of chromosome 7 aneuploidy with malignancy was significant in BRAF mutated melanocytic tumors (35/66 versus 0/27, P < 0.05). Our results suggest that, among the high number of genetic alterations present in melanomas, a frequent oncogenic pathway is characterized by an early gain of function mutation in BRAF and a late transforming mutation in another gene responsible for chromosomal instability. However, this has to be confirmed in cell models.
Conclusions
BRAF inhibitors are widely used to treat patients with BRAF mutated melanoma, but most metastatic patients with initial tumor response develop acquired resistance with a median PFS of less than 7 months [10, 12]. Biomarkers of long-term response are still missing; however a high BRAF-M% was recently reported to be correlated with a prolonged response. We show here that only two thirds of BRAF V600E melanomas have a heterozygous mutation. Thus quantitative, rather than qualitative, evaluation of BRAF mutation deserves to be considered as a standard item in reporting the mutational status of melanoma. Prospective clinical studies are necessary to determine the BRAF-M% prognostic impact in term of response rate or prolonged response to BRAF inhibitors, and to confirm that BRAF-M% could be used as a biomarker of long-term response in clinical practice.
Abbreviations
- BAC:
-
Bacterial artificial chromosome
- BRAF-M%:
-
Percentage of BRAF mutant alleles
- dPCR:
-
Picoliter droplet PCR
- FFPE:
-
Formalin fixed paraffin embedded
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- rtPCR:
-
real-time PCR
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- TMA:
-
Tissue microarray
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Albino AP, Nanus DM, Mentle IR, Cordon-Cardo C, McNutt NS, Bressler J, et al. Analysis of ras oncogenes in malignant melanoma and precursor lesions: correlation of point mutations with differentiation phenotype. Oncogene. 1989;11:1363–74.
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–54.
Lee JH, Choi JW, Kim YS. Frequencies of BRAF and NRAS mutations are different in histological types and sites of origin of cutaneous melanoma: a meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:776–84.
Omholt K, Platz A, Kanter L, Ringborg U, Hansson J. NRAS and BRAF mutations arise early during melanoma pathogenesis and are preserved throughout tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:6483–8.
Akslen LA, Angelini S, Straume O, Bachmann IM, Molven A, Hemminki K, et al. BRAF and NRAS mutations are frequent in nodular melanoma but are not associated with tumor cell proliferation or patient survival. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:312–7.
Long GV, Menzies AM, Nagrial AM, Haydu LE, Hamilton AL, Mann GJ, et al. Prognostic and clinicopathologic associations of oncogenic BRAF in metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1239–46.
Greaves WO, Verma S, Patel KP, Davies MA, Barkoh BA, Galbincea JM, et al. Frequency and spectrum of BRAF mutations in a retrospective, single-institution study of 1112 cases of melanoma. J Mol Diagn. 2013;15:220–6.
Yang H, Higgins B, Kolinsky K, Packman K, Go Z, Iyer R, et al. RG7204 (PLX4032), a selective BRAFV600E inhibitor, displays potent antitumor activity in preclinical melanoma models. Cancer Res. 2010;70:5518–27.
Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A, McArthur GA, Sosman JA, et al. Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:809–19.
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, et al. BRIM-3 Study Group. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2507–16.
Sosman JA, Kim KB, Schuchter L, Gonzalez R, Pavlick AC, Weber JS, et al. Survival in BRAF V600-mutant advanced melanoma treated with vemurafenib. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:707–14.
Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Demidov LV, Jouary T, Gutzmer R, Millward M, et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380:358–65.
Lito P, Rosen N, Solit DB. Tumor adaptation and resistance to RAF inhibitors. Nat Med. 2013;19:1401–9.
Lebbé C, How-Kit A, Battistella M, Sadoux A, Podgorniak MP, Sidina I, et al. BRAF(V600) mutation levels predict response to vemurafenib in metastatic melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2014;24:415–8.
Willmore-Payne C, Holden JA, Hirschowitz S, Layfield LJ. BRAF and c-kit gene copy number in mutation-positive malignant melanoma. Hum Pathol. 2006;37:520–7.
Poulikakos PI, Persaud Y, Janakiraman M, Kong X, Ng C, Moriceau G, et al. RAF inhibitor resistance is mediated by dimerization of aberrantly spliced BRAF(V600E). Nature. 2011;480:387–90.
Colomba E, Hélias-Rodzewicz Z, Von Deimling A, Marin C, Terrones N, Pechaud D, et al. Detection of BRAF p.V600E mutations in melanomas: comparison of four methods argues for sequential use of immunohistochemistry and pyrosequencing. J Mol Diagn. 2013;15:94–100.
Didelot A, Le Corre D, Luscan A, Cazes A, Pallier K, Emile JF, et al. Competitive allele specific TaqMan PCR for KRAS, BRAF and EGFR mutation detection in clinicalformalin fixed paraffin embedded samples. Exp Mol Pathol. 2012;92:275–80.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Method Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Taly V, Pekin D, Benhaim L, Kotsopoulos SK, Le Corre D, Li X, et al. Multiplex picodroplet digital PCR to detect KRAS mutations in circulating DNA from the plasma of colorectal cancer patients. Clin Chem. 2013;59:1722–31.
Emile JF, Diamond EL, Hélias-Rodzewicz Z, Cohen-Aubart F, Charlotte F, Hyman DM, et al. Recurrent RAS and PIK3CA mutations in Erdheim-Chester disease. Blood. 2014;124:3016–9.
Moreau S, Saiag P, Aegerter P, Bosset D, Longvert C, Hélias-Rodzewicz Z, et al. Prognostic value of BRAFV600 mutations inmelanoma patients after resection of metastatic lymph nodes. Ann SurgOncol. 2012;19:4314–21.
Marin C, Beauchet A, Capper D, Zimmermann U, Julié C, Ilie M, et al. Detection of BRAF p.V600E Mutations in Melanoma by Immunohistochemistry Has a Good Interobserver Reproducibility. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014;138:71–5.
Kim MH, Bae JS, Lim DJ, Lee H, Jeon SR, Park GS, et al. Quantification of BRAF V600E alleles predicts papillary thyroid cancer progression. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21:891–902.
Spittle C, Ward MR, Nathanson KL, Gimotty PA, Rappaport E, Brose MS, et al. Application of a BRAF pyrosequencing assay for mutation detection and copy number analysis in malignant melanoma. J Mol Diagn. 2007;9:464–71.
Poulikakos PI, Zhang C, Bollag G, Shokat KM, Rosen N. RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF. Nature. 2010;464:427–30.
Søndergaard JN, Nazarian R, Wang Q, Guo D, Hsueh T, Mok S, et al. Differential sensitivity of melanoma cell lines with BRAFV600E mutation to the specific Raf inhibitor PLX4032. J Transl Med. 2010;8:39.
Yancovitz M, Litterman A, Yoon J, Ng E, Shapiro RL, Berman RS, et al. Intra- and inter-tumor heterogeneity of BRAF(V600E))mutations in primary and metastatic melanoma. PLoS One. 2012;7:e29336.
Wilmott JS, Menzies AM, Haydu LE, Capper D, Preusser M, Zhang YE, et al. BRAF(V600E) protein expression and outcome from BRAF inhibitor treatment in BRAF(V600E) metastatic melanoma. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:924–31.
Curtin JA, Fridlyand J, Kageshita T, Patel HN, Busam KJ, Kutzner H, et al. Distinct sets of genetic alterations in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2135–47.
Greshock J, Nathanson K, Medina A, Ward MR, Herlyn M, Weber BL, et al. Distinct patterns of DNA copy number alterations associate with BRAF mutations in melanomas and melanoma-derived cell lines. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009;48:419–28.
Stark M, Hayward N. Genome-wide loss of heterozygosity and copy number analysis in melanoma using high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism arrays. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2632–42.
Jönsson G, Dahl C, Staaf J, Sandberg T, Bendahl PO, Ringnér M, et al. Genomic profiling of malignant melanoma using tiling-resolution arrayCGH. Oncogene. 2007;26:4738–48.
Gast A, Scherer D, Chen B, Bloethner S, Melchert S, Sucker A, et al. Somatic alterations in the melanoma genome: a high-resolution array-based comparative genomic hybridization study. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2010;49:733–45.
Maldonado JL, Fridlyand J, Patel H, Jain AN, Busam K, Kageshita T, et al. Determinants of BRAF mutations in primary melanomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:1878–90.
Long GV, Wilmott JS, Capper D, Preusser M, Zhang YE, Thompson JF, et al. Immunohistochemistry is highly sensitive and specific for the detection of V600E BRAF mutation in melanoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013;37:61–5.
Pollock PM, Harper UL, Hansen KS, Yudt LM, Stark M, Robbins CM, et al. High frequency of BRAF mutations in nevi. Nat Genet. 2003;33:19–20.
Bauer J, Bastian BC. Distinguishing melanocytic nevi from melanoma by DNA copy number changes: comparative genomic hybridization as a research and diagnostic tool. Dermatol Ther. 2006;19:40–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Arthur Frohlich, Maxence Tondu, Mariama Bakari, Glwadys Faucher, Dominique Péchaud, Yolaine Pothin, Sylvie Surel and Nathalie Terrones for technique contribution and/or data collection, Dr Alain Beauchet for statistical analysis and Astrid Blom for article review. This work was supported partly by grants from the Association Vaincre le Mélanome, Ligue Contre le Cancer (Comité 92 WB2013-232), and Association pour la Recherche et l’Enseignement en Pathologie (AREP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
VT has received honoraria from RainDance Technologies. JFE received honoraria from Roche and Glaxo Smith Kline for counseling on patients with melanomas on the diagnosis and/or treatment with BRAF inhibitors. PS received honoraria for counseling on diagnosis and/or treatment of patients with melanomas from Roche and Glaxo Smith Kline.
Authors' contributions
Conception and design: PS and JFE. Development of methodology: ZHR, LB, CLG, VT and JFE. Study supervision: ZHR, PS and JFE. Writing of the manuscript: ZHR, EFB, JFE. All authors participated in the acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data (acquired and managed patients, provided facilities, etc.). All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Elisa Funck-Brentano and Laure Baudoux contributed equally to this work.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Oligonucleotides used for BRAF gDNA/cDNA analysis and BRAF dPCR.
Additional file 2:
Correlation analysis of BRAF V600E mutated allele frequency. A) in 77 FFPE melanoma samples by pyrosequencing and rtPCR. B) in gDNA and cDNA in 27 frozen melanoma samples.
Additional file 3:
Picoliter-droplet digital PCR (dPCR) analysis forBRAFV600E in melanomas. A) Representative results of dPCR analysis for BRAF V600E on DNA obtained from 2 melanomas with different percentage of mutated allele evaluated by pyrosequencing. On the x and y axis are reported the fluorescence intensity of droplets positive for BRAF V600E and BRAF wild-type, respectively. The percentage of BRAF V600E, BRAF wild-type and empty droplets are reported in images. B) Comparison of BRAF mutated allele frequency detected by pyrosequencing and dPCR for 7 melanoma samples.
Additional file 4:
Workflow for melanoma and melanocytic nevi samples regarding the type of molecular analysis carried out.
Additional file 5:
Chromosome 7 alterations by Illumina BeadChip HumanCore SNP array. Examples of chromosome 7 alterations in 5 BRAF V600E mutated and in one BRAF wild-type melanoma (C). In each case, logR2 ratios for the SNP and B allele frequency are plotted on the X axis above the chromosome ideogram. For logR2 ratios, values centered on 0 indicate diploid copy number. Values under and above 0 indicate losses and gains respectively. For B allele frequency, values differ from around 0.5 indicated LOH.
Additional file 6:
Summary of pyrosequencing and FISH results. BRAF-M% and FISH results obtained for 125 melanomas analyzed by FISH with BRAF BAC/chromosome 7 centromere probes.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Hélias-Rodzewicz, Z., Funck-Brentano, E., Baudoux, L. et al. Variations of BRAF mutant allele percentage in melanomas. BMC Cancer 15, 497 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1515-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1515-3