Erratum
In the original version of this article [1], published on 6 July 2017, the incorrect nomenclature “c.5077_5078insCCAG p.Gly1693Alafs*8” was used for the truncating mutation caused by the four-base pair change. The correct nomenclature for this mutation should be “c.5073_5076dup p. Gly1693Profs*8”, according to the sequence variant nomenclature of Human Genome Variant Society (HGVS: http://varnomen.hgvs.org/) as well as the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD: www.hgmd.org).
The correction of the nomenclature doesn’t impact the conclusion of the article. The extra 4 four-base-pair Indel, even in either original (mistakenly interpreted as the “CCAG” is inserted between the first [G] and second base [G] of Gly codon 1693 [G∨GT]: ∨ indicates the place where the mutation arises) or corrected nomenclature (“CCAG” is duplicated just one base-pair upstream to the first base [G] of Gly codon 1693 [∨GGT]), gives rise to the biologically same, frame-shift, truncated, “Null” LAMB2 protein.
The original version of this article [1] also contains a typographical error in the "Genetic analysis" and an additional error in the caption of "Fig. 2", where the words "paternal" and "maternally" are mixed up.
In this Erratum the original nomenclature has been listed (bold) and the corrected nomenclature has also been listed (bold). The same has been done for the typographical error and the additional error.
The typographical error has been corrected in the original publication. The nomenclature and the additional correction were not corrected in the original article.
Original publication
-
1.
In the “Abstract”:
Whole-exome sequencing revealed that the affected child was compound heterozygous for novel truncating LAMB2 mutations: a 4-bp insertion (p.Gly1693Alafs*8) and a splicing donor-site substitution (c.1225 + 1G > A), presumably deleting the coiled-coil domains that form the laminin 5–2-1 heterotrimer complex.
-
2.
In the “Genetic analysis”:
Sequencing analysis demonstrated that the affected child was a compound heterozygote for LAMB2 mutations: a 4-bp insertion (c.5077_5078insCCAG, exon 30) and a G to A substitution of the 1++1 splice donor site (c.1225 + 1 G > A, exon 9) (Figs. 2 and 3, Additional file 1). Both mutations are novel. The former is paternally transmitted, whereas the latter is maternal. The c.5077_5078insCCAG insertion causes a frame shift, thereby truncating C-terminal 99 amino acids (p.Gly1693Alafs*8).
-
3.
In “Fig. 2” and the caption:

Figure 2 Mutational analysis of LAMB2. The patient was compound heterozygous for two mutations. One is paternal allele of splice-donor site mutation (c.1225 + 1G > A). Another is maternally transmitted, four base-pair insertion leading to early termination (c.5077_5078insCCAG;p.Gly1693Alafs*8). F: father; M: mother; Pt: patient; WT: wild-type. The nucleotide numbering is according to the reference sequence GenBank accession NM_002292.3 with the first nucleotide of the ATG start codon on position +1.
-
4.
In “Fig. 3”:
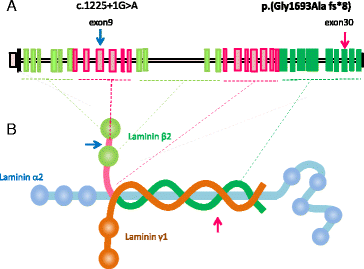
Correct nomenclature/text
-
1.
In the “Abstract”:
Whole-exome sequencing revealed that the affected child was compound heterozygous for novel truncating LAMB2 mutations: a 4-bp duplication (Gly1693Profs*8) and a splicing donor-site substitution (c.1225 + 1G > A), presumably deleting the coiled-coil domains that form the laminin 5–2-1 heterotrimer complex.
-
2.
In the “Genetic analysis”:
Sequencing analysis demonstrated that the affected child was a compound heterozygote for LAMB2 mutations: a 4-bp duplication (c.5073_5076dup p.Gly1693Profs*8, exon 30) and a G to A substitution of the +1 splice donor site (c.1225 + 1 G > A, exon 9) (Figs. 2 and 3, Additional file 1). Both mutations are novel. The former is paternally transmitted, whereas the latter is maternal. The 4-bp c.5073_5076 duplication causes a frame shift, thereby truncating C-terminal 99 amino acids (p.Gly1693Profs*8).
-
3.
In “Fig. 2” and the caption:
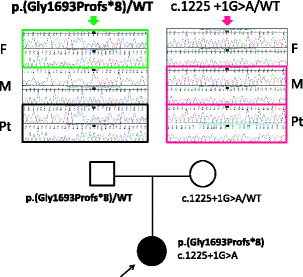
Figure 2 Mutational analysis of LAMB2. The patient was compound heterozygous for two mutations. One is maternal allele of splice-donor site mutation (c.1225 + 1G > A). Another is paternally transmitted, four base-pair insertion leading to early termination (c.5073_5076dup p.Gly1693Profs*8). F: father; M: mother; Pt: patient; WT: wild-type. The nucleotide numbering is according to the reference sequence GenBank accession NM_002292.3 with the first nucleotide of the ATG start codon on position +1.
-
4.
In “Fig. 3”:
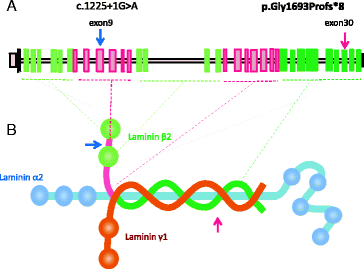
Reference
Kino J, et al. Nephron development and extrarenal features in a child with congenital nephrotic syndrome caused by null LAMB2 mutations. BMC Nephrol. 2017;18:220. doi:10.1186/s12882-017-0632-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The online version of the original article can be found under doi:10.1186/s12882-017-0632-4
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Kin, J., Tsukaguchi, H., Kimata, T. et al. Erratum to: Nephron development and extrarenal features in a child with congenital nephrotic syndrome caused by null LAMB2 mutations. BMC Nephrol 18, 271 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-017-0682-7
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-017-0682-7





