Abstract
Background
Antibiotic overuse is driving the emergence of antibiotic resistance worldwide. Good data on prescribing behaviours of healthcare providers are needed to support antimicrobial stewardship initiatives. This study examined the differences in antibiotic prescribing rates of public and private primary care clinics in Malaysia.
Methods
We used data from the National Medical Care Survey (NMCS), a nationwide cluster sample of Malaysian public and private primary care clinics in 2014. NMCS contained demographic, diagnoses and prescribing from 129 public clinics and 416 private clinics. We identified all encounters who were prescribed antibiotic and analyse the prescribing rate, types of antibiotics, and diagnoses that resulted in antibiotic.
Results
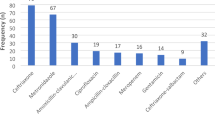
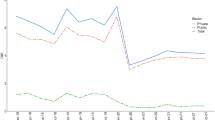
Five thousand eight hundred ten encounters were prescribed antibiotics; antibiotic prescribing rate was 21.1 % (public clinics 6.8 %, private clinics 30.8 %). Antibiotic prescribing was higher in private clinics where they contributed almost 87 % of antibiotics prescribed in primary care. Upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) was the most frequent diagnosis in patients receiving antibiotic therapy and accounted for 49.2 % of prescriptions. Of the patients diagnosed with URTI, 46.2 % received antibiotic treatment (public 16.8 %, private 57.7 %). Penicillins, cephalosporins and macrolides were the most commonly prescribed antibiotics and accounted for 30.7, 23.6 and 16.0 % of all antibiotics, respectively. More recently available broad-spectrum antibiotics such as azithromycin and quinolones were more frequently prescribed in private clinics.
Conclusions
Antibiotic prescribing rates are high in both public and private primary care settings in Malaysia, especially in the latter. This study provides evidence of excessive and inappropriate antibiotic prescribing for self-limiting conditions. These data highlights the needs for more concerted interventions targeting both prescribers and public. Improvement strategies should focus on reducing inappropriate prescribing.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Antibiotic resistance is a globally significant threat to public health [1]. A recent report from the World Health Organization (WHO) documented high rates of resistance across a range of bacteria that cause common healthcare-associated and community-acquired infections [2]. Antibiotic resistance is directly related to the rate of antibiotic use in the community [3–5]. There is, however, surprisingly little national data on non-hospital (community) antibiotic use. Furthermore, the data that are available are from studies in high-income countries [4, 5]. Descriptive national data on community antibiotic use from low- and middle-income countries, however, is essential for understanding where over-prescribing of antibiotics may be occurring and the patient and provider characteristics that are associated with higher rates of antibiotic prescription. Understanding these characteristics will help to inform regulatory and health education strategies.
Where data are available on low- and middle-income countries’ antibiotic use in the community, they are usually at a sub-national level. For example, Hadi et al., in their systematic review of non-hospital antibiotic use, identified 11 studies from ten countries [6]. Only one of those studies was related to national data, and that study lacked linked patient characteristics and provider information. The WHO reported a series of pilot studies on community antibiotic use in India and South Africa [7]. However, these studies were based on five surveillance settings and were not nationally representative and did not include community antibiotic use and patient and provider characteristics associated with antibiotic use. In Malaysia, antibiotics are commonly prescribed by primary care providers and most frequently prescribed for people with respiratory tract infections [8–10]. However, data are available only from small-scale studies of selected primary care clinics in certain areas, which may have led to inaccurate estimates of antibiotic use in primary care. In this paper, we use data from the National Medical Care Survey (NMCS) 2014 to describe the frequency and characteristics of antibiotic prescribing in Malaysian primary care by detailing the type of antibiotics and their indications. These data have then been compared with reports from other countries and recommendations made to bring about more judicious antibiotic use in the Malaysian primary care setting.
Methods
Setting
Malaysia has a dual public-private health system with 871 public primary care clinics and 5198 private primary care clinics [11, 12]. Primary care functions as a partial gatekeeper to secondary care; people can bypass a referral from public or private practitioners and go directly to specialists and hospitals. The public healthcare system is heavily subsidised by the government; outpatient primary care entails a nominal payment of 1 Malaysian Ringgit ($0.25 USD) for consultations, investigations and medications. Private clinics are usually less crowded, have longer and more flexible opening hours, and are accessible through a variety of payment models (including out-of-packet payment, private insurance and coverage by third-party payers) [12]. A morbidity survey conducted in 2008 found that patients with chronic diseases were more likely to consult public clinics while private clinics cater mostly to preventive care and acute illnesses [13]. In 2008, public clinics accounted for 38 % of outpatient visits despite accounting for only 11 % of primary care clinics in Malaysia [14]. Malaysian healthcare reform is currently underway to improve the integration of public and private healthcare and to bring about more consistent clinical services and standard of care in both sectors [15].
Data source and patient identification
The NMCS is a primary care survey conducted by the Clinical Research Centre Malaysia that collected information on clinical activities and prescriptions from primary care clinics in Malaysia. The study was conducted in 2014 and a detailed description of the NMCS methods is described elsewhere [16]. Briefly, NMCS is a national study of primary care activities whereby primary care clinics from public and private sectors in 14 states in Malaysia were sampled through stratified random sampling. The sampled clinics were required to provide records of patient encounters for a given date that was randomly assigned to each clinic. Doctors working on the survey day were asked to fill in a case report form to record information on patient demographics, reasons for encounter, diagnoses or problems managed, and interventions (medications, laboratory investigations, procedure/counselling, referral). Reasons for encounter, diagnoses and investigations were coded using the International Classification of Primary Care (ICPC-2) [17]. Medications were classified according to WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) codes [18]. Coding was performed by trained personnel and quality-control measures undertaken to ensure reliability of the data [16].
From NMCS records, we identified patients who were prescribed at least one systemic antibiotic. Systemic antibiotic were defined from the ATC code J01 (systemic antibacterials) and P01AB01 (oral metronidazole). Our primary outcome measure was antibiotic prescribing rate in public and private primary care clinics. We also determined the types of antibiotics prescribed and common diagnoses that resulted in prescription of antibiotics.
Data analysis
Data were analysed and adjusted for the cluster study design using the survey function in STATA version 13 [19, 20]. Post-stratification weights were applied to the data to account for over or underrepresentation and non-response. Results were reported as the number of observations and percentages. The chi-square test was used to compare the antibiotic prescription rates in public and private clinics.
Ethical approval
The NMCS received ethical approval from the Medical Research and Ethics Committee of the Ministry of Health Malaysia (NMRR-09-842-4718). A public notice was placed at each participating clinic to inform patients of the ongoing study and that data would be collected for research purposes only. Patients who do not want to be part of the study may opt out by informing the doctor and their data were not collected.
Results
NMCS 2014 recorded 27,587 patient encounters from 545 primary care clinics. Of these, 5810 resulted in antibiotic prescription, corresponding to an overall prescribing rate of 21.1 % (Table 1). In 197 (3.4 %) of these encounters, more than one antibiotic was prescribed. The antibiotic prescribing rate was lower in public clinics (6.8 %) compared with private clinics (30.8 %). Private clinics accounted for approximately 60 % of all patient encounters, but around 87 % of all antibiotics prescribed in primary care.
Table 2 shows the sociodemographic profiles of patients prescribed antibiotics. More female patients were given antibiotics in public clinics compared with male patients, while the reverse was true in private clinics. Antibiotics were mostly prescribed to patients aged 20–39 years. The distribution of the ten most common clinical diagnoses resulting in antibiotic prescription is presented in Table 3. Overall, acute upper respiratory tract infections (URTI) accounted for almost half of all antibiotics prescribed. Among patients with a diagnosis of URTI, 16.8 % were prescribed with antibiotics in public clinics whereas a higher prescribing rate was observed in private clinics (57.7 %). Private clinics prescribed more antibiotics for all ten diagnoses, in particular, URTI, fever (not otherwise classified), gastroenteritis and asthma.
The antibiotic groups prescribed in descending order of preference were: penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides, quinolones and tetracyclines (Table 4). Prescriptions of more recently available broad-spectrum antibiotics such as quinolones, some macrolides (e.g., azithromycin) and lincosamides were more frequent in private clinics; these drugs were not held in the drug formulary of public primary care clinics. Most of these antibiotics were in oral dosage form with only 2.0 % prescribed as parenteral. For upper respiratory tract infections (URTI) and acute tonsillitis, the drug choices were understandably not so varied. However, the prescription of narrow-spectrum penicillin (phenoxymethyl penicillin) was rare, even for acute tonsillitis (Table 5).
Discussion
In this study, data from a nationally representative sample of Malaysian primary care clinics revealed a high level of antibiotic prescribing in which at least one of five encounters resulted in prescription of an antibiotic. Antibiotic prescribing predominated in private clinics where they contributed 87 % of the total antibiotics prescribed in primary care. Notably, URTI, which is primarily viral in nature, accounted for half of all antibiotics prescribed. For most patients with respiratory tract infection, antibiotic use is unnecessary and these results suggest that antibiotics were not clinically indicated and are therefore overused in primary care clinics in Malaysia.
Excessive or suboptimal use of medicine in general, and antibiotics in particular, is a worldwide concern [21, 22]. A systematic review of medicine use in developing and transitional countries for the period 1990–2006 by the WHO reported that the overall antibiotic prescribing rate stabilised at 40–50 % while URTI-specific antibiotic prescribing rates has shown an increasing trend to 71 % in the period 2004–2006 [22, 23]. At first glance, the current Malaysian antibiotic prescribing rates (all encounters: 21.1 %, URTI encounters: 46.2 %) appear to be somewhat lower than the average rates from developing and transitional countries. However, the antibiotic prescribing rates in the review by WHO were generated using different methodologies from the present study and are therefore not entirely comparable.
The antibiotic prescribing rates in public and private clinics in our study were 6.8 and 30.8 %. A national morbidity and treatment survey of primary care clinics in 2008 revealed antibiotic prescribing rates in public and private clinics were 13.7 and 30.0 %, respectively (unpublished data, personal communication with Dr. Nordin Saleh, Ministry of Health, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia). Thus, the antibiotic prescribing rate in public primary care clinics in Malaysia may be declining, while that of private clinics has remained relatively stable but at a high level. However, when compared with more developed countries, the antibiotic prescribing rates in Malaysia are still a cause for concern. For example, the URTI-specific antibiotic prescribing rate in Malaysia as seen in our study was 46.2 %, but the corresponding rates in the Netherlands and Hong Kong in 2010 were 17 and 5 %, respectively [24, 25].
Antibiotic prescribing rates in Malaysian primary care are much higher in private clinics compared with public clinics. Antibiotic over-prescribing (in private more than public clinics) has also been observed in surveys undertaken in Pakistan, India and several African countries [26–28]. In a systematic review of studies conducted in low- and middle-income countries by Basu et al., diagnostic accuracy and guideline adherence were more likely to be suboptimal in private primary care settings compared with the public sector [29]. The systematic review by Berendes et al., however, concluded that the quality of care from public and private primary care in low- and middle-income countries was generally of poor quality, although the private sector did perform better with regard to drug availability, responsiveness and client-centredness [30]. Our current survey highlights the problem of antibiotic overuse in Malaysian private primary care, both with respect to the quantity of excessive antibiotic prescribing as well as inappropriate antibiotic choice. Antibiotic prescribing in Malaysian private primary care was also noted to be excessive for several clinical conditions other than URTI, including acute bronchitis, acute gastroenteritis and asthma.
Higher antibiotic prescribing in private primary care clinics is partly owing to the higher proportion of acute self-limiting illnesses, such as viral fever and common colds. Furthermore, several reasons may explain the higher antibiotic prescribing rates in private clinics, among them that private general practitioners are more responsive to the patient’s expectation for antibiotics and the financial incentive of medication overuse, including that of antibiotics, as well as suboptimal knowledge about the aetiology of URTI and lack of awareness of the emergence of antibiotic resistance. Several local studies have documented misconceptions about the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy for URTI among the Malaysian general public and their healthcare providers, together with a lack of awareness of the harm of antibiotic resistance [9, 31–34].
Attempts to improve antibiotic prescribing practices in developing countries have been documented by several systematic reviews [35, 36]. These reviews have called for more multifaceted intervention studies over a longer time period to assess the sustainability of the interventions. A systematic review of antibiotic stewardship programmes in the outpatient setting included 50 studies, most conducted in developed countries, and showed that such programmes can improve antimicrobial prescribing without adversely affecting patient outcomes [37]. In Malaysia, antibiotic guidelines focusing on pharyngitis were introduced in 2003 [38] and were followed by national antibiotic guidelines in 2008 (updated in 2014) [39, 40]. It is possible that these clinical practice guidelines may have promoted more judicious antibiotic use among public primary care doctors. The current effort to improve antibiotic stewardship in Malaysia is still in the early stages [41, 42]. There remains a need to focus beyond the public health system to include the private healthcare setting as well. However, effective ways to bring about change in the latter remain unclear; systematic reviews have not identified any successful intervention programmes conducted in private primary care clinics [35–37]. It has been shown that more judicious antibiotic use in Malaysian primary care can occur if the right type of intervention is implemented, such as academic detailing by senior family physicians and feedback of prescribing data to primary care doctors [10, 43]. Public health education of the harm of excessive antibiotic use is currently being carried out in Malaysia and needs to be persistent [44, 45]. This is in keeping with reviews from high-income countries that suggest that a public health campaign can bring about more prudent antibiotic use [46]. Thus, by reaching out to the public at large, it is hoped that that patients will be less likely to insist on antibiotics whenever they consult primary care doctors for minor respiratory or febrile illness. In tandem with public health education, continuing medical education for practicing doctors needs to highlight the ongoing problem of antibiotic overuse and the emergency of antibiotic resistance. This has shown to be effective in Hong Kong where vocationally trained family physicians were less likely to prescribe unnecessary antibiotics [47].
Strength and limitations of study
Our study has a number of important features. The large number of patient encounters obtained from clinics sampled across the country has allowed us to study clinical practice in primary care clinics. Moreover, our study used records from NMCS that collected data on patient visits in public and private clinics, allowing for comparison between the sectors. A limitation of the study is that the findings reflect practice observed in primary care settings; it does not include consultations within hospital outpatient or emergency departments. We also did not collect data from community pharmacies; hence, the supply of antibiotics to patients from community pharmacies was not considered. In Malaysia, antibiotic is not available over the counter and under the Malaysian Poisons Act the purchase of antibiotics requires prescription from physicians. However, dispensing separation has not yet taken place in Malaysia and very few prescriptions were filled at private pharmacies [48].
Conclusions
This study has shown that antibiotics are frequently prescribed in primary care clinics and provides evidence of antibiotic prescribing for self-limiting conditions. Excessive and inappropriate antibiotic use in the Malaysian primary care setting, especially in private clinics, highlights the need for more concerted interventions targeting prescribers as well as general public. Improvement strategies should focus on reducing inappropriate prescribing. This should include simultaneous education of the public and healthcare providers via the mass media, professional societies and within the clinic setting. Improving prescribing habits in primary care is necessary to reduce the unnecessary use of antibiotics and limit subsequent antibiotic resistance.
Ethics and consent to participate
This study was reviewed and approved by the Medical Research and Ethics Committee of the Ministry of Health Malaysia. A public notice was placed at each participating clinics to inform patients of the ongoing study and patients who do not wish to participate may opt out from the study. Aggregate data was used, with no identifying personal details published.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
All the data supporting the findings are available within the manuscript, additional data available upon request.
Abbreviations
- ATC:
-
Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical
- ICPC:
-
International Classification of Primary Care
- NMCS:
-
National Medical Care Survey
- URTI:
-
upper respiratory tract infection
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
McKenna M. Antibiotic resistance: the last resort. Nature. 2013;499:394–6.
World Health Organization. Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance 2014. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014.
Costelloe C, Metcalfe C, Lovering A, Mant D, Hay AD. Effect of antibiotic prescribing in primary care on antimicrobial resistance in individual patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2010;340:c2096.
Goossens H, Ferech M, Vander Stichele R, Elseviers M. Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: a cross-national database study. Lancet. 2005;365(9459):579–87.
Albrich WC, Monnet DL, Harbarth S. Antibiotic selection pressure and resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10(3):514–7.
Hadi U, Kolopaking E, Gardjito W, Gyssens I, Van den Broek P. Antimicrobial resistance and antibiotic use in low-income and developing countries. Folia Medica Indonesiana. 2006;42(3):183–9.
World Health Organization (WHO). Community-based surveillance of antimicrobial use and resistance in resource-constrained settings. Report on five pilot projects. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2009.
Teng CL, Tong SF, Khoo EM, Lee V, Zailinawati AH, Mimi O, Chen WS, Nordin S. Antibiotics for URTI and UTI -- prescribing in Malaysian primary care settings. Aust Fam Physician. 2011;40(5):325–9.
Teng CL, Nik-Sherina H, Ng CJ, Chia YC, Atiya AS. Antibiotic prescribing for childhood febrile illness by primary care doctors in Malaysia. J Paediatr Child Health. 2006;42(10):612–7.
Mohd Fozi K, Kamaliah MN. The effect of profiling report on antibiotic prescription for upper respiratory tract infection. Malays Fam Physician. 2013;8(2):26–31.
Hwong WY, Sivasampu S, Aisyah A, Shantha Kumar C, Goh PP, Hisham AN. National healthcare establishment & workforce statistics (primary care) 2012. Kuala Lumpur: National Clinical Research Centre; 2014.
Safurah J, Kamaliah MN, Khairiyah AM, Nour Hanah O, Healy J, et al. Malaysia health system review. Health Systems in Transition, Vol. 3 No.1 2013. Manila: Asia Pacific Observatory on Health Systems and Policies; 2013.
Mimi O, Tong SF, Nordin S, Teng CL, Khoo EM, Abdul-Rahman A, Zailinati AH, Lee VKM, Chen WS, Shihabudin WM, et al. A comparison of morbidity patterns in public and private primary care clinics in Malaysia. Malays Fam Physician. 2011;6:1.
Ministry of Health. Country health plan, 10th Malaysia Plan 2011–2015. Putrajaya: Ministry of Health; 2010.
Kamaliah MN. Primary health care reform in 1CARE for 1 Malaysia. Int J Public Health Res. 2011; Special Issue: 50-56.
Sivasampu S, Yasmin Farhana AW, Ong SM, Goh PP, Noor Hisham A. National Medical Care Statistics (NMCS) 2014. Kuala Lumpur: National Clinical Research Centre; 2015. http://www.crc.gov.my/nhsi/national-medical-care-statistics-primary-care-2014/. Accessed 20 November 2015.
WONCA International Classification Committee. ICPC-2. International Classification of Primary Care. Second edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1998.
Guidelines for ATC Classification and DDD Assignment 2012. Oslo: WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. http://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_publications/guidelines/. Accessed 15 Apr 2015.
Stata. Release 13. Statistical software. College Station: StataCorp LP; 2013.
STATA Survey Data Reference. Manual. Release 13. A Stata Press Publication. College Station: StataCorp LP.; 2013.
Van Boeckel TP, Gandra S, Ashok A, Caudron Q, Grenfell BT, Levin SA, Laxminarayan R. Global antibiotic consumption 2000 to 2010: an analysis of national pharmaceutical sales data. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(8):742–50.
Holloway KA, Ivanovska V, Wagner AK, Vialle-Valentin C, Ross-Degnan D. Have we improved use of medicines in developing and transitional countries and do we know how to? Two decades of evidence. Trop Med Int Health. 2013;18(6):656–64.
Holloway K, van Dijk L. The world medicines situation 2011 - rational use of medicines. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011.
van den Broek d’Obrenan J, Verheij TJ, Numans ME, van der Velden AW. Antibiotic use in Dutch primary care: relation between diagnosis, consultation and treatment. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69(6):1701–7.
Kung K, Wong CK, Wong SY, Lam A, Chan CK, Griffiths S, Butler C. Patient presentation and physician management of upper respiratory tract infections: a retrospective review of over 5 million primary clinic consultations in Hong Kong. BMC Fam Pract. 2014;15:95.
Siddiqi S, Hamid S, Rafique G, Chaudhry SA, Ali N, Shahab S, Sauerborn R. Prescription practices of public and private health care providers in Attock District of Pakistan. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2002;17(1):23–40.
Indira K, Devi R, Pillay R, Jeyseelan L, Chandy S, Kumar R, et al. The INCLEN India Infectious DiseaseInitiative (IIDI) - USAID / INCLEN Final Report 2004. Annex 19. Antibiotic Prescribing Pattern (APP) and Related Factors in Primary and Secondary Health Care Facilities of Government and Private Settings. Final Report. Chennai: Inclen Trust; 2004.
Ofori-Asenso R, Agyeman AA. A review of injection and antibiotic use at primary health care (public and private) centers in Africa. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2015;7(3):175–80.
Basu S, Andrews J, Kishore S, Panjabi R, Stuckler D. Comparative performance of private and public healthcare systems in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2012;9(6):e1001244.
Berendes S, Heywood P, Oliver S, Garner P. Quality of private and public ambulatory health care in low and middle income countries: systematic review of comparative studies. PLoS Med. 2011;8(4):e1000433.
Hassali MA, Kamil TK, Md Yusof FA, Alrasheedy AA, Yusoff ZM, Saleem F, Al-Tamimi SK, Wong ZY, Aljadhey H, Godman B. General practitioners’ knowledge, attitude and prescribing of antibiotics for upper respiratory tract infections in Selangor, Malaysia: findings and implications. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2015;13(4):511–20.
Oh AL, Hassali MA, Al-Haddad MS, Syed Sulaiman SA, Shafie AA, Awaisu A. Public knowledge and attitudes towards antibiotic usage: a cross-sectional study among the general public in the state of Penang, Malaysia. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2011;5(5):338–47.
Chan GC, Tang SF. Parental knowledge, attitudes and antibiotic use for acute upper respiratory tract infection in children attending a primary healthcare clinic in Malaysia. Singapore Med J. 2006;47(4):266–70.
Lim VKE, Cheong YM, Abu Bakar S. Knowledge of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance patterns among Malaysian doctors. J Infect Dis Antimicrob Agents. 1995;12(3):123–8.
Ivanovska V, Holloway K. Interventions to improve antibiotic prescribing in upper middle income countries: a systematic review of the literature 1990–2009. Macedonian J Med Sci. 2013;6(1):84–91.
Bbosa G, Wong G, Kyegombe D, Ogwal-Okeng J. Effects of intervention measures on irrational antibiotics/antibacterial drug use in developing countries: a systematic review. Health. 2014;6(2):171–87.
Drekonja DM, Filice GA, Greer N, Olson A, MacDonald R, Rutks I, Wilt TJ. Antimicrobial stewardship in outpatient settings: a systematic review. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2015;36(2):142–52.
Tan K. Clinical practice guidelines on management of sore throat. Kuala Lumpur: Ministry of Health; 2003.
Lee CKC. National antibiotic guideline 2008. Kuala Lumpur: Ministry of Health; 2008.
Lee CKC. National antibiotic guideline. 2nd ed. Kuala Lumpur: Ministry of Health; 2014.
Lim V. Antibiotic stewardship. Int e-Journal Sci Med Educ. 2012;6:S75–9.
Ministry of Health Malaysia. Protocol on Antimicrobial Stewardship Program in Healthcare Facilities. Kuala Lumpur: Ministry of Health; 2014.
Teng CL, Achike FI, Phua KL, Nurjahan MI, Mastura I, Asiah HN, Mariam AM, Narayanan S, Norsiah A, Sabariah I, et al. Modifying antibiotic prescribing: the effectiveness of academic detailing plus information leaflet in a Malaysian primary care setting. Med J Malaysia. 2006;61(3):323–31.
‘Superbugs’ spur campaign for stricter use of antibiotics. The Star. Malaysia; 29 September 2012. http://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2012/09/29/superbugs-spur-campaign-for-stricter-use-of-antibiotics/. Accessed 15 Aug 2015.
Don’t ask for antibiotics if not needed. In: The Star. Malaysia; 31 May 2015. http://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2015/05/31/dont-ask-for-antibiotics-if-not-needed-doc-tough-toconvince-such-patients/. Accessed 15 Aug 2015.
Huttner B, Goossens H, Verheij T, Harbarth S. Characteristics and outcomes of public campaigns aimed at improving the use of antibiotics in outpatients in high-income countries. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010;10(1):17–31.
Lo YY, Lam CL, Mercer SW, Fong DY. Does vocational training in family medicine have an impact on antibiotic prescribing pattern? Fam Pract. 2011;28(1):56–62.
Chua SS, Lim KP, Lee HG. Utilisation of community pharmacists by the general public in Malaysia. Int J Pharm Pract. 2013;21(1):66–9.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the Director General of Health, Ministry of Health Malaysia for the permission to publish the findings. We would like to thank doctors in the public and private primary care clinics for their participation in this survey, and the team members of the National Medical Care Survey for assisting in the data collection and data entry. We also would like to express our great appreciation to Dr. Benedict Sim Lim Heng (Infectious Disease Consultant, Sungai Buloh Hospital) for his valuable comments to our manuscript, and Professor Dr. Daniel D Reidpath (Professor of Population Health, Monash University Malaysia) for his help in editing the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Health, Malaysia (grant number: NMRR-09-842-4718). The principal investigator and researchers involved in the design of the study, collection and analysis of the study are employees of the Ministry of Health Malaysia. The opinions, results and conclusions reported in this paper are those of the authors and are independent from the funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
NAR participated in the planning and execution of the study, data analysis and interpretation, wrote and edited the manuscript. CLT assisted the design and pilot testing of the survey forms, participated in the data analysis and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript. SS conceived, designed and executed the study, and edited the manuscript. All authors read an approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Ab Rahman, N., Teng, C.L. & Sivasampu, S. Antibiotic prescribing in public and private practice: a cross-sectional study in primary care clinics in Malaysia. BMC Infect Dis 16, 208 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-016-1530-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-016-1530-2