Abstract
Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), one of the most common malignant tumors worldwide, ranks as the fifth most common cancer and has been the second most frequent cause of cancer-related death. RNA binding proteins (RBPs) are proteins that interact with different classes of RNA and are commonly detected in cells.
Methods
We used RNA sequencing data from TCGA to display dysfunctional RBPs microenvironments and provide potential useful biomarkers for HCC diagnosis and prognosis.
Results
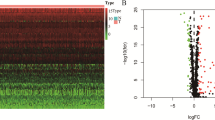
330 differently expressed RBPs (208 upregulated and 122 downregulated) were identified. KEGG were mainly enriched in RNA degradation, Influenza A, Hepatitis C, RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway, Herpes simplex virus 1 infection and RNA transport. CBioPortal results demonstrated that these genes were altered in 50 samples out of 357 HCC patients (14%) and the amplification of BRCA1 was the largest frequent copy-number alteration.
Conclusion
Based on the online database, we identified novel RBPs markers for the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), one of the most common malignant tumors worldwide, ranks as the fifth most common cancer and has been the second most frequent cause of cancer-related death with over 500,000 newly diagnosed per year [1]. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and viral hepatitis are the most common causes of cirrhosis, with approximately four fifths of cases progressing to liver cancer [2, 3]. Owing to HCC recurrence, the prognosis for HCC is also dismal, and the 5-year overall survival (OS) rate is below 50% [4]. Notwithstanding rapid advances in medical technology, there is still no effective treatment strategy for HCC patients [5]. Serum markers such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) are known to be used in clinical practice, but they are not adequate enough in specificity and sensitivity [6]. Therefore, it is necessary to search effective biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of HCC patients.
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are proteins that interact with various kinds of RNA and are commonly detected in cells. RBP affects post-transcription and regulates cell physiology, and is involved in controlling RNA stability, alternative splicing, translation, apoptosis, modification, and localization [7]. A total of 1542 RBPs were identified in human cells by high-throughput screening, accounting for 7.5% of all protein-coding genes [8]. Over the past few decades, genome-wide techniques have shown that many RBPs functions are abnormal in cancers and their expressions are associated with disease prognosis. Kudinov et al. [9] reported that RBP Musashi-1 (MS1) and Musashi-2 (MS2) can operate necessarily in oncogenic signaling pathways, involving in NUMB/Notch, TGFβ/SMAD3, PTEN/mTOR, cMET, MYC, etc. Similarly, study revealed RPS3 in the post-transcriptional can regulate the expression of SIRT1 to promote hepatocarcinogenesis [10]. Study also demonstrated that RBPs level was an independent risk factor involved in early intrahepatic recurrence of HCC among 2 years after surgery and suppression of RBPs obviously suppressed cell invasion as well as proliferation [11]. However, only a small number of RBPs have been studied in depth, and so far, RBPs have been found to play a key role in cancer. At the same time, there is no features to systematically assess cancer-related RBPs and predict OS in HCC patients. Therefore, we used RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data based on the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to reveal abnormalities in the microenvironment of RBPs, the potential molecular function, the clinical significance of RBPs, and to furnish prospective beneficial biomarkers for HCC prognosis.
Methods
Data gathering
RNA-seq data from 424 (50 normal and 374 tumor) and comparative clinical data were identified and downloaded from the level 3 gene expression information (standardized FPKM) of the TCGA-HCC cohort. The collected clinical pathological data included gender, age, stage, grade, TMN classification, survival status and number of days of survival. 1542 RBPs were get from Gerstberger et al. [7] study, the detailed information was shown in Additional file 2: Table S1. HCC patients (231 patients) from the ICGC (LIRI-JP) cohort were used for validation.
Building and validating the prognostic RBPs-based signature
After normalized the mRNA expression profiles through edgerR (R package). |log2FC|≥ 0.5 and FDR < 0.05 were determined as differently expressed RBPs. Through caret (R package) with function create data partition divided HCC cohort into two groups: a training set and a testing set. A univariate COX regression model was built via the RBPs’s levels, T, N, M, age, gender, stage, and survival information in the training cohort. Then, using significant RBPs got from univariate COX regression models and clinical factors to multivariate COX proportional hazard regression models. At the same time, RBPs’s levels that were significant both in univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis were choose as characteristically RBPs. The prognostic signature as risk score = (Coefficient RBP1 × expression of RBP1) + (Coefficientm RBP2 × expression of RBP2) + ⋯ + (Coefficient RBPn × expression RBPn). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted to prediction accuracy of the prognostic signatures for HCC patients.
Enrichment analysis of prognostic RBPs
Cytoscape is used to visualize the interaction network between protein–protein interaction (PPI). The plug-in Molecular Complex Detection (MCODE) of Cytoscape was applied to selected the most significant module in the PPI networks. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) is a database for exploring high-level gene functions and associating genomic data from large-scale molecular datasets. Gene ontology (GO) function analysis (biological processes (BP), cellular components (CC) and molecular functions (MF) is a tool to analyze biological process and annotate genes. We explored the function of the identified both upregulated and downregulated RBPs biological analyses using GO and KEGG via R language ggplot2 package.
Externally validated prognostic RBPs signatures
Tumor IMmune Estimation Resource (TIMER) database used to compared mRNA level between different cancers; The Human Protein Atlas database (HPA) further proved the expression of prognostic genes and CBioportal to study genetic alterations. All data processing based on P less than 0.05.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using R (version 3.5.3) and R bioconductor software packages. Benjamini–Hochberg's method was used to convert P values to FDR. Perl language was used for data matrix and data processing and a P value less than 0.05 was used. Normally and non-normally distributed variables were analyzed using the unpaired student’s t test and the Wilcoxon test, respectively. The relationship between our model and clinicopathological manifestations was evaluated using chi-square test.
Results
Enrichment analysis of identified RBPs
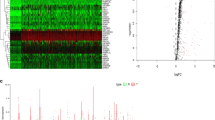
Figure 1 presents a flow chart of this study scheme. We first identified 330 differently expressed RBPs (208 upregulated and 122 downregulated Additional file 2: Table S2). We next explored the function of the identified upregulated and downregulated RBPs, respectively. In upregulated RBPs group, BP of target genes were enriched in RNA splicing, ncRNA processing, tRNA metabolic process, RNA localization, tRNA processing; MF were mainly enriched in catalytic activity, mRNA/tRNA/ snRNA binding, ribonuclease activity; CC were mainly enriched in spliceosome complex, cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule, ribonucleoprotein granule; KEGG were mainly enriched in spliceosome, mRNA surveillance pathway, RNA transport, RNA degradation, Ribosome. In addition, in downregulated RBPs group, BP of target genes were enriched in regulation of translation, regulation of cellular amide metabolic process, RNA phosphodiester bond hydrolysis; MF were mainly enriched in single-stranded RNA binding, double-stranded RNA binding, catalytic activity, acting on RNA, mRNA 3'-UTR binding; CC were mainly enriched in cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule, ribonucleoprotein granule, CCR4-NOT complex, P-body, ribosome; KEGG were mainly enriched in RNA degradation, Influenza A, Hepatitis C, RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway, Herpes simplex virus 1 infection, RNA transport Fig. 2 and Additional file 2: Table S3.
PPI network construction and hub module screening
To better known the possible molecular functions of these differentially expressed RBPs, we constructed the PPI using Cytoscape the STRING database, and via MCODE to selected hub genes. Finally, 11 hub genes (BLAVL2, IFIT5, EEF1A2, RFR21, CDX9, PABPC1L, TEX13A, NUPL2, DARS2, RNF17, and PARP1) and top 3 significant modules. The PPI network contained overall 311 nodes and 2942 edges (Fig. 3A); module 1 involved in 53 nodes and 709 edges (Fig. 3B); module 2 included 19 nodes and 97 edges (Fig. 3C); and module 3 included 27 nodes and 134 edges (Fig. 3D). We next extracted and combined all the genes from these 3 modules and also constructed the PPI network (Fig. 3E).
Building the prognostic RBPs-based signature
To screen the prognostic RBPs, differently expressed RBPs were conducted in univariate COX analysis. Then, 32 RBPs of great significance in univariate COX analysis were included in multivariate COX analysis. Finally, 8 differently expressed RBPs (SNRPD1, IARS, BRCA1, EZH2, RUVBL1, TST, TCOF1, and AZGP1) were selected as independent prognosis factors of HCC patients in the training set Fig. 4. Thus, the formula for our model was: Risk Score = (0.484 × expression IARS) + (0.180 × expressionEZH2) + (1.335 × expressionRUVBL1) + (0.495 × expressionTST) + (0.612 × expressionTCOF1) − (0.872 × expressionSNRPD1) − (0.676 × expressionBRCA1) − (0.218 × expressionAZGP1). In addition, in our study cohort, the risk score of individual patients was estimated. Using the median risk score value as a cut-off the cohorts were then divided into high- and low-risk groups in training set and testing set.
Survival results and multivariate examination
The Kaplan–Meier curves of the two cohorts can detect the predictive value of the signature based on 8-RBPs in the OS. Patients with high risk have a bad survival than the low-risk group both in training cohort (P = 4.458e − 05, Fig. 5A) and testing cohort (P = 2.796e − 04, Fig. 5B). We also used the ROC curves to investigate whether the expression pattern of survival-related RBPs could provide an early prediction for the occurrence of HCC. Here, we found an AUC of 0.786 in training set and 0.689 in testing set, meaning that the sensitivity and specificity of this prognostic model are moderate Fig. 5C, D. At the same time, we also established patient’s risk survival status plot, and as the patient's risk score increases, the number of dead patients also increases Fig. 5E, F. Next, in order to establish a prognostic model based on 8-RBPs, univariate and multivariate COX analysis was used to determine risk factors. Ultimately, the 8-RBPs based signature were convinced as independent prognosis factors of OS Table 1. Finally, combined with clinical pathology and prognostic models, a nomogram was constructed. Combining our prognostic model with clinical pathology can improve the predictive sensitivity and specificity of OS predictions at 1, 2, and 3 years, and bring some net benefits that may be useful for clinical management Fig. 6A. To test the robustness of the signature constructed from the TCGA cohort, the patients from the ICGC cohort were also categorized into high- or low-risk groups by the median value calculated with the same formula as that from the TCGA cohort. Similarly, patients in the high-risk group were more likely to encounter death earlier and the AUC of the 10-gene signature was 0.705. We also established patient's risk survival status plot, and as the patient's risk score increases, the number of dead patients also increases Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Online database analysis
Mutation and copy-number alteration (CNA) of these 8 RPPs conducted by the cBioPortal online tool. The results demonstrated that these genes were altered in 50 samples out of 357 HCC patients (14%) and the amplification of BRCA1 was the largest frequent copy-number alteration Fig. 6B. In order to further analysis the expression of these 8 RBPs, immunohistochemistry results from the HPA database to illustrate that SNRPD1, IARS, BRCA1, EZH2, RUVBL1, TST, TCOF1, and AZGP1 were significantly increased in tumor tissues Fig. 7. Meanwhile, we also used TIMER database to study the differential expression between tumor and adjacent normal tissues for these 8 RBPs across all TCGA tumors Fig. 8. We finally used Kaplan–Meier plotter to analyze the prognostic relevance of the these 8 RBPs, the results indicated that the high expression of SNRPD1, IARS, BRCA1, EZH2, RUVBL1, and TCOF1 was related to a poor prognostic, while the high expression of AGZP1 was related to a good prognostic and the expression of TST was meaningless to HCC patient’s overall survival Fig. 9.
Discussion
Alterations in post-transcriptional events are a critical step in tumor initiation and progression, while RBP-mediated control has not yet well been developed in cancers. RBPs has a wide range of functions, including regulation of mRNA’s stability/splicing/editing/translation/export/positioning/polyadenylation and miRNA biogenesis, which ultimately affect the expression of individual gene and serve as the key molecular connections in cancer [12]. Therefore, understanding the basic mechanisms of RBPs regulation may provide useful insights for the development of effective cancer treatments. In this study, we determined a novel and effective RBPs-based signature prognostic using online data set, and our signature may act for the RBPs status of HCC patients and provide potential biomarkers for clinical therapeutic intervention.
In our study, a comprehensive analysis of RBPs as well as downloaded clinical data from HCC-TCGA has been studied. We first identified 208 upregulated and 122 downregulated RBPs in HCC patients and explored the functions of these RBPs. Gene ontology function were mainly enriched in post-transcriptional events and KEGG were mainly enriched in spliceosome, mRNA surveillance pathway, RNA transport, RNA degradation, Influenza A, Hepatitis C, RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway and Herpes simplex virus 1 infection. The retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs) belong to the cytosolic host RNA helicases family that identify distinct nonself RNA signatures and trigger innate immune responses against some RNA viruses by signaling via the required adaptor protein mitochondrial antiviral signaling (MAVS) [13]. Innate immune activation and signaling through the RLRs pathway relied on viral replication, where the host response can obviously limit replication in target cells [14]. It’s well known that virus infection palys an indispensable role in HCC occurrence and development. Our results found the downregulated RBPs mainly enriched in viruses-related signaling pathway and may provide novel insight into further researches in future.
We next identified 8 RBPs (SNRPD1, IARS, BRCA1, EZH2, RUVBL1, TST, TCOF1, and AZGP1) which were selected as independent prognosis factors of HCC patients. Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein D1 polypeptide (SNRPD1), which encodes a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein is a part of the SNRNP core protein family. The mutations SNRPD1 antigenic targets are related to autologous T cell responses in the melanoma model [15]. SiRNA-mediated depletion of SNRPD1 leads to a significant reduction in cell viability in breast cancer, lung cancer, and leads to autophagy by mTOR pathway [16]. Kopajtich et al. [17] found that isoleucine-tRNA synthetase (IARS) missense mutations can cause hereditary weak calf syndrome and thus lead to infantile hepatopathy. It has been also confirmed in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissues that IARS levels involved in aminoacyl tRNA biosynthesis were elevated [18]. BRCA1 DNA repair associated (BRCA1) is a tumor suppressor which maintaining genomic stability and associates with RNA polymerase II. A recent study indicated that PARP inhibitor (olaparib), could increase the cytotoxicity in HCC cells with a lower BRCA1 expression [19]. The enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) and the catalytic component of polycomb inhibition complex 2 (PRC2) are associated with the expression of homologous genes (Hox) and early stages of inactivating X chromosome [20]. HBV HBx regulatory protein and lncRNA DLEU2 co-recruitment on the cccDNA replaces EZH2 from the viral chromatin to promote transcription and viral replication [21]. RuvB like AAA ATPase 1 (RUVBL1) is a protein that has both DNA-dependent ATPase and DNA helicase activities. It regulates insulin signaling via the Akt/mTOR pathway in vivo and in normal liver cells and HCC cells in vitro [22]. Thiosulfate sulfurtransferase (TST), also known as Rhodanese, interact with 5S ribosomal RNA and promote its into mitochondria. TST like domain-containing 1 (TSTD1) might play a role in sulfide-based signaling and overexpression in colon cancer [23]. TST’s functions also include modification of iron-sulfur clusters, sulfur metabolism, and the reduction of antioxidant glutathione and thioredoxin [24]. Treacle ribosome biogenesis factor 1 (TCOF1) participates in ribosomal DNA gene transcription and maintains genomic integrity after DNA damage [25]. Heterozygous mutations of TCOF1 are related to craniofacial disorder and compromise nucleolar homeostasis, thus activate the tumor-suppressor protein [26]. Study found that alpha-2-glycoprotein 1 (AZGP1) inhibited HCC cell invasion and migration by the regulation of the PTEN/Akt and CD44s pathways [27]. The absence of AZGP1 may trigger epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by TGFβ1-ERK2 signaling [28]. In total, the RBPs identified by our study may plays a critical role in the HCC occurrence and development.
Meanwhile, we also using online database to predict the potential function of these 8 RBPs including mutation and copy-number alteration; immunohistochemistry expression and pan-cancer expression. Though post-transcriptional plays a critical role in HCC, RBPs that affected genes still are unclear. In this study, we tried to integrates some RBPs biomarkers to assess the prognosis of treatment effects. This model can promote the determination of novel biomarkers and precise medical targets of diseases in HCC. Meanwhile, the model can also help with prognosis prediction, diagnosis and strategies of patients with distinct epigenetic subtypes of HCC. The signatures in our study might offer potential useful biomarkers for cancer treatment and prediction therapy response. However, our signatures have to prove in further independent cohorts and predictive RBPs functional by experiments. Meanwhile, our research has limitations. Firstly, our outcomes have not been validated in clinical samples. Secondly, our results do not provide accurate clinical data due to the relatively small number of patients. Finally, due to our RBPs were got from Gerstberger et al. study, some information may be inaccurate, such as BRCA1 may not belong to RBPs, so it should be caution when clarifying our research. Although our research wishes to explored the probability of establishing a prognostic prediction model, it is still in its infancy and needs improvement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, from the TCGA database and other bioinformatics ways, we have found prognostic RBPs as well as built a prognostic prediction model for HCC patients. The model might assist us identify novel biomarkers and help to predict prognosis of disease, clinical diagnosis and management.
Availability of data and materials
The scripts (Perl and R) used to calculate read counts mapped to Refseq-defined exons and introns are available at https://github.com/tianjiagene/GneneBlockReadCount. The two public RNA-seq data were from TCGA database and ICGC database.
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108.
Tang Y, Wang H, Ma L, Zhang X, Yu G, Li J, Ye H. Diffusion-weighted imaging of hepatocellular carcinomas: a retrospective analysis of correlation between apparent diffusion coefficients and histological grade. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016;41(8):1539–45.
Coskun M. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver: evaluation using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Exp Clin Transplant. 2017;15(Suppl 2):36–44.
Lang H, Sotiropoulos GC, Brokalaki EI, et al. Survival and recurrence rates after resection for hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic livers. J Am Coll Surg. 2007;205(1):27–36.
Jiao Y, Fu Z, Li Y, Meng L, Liu Y. High EIF2B5 mRNA expression and its prognostic significance in liver cancer: a study based on the TCGA and GEO database. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:6003–14.
Byeon H, Lee SD, Hong EK, Lee DE, Kim BH, Seo Y, Joo J, Han SS, Kim SH, Park SJ. Long-term prognostic impact of osteopontin and Dickkopf-related protein 1 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Pathol Res Pract. 2018;214(6):814–20.
Perron G, Jandaghi P, Solanki S, Safisamghabadi M, Storoz C, Karimzadeh M, Papadakis AI, Arseneault M, Scelo G, Banks RE, Tost J, Lathrop M, Tanguay S, Brazma A, Huang S, Brimo F, Najafabadi HS, Riazalhosseini Y. A general framework for interrogation of mRNA stability programs identifies RNA-binding proteins that govern cancer transcriptomes. Cell Rep. 2018;23(6):1639–50.
Gerstberger S, Hafner M, Tuschl T. A census of human RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(12):829–45.
Kudinov AE, Karanicolas J, Golemis EA, et al. Musashi RNA-binding proteins as cancer drivers and novel therapeutic targets. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(9):2143–53.
Zhao L, Cao J, Hu K, et al. RNA-binding protein RPS3 contributes to hepatocarcinogenesis by post-transcriptionally up-regulating SIRT1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(4):2011–28.
Iida M, Iizuka N, Tsunedomi R. Overexpression of the RD RNA binding protein in hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2012;28(2):728–34.
Campos-Melo D, Droppelmann CA, Volkening K, et al. RNA-binding proteins as molecular links between cancer and neurodegeneration. Biogerontology. 2014;15(6):587–610.
Quicke KM, Diamond MS, Suthar MS. Negative regulators of the RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway. Eur J Immunol. 2017;47(4):615–28.
Kell AM, Hemann EA, Turnbull JB, et al. RIG-I-like receptor activation drives type I IFN and antiviral signaling to limit Hantaan orthohantavirus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2020;16(4):e1008483.
Lennerz V, Fatho M, Gentilini C, et al. The response of autologous T cells to a human melanoma is dominated by mutated neoantigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(44):16013–8.
Quidville V, Alsafadi S, Goubar A, et al. Targeting the deregulated spliceosome core machinery in cancer cells triggers mTOR blockade and autophagy. Cancer Res. 2013;73(7):2247–58.
Kopajtich R, Murayama K, Janecke AR, et al. Biallelic IARS mutations cause growth retardation with prenatal onset, intellectual disability, muscular hypotonia, and infantile hepatopathy. Am J Hum Genet. 2016;99(2):414–22.
Hsu CW, Chang KP, Huang Y, et al. Proteomic profiling of paired interstitial fluids reveals dysregulated pathways and salivary NID1 as a biomarker of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cell Proteom. 2019;18(10):1939–49.
Zhao J, Sun Y, Lin H, et al. Olaparib and enzalutamide synergistically suppress HCC progression via the AR-mediated miR-146a-5p/BRCA1 signaling. FASEB J. 2020;34(4):5877–91.
Schuettengruber B, Chourrout D, Vervoort M, Leblanc B, Cavalli G. Genome regulation by polycomb and trithorax proteins. Cell. 2007;128:735–45.
Salerno D, Chiodo L, Alfano V, Floriot O, Cottone G, Paturel A, Pallocca M, Plissonnier ML, Jeddari S, Belloni L, Zeisel M, Levrero M, Guerrieri F. Hepatitis B protein HBx binds the DLEU2 lncRNA to sustain cccDNA and host cancer-related gene transcription. Gut. 2020;69(11):2016–24.
Mello T, Materozzi M, Zanieri F, et al. Liver haploinsufficiency of RuvBL1 causes hepatic insulin resistance and enhances hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Int J Cancer. 2020;146(12):3410–22.
Libiad M, Motl N, Akey DL, Sakamoto N, Fearon ER, Smith JL, Banerjee R. Thiosulfate sulfurtransferase-like domain-containing 1 protein interacts with thioredoxin. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(8):2675–86.
Kruithof PD, Lunev S, Aguilar Lozano SP, et al. Unraveling the role of thiosulfate sulfurtransferase in metabolic diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(6):165716.
Ciccia A, Huang JW, Izhar L, et al. Treacher Collins syndrome TCOF1 protein cooperates with NBS1 in the DNA damage response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(52):18631–6.
Calo E, Gu B, Bowen ME, et al. Tissue-selective effects of nucleolar stress and rDNA damage in developmental disorders. Nature. 2018;554(7690):112–7.
Tian H, Ge C, Zhao F, et al. Downregulation of AZGP1 by Ikaros and histone deacetylase promotes tumor progression through the PTEN/Akt and CD44s pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2017;38(2):207–17.
Xu MY, Chen R, Yu JX, et al. AZGP1 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and hepatic carcinogenesis by blocking TGFβ1-ERK2 pathways. Cancer Lett. 2016;374(2):241–9.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work is not supported by grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.Z.H. designed and analyzed the research study; W.Z.H. and H.H.M. wrote and revised the manuscript, W.Z.H. and Y.D.L. collected the data and all authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1
. Figure S1. Survival results and multivariate examination in ICGC cohort. A: Survival results in ICGC; B: ROC results in ICGC; C: Risk survival status plot in ICGC.
Additional file 2
. Table S1: The detailed information of 1,542 RNA binding proteins. Table S2: The detailed information of 330 differently expressed RBPs (208 upregulated and 122 downregulated). Table S3: The detailed information of function of the identified upregulated and downregulated RNA binding proteins, respectively.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, ZH., Huang, HM. & Yang, DL. Integrated analysis of the functions and prognostic values of RNA binding proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol 21, 265 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-021-01843-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-021-01843-0