Abstract
Background
This study aimed to identify the significant physical, psychological, and social determinants associated with EuroQuol-5D (EQ-5D) among Chinese older people with chronic musculoskeletal pain, and to evaluate how these determinants affected the five dimensions of EQ-5D.
Method
This is a cross-sectional study. Data were collected through a cohort involving 946 community-dwelling older people aged ≥ 60 with chronic musculoskeletal pain in Hong Kong. Selected independent variables were categorized into physical, psychological, and social domains. Physical variables included age, sex, body mass index (BMI), pain severity score, number of pain regions, the most painful site, and the number of comorbidities. Psychological variables included depression level measured using the 9-question Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), and anxiety level measured using the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Assessment (GAD-7). Social variables included living, marital, and social welfare recipient’s status. The dependent variables comprised the index scores and the five dimensions of the EQ-5D descriptive system. Ordinal least squares (OLS) model and logistic regression model were used for data analysis.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 67.1 (SD = 5.1), with 77.6% being female. Higher pain severity scores (beta (β) coefficient =-0.044, P < 0.001), depression scores (β=-0.007, P < 0.001) and higher anxiety scores (β=-0.01, P < 0.001) were associated with lower EQ-5D index scores. Specifically, knee pain (β=-0.061, P < 0.001) was significantly associated with lower EQ-5D index scores. Participants with higher pain severity and depression scores were more likely to report problems in most EQ-5D dimensions. Participants with anxiety primarily faced challenges related to mood, and those with knee pain were more likely to have problems with mobility and daily activities.
Conclusion
Among the selected determinants in our study, pain intensity, depression, anxiety, and knee pain were identified as key determinants associated with reduced HRQoL in older Chinese people with chronic musculoskeletal pain. Each of these determinants showed distinct associations with different dimensions of the EQ-5D, potentially informed resource allocation and the development of targeted interventions to improve the overall HRQoL of this specific population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Chronic musculoskeletal pain is a highly prevalent condition that significantly impacts individuals worldwide, resulting in significant physical, psychological, and social impairment [1, 2]. According to Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2019, musculoskeletal pain conditions affect approximately 1.71 billion people globally, ranking high as one of the leading causes of disability worldwide [3]. Chronic musculoskeletal pain is particularly common among older adults, with prevalence rates ranging from 40–60%[4]. According to the World Health Organization report, musculoskeletal health conditions represent a global threat to healthy aging, with considerable negative effects on the older population [5].
Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) is a crucial indicator of the overall well-being and satisfaction experienced by individuals with a disease. It offers valuable insights into how the disease impacts various aspects of their daily lives, encompassing physical functioning, mental health, social interactions, and overall life contentment [6]. Considering HRQoL empowers healthcare providers to deliver more personalized, patient-centered care that addresses specific areas of impairment and enhances the overall quality of life for patients [7]. Moreover, it assists healthcare professionals in making informed treatment decisions that not only target disease symptoms, but also optimize patients’ overall well-being and functioning [8]. Additionally, by assessing HRQoL, policymakers and healthcare systems can effectively allocate resources to interventions with the highest potential for improving HRQoL outcomes [9].
Previous studies have extensively explored determinants impacting HRQoL among older individuals with various chronic diseases. For instance, research focusing on elderly hypertensive patients in China revealed that factors such as gender, age, income, and coexisting diseases significantly influenced their HRQoL. Similarly, a study on diabetes mellitus patients in India identified age, rural background, and symptoms of depression as key predictors of poorer quality of life, emphasizing the need for comprehensive and collaborative care [10, 11]. Despite the high prevalence of chronic musculoskeletal pain in older people and its established association with significantly lower HRQoL, [12,13,14] a notable research gap persisted in identifying key determinants of HRQoL in this demographic. Moreover, there was a lack of detailed understanding regarding the extent to which each determinant influences HRQoL in these individuals. Our study aimed to address this gap by examining the physical, psychological, and social determinants of HRQoL in older Chinese people with chronic musculoskeletal pain, and evaluating how these determinants affect the individual dimensions represented in HRQoL assessments. By identifying the most influential determinants of HRQoL in older individuals with chronic musculoskeletal pain, our study guides a strategic allocation of healthcare resources. It enables healthcare policymakers and practitioners to prioritize interventions and resources effectively, focusing on the areas with the most significant impact on HRQoL. Furthermore, by quantifying the impact of each determinant on the individual dimensions of HRQoL, we facilitate the creation of dimension-specific strategies to meet the needs of older adults with chronic musculoskeletal pain. This targeted intervention design enables us to effectively address specific aspects of HRQoL, thereby improving their well-being.
Methods
Study design
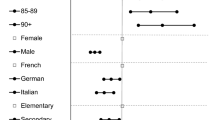
This cross-sectional study was conducted as part of the “CUHK-Jockey Club Pain Relief Project for Seniors,” a community-based charity program aimed at providing comprehensive non-pharmacological interventions to older adults suffering from chronic musculoskeletal pain. Data were collected from a cohort database established on January 1, 2019, which aimed to gather baseline health profiles of participants, monitor the longitudinal effects of pain on physical and psychosocial outcomes, and evaluate the potential impact of pain on healthcare utilization, quality of life, and mortality. The representativeness of the sample had been tested by measuring the differences between the sociodemographic of the present sample against the population aged ≥ 60 years reported in the Hong Kong census statistics 2022. (Appendix 1)
Participants
The inclusion criteria included participants aged 60 years old or above; presented with chronic musculoskeletal pain, defined as regional pain (joints, limbs, back, neck), with degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis, or musculoskeletal complaints that fall under the “chronic primary pain” classification of the International Classification of Disease-11 (ICD-11) [15]; and with pain that persisted or recurred ≥ 3 months [16]. Participants with cancer-related musculoskeletal pain were excluded; otherwise, no other specific exclusion criteria were adopted, although participants should have the ability to walk to the survey site, report data, and understand and sign an informed consent form.
Settings
The study recruited participants from the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) using a convenience sampling method. Participants were recruited through various community channels, including press conferences, television and radio programs, social media, digital platforms (such as websites and Facebook), and referrals from public and private primary care clinics. Data collection for the study was conducted through a two-step process. Initially, trained research assistants performed phone screenings to identify eligible participants. After that, individuals who met the study criteria were invited to provide written informed consent and participate in detailed face-to-face assessments. These assessments took place at a community-based interdisciplinary pain service center, led by experienced primary care providers.
Independent variables
The biopsychosocial model, first proposed by George Engel in 1977, marked a significant shift from the traditional biomedical model by emphasizing the integration of biological, psychological, and social factors in understanding health and illness [17]. The model was subsequently adapted and refined by researchers such as Gatchel et al. for application in the context of pain, providing a comprehensive framework for pain assessment and management [18]. The biopsychosocial model of pain suggested that the perception of pain arose from the dynamic interplay among biological, psychological, and social factors. The model emphasized how the interaction among these factors influenced the patient’s individualized pain experience, potentially leading to a decline in quality of life [19, 20].
In our analysis, determinants were selected and categorized in accordance with the biopsychosocial model of pain, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of their impact. The selection was further guided by existing research studies on quality of life determinants in chronic pain patients, [13, 21, 22] as well as the Core Outcome Domains for Chronic Pain Clinical Trials as recommended by IMMPACT [23].
The independent variables were grouped into the following domains:
-
Physical domain: age, sex, body mass index (BMI), Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) severity score, [24, 25] number of pain regions, the most painful region (neck, shoulder, back, knee, foot, and ankle), and number of comorbidities.
-
Psychological domain: depression level measured by the 9-question Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), [26] and anxiety level measured by the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Assessment (GAD-7) [27].
-
Social domain: living arrangements (living alone or with family), marital status (single or married), and social welfare support status (whether they received community social security allowance).
Dependent variable
The dependent variable was HRQoL, measured by the Hong Kong Chinese Version of the EuroQol-5 Dimension (EQ-5D) [28]. It consists of a descriptive system with five dimensions (mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression), each having five levels that capture the range of possible responses. The EQ-5D allows individuals to self-report their health status based on these dimensions and levels, and the results can be converted into a single health preference index, providing an overall assessment of HRQoL.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive data were reported as percentages or means ± standard deviations. Ordinal least squares (OLS) model was used to study the relationship between different continuous and categorical independent variables with EQ-5D index score, and beta (β) coefficients were calculated. Binary multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to examine the odds ratios (OR) of participants reporting “having problems” in each dimension of the EQ-5D. Score of 1 in each dimension signifies “full health,” while a score greater than 1 indicates the individual is “reporting having problems” in that specific dimension. For the logistic regression analysis, a coding system was employed, where 0 represented reporting “full health,” and 1 represented reporting “having problems” in that dimension. Pairwise deletion was employed for missing values. Data analysis was conducted using R Statistical Software (version 4.1.3).
Sample size calculation
The required sample size for our regression analysis was determined using the G*Power v3.1 statistical software [29]. In our regression model, encompassing fifteen predictors, we set an alpha level at 0.05, a conservative estimated effect size of 0.02, and a power of 0.90. Employing these parameters, an a priori power analysis conducted via G*Power software indicated a minimum sample size of 528 participants [30].
Ethical consideration
The study was approved by relevant research ethics committee (CREC no. 2018.540). Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants.
Results
A total of 946 participants were recruited with a mean age of 67.1 ± 5.1 years old and 77.6% were female. The mean BPI severity score was 4.2 ± 1.9; the mean number of painful regions was 3.4 ± 1.9, with the knee most commonly reported as the most painful region (39.2%). The mean scores for the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 were 6.3 ± 4.9 and 6.1 ± 5.3, respectively. The mean EQ-5D index was 0.70 ± 0.21. Baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
The associations between individual physical, psychological, and social determinants with the EQ-5D index are summarized in Table 2. In the physical domain, higher BPI severity scores (β = -0.044, P < 0.01) and reporting knee pain (β = -0.061, P < 0.001) were found to be significantly associated with lower EQ-5D index scores. In the psychological domain, higher scores on the PHQ-9 (β = -0.007, P < 0.001) and GAD-7 (β = -0.01, P < 0.001) were significantly associated with lower EQ-5D index scores. No significant variables in the social domain were found to be associated with EQ-5D index scores.
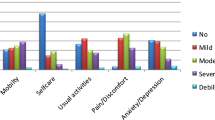
The effects of individual determinants on the five dimensions of EQ-5D are summarized in Table 3. Individuals with higher BPI severity scores were more likely to report “having problems” in the dimensions of mobility (OR = 1.44, p < 0.001), self-care (OR 1.27, P < 0.001), usual activities (OR 1.34, P < 0.001) and pain (OR2.43, P < 0.001). Individuals with higher PHQ-9 were more likely to report “having problems” in the dimensions of mobility (1.08, P = 0.002), self-care (1.07, P = 0.015), usual activities (1.08, P < 0.001), and mood (OR 1.11, P < 0.001). Those with higher GAD-7 only reported “having problems” in the dimension of mood (OR 1.27, P < 0.001). Individuals with knee pain reported “having problems” in the dimensions of mobility (OR 6.64, P < 0.001) and usual activities (OR 1.91, P < 0.001).
Discussion
In summary, older Chinese individuals with chronic musculoskeletal pain have a lower HRQoL compared to the general population in Hong Kong. This is evident from the distinct EQ-5D index score of 0.70, in contrast to the higher score of 0.92 observed in the general population [31]. In the context of the biopsychosocial model of pain, our study found that physical factors such as pain intensity and knee pain, and psychological factors like depression and anxiety, were significantly associated with lower HRQoL.
We further investigated the impact of pain intensity, knee pain, depression, and anxiety on different dimensions of EQ-5D. Our findings revealed that individuals with higher BPI severity scores were more likely to report “having problems” in four out of five EQ-5D dimensions, namely “mobility,” “self-care,” “usual activities,” and “pain/discomfort.” Interestingly, our study did not find a significant association between pain intensity and the “anxiety/depression”. This aligns with a previous study conducted by Björn Gerdle et al., which suggested that although anxiety and depression symptoms often accompany chronic pain, the correlation between pain intensity and psychological distress levels is relatively weak [32]. This complexity can be attributed to the intricate relationship between pain intensity and psychological distress, which can be influenced by individual coping strategies, attention, cognition, and emotion regulation [33, 34].
Compared to other musculoskeletal regions, older individuals who reported knee pain as their most severe pain region showed a significant association with reduced HRQoL. This aligns with previous studies which showed that knee pain was significantly associated with lower HRQoL in older populations [35, 36]. It is worth noting that knee pain was only found to be associated with the “mobility” and “usual activity” dimensions of EQ-5D. This was consistent with a previous study which found that mobility limitation reduces HRQoL [37]. Therefore, we suggest that when developing treatment strategies for knee pain in older individuals, interventions and resources should prioritize to enhance mobility and ability to perform usual activities, thus potentially improve their overall HRQoL.
Depression and anxiety are well-known to be associated with reduced HRQoL among patients with chronic pain [38, 39]. In terms of their influence on the individual dimensions of EQ-5D, the PHQ-9 was found to be significantly associated with “mobility,” “self-care,” “usual activities,” and “anxiety/depression.” On the other hand, the GAD-7 was only associated with the “anxiety/depression” dimension. Again, we did not find any association between psychological distress and the “pain/discomfort” dimension. These findings hold important clinical implications. When encountering chronic pain patients with depression, it is essential to not only manage the depressive symptoms but also focus on enhancing their physical functioning and self-management skills in order to improve their overall HRQoL. On the other hand, for those with comorbid anxiety, treatment can be specifically targeted at dealing with anxiety in order to improve their overall HRQoL.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate the individual contributions of physical, psychological, and social factors on HRQoL within a single cohort of older individuals with chronic musculoskeletal pain. There were several limitations in this study. Firstly, participants were recruited using convenience sampling, a non-random method that could introduce statistical errors in group selection and potentially affect the validity of the results. This approach also carried a risk of self-selection bias, as those who volunteered might possess characteristics not representative of the general population of older adults. Secondly, the recruitment focused exclusively on community-dwelling individuals, which may limit the generalizability of our results to older adults with limited mobility or those residing in nursing homes. Lastly, our analysis was limited to selected determinants. While we focused on selected determinants across biological, psychological, and social domains, certain factors such as cognitive function and chronic medication use, were not included in the analysis. Additionally, although we addressed several social factors, our analysis did not provide a comprehensive coverage of all aspects of individuals’ social backgrounds.
Our findings have several clinical implications. Firstly, based on the biopsychosocial model of pain, we identified key determinants of HRQoL in older people with chronic musculoskeletal pain, emphasizing the need to address pain intensity, knee pain, depression, and anxiety as priorities for resource allocation. Secondly, our evaluation of individual determinants on the five dimensions of EQ-5D informs the development of targeted treatment strategies to enhance overall HRQoL. For instance, reducing pain intensity should focus on improving mobility, self-care, and the ability to perform usual activities. Interventions targeting knee pain should prioritize improvements in mobility and self-care. Patients with comorbid depression and chronic pain would benefit from multidisciplinary care, while individuals with comorbid anxiety may benefit from targeted treatment addressing their anxiety symptoms.
Conclusion
Among the selected determinants in our study, pain intensity, depression, anxiety, and knee pain were identified as key determinants associated with reduced HRQoL. Older people with higher pain intensity and greater depressive symptoms were more likely to encounter difficulties across various dimensions of the EQ-5D. Participants with anxiety primarily faced challenges related to mood, and those with knee pain were more likely to have problems with mobility and daily activities. These findings have the potential to guide the allocation of resources and the development of targeted interventions aimed at enhancing HRQoL.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- HRQoL Health:
-
Related Quality of Life
- EQ:
-
5D EuroQuol-5D
- BMI Body:
-
Mass index
- BPI:
-
Brief Pain Inventory
- PHQ-9:
-
9-question Patient Health Questionnaire
- GAD-7:
-
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Assessment
- GBD:
-
Global Burden of Disease
- ICD-11:
-
International Classification of Disease-11
- HKSAR:
-
Hong Kong Special Administrative Region
- OLS:
-
Ordinal least squares
- OLS:
-
Ordinal least squares
- β:
-
Beta
- OR:
-
Odds ratios
- CREC:
-
Clinical Research Ethics Committee
References
Leveille SG, Ling S, Hochberg MC, et al. Widespread Musculoskeletal Pain and the progression of disability in older Disabled women. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(12):1038–46. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-135-12-200112180-00007.
Scudds RJ, Robertson JM. Empirical evidence of the association between the presence of musculoskeletal pain and physical disability in community-dwelling senior citizens. Pain. 1998;75(2):229–35.
Cieza A, Causey K, Kamenov K, et al. Global estimates of the need for rehabilitation based on the Global Burden of Disease study 2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2021;396(10267):2006–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)32340-0. [published Online First: 20201201].
Hay SI, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1260–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32130-X.
Briggs AM, Cross MJ, Hoy DG, et al. Musculoskeletal health conditions represent a global threat to healthy aging: a report for the 2015 World Health Organization world report on ageing and health. Gerontologist. 2016;56(suppl2):243–S55.
Calvert MJ, Freemantle N. Use of health-related quality of life in prescribing research. Part 1: why evaluate health‐related quality of life? J Clin Pharm Ther. 2003;28(6):513–21.
Kuipers SJ, Cramm JM, Nieboer AP. The importance of patient-centered care and co-creation of care for satisfaction with care and physical and social well-being of patients with multi-morbidity in the primary care setting. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-018-3818-y. [published Online First: 20190108].
Patrick DL, Erickson P. Assessing health-related quality of life for clinical decision-making. Quality of life assessment: key issues in the 1990s: Springer 1993:11–63.
Dolan P. The measurement of health-related quality of life for use in resource allocation decisions in health care. Handb Health Econ. 2000;1:1723–60.
Zheng E, Xu J, Xu J, et al. Health-Related Quality of Life and its influencing factors for Elderly patients with hypertension: evidence from Heilongjiang Province, China. Front Public Health. 2021;9:654822. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.654822. [published Online First: 20210316].
Gupta J, Kapoor D, Sood V. Quality of life and its determinants in patients with diabetes Mellitus from Two Health institutions of Sub-himalayan Region of India. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2021;25(3):211–19. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijem.IJEM_246_21. [published Online First: 20211026].
Wahl AK, Rustøen T, Rokne B, et al. The complexity of the relationship between chronic pain and quality of life: a study of the general Norwegian population. Qual Life Res. 2009;18(8):971–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-009-9515-x. [published Online First: 20090818].
Garnaes KK, Mørkved S, Salvesen Ø, et al. What factors are associated with health-related quality of life among patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain? A cross‐sectional study in primary health care. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):102. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-020-03914-x.
Bonanni R, Cariati I, Tancredi V, et al. Chronic Pain in Musculoskeletal diseases: do you know your enemy? J Clin Med. 2022;11(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092609. [published Online First: 20220506].
Nicholas M, Vlaeyen JW, Rief W, et al. The IASP classification of chronic pain for ICD-11: chronic primary pain. Pain. 2019;160(1):28–37.
Treede R-D, Rief W, Barke A et al. A classification of chronic pain for ICD-11. Pain 2015;156(6):1003.
Engel GL. The need for a new medical model: a challenge for biomedicine. Science. 1977;196(4286):129–36. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.847460.
Gatchel RJ, Peng YB, Peters ML, et al. The biopsychosocial approach to chronic pain: scientific advances and future directions. American Psychological Association; 2007. pp. 581–624.
Bevers K, Watts L, Kishino N, et al. The Biopsychosocial Model of the Assessment, Prevention, and treatment of Chronic Pain. US Neurol. 2016;12:98. https://doi.org/10.17925/USN.2016.12.02.98.
Fillingim RB. Individual differences in pain: understanding the mosaic that makes pain personal. Pain. 2017;158(Suppl 1):11–s18. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000775.
Demircioğlu A, Özkal Ö, Dağ O. Multiple factors affecting Health-Related Quality of Life in Women with Chronic Multisite Musculoskeletal Pain: a cross-sectional study in Ankara, Turkey. Eval Health Prof. 2022;45(2):115–25. https://doi.org/10.1177/01632787211049273.
Agnus Tom A, Rajkumar E, John R, et al. Determinants of quality of life in individuals with chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Health Psychol Behav Med. 2022;10(1):124–44. [published Online First: 20220105].
Turk DC, Dworkin RH, Allen RR, et al. Core outcome domains for chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2003;106(3):337–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2003.08.001.
Tan G, Jensen MP, Thornby JI, et al. Validation of the brief Pain Inventory for chronic nonmalignant pain. J Pain. 2004;5(2):133–37.
Keller S, Bann CM, Dodd SL, et al. Validity of the brief pain inventory for use in documenting the outcomes of patients with noncancer pain. Clin J Pain. 2004;20(5):309–18. [published Online First: 2004/08/24].
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL. The PHQ-9: a new depression diagnostic and severity measure. Psychiatric Annals. 2002;32(9):509–15.
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(10):1092–97.
Wong ELY, Ramos-Goñi JM, Cheung AWL et al. Assessing the Use of a Feedback Module to Model EQ-5D-5L Health States Values in Hong Kong. Patient 2018;11(2):235– 47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40271-017-0278-0.
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, et al. G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2007;39(2):175–91. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03193146.
Cohen J, Cohen P, West SG, Aiken LS. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (3rd ed.). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/97802037744412002.
Wong EL, Cheung AW, Wong AY, et al. Normative Profile of Health-Related Quality of Life for Hong Kong General Population using preference-based instrument EQ-5D-5L. Value Health. 2019;22(8):916–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2019.02.014. [published Online First: 20190727].
Gerdle B, Dragioti E, Rivano Fischer M, et al. Pain intensity and psychological distress show different associations with interference and lack of life control: a clinical registry-based cohort study of > 40,000 chronic pain patients from SQRP. Front Pain Res. 2023;4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpain.2023.1093002.
Linton SJ, Shaw WS. Impact of psychological factors in the experience of pain. Phys Ther. 2011;91(5):700–11. https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20100330. [published Online First: 20110330].
Linton SJ, Bergbom S. Understanding the link between depression and pain. Scand J Pain. 2011;2(2):47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjpain.2011.01.005. [published Online First: 20110401].
Mahir L, Belhaj K, Zahi S, et al. Impact of knee osteoarthritis on the quality of life. Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. 2016;59:e159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rehab.2016.07.355.
Fransen M, Su S, Harmer A, et al. A longitudinal study of knee pain in older men: Concord Health and Ageing in Men Project. Age Ageing. 2014;43(2):206–12. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/aft188. [published Online First: 20131205].
Stubbs B, Schofield P, Patchay S. Mobility limitations and fall-related factors contribute to the reduced health-related quality of life in older adults with Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain. Pain Pract. 2016;16(1):80–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/papr.12264.
Elliott TE, Renier CM, Palcher JA. Chronic pain, depression, and quality of life: correlations and predictive value of the SF-36. Pain Med. 2003;4(4):331–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4637.2003.03040.x.
Bair MJ, Wu J, Damush TM, et al. Association of depression and anxiety alone and in combination with chronic musculoskeletal pain in primary care patients. Psychosom Med. 2008;70(8):890–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/PSY.0b013e318185c510. [published Online First: 20080916].
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was funded by the Hong Kong Jockey Club Charities Trust “Pain Relief Project for Seniors” (Project no.: 2018-0093) which had no role in study design, data collection, analysis, and interpretation, preparation of manuscript and decision to publish.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HPYF was responsible for literature search, data analysis and interpretation, and writing the first draft of the manuscript. SYKC and MKWL were responsible for investigation, methodology and project administration. HHML was responsible for data interpretation, and writing the first draft of manuscript. BW was responsible for data curation, data analysis and interpretation. SYSW was responsible for conceptualisation and methodology. RWSS was responsible for conceptualization, methodology, project administration, data interpretation and review of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Joint Chinese University of Hong Kong New Territories East Cluster Clinical Research Ethics Committee (CREC no. 2018.540). Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Fong, HY., Choi, SK., Leung, MW. et al. Determinants of health-related quality of life in older people with chronic musculoskeletal pain: a cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr 24, 119 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-024-04669-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-024-04669-z