Abstract
Background
Daclizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody against CD25 that modulates interleukin 2 signaling. The SELECT TRILOGY of clinical studies (SELECT/SELECTION/SELECTED) evaluated the safety and efficacy of daclizumab in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). We report the long-term safety and efficacy of daclizumab 150 mg subcutaneous every 4 weeks in patients with RRMS in the SELECTED open-label extension study.
Methods
An interim intent-to-treat analysis of all enrolled patients was performed in January 2014 for this ongoing study.
Results
The SELECTED study enrolled 90 % of patients who completed SELECTION. In the safety and efficacy analysis (N = 410), median treatment time in SELECTED was 25 months (range, <1–45). Adverse events (AEs) were reported in 76 % of patients, serious AEs (SAEs) excluding MS relapse in 16 %, and treatment discontinuation due to AEs including multiple sclerosis (MS) relapse in 12 %. AEs were primarily of mild to moderate severity, and common AEs (≥10 %), excluding MS relapse, were nasopharyngitis (12 %) and upper respiratory tract infection (12 %). Most commonly reported SAEs (in ≥3 patients), excluding MS relapses, were increased serum hepatic enzymes, pneumonia, ulcerative colitis, and urinary tract infection (<1 % each). Incidences of AE groups of interest include cutaneous events (28 %), cutaneous SAEs (2 %), gastrointestinal SAEs (2 %), hepatic SAEs, (1 %) and malignancies (1 %). The incidence of AEs, SAEs, and treatment-related study discontinuations did not increase over time and no deaths were reported. The adjusted annualized relapse rate (95 % confidence interval (CI)) analyzed at 6-month intervals was 0.15 (0.10–0.22) for weeks 97–120 and 0.15 (0.10–0.21) for weeks 121–144. In year 3, the adjusted mean (95 % CI) number of new/newly enlarging T2 hyperintense lesions was 1.26 (0.93–1.72) and the mean (median) annualized change in brain volume was −0.32 % (−0.34 %).
Conclusions
The AE incidence did not increase with extension of therapy into year 3 in SELECTED; the safety profile was similar to that previously observed. The clinical efficacy of daclizumab was sustained over the 3 years comprising the SELECT TRILOGY, although potential selection bias cannot be excluded.
Trial registration
Clinicaltrials.gov NCT01051349; first registered January 15, 2010.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Effective disease activity control in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) is critical for improved long-term outcomes and requires long-term treatment. Hence, it also is essential to establish the long-term safety and efficacy of multiple sclerosis (MS) disease-modifying therapies (DMTs).
Interleukin 2 (IL-2) signaling has a central role in both immune system activation and regulation [1]. IL-2 receptors are expressed on a variety of immune cells, including CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, regulatory T cells, CD56bright natural killer cells, and myeloid dendritic cells [2]. IL-2 signaling supports immune system activation through CD4+ and CD8+ T cell cytokine secretion, T effector cell expansion, and CD8+ T cell and CD56bright natural killer cell cytotoxicity, while also supporting immune system regulation by promoting regulatory T cell expansion and survival [2].
Daclizumab high-yield process (daclizumab)Footnote 1 is a humanized monoclonal antibody that modulates IL-2 signaling by binding to the IL-2 receptor alpha chain (CD25), thereby inhibiting assembly of the high-affinity IL-2 receptor (CD25/CD122/CD132) and shifting IL-2 signaling to cells that express the intermediate-affinity IL-2 receptor (CD122/CD132) [2]. This transient shift antagonizes proinflammatory activated T cells and leads to the expansion of immunoregulatory CD56bright natural killer cells [2]. Daclizumab is hypothesized to inhibit disease activity and slow disease progression by enhancing endogenous mechanisms of immune tolerance through expansion of immunoregulatory CD56bright natural killer cells and reducing early T cell activation [2].
The SELECT TRILOGY (SELECT [3], SELECTION [4], SELECTED) of clinical studies was designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of daclizumab in patients with RRMS. SELECT was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, phase 2 study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of daclizumab 150 and 300 mg subcutaneous (SC) every 4 weeks for 1 year versus placebo [3]. In SELECTION, a 1-year double-blind extension of SELECT, placebo-treated patients were randomized to daclizumab 150 or 300 mg SC, and daclizumab-treated patients either continued their previous dosage of daclizumab or underwent a 24-week washout period followed by re-initiation of daclizumab at their previous dose [4]. SELECTED is an ongoing, open-label, extension study of SELECTION that is being conducted to assess the long-term safety and efficacy of daclizumab monotherapy (150 mg SC every 4 weeks).
In SELECT, daclizumab 150 mg reduced adjusted annualized relapse rate (ARR), disability progression, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) lesion activity compared with placebo [3]. Infections, cutaneous adverse events (AEs), and hepatic enzyme elevations were more common with daclizumab compared with placebo in SELECT [3]. In SELECTION, the incidence of AEs was similar to that observed in SELECT and efficacy was maintained in the second year among patients receiving continuous daclizumab treatment [4]. This paper reports interim safety and efficacy data for an international cohort of patients with RRMS treated with 150 mg daclizumab in SELECTED.
Methods
Study design
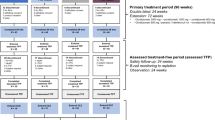
SELECTED is an ongoing, single-arm, open-label extension study to evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of daclizumab 150 mg SC every 4 weeks for up to 6.5 years from enrollment in patients with RRMS who completed SELECT and SELECTION (Fig. 1). The study is being conducted at 66 investigational sites in eight countries: the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, India, Poland, Russia, Ukraine, and the United Kingdom. The first patient was enrolled and treated on 31 March 2010; enrollment is now completed and the study is ongoing. The primary objective of SELECTED is to assess the safety of extended treatment with daclizumab monotherapy in patients with RRMS; efficacy is being assessed as a secondary objective.
Patient eligibility was determined at week 52 of SELECTION, and this visit also served as the baseline visit of SELECTED. At enrollment in SELECTED, patients had previously received 1–2 years of treatment with daclizumab 150 or 300 mg SC (with or without a washout with total duration of 24 weeks comprised of the last 4 weeks of SELECT and the 20 weeks of SELECTION). All eligible patients received daclizumab 150 mg SC every 4 weeks, and had clinic visits scheduled every 4 weeks for the first 12 weeks in the study, followed by clinic visits scheduled every 12 weeks for up to 6 years of continuous treatment.
Patients
To be included in the study, patients must have completed 52 weeks of both SELECT and SELECTION, been compliant with the SELECTION protocol, provided informed consent for SELECTED, and met other general eligibility criteria. Women of childbearing potential must have agreed to practice effective contraception during the study and for 4 months after their last dose of study treatment. Key exclusion criteria included: a significant change in medical status from a previous study that precluded administration of daclizumab, permanent discontinuation of study treatment in SELECTION due to an AE, enrollment in any other investigational drug study, or ongoing treatment with any approved or experimental DMT for MS. Eligibility criteria for SELECT and SELECTION have been reported previously [3, 4].
Safety assessment
Safety and tolerability assessments included AE monitoring, physical and neurological exams, vital signs, electrocardiograms, and clinical lab evaluations (hematology, blood chemistry, liver function panel, and urinalysis). For each AE, investigators rated its severity based on guidance in the protocol and determined whether it also met the regulatory criteria for a serious AE (SAE). Patients who experienced a clinically significant cutaneous AE (defined as rash, dermatitis, eczema, acne, or folliculitis) were referred to a dermatologist. Liver function testing (including alanine transaminase [ALT], aspartate transaminase [AST], and total bilirubin) was performed monthly.
Efficacy assessment
Relapses were defined as new or recurrent neurological symptoms, not associated with fever or infection, lasting at least 24 h, and accompanied by new objective neurological findings upon examination by the neurologist. New or recurrent neurological symptoms that evolved gradually over months were considered disability progression, not an acute relapse. New or recurrent neurological symptoms that occurred less than 30 days following the onset of a protocol-defined relapse were considered part of the same relapse. Brain MRI scans were performed annually and read for efficacy outcomes at a central reading institution (Medical Image Analysis Center, Basel, Switzerland).
Statistical analysis
For both safety and efficacy parameters, changes from baseline were evaluated based on the first dose of daclizumab in either SELECT (patients randomized to daclizumab in SELECT) or SELECTION (patients randomized to placebo in SELECT and daclizumab in SELECTION; Fig. 1).
Safety
The safety analysis was performed on all patients who received at least one dose of daclizumab in SELECTED. All treatment-emergent AEs during SELECTED were included in the evaluation of safety. Treatment-emergent AEs included any event that either occurred or worsened in severity after the first dose of study treatment in SELECTED up to 180 days after the last dose of daclizumab. AEs were coded using the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) Version 16.1. Hepatic events were identified with the Standardized MedDRA Query (SMQ) “drug related hepatic disorders.”
Efficacy
The intent-to-treat efficacy analysis was performed on SELECTED patients starting from the first dose of daclizumab treatment in patients randomized to daclizumab in SELECT or first dose in SELECTION for patients randomized to placebo in SELECT and daclizumab in SELECTION. The ARR was calculated by tabulating the total number of relapses experienced divided by the total number of patient-years. The adjusted ARR was estimated from a Poisson regression adjusted for the number of relapses in the year before study entry. Relapse rates were also estimated by time interval from the first dose of daclizumab received (0–24, 25–48, 49–72, 73–96, 97–120, 121–144 weeks). The adjusted mean number of T2 hyperintense lesions during years 1, 2, and 3 of daclizumab treatment was estimated from a negative binomial regression adjusted for baseline number of T2 hyperintense lesions. The annualized percentage brain volume change (PBVC) was determined with Structural Image Evaluation using Normalization of Atrophy (SIENA) and was calculated as percentage change divided by the number of days since the last scan, multiplied by 365.25.
This report adheres to CONSORT guidelines.
Results
Patients
Of all patients who completed SELECTION, 410 (90 %) enrolled and were dosed with daclizumab in SELECTED (Fig. 2). The safety and efficacy populations for this interim analysis were the same, comprising all patients who were dosed in SELECTED. SELECTED baseline patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. At the time of this interim analysis, study enrollment was complete, and all 410 enrolled patients had received at least one dose of daclizumab in SELECTED. The median time on daclizumab treatment in SELECTED was 25 (range, <1–45) months (854 patient-years). Across the SELECT TRILOGY, patients in SELECTED had received a median of 48 (range, 13–74) doses of daclizumab. At the time of the interim analysis, 296 (72 %) patients had received more than 40 total doses and 168 (41 %) had received more than 50 total doses. During the study period covered by the interim analysis, 104 (25 %) patients discontinued treatment and 92 (22 %) patients withdrew from the study (Fig. 2).
Safety overview and incidence of AEs and SAEs
AEs were summarized by three time periods and overall. The yearly incidence of AEs, SAEs, and AEs leading to discontinuation did not increase over time and no deaths were reported (Table 2). Forty-eight (12 %) patients discontinued treatment due to AEs (Table 3). Common AEs that occurred in 10 % of patients or more were MS relapse (22 %), nasopharyngitis (12 %), and upper respiratory tract infection (12 %; Table 4). The most frequently reported SAEs excluding MS relapse, were hepatic enzyme elevations, pneumonia, ulcerative colitis, and urinary tract infection (each in three patients [each less than 1 %]; Table 5).
Infections
Infections were reported in 50 % of patients, with serious infections reported in 3 %. The incidence of infections did not increase over time, reported in 34 % of patients during weeks 1–48, 30 % during weeks 49–96, and 24 % during weeks 97 and above. The majority of infections were mild or moderate in severity. Less than 1 % of patients discontinued treatment due to infections. The common AEs of infections (occurring in 10 % or more of patients) were nasopharyngitis and upper respiratory tract infections. Serious infections occurring in two or more patients were pneumonia, urinary tract infection, and bronchitis (Table 6). There were two reports of potential opportunistic infections; one non-serious case of vulvovaginal candidiasis, which was treated with clotrimazole cream and resolved in 1 week, and one case of pulmonary tuberculosis, which occurred after receiving daclizumab for 2.5 years (33 total doses) in a Ukrainian patient where tuberculosis is endemic [5]; treatment was discontinued for this patient and the patient withdrew from the study. Daclizumab was temporarily interrupted in two patients due to serious infections; diverticulitis and bacterial pneumonia (one patient each), the latter was treated with clavulanate/amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and levofloxacin. In both cases, the events resolved and study treatment was resumed.
Cutaneous AEs
Cutaneous events were reported in 28 % of patients, with serious cutaneous AEs in 2 %. The only cutaneous SAE reported in more than one patient was urticaria (in two patients; Table 6). One serious cutaneous AE was reported as Stevens-Johnson syndrome by the treating neurologist, but the diagnosis was not supported by the case details per the central independent dermatologist and the local site dermatologist assessments. The case did not meet the standard diagnostic criteria for Stevens-Johnson syndrome, as it was moderate in intensity, localized, lacked any bullous or necrotic skin lesions, and had no areas of loss, including full-thickness of the epidermis.
The most common cutaneous AEs were rash (7 %), allergic dermatitis (5 %), and eczema (3 %); the yearly incidence did not increase over time. The majority of patients experienced cutaneous AEs that were mild or moderate in severity; four (less than 1 %) patients experienced severe cutaneous AEs. Cutaneous events led to discontinuation of study treatment in 3 % of patients.
Hepatic AEs
Adverse events of drug-related hepatic disorders, per SMQ, were reported in 15 % of the patients with SAEs reported in 1 % (Table 6). Overall, the incidence of ALT or AST elevations ≥3 × upper limit of normal (ULN) was 9 % and ALT or AST elevations >5 × ULN was 4 %. Two patients had liver transaminases elevations >3 × ULN with concurrent elevation of bilirubin values >2 × ULN. One of these patients experienced toxic liver disease considered to be secondary to treatment with valproate approximately 2.5 months after discontinuing study treatment. The second patient experienced jaundice with elevated liver function tests approximately 8 weeks after study treatment discontinuation following treatment of a skin event with herbal supplements and the use of influenza medication containing paracetamol.
Gastrointestinal AEs
Gastrointestinal AEs, defined as AEs in the MedDRA System Organ Class of Gastrointestinal Disorders, were reported in 16 % of patients, with the majority of patients experiencing events that were mild or moderate in severity. The incidence of serious gastrointestinal AEs was 2 %. The incidence of gastrointestinal events that led to discontinuation of study treatment was less than 1 %. Six (1 %) patients reported serious inflammatory gastrointestinal events, including three cases of ulcerative colitis and one case each of colitis, Crohn’s disease, and hemorrhagic enterocolitis. Treatment included discontinuation of study treatment and standard therapies for colitis, including mesalazine, sulfasalazine, corticosteroids, and azathioprine. The majority of AEs resolved or were stable with no flares following discontinuation of study treatment and/or treatment with standard therapies for colitis.
Malignancies
Based on the search using the SMQ of “malignant or unspecified tumors” and medical review, there were four (1 %) patients reported with events classified as malignant neoplasms, one each of: (a) breast cancer, diagnosed following treatment with placebo for 1 year and daclizumab 150 mg SC for 3 years and 2 months; (b) basal cell carcinoma, diagnosed following treatments with placebo for 1 year, daclizumab 300 mg SC for 1 year, and daclizumab 150 mg SC for 2 years and 9 months; (c) anal cancer, diagnosed following treatment with daclizumab 300 mg SC for 1 year, washout and re-initiation of daclizumab 300 mg SC for 1 year, and daclizumab 150 mg SC for approximately 5 months; and (d) pulmonary carcinoid tumor, diagnosed after treatment with placebo for 1 year, daclizumab 300 mg SC for 1 year, and daclizumab 150 mg SC for approximately 2 years. Of these cases of malignancy, anal cancer and pulmonary carcinoma were considered related to study treatment by the investigators. Overall, there was no observed pattern to the type of malignancies.
Efficacy
The adjusted ARR analyzed at 6-month intervals from the first dose of daclizumab was 0.21 (95 % confidence interval (CI), 0.16–0.29) for weeks 0–24 and decreased to 0.15 (95 % CI, 0.10–0.21) by the weeks 121–144 interval (Fig. 3). The adjusted mean (95 % CI) number of new/newly enlarging T2 hyperintense lesions was 1.95 (1.60–2.37) in year 1 and decreased to 1.26 (0.93–1.72) by year 3 of treatment with daclizumab (Fig. 4). The mean (median) annualized PBVC was −0.77 % (−0.63 %) in year 1 and decreased to −0.32 % (−0.34 %) by year 3 of treatment with daclizumab (Fig. 5).
Adjusted annualized relapse rate (ARR) by 6-month intervals. Results from the SELECT placebo group have been published previously [3]. Adjusted ARR in SELECTED was estimated from a Poisson regression adjusted for the number of relapses in the year before study entry. Rates were estimated by time interval from the first dose of daclizumab received. *Gold et al. [3]
Adjusted mean number of new/newly enlarging T2 hyperintense lesions. Results from the SELECT placebo group have been published previously [3]. The adjusted mean number of T2 hyperintense lesions was estimated from a negative binomial regression adjusted for baseline number of T2 hyperintense lesions. *Gold et al. [3]
Mean (median) annualized percentage brain volume change (PBVC). Results from the SELECT placebo group have been published previously [3]. The annualized PBVC was determined with Structural Image Evaluation using Normalization of Atrophy (SIENA) and was calculated as percentage change divided by the number of days since the last scan multiplied by 365.25. For PBVC endpoints, patients with any post-baseline magnetic resonance imaging assessment in the efficacy population were included in the analysis. *Gold et al. [3]
Discussion
These interim findings from the SELECTED extension study indicate that although AEs continued to occur during the 3rd year of patient treatment, there was no significant increase in the incidence of AEs and the safety profile remained consistent over time during extended treatment with daclizumab 150 mg SC in SELECTED, and that efficacy benefits were maintained for up to 3 years of treatment. The overall safety profile of daclizumab 150 mg SC in SELECTED was consistent with that observed in the previous studies, SELECT and SELECTION [3, 4] and in the 2- to 3-year, active-control phase 3 study of daclizumab 150 mg compared with interferon beta-1a [6]. In SELECT, infections, cutaneous AEs, and hepatic enzyme elevations were more common in daclizumab-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients [3], and the incidence of AEs did not increase in the second year of treatment with daclizumab while in SELECTION [4]. Similarly, 28 % in the safety population in this analysis reported cutaneous events compared with 13 % of patients in the placebo group in SELECT over a 52-week treatment period [3].
The yearly incidences of serious infections, cutaneous events, and liver enzyme abnormalities in this interim analysis of up to 3 additional years of daclizumab 150 mg SC treatment in SELECTED were similar to those observed in the first and second years of treatment in previous studies [3, 4], suggesting there was no apparent negative cumulative impact of long-term daclizumab treatment, especially with respect to hepatic function. Based on available data, there does not appear to be an increased rate of malignancy with extended daclizumab treatment; however, there is no comparator arm in this long-term follow-up. AEs associated with daclizumab treatment were generally self-limited or responsive to standard medical care. MS relapses categorized as SAEs were reported in 8 %, 6 % and 5 % of patients in Years 1, 2, and 3 of this study, respectively, compared with 21 % of patients treated with placebo during the treatment period of the SELECT study (unpublished observations, Biogen). One of the criteria used to define a SAE was any event requiring hospitalization or prolongation of hospitalization, and, thus, any such event was classified as an SAE. Adjusted ARR, the number of new/newly enlarging T2 hyperintense lesions, and the rate of brain volume loss remained low in year 3 of daclizumab 150 mg SC treatment, showing that the efficacy of daclizumab 150 mg SC is maintained for up to 3 years of treatment. Across the outcome measures evaluated, clinical and MRI MS disease activity in the third year of treatment with daclizumab 150 mg SC was consistently lower than that observed in the placebo group in year 1 in SELECT [3].
Limitations generally associated with long-term extension studies should be taken into consideration when interpreting the interim results of this study. Most importantly, SELECTED was an open-label study without a control group, similar to other open-label long-term extension studies [7, 8]. Secondly, despite the fact that there was a high re-enrollment rate from study to study in the SELECT TRILOGY [4] and a low rate of discontinuation due to AEs, patients non-responsive to treatment or those who are doing less well on treatment may have chosen not to continue to SELECTED, resulting in possible selection bias, favoring the retention of patients who either respond to or better tolerate daclizumab [4]. While this interim analysis may be affected by selection bias, any potential selection bias may be partially offset once the 6-year treatment period and 6-month postdosing safety follow-up for SELECTED are complete.
Previous patient exposure to the study drug was variable, ranging from 1–2 years treatment prior to SELECTED, either at the 300 mg or 150 mg dose, with or without a 24-week washout period at the beginning of year 2. This heterogeneity limits the strength of the efficacy conclusions; however, the results were consistent with analyses performed on the subset of SELECTED patients continuously treated with daclizumab 150 mg [9]. This variability may be more reflective of clinical practice rather than a typical clinical trial. Although conclusions regarding efficacy are limited by the lack of a control group, the effects of daclizumab on clinical and radiologic disease activity observed in year 1 were maintained for up to 3 years of treatment.
Conclusions
The evaluation of long-term safety and efficacy of DMTs is important given the chronic nature of MS and the need for long-term treatment. Overall, the SELECTED findings provide evidence that risks associated with daclizumab were consistent with previous clinical trial experience with extended treatment, and reductions in MS disease activity on clinical and MRI outcomes were preserved over 3 years of treatment with daclizumab 150 mg SC. These findings suggest that daclizumab 150 mg SC may have a favorable benefit-risk profile for extended treatment in patients with RRMS. The SELECTED study is ongoing and the SELECT TRILOGY of clinical studies will provide data on up to 8 years of treatment, to inform the long-term safety and efficacy profile of daclizumab 150 mg SC monotherapy in patients with RRMS.
Abbreviations
AE, adverse event; ALT, alanine transaminase; ARR, annualized relapse rate; AST, aspartate transaminase; CI, confidence interval; DMT, disease-modifying therapy; EDSS, Expanded Disability Status Scale; Gd+, gadolinium-enhancing; IL-2, interleukin 2; MedDRA, Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MS, multiple sclerosis; PBVC, percentage brain volume change; RRMS, relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis; SAE, serious adverse event; SC, subcutaneous; SD, standard deviation; SIENA, Structural Image Evaluation using Normalization of Atrophy; SMQ, Standardized Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities Query; SOC, System Organ Class; ULN, upper limit of normal
Notes
Daclizumab HYP, approved as Zinbryta™, has a different form and structure from an earlier form of daclizumab (Zenapax).
References
Waldmann TA. The IL-2/IL-2 receptor system: a target for rational immune intervention. Immunol Today. 1993;14:264–70.
Wiendl H, Gross CC. Modulation of IL-2Rα with daclizumab for treatment of multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013;9:394–404.
Gold R, Giovannoni G, Selmaj K, Havrdova E, Montalban X, Radue EW, et al. Daclizumab high-yield process in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (SELECT): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2013;381:2167–75.
Giovannoni G, Gold R, Selmaj K, Havrdova E, Montalban X, Radue EW, et al. Daclizumab high-yield process in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (SELECTION): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind extension trial. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:472–81.
World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2013 [Ukraine country profile]. http://www.who.int/tb/country/data/profiles/en/. Accessed 12 October 2015.
Kappos L, Wiendl H, Selmaj K, Arnold DL, Havrdova E, Boyko A, et al. Daclizumab HYP versus interferon beta-1a in relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1418–28.
Herndon RM, Rudick RA, Munschauer FE III, Mass MK, Salazar AM, Coats ME, et al. Eight-year immunogenicity and safety of interferon beta-1a-Avonex® [superscript] treatment in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2005;11:409–19.
Goodman AD, Bethoux F, Brown TR, Schapiro RT, Cohen R, Marinucci LN, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of dalfampridine for walking impairment in patients with multiple sclerosis: results of open-label extensions of two Phase 3 clinical trials. Mult Scler. 2015;21:1322–31.
Radue E-W, Giovannoni G, Gold R, Selmaj K, Havrdova E, Stefoski D, et al. Long-term efficacy of daclizumab HYP in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: 3 year results from the SELECTED extension study. Neurology. 2015;84:P7.226.
Acknowledgments
Biogen and AbbVie Biotherapeutics Inc. provided funding for medical writing support in the development of this manuscript. Karen Spach from Excel Scientific Solutions wrote the first draft of the manuscript based on input from authors, and Elizabeth Cassell from Excel Scientific Solutions copyedited and styled the manuscript per journal requirements. Biogen and AbbVie Biotherapeutics Inc. reviewed and provided feedback on the paper to the authors. The authors had full editorial control of the paper, and provided their final approval of all content.
Initial analyses of these data were presented at the 67th American Academy of Neurology (AAN) Annual Meeting, 18–25 April 2015, Washington, DC, USA, and the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC) 2015 Annual Meeting, 27–30 May 2015, Indianapolis, IN, USA.
Funding
This study was supported by Biogen and AbbVie Biotherapeutics Inc.
Availability of data and materials
Data available upon request and detailed at this website (http://clinicalresearch.biogen.com/). The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article will be available August 2017 on www.clinicaltrials.gov and http://clinicalresearch.biogen.com/.
Authors’ contributions
All authors (RG, E-WR, GG, KS, EH, DS, TS, XM, SC, KU, SJG, GO, JE) participated in the direction of analyses and interpretation of data, were members of the writing group and agreed on the content of the report, reviewed drafts, and approved the final version. The data were collected by the study investigators. E-WR directed the central magnetic resonance imaging reading. KU directed the statistical analyses. All (RG, E-WR, GG, KS, EH, DS, TS, XM, SC, KU, SJG, GO, JE) authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
RG: consulting fees from Bayer HealthCare, Biogen, Merck Serono, Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis, and Teva; editor of Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders; research support from Biogen, Genzyme, Merck Serono, Novartis, and Teva; E-WR: speaker fees from Actelion, Basilea, Bayer HealthCare, Biogen, Merck Serono, and Novartis; research support from Actelion, Bayer HealthCare, Biogen, Merck Serono, and Novartis; GG: consulting fees from and advisory boards for AbbVie Biotherapeutics Inc., Biogen, Canbex, Ironwood, Merck, Merck Serono, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, Synthon, Teva, and Vertex; honoraria from AbbVie Biotherapeutics Inc., Biogen, Bayer HealthCare, Merck Serono, Sanofi-Aventis, and Teva; co-editor in chief of Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders; research support from Biogen, Genzyme, Ironwood, Merck Serono, and Novartis; KS: consulting fees from Genzyme, Novartis, Ono, Roche, Synthon, and Teva; speaker fees from Biogen; EH: consulting fees/honoraria from and advisory boards for Bayer HealthCare, Biogen, Novartis, Merck Serono, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Teva; research support from Biogen and the Czech Ministries of Education (PRVOUK-P26/LF1/4); DS: consulting fees from Acorda, Biogen, Serono, and Teva Neuroscience; speaker fees from Acorda, Biogen, Elan, EMD Serono, and Teva Neuroscience; royalty payments of licensed drug from Acorda; research support from Biogen, Novartis, Pfizer, and Serono; TS: the University Hospital Basel (previous employer) and/or current (DKD Helios Klinik Wiesbaden) employer of TS received speaker fees/advisory board funds from Actelion, ATI, Biogen, ElectroCore, Genzyme, Novartis, Mitsubishi Pharma Europe, and TEVA; research grants from EFIC-Grünenthal, Novartis Switzerland, the Swiss Multiple Sclerosis Society, and the Swiss National Science Foundation; XM: speaker fees/travel expense reimbursement from and steering committee/advisory boards for Actelion, Almirall, Bayer HealthCare, Biogen, Genzyme, Merck, Neurotec, Novartis, Octapharma, Receptos, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Teva, and Trophos; SC: advisory boards for Biogen, Genzyme, Mallinckrodt, and Novartis; speaker bureaus for Acorda, Biogen, Genzyme, and Novartis; research support from Biogen, Genzyme, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Opexa, and Roche; SJG: employee of and holds stock/stock options in AbbVie Biotherapeutics Inc.; GO, former employee and holds stock/stock options of Biogen. KU and JE: employees of and holds stock/stock options in Biogen; KU: family member holds stock in Sinovac Biotech.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Institutional review board/ethics committee approval was obtained at each center; all patients provided written informed consent to participate in SELECTED. A full listing of the Ethics Committees who approved the study are provided in Additional file 1: Table S1. The study was performed in accordance with the International Conference on Harmonisation Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice, the European Union Clinical Trial Directive 2001/20/EC, and the ethical principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent to participate was obtained in SELECT and SELECTED [3, 4].
SELECTED Investigators
Czech Republic : Michal Dufek, Pavel Stourac, Radomir Talab, Marta Vachova, Denisa Zimova; Germany : Ralf Linker, Patrick Oschmann, Björn Tackenberg, Uwe Zettl; Hungary : Dániel Bereczki, Béla Clemens, Attila Csányi, Tunde Csepany, Péter Diószeghy, András Folyovich, Péter Harcos, Zita Jobbágy, Etelka Jófejű, Gabriella Kovács, Krisztina Kovács, Zsuzsanna Lohner, Mária Sátori, Attila Valikovics; India : Raja Ram Agrawal, Pahari Ghosh, Thomas Mathew, AK Meena, Sangeeta Ravat; Poland : Anna Członkowska, Wieslaw Drozdowski, Waldemar Fryze, Anna Kamińska, Gabriela Kłodowska-Duda, Jan Kochanowicz, Krzysztof Selmaj, Zbigniew Stelmasiak, Andrzej Szczudlik, Janusz Zbrojkiewicz; Russia : Alexey Boiko, Farit Khabirov, Rim Magzhanov, Nadezhda Malkova, Natalia Nikolaevna Maslova, Zahira Mizieva, Irina Poverennova, Semen Prokopenko, Alexey Rozhdestvensky, Irina Sokolova, Nikolay Spirin, Olga Vorobeva, Leonid Zaslavsky; Ukraine : Nataliya Buchakchyys'ka, Tetyana Kobys, Olexander Kozyolkin, Nataliya Lytvynenko, Olena Moroz, Borys Palamar, Valeriy Pashkovskyy, Olena Statinova, Larysa Sokolova, Nataliya Voloshina; United Kingdom : Cris Constantinescu, Clive Hawkins, Jeremy Hobart, Basil Sharrack, Eli Silber.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Additional file 1: Table S1.
List of IECs and/or IRBs for SELECTED. (DOCX 20 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Gold, R., Radue, EW., Giovannoni, G. et al. Safety and efficacy of daclizumab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: 3-year results from the SELECTED open-label extension study. BMC Neurol 16, 117 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-016-0635-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-016-0635-y