Abstract
Background
Women’s diet and nutritional status during pregnancy are important in influencing birth outcomes. We conducted a systematic scoping review of the best available evidence regarding dietary intake of Malaysian pregnant women, and the associations of maternal diet, anthropometry, and nutrition-related co-morbidities with the infant’s birth weight (IBW). The study objectives were to examine: (1) the adequacy of micronutrient intake among pregnant women; and (2) the association of maternal factors (anthropometry, diet, plasma glucose and blood pressure) during pregnancy with IBW.
Methods
Eleven search engines such as Proquest, EbscoHost, Scopus, Cochrane Library, Science Direct, Wiley Online Library, PubMed, Google Scholar, MyJournal, BookSC and Inter Library Loan with Medical Library Group were extensively searched to identify the primary articles. Three reviewers independently screened the abstracts and full articles based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Extracted data included details about the population characteristics, study methods and key findings related to the review objectives. Seventeen studies published from 1972 to 2021 were included, following the PRISMA-ScR guideline.
Results
Studies showed that maternal micronutrient intakes including calcium, iron, vitamin D, folic acid, and niacin fell short of the national recommendations. Increased maternal fruit intake was also associated with increased birth weight. Factors associated with fetal macrosomia included high pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI), excess gestational weight gain (GWG) and high blood glucose levels. Low pre-pregnancy BMI, inadequate GWG, intake of confectioneries and condiments, and high blood pressure were associated with low birth weight.
Conclusion
This review identified several factors such as the mother’s food habits, comorbidities, BMI and gestational weight gain as the determinants of low birth weight. This implies that emphasis should be given on maternal health and nutrition for the birth outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The nutritional status of women prior to conception and during pregnancy is important for fetal growth and development. The first 1000 days of life (i.e., the period of conception up to the first two postnatal years) emphasize the importance of optimal maternal nutritional status in determining early infant development and risk of nutrition-related chronic diseases in adulthood [1]. Maternal undernutrition and insufficient gestational weight gain (GWG) are key contributors to increased incidence of preterm birth (PTB), low birth weight (LBW) and poor fetal growth [2, 3]. On the other hand, maternal obesity, adiposity and excessive GWG are associated with several issues in child birth and subsequent health of the child including caesarean section delivery, late antepartum death, excessive fetal growth, macrosomia and childhood obesity [4,5,6]. There is no published national data on macrosomia in Malaysia. Maternal micronutrient deficiencies such as iron, folic acid, zinc, vitamin A and vitamin D are also found to impose adverse effects on pregnancy and infant outcomes.
In May 2012, the 65th World Health Assembly endorsed the Comprehensive Implementation Plan on Maternal, Infant and Young Child Nutrition (MIYCN). This plan specified a set of six global nutrition targets, including a 30% reduction of LBW. Based on a nationwide survey done among Malaysians, 1 out of 10 livebirth babies were born LBW (NHMS 2016). This is similar to neighboring countries Thailand (9.2%) but lower than Indonesia (20.2%) [7]. While there are several factors underlying the LBW occurrence, understanding maternal diet and nutritional-related factors during pregnancy serve as an important indicator to modifiable risks. Given that Malaysia is unique with its multiracial and multicultural practice in eating, it is important to recognize how maternal nutrition influences pregnancy outcomes in this country. This will facilitate effort to address the challenge of local maternal nutritional issue for ensuring optimal pregnancy outcomes and subsequently, infant health. Hence, addressing the challenge of maternal nutritional status is a major priority in the region ensuring optimal pregnancy outcomes and subsequently, infant health.
The scoping review was conducted to better understand the areas of priority research in maternal diet and nutritional status of the mother and the child in Malaysia. For those research needs, the scoping review was done for the case of Malaysia, because of the unavailability of data on maternal nutritional status with low birth weight in the country. The present review aims to examine the best available evidence regarding dietary intake of Malaysian pregnant women, and the association of diet, anthropometry, and existing co-morbidities during pregnancy with birth outcomes. The objectives are to evaluate: 1) The adequacy of selected dietary micronutrient intake among pregnant women; 2) The association of the following maternal nutritional factors on infant’s birth weight defined in terms of macrosomia and LBW: pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI), and GWG; 3) Maternal food group intake; and 4) Selected co-morbidities during pregnancy with the infant’s birth weight, such as maternal high blood glucose and high blood pressure.
Materials and methods
The scoping review framework by Arksey and O’Malley was used as a guide to conduct the review [8]. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines (2018) was followed to report this study [9]. The protocol for this review has not been registered.
Identifying relevant studies
The data search strategy comprised of primary studies, grey literature and annual reports published from 1972 to 2021. The following databases were used: Proquest, EbscoHost, Scopus, Cochrane Library, Science Direct, Wiley Online Library, PubMed, Google Scholar, MyJournal (an online system provided by Malaysia Citation Centre of Ministry of Education), BookSC and Inter Library Loan with Medical Library Group. Search terms used were: Malaysia, maternal nutrition, diet, pregnancy, birth outcome, birth weight, macrosomia, premature, low birth weight, intrauterine growth restriction, gestational diabetes, plasma glucose, blood pressure, obesity, gestational weight gain, anemia, folic acid deficiencies and iron deficiencies. The last search was performed on 25 August 2021. The search strategy is shown in Table 1.
Inclusion criteria
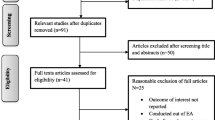
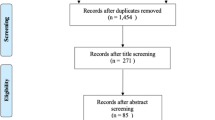
The screening process was conducted in accordance with the scoping review framework by Arksey and O’Malley and recommendations made by Levac et al. [8, 10]. Three researchers (HJ, SK and SL) independently screened the titles and retrieved the abstracts based on the inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria as mentioned in Table 2. Selected abstracts were reviewed to assess their eligibility for full text review. Subsequently, the full text articles of eligible abstracts were retrieved and assessed independently by three reviewers to determine whether they answered the specific research questions for this review and fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Studies were included in the review if consensus was achieved by all three researchers. Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram for the selection of articles in this review.
Charting and summarizing the data
Data were extracted independently by three reviewers. To map the existing literature on the review objectives, findings were grouped by adequacy of dietary intake, nutritional factors and infant birth weight, maternal anthropometry and birth weight (pre-pregnancy BMI, GWG, Mid-upper arm circumference), food group intake and birth weight as well as nutrition-related co-morbidities in pregnancy and birth weight. General and specific information about the studies which included author(s), year of publication, study design, sample characteristics, sample size, exposure and outcomes that were relevant to the objectives of the review were charted in Table 2.
Quality Appraisal
Studies were appraised by three researchers for quality [8,9,10,11]. Three researchers (HJ, SK, and SL) independently evaluated the quality of the 17 studies from a rating scale of 0 to 4 based on the following criteria: (a) Study design: studies employing cross-sectional, case–control, or cohort design = 1, otherwise = 0; (b) Sample size: large = 1, small = 0; (c) Use of validated questionnaires or standardized tools for data collection, such as measurement of dietary intake using Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) = 1, not specific or otherwise = 0; and (d) Sampling method: random sampling or reduced bias = 1, non-random or convenience sampling or presence of bias = 0 [12]. An average value of the three scores was presented as the final score because there were no significant inter-observer variations in the assessment of the quality of the included articles. The scores were grouped as follows: 1 = poor; 2 = moderate; 3–4 = high quality.
Results
Out of the 17 studies that were included in the review, 8 studies investigated infant birth weight while only 4 studies included macrosomia as the outcome variable. There were 4 studies that examined the adequacy of micronutrient intakes and 1 study investigated food group intake among pregnant women. Table 3 shows the characteristics of the studies that were included, sorted in the order of the publication date.
Adequacy of dietary intake
Table 3 shows the results of studies that examined micronutrient intakes among pregnant women. Only 5 studies were identified. Studies consistently showed that pregnant women did not meet the Recommended Nutrient Intakes (RNI) for dietary calcium [21, 22, 24], vitamin D [21, 24, 29], and iron [21, 27].
Nutritional factors and infant birth weight
The results of studies that examined the association of nutritional factors (maternal anthropometry and food group intake) with infant birth weight were included in Table 3. Fourteen studies were identified. Studies showed an association between high maternal BMI and macrosomic babies, while low maternal BMI was associated with LBW babies.
Nutritional factors and infant birth weight
The studies that examined the association of nutritional factors (maternal anthropometry and food group intake) with infant birth weight were included in Table 3. Twelve studies were identified; five of them investigated pre-pregnancy BMI and GWG, four studied gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), and one examined hypertension among pregnant women. However, there was only one study that examined MUAC and food group intake. Studies showed an association between high maternal BMI and macrosomic babies, while low maternal BMI was associated with LBW babies.
Maternal anthropometry and birth weight
Pre-pregnancy BMI
High pre-pregnancy body weight and BMI were associated with less LBW deliveries [13, 20, 30], but increased the birth of macrosomic babies [23]; while low pre-pregnancy BMI increased LBW deliveries [20].
GWG
Excessive GWG was associated with increased frequency of macrosomia [23], particularly evident in overweight and obese pregnant women [16] while insufficient GWG was associated with increased frequency of LBW babies, independent of pre-pregnancy BMI [16].
Mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC)
One study showed that low MUAC was associated with increased LBW deliveries in rural, but not in urban women [25].
Food group intake and birth weight
One study showed that higher fruit intake was associated with greater birth weight, while intakes of confectioneries and condiments were both associated with lower birth weight [17].
Nutrition-related co-morbidities in pregnancy and infant birth weight
The results of studies that examined the effects of co-morbidities (hyperglycemia and hypertension during pregnancy) on infant birth weight were shown in Table 3. Maternal hyperglycemia, defined as gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) or high plasma glucose, was associated with increased macrosomic or large-for-gestational-age deliveries in three [15, 18, 23] out of four studies. There was no association between maternal hyperglycemia and LBW [13, 15, 18]. Maternal hypertension, defined as high systolic and/ or diastolic blood pressure, was associated with increased LBW deliveries in three studies [13, 14, 20].
Quality appraisal and study findings
Out of the 17 studies, 10 (59%) scored 3, meaning high quality and 6 (35%) scored 2, meaning moderate quality, and only one study [16] scored 1 or low.
The research findings were quite consistent with the quality of the studies. A couple of studies that were rated moderate [13, 20] and one, which was rated high [26] showed significant association of pre-pregnancy weight of women with low birth weight babies. Conversely, more vegetable and fruit intakes during pregnancy were associated with higher birth weight, higher birth length and higher head circumference in a study that was moderate in rating [17].
Two studies with good quality and four studies with moderate quality showed that factors associated with increased infant’s birth weight (macrosomia) were high pre-pregnancy BMI, excess GWG and high blood glucose levels.
Maternal hyperglycemia, defined as gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) or high plasma glucose, was associated with increased macrosomic or large-for-gestational-age deliveries in three studies [15, 18, 23]. Women with diabetes, especially those on insulin were more likely to give birth to babies with macrosomia in two of the three studies rated moderate [15, 18]. In another study, rated high quality [23], high pre-pregnancy BMI (≥25 vs. < 20 kg/m2) was associated with higher odds of macrosomic babies.
Dietary iron intake was below the Malaysian recommended iron for pregnant women in a high quality study [27]. Similarly, low intake of vitamin D was identified in three-quarters of pregnant women compared with the recommended national intakes in another high quality study [29].
Discussion
This review showed that maternal micronutrient intakes were below the recommended levels, specifically vitamin D, calcium and iron, as shown by two high quality studies [27, 29]. Two moderately rated studies and one high quality study reported that factors associated with increased infant’s birth weight (macrosomia) were high pre-pregnancy BMI, excess GWG and high blood glucose levels. Increased fruit intake also increased birth size among study samples comprised mainly of normal weight infants, which is only reported in moderate quality study [18]. Meanwhile, LBW was associated with low pre-pregnancy BMI, inadequate GWG, intake of confectioneries and condiments, and high blood pressure. These findings are contributed by four moderate quality studies.
In general, the findings of this review from Malaysia are in line with studies from both Asian and Western settings that report an unfavorable nutritional-related maternal environment during pregnancy including underweight or overweight/obesity, suboptimal GWG, poor dietary intake, hyperglycemia and/or hypertension were associated with abnormal birth weight deliveries [2,3,4,5,6, 31,32,33,34,35].
These results are consistent with the emerging evidence showing the associations of pre-pregnancy BMI, GWG, pre-existing diabetes, GDM and maternal dietary factors with adverse birth outcomes including LBW, preterm birth, macrosomia, adiposity, neonatal hypoglycemia and caesarean delivery.
Dietary intake of pregnant women in terms of micronutrients
Hamid and colleagues reported earlier that among rural pregnant women, 37% displayed serum vitamin D deficiency in their third trimester, potentially resulting in low vitamin D concentrations in breast milk at birth [22]. Meanwhile, among urban pregnant women, hypocalcemia was shown in 26% women who were mostly deficient in vitamin D levels [23]. Both vitamin D and calcium complement each other and are important in maintaining bone health and reducing preeclampsia risk during pregnancy. It has been demonstrated that pregnant women consuming less than two glasses of milk per day were at higher risk of developing hypocalcemia [23]. Higher intake of dietary vitamin D has been shown to be associated with a lower odds of vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy [29]. Emphasizing greater intake of vitamin D through diet could help as Malaysian women have been studied to have low sunlight exposure resulting in higher vitamin D deficiency [36]. Hence, efforts to supplement or improve dietary sources of vitamin D are needed as vitamin D has been established to help reduce pregnancy complications [24].
Multiple reviews have consistently revealed that suboptimal intakes of vitamin D, calcium and iron, are widely prevalent among pregnant women especially in those from low- and middle-income countries [37,38,39]. More studies are warranted to explore the role of sunlight exposure and dietary vitamin D intake towards vitamin D status among pregnant women.
The majority of pregnant women in Malaysia were not able to achieve their recommended intake for iron through the diet [21, 27, 40], which is the same scenario as observed in other countries [41, 42]. This is particularly evident in Indian ethnicity, exposing Indian women to a higher risk of developing iron-deficiency anemia during pregnancy [43,44,45]. This could be due to the common practices of vegetarian diet among Indians who do not receive adequate iron-rich foods in their meals [46]. Poverty, low education, and lack of iron-rich sources in food intake are often regarded as reasons to poor dietary intake of iron among women in developing nations [41, 45, 47, 48]. Thus, education on iron-rich food intake and iron supplementation compliance should be emphasized for improved maternal iron status [49]. Previous study demonstrated the effectiveness of Health Belief Model-based educational intervention in improving the compliance to iron supplementation among pregnant women, highlighting the potential of reducing anemia through encouraging preventive healthy behaviours [27]. Currently, there is a lack of studies focusing on obesity with anemia among pregnant women although obesity is an important risk factor for anemia [50]. As such, with the rising trend of obesity in Malaysia [51], future research should focus on studying the role of obesity in anemia development among pregnant women.
Nutritional factors and their association with offspring birth weight
Anthropometry
The few studies have shown that maternal pre-pregnancy BMI and GWG are positively associated with birth weight among Malaysian women. An evidence derived from the only prospective cohort study in this review [30] showed that infants born to mothers of higher pre-pregnancy BMI were consistently heavier throughout their first year of life. This is consistent with pooled data from both developed and developing countries, reporting a 1.5-fold higher risk of LBW in underweight women compared with those of normal weight [52]. Besides, earlier studies found that those women with low GWG (< 10 kg) and high GWG (≥10 kg) were more likely to have LBW and macrosomia, respectively [14, 23]. A later study using updated Institute of Medicine (IOM) guidelines in 2009 showed that only among women with normal pre-pregnancy BMI (18.5–24.9 kg/m2), low GWG (< 11.5 kg) was associated with LBW, as well as PTB [16]. A recent study also supported the association between inadequate GWG and LBW [26]. An evidence from meta-analysis indicated that women with GWG above and below IOM guidelines had approximately 2-fold higher risk of delivering macrosomic and small-for-gestational age/PTB babies, respectively [53]. Irregular and higher GWG trajectories throughout the second and third trimesters were associated with LBW and PTB, respectively [28]. Hence, measuring the GWG trajectory may be more useful to provide information on timely weight management among pregnant women.
Food group intake
Individual nutrients or foods were examined in two studies in Malaysia, whereby more fruit and vegetable intake at late pregnancy were associated with larger birth sizes [17, 54]. Though single food item was studied instead of the whole diet, these studies were supported by another study reporting that maternal dietary pattern at late-second trimester with high intake of vegetables, fruit, white rice, and low intake of fast foods and flavored rice were associated with large birth size and lower PTB risk [31]. Similarly, as reviewed by another study, improved diet quality during pregnancy was associated with longer and heavier babies but within normal growth [55]. The protective benefits of fruits and vegetables against poor birth outcome should be further explored particularly in understanding the mechanistic biological effects.
Nutrition-related co-morbidities during pregnancy and their association with offspring birth weight
High blood glucose
Malaysian pregnant women with diabetes, including both pre-existing diabetes and GDM were associated with macrosomia [15, 18]. Promising evidence has been emerged from the multicenter study [56] and systematic review worldwide [32], showing there is a consistent graded linear association between maternal glucose levels during pregnancy and birth weight/adiposity. However, such a continuous effect of hyperglycemia on adverse birth outcomes have not been investigated across Malaysian studies. Neonatal hypoglycemia, PTB, cesarean section and induction of labor are also the risks for women with diabetes, as reported here [15, 18, 19] and other review [32]. This reflects that overall outcomes of women with diabetes remained poor though under dietary and/ or insulin management. In addition, study by Muna et al. [57] observed that there was a reduction in serum leptin levels among GDM women on a controlled diet. Generally, women with GDM had higher circulating leptin in comparison to normal pregnant women, emphasizing the importance of dietary management in controlling metabolic profile [58].
A study by Ismail and co-researchers suggests that higher BMI status in women with diabetes predisposes them to a higher insulin resistance state [19]. Additionally, higher rate of obesity (~ 50%) was observed in women with diabetes compared with healthy control [18, 19]. Overweight/ obese women with diabetes tended to have a higher insulin resistance during pregnancy than those healthy counterparts, associating it with pregnancy complications [19]. This suggests the importance of having optimal maternal weight to reduce the risk of pregnancy complications.
High blood pressure
Hypertension in pregnancy includes gestational hypertension, preeclampsia and eclampsia, were associated with LBW deliveries among Malaysian women. This is in agreement with previous reports from both developed and developing countries, showing high rate of LBW or small-for-gestational-age in women developing hypertension in pregnancy [33,34,35]. Not only imposing adverse effect on fetal growth, but hypertension in pregnancy has also been shown to influence long-term cardio-metabolic health outcomes in the offspring. This is evidenced by the consistent association shown between gestational hypertension and a higher offspring blood pressure as documented by a recent systematic review [59]. Indeed, a population-based cohort in Sweden (n = 13,893) further demonstrated that adult offspring of mothers with hypertension in pregnancy had an adverse cardio-metabolic trajectory, including higher risk of hypertension, higher BMI, higher plasma glucose at age of 40 years, compared with offspring of mothers who did not have hypertension in pregnancy [60]. These associations may be potentially mediated by the intrauterine growth restriction as indicated by LBW which warrant further investigations.
Only a limited number of research related to maternal diet and nutrition were identified over the past decades. Most of the studies in this review focused on iron-deficiency anemia and vitamin D deficiency. There is an urgent need to investigate the role of other dietary patterns and micronutrient deficiencies in determining birth outcomes among Malaysian women. Furthermore, the focus of Malaysian studies was more on certain maternal nutrition-related indicators rather than other aspects of maternal nutrition status, nutrient intake, and dietary pattern. Dietary factors influence towards maternal nutritional status remains understudied in Malaysia with most studies being cross-sectional instead of longitudinal. More attention should be focused on a wider range of micronutrient deficiencies. Importantly, more research is required, particularly prospective cohort study, case-control study, and randomized control trial of maternal nutritional intervention, to explore the maternal dietary practices and to understand the effects of maternal nutritional status on birth outcomes. This is critical in developing targeted interventions for Malaysian women of reproductive age, in order to initiate appropriate health management as early as possible to improve offspring outcomes.
Limitations
Despite the information compiled in this review involves a total of 11,870 sample population, several limitations including the study quality are subjected to bias. The scope of this review was limited to the Malaysian population. The study results must not be generalized to other populations. Secondly, because of the nature of a scoping review, multiple structured searches are required. Even though this review identified articles using 10 or more sources, there is always a possibility that some of the important articles could have been missed. The absence of current studies is a limitation. Another limitation could be the lack of training of the reviewers on quality appraisal prior to the research. We suggest such training of the reviewers should reduce the risk of bias and ensure reliability and consistency in the quality appraisal ratings. The scale that was used to assess risk of bias could be rather insensitive – there were only four items, and the type of the study design (e.g. cross-sectional, case-control and cohort studies) were all weighted equally.
Although the findings of maternal nutritional-related indicators such as pre-pregnancy BMI, GWG, glucose and dietary intake in relation to birth outcomes that were covered under this review have been supported by literature, the comparability between the included studies is constrained by a limited number of available reports, along with variations in study design, variable assessment method and period across studies. Dietary factors influence towards maternal nutritional status remains understudied in Malaysia with most studies being cross-sectional instead of longitudinal. More attention should be focused on a wider range of micronutrient deficiencies. Importantly, more research is required, particularly prospective cohort study, case-control study and randomized control trial of maternal nutritional intervention, to explore the maternal dietary practices and to understand the effects of maternal nutritional status on birth outcomes. This is critical in developing targeted interventions for Malaysian women of reproductive age, in order to initiate appropriate health management as early as possible to improve offspring outcomes.
Conclusions and recommendations
This review demonstrated that maternal nutrition status plays a significant role in birth outcomes related to infant birth weight. Reviewed studies consistently showed that increased infant birth weight (macrosomia) was associated with high pre-pregnancy BMI, excess GWG and high blood glucose levels. At the same time, a few studies also demonstrated the association of poor maternal nutritional status (such as low MUAC) with adverse pregnancy outcome of LBW.
This review reaffirms the importance of maternal nutrition on maternal and infant outcome but highlights that this area remains understudied in Malaysia. Therefore, there is a need to explore other aspects of maternal nutrition before and during pregnancy. Findings of this review could support the planning or future research and interventions for Malaysian population, both in the rural and urban setting. Meanwhile, the role of dietary factors on maternal health outcomes including maternal nutritional, metabolic, mental and overall wellbeing should be emphasized. This is critical in developing targeted interventions for Malaysian women of reproductive age, in order to initiate appropriate health management as early as possible to improve the outcomes of the offspring.
Although the neighboring countries such as Thailand and Indonesia have almost a similar prevalence of LBW as compared with Malaysia, further studies may be undertaken to compare the determinants associated with LBW in the three neighboring countries.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Cusick SE, Georgieff MK. The role of nutrition in brain development the golden opportunity of the “first 1000 days”. J Pediatr. 2016;175:16–21.
King JC. The risk of maternal nutritional depletion and poor outcomes increases in early or closely spaced pregnancies. J Nutr. 2003;133:1732–6.
Triunfo S, Lanzone A. Impact of maternal under nutrition on obstetric outcomes. J Endocrinol Investig. 2015;38:31–8.
Ruager-Martin R, Hyde MJ, Modi N. Maternal obesity and infant outcomes. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86:715–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2010.08.007.
Lawlor DA, Relton C, Sattar N, Nelson SM. Maternal adiposity—a determinant of perinatal and offspring outcomes? Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8:679–88. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2012.176.
Kaar JL, Crume T, Brinton JT, Bischoff KJ, McDuffie R, Dabelea D. Maternal obesity, gestational weight gain, and offspring adiposity: the EPOCH study. J Pediatr. 2014;165:509–15.
Chiowanich P, Mangklabruks A, Rerkasem A, Wongthanee A, Rerkasem K, Chiowanich P, et al. The risk factors of low birth weight infants in the northern part of Thailand. J Med Assoc Thail. 2012;95:358–65.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol Theory Pract. 2005;8:19–32.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:467–73. https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5:1–9.
JBI Critical Appraisal Tools. Joanna Briggs Institute, the University of Adelaide, South Australia. https://joannabriggs.org/criticalappraisal-tools. Accessed 9 Apr 2021.
Jones EA, Mitra AK, Bhuiyan AR. Impact of COVID-19 on mental health in adolescents: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:2470.
Boo NY, Lim SM, Koh KT, Lau KF, Ravindran J. Risk factors associated with low birth weight infants in the Malaysian population. Med J Malaysia. 2008;63:306–10.
Rahman LA, Hairi NN, Salleh N. Association between pregnancy induced hypertension and low birth weight; a population based case-control study. Asia-Pacific J Public Heal. 2008;20:152–8.
Tan PC, Ling LP, Omar SZ. The 50-g glucose challenge test and pregnancy outcome in a multiethnic Asian population at high risk for gestational diabetes. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2009;105:50–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2008.11.038.
Rozlan N, Majid HAMA, Abas SS, Danis A, Isa KAM. The association of gestational weight gain and the effect on pregnancy outcome defined by BMI group among women delivered in hospital Kuala Lumpur (HKL), Malaysia: a retrospective study. Asian J Clin Nutr. 2012;4:160–7.
Loy S-L, Marhazlina M, Jan Mohamed HJ. Association between maternal food group intake and birth size. Sains Malaysiana. 2013;42:1633–40.
Kampan N, Azman H, Hafiz I, Mohammad H, Chuah SY, Abdul Ghani NA, et al. Outcome of pregnancy among Malaysian women with diabetes mellitus - a single Centre experience. Malaysian J Public Heal Med. 2013;13:1–10.
Mohamed Ismail NA, Mohd Kasim M, Noor Aizuddin A, Umar NA. Homeostatic indices of insulin resistance among gestational diabetics in anticipating pregnancy complications. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2013;29:691–4.
Yadav H, Lee N. Maternal factors in predicting low birth weight babies. Med J Malaysia. 2013;68:44.
Manaf ZA, Johari N, Lee YM, Ng SY, Chua KY, Loke WT. Nutritional status and nutritional knowledge of Malay pregnant women in selected private hospitals in Klang Valley. J Sains Kesihat Malaysia (Malaysian J Heal Sci). 2014;12:53–62.
Jan Mohamed HJ, Rowan A, Fong B, Loy S-L. Maternal serum and breast milk vitamin D levels: findings from the Universiti Sains Malaysia pregnancy cohort study. PLoS One. 2014;9:e100705.
Yadav H, Lee N. Factors influencing macrosomia in pregnant women in a tertiary care hospital in Malaysia. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2014;40:439–44.
Yeop NSH, Isa ZM, Shamsuddin K, Khor GL, Mahdy ZA, Hassan H, et al. Hypocalcaemia and its contributing factors among first trimester pregnant women in an urban area in Malaysia. Nutr Food Sci. 2018;48:165–76.
Kaur S, Ng CM, Badon SE, Jalil RA, Maykanathan D, Yim HS, et al. Risk factors for low birth weight among rural and urban Malaysian women. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(Suppl 4):539.
Edi M, Chin YS, Woon FC, Appannah G, Lim PY. Inadequate gestational weight gain and exposure to second-hand smoke during pregnancy increase the risk of low birth weight: a cross-sectional study among full-term infants. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:1–12.
Hassan H, Manaf RA, Said SM, Appannah G. The effectiveness of theory-based intervention to improve haemoglobin levels among women with anaemia in pregnancy. Med J Malaysia. 2020;75:626–34.
Yong HY, Mohd Shariff Z, Appannah G, Rejali Z, Mohd Yusof BN, Bindels J, et al. Rate of gestational weight gain trajectory is associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes. Public Health Nutr. 2020;23:3304–14.
Woon FC, Chin YS, Ismail IH, Batterham M, Abdul Latiff AH, Gan WY, et al. Vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy and its associated factors among third trimester Malaysian pregnant women. PLoS One. 2019;14(6):e0216439.
Zalbahar N, Jan Mohamed HJ, Loy SL, Najman J, McIntyre HD, Mamun A. Association of parental body mass index before pregnancy on infant growth and body composition: evidence from a pregnancy cohort study in Malaysia. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2015;10:S35–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2015.08.002.
Chia A, De SJV, Colega M, Chen L, Chan Y, Aris IM, et al. A vegetable, fruit, and white rice dietary pattern during pregnancy is associated with a lower risk of preterm birth and larger birth size in a multiethnic Asian cohort: the growing up in Singapore towards healthy outcomes (GUSTO) cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;104:1416–23.
Farrar D, Simmonds M, Bryant M, Sheldon TA, Tuffnell D, Golder S, et al. Hyperglycaemia and risk of adverse perinatal outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2016;354:i4694.
Buchbinder A, Sibai BM, Caritis S, Macpherson C, Hauth J, Lindheimer MD, et al. Adverse perinatal outcomes are significantly higher in severe gestational hypertension than in mild preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;186:66–71.
Bridwell M, Handzel E, Hynes M, Jean-louis R, Fitter D, Hogue C, et al. Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy and maternal and neonatal outcomes in Haiti: the importance of surveillance and data collection. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19:208.
Berhe AK, Ilesanmi AO, Aimakhu CO, Mulugeta A. Effect of pregnancy induced hypertension on adverse perinatal outcomes in Tigray regional state, Ethiopia: a prospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20:1–11.
Shafinaz IS, Moy FM. Vitamin D level and its association with adiposity among multi-ethnic adults in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: a cross sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2016;16:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-2924-1.
Stevens GA, Finucane MM, De-Regil LM, Paciorek CJ, Flaxman SR, Branca F, et al. Global, regional, and national trends in haemoglobin concentration and prevalence of total and severe anaemia in children and pregnant and non-pregnant women for 1995-2011: a systematic analysis of population-representative data. Lancet Glob Heal. 2013;1:16–25.
Cormick G, Betrán AP, Romero IB, Lombardo CF, Gülmezoglu AM, Ciapponi A, et al. Global inequities in dietary calcium intake during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG An Int J Obstet Gynaecol. 2019;126:444–56.
Kiely ME, Wagner CL, Roth DE. Vitamin D in pregnancy: Where we are and where we should go. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020;201:105669.
Khatijah S, Rosnah S, Rahmah M. Prevalen anemia semasa mengandung dan faktor faktor pempengaruhinya di Johor Bahru. Malaysian J Public Heal Med. 2010;10:70–83.
Piammongkol S, Marks GC, Williams G, Chongsuvivatwong V. Food and nutrient consumption patterns in third trimester Thai-Muslim pregnant women in rural southern Thailand. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2004;13:236–41.
Sukrat B, Suwathanapisate P, Siritawee S, Poungthong TP, K. The prevalence of iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women in Nakhonsawan, Thailand. Med J Med Assoc Thail. 2010;93:765–70.
Haniff J, Das A, Teck Onn L, Won Sun C, Nordin NM, Rampal S, et al. Anemia in pregnancy in Malaysia: a cross-sectional survey. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007;16:527–36.
Siong TE, Kandiah M, Ali J, Kandiah V, Zahari MR, Kuladevan R, et al. Nutritional anemia in pregnancy: a study at the maternity hospital, Kuala Lumpur. Malays. J Reprod Health. 1984;2:32–50.
Singh S, Jeevan J, Geddam B, Reddy GB, Pallepogula DR, Pant HB, et al. Folate, vitamin B12, ferritin and haemoglobin levels among women of childbearing age from a rural district in South India. BMC Nutr. 2017;3:1–9.
Chai ZF, Gan WY, Chin YS, Ching YK, Appukutty M. Factors associated with anemia among female adult vegetarians in Malaysia. Nutr Res Pract. 2019;13:23–31.
Suega K, Dharmayuda TG, Sutarga IM, Bakta IM. Iron-deficiency anemia in pregnant women in Bali, Indonesia: a profile of risk factors and epidemiology. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2002;33:3–6.
Ziaei S, Mehrnia M, Faghihzadeh S. Iron status markers in nonanemic pregnant women with and without iron supplementation. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2008;100:130–2.
Nik Rosmawati N, Mohd Nazri S. The rate and risk factors for Anemia among pregnant mothers in Jerteh Terengganu, Malaysia. J Community Med Health Educ. 2012;2:10–3.
Aigner E, Feldman A, Datz C. Obesity as an emerging risk factor for iron deficiency. Nutrients. 2014;6:3587–600.
Lee YY, Muda WAMW. Dietary intakes and obesity of malaysian adults. Nutr Res Pract. 2019;13:159–68.
Han Z, Mulla S, Beyene J, Liao G, Mcdonald SD. Maternal underweight and the risk of preterm birth and low birth weight: a systematic review and meta-analyses. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40:65–101.
Goldstein RF, Abell SK, Ranasinha S, Misso M, Boyle JA, Black MH, et al. Association of gestational weight gain with maternal and infant outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Jama. 2017;317:2207–25.
Loy S-L, Marhazlina M, Nor Azwany Y, Jan Mohamed HJ. Higher intake of fruits and vegetables in pregnancy is associated with birth size. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Heal. 2011;42:1214.
Martin JC, Zhou SJ, Flynn AC, Malek L, Greco R, Moran L. The assessment of diet quality and its effects on health outcomes pre-pregnancy and during pregnancy. Semin Reprod Med. 2016;34(02):083–92.
Metzger B, Contreras M, Sacks D, Watson W, Dooley S, Foderaro M, et al. Hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1991–2002.
Muna KAK, Mokhtar A, Saad MA, Ahmed AA, Akbar JB. The effect of diet control on the leptin levels in diabetic pregnant women. Int Med J Malaysia. 2015;14:59–63.
Soheilykhah S, Mojibian M, Rahimi-saghand S. Maternal serum leptin concentration in gestational diabetes. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2011;50:149–53.
Jansen MAC, Pluymen LPM, Dalmeijer GW, Groenhof TKJ, Uiterwaal CS, Smit HA, et al. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and cardiometabolic outcomes in childhood: a systematic review. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2019;26:1718–47.
Kurbasic A, Fraser A, Mogren I, Hallmans G, Franks PW, Rich-edwards JW, et al. Maternal hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and offspring risk of hypertension: a population-based cohort and sibling study. Am J Hypertens. 2019;32:331–4.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the contribution of the late Dr. Noor Safiza Mohamad Nor from Ministry of Health who provided guidance in the early stage of this research. Also, thanks go to Ms. Noraida Hassan from Hamdan Tahir Library, Universiti Sains Malaysia for her assistance in the article search. This research is funded by the International Life Sciences Institute Southeast Asia (ILSI SEA) Region (ILSI-USAINS-H008).
Funding
H.J received a grant from the International Life Sciences Institute Southeast Asia (ILSI SEA) Region (ILSI-USAINS-H008). ILSI is funded primarily by its industry members.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.J was responsible for overall scientific supervision, wrote parts of the paper, and approved the final draft. S.K, T.A.N., L.S.L and S.H. assisted in the literature search, analyzed data, wrote parts of the paper, and approved the final draft. A.K.M and M.S.A. conceptualized the study, wrote parts of the paper and edited the final draft of the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funding agencies had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results. The views expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of their respective institutions.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, H.J.J., Loy, S.L., Mitra, A.K. et al. Maternal diet, nutritional status and infant birth weight in Malaysia: a scoping review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 22, 294 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-022-04616-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-022-04616-z