Abstract
Objective
To construct a nutrition support program for middle-aged and elderly patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) during hospitalization.
Methods
Based on the JBI Evidence-Based Health Care Model as the theoretical framework, the best evidence was extracted through literature analysis and a preliminary nutrition support plan for middle-aged and elderly ADHF patients during hospitalization was formed. Two rounds of expert opinion consultation were conducted using the Delphi method. The indicators were modified, supplemented and reduced according to the expert’s scoring and feedback, and the expert scoring was calculated.
Results
The response rates of the experts in the two rounds of consultation were 86.7% and 100%, respectively, and the coefficient of variation (CV) for each round was between 0.00% and 29.67% (all < 0.25). In the first round of expert consultation, 4 items were modified, 3 items were deleted, and 3 items were added. In the second round of the expert consultation, one item was deleted and one item was modified. Through two rounds of expert consultation, expert consensus was reached and a nutrition support plan for ADHF patients was finally formed, including 4 first-level indicators, 7 s-level indicators, and 24 third-level indicators.
Conclusion
The nutrition support program constructed in this study for middle-aged and elderly ADHF patients during hospitalization is authoritative, scientific and practical, and provides a theoretical basis for clinical development of nutrition support program for middle-aged and elderly ADHF patients during hospitalization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is a common cardiovascular disease, which is the final stage of various cardiac lesions [1]. It is characterized by abnormal cardiac structure or function that impairs ventricular filling or ejection capacity, resulting in pulmonary congestion or systemic congestion, with or without tissue organ hypoperfusion [2]. Acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) refers to the rapid onset or worsening of symptoms and signs due to cardiac dysfunction, accompanied by elevated plasma natriuretic peptide levels [3]. ADHF is a common emergency condition that requires rapid diagnosis and urgent treatment, otherwise it may lead to serious complications and death [4]. The elderly population is a high-risk group for heart failure, and the incidence and mortality of heart failure increase with age [5]. Elderly ADHF patients often have multiple comorbidities and precipitating factors, such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, diabetes, renal insufficiency, anemia, infection, etc., which increase the complexity and difficulty of treatment [6,7,8]. In addition, elderly ADHF patients are prone to malnutrition or deterioration during hospitalization, affecting prognosis and quality of life [9].
Malnutrition and physical decline are common in elderly heart failure patients, and both are associated with adverse outcomes [10, 11]. Kałużna-Oleksy et al. has revealed that up to half of the patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction are at risk of malnutrition, with 2.9% suffering from it, and no significant differences in nutritional status between genders [12]. Studies have shown that malnutrition is an independent risk factor for the prognosis of heart failure patients, and ADHF patients have a malnutrition rate of 75-90% [13, 14]. Effective nutrition support is essential for the recovery of ADHF patients during hospitalization, which can reduce the recurrence of acute decompensation of chronic heart failure, alleviate heart failure symptoms, and improve the nutritional status and prognosis of patients [15]. However, there is no standardized nutrition support protocol in clinical practice. Therefore, based on literature review and clinical expert discussion, this study uses the Delphi method to construct a nutrition support protocol for elderly ADHF patients during hospitalization, providing a theoretical basis for nutrition support for elderly ADHF patients during hospitalization.
Methods
Establishment of the research group
The research team consisted of one doctoral supervisor, two nursing postgraduates, one deputy chief physician of the cardiovascular department, one head nurse, and one nutritionist. The main tasks of the research team included literature search and evaluation, expert inquiry form development, expert selection, expert recommendation analysis and integration, and protocol determination.
Literature search and selection criteria
Following the Evidence Pyramid “6S” model, we searched domestic and international guideline websites, databases and related websites, including BMJ Best Practice, Up To Date, Guidelines International Network (GIN), National Guideline Clearinghouse (NGC), Medlive (Yi Mai Tong), Cochrane Library, Joanna Briggs Institute, PubMed, Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN), National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE), National Clinical Practice Guidelines Database (NGC), China Science and Technology Journal Database, Wanfang, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and China Biomedical Literature Database for studies on nutritional plans for acute and chronic heart failure patients published from the inception of each database to December 2021. The search terms included “heart failure; chronic heart failure, acute heart failure, acutely decompensated chronic heart failure, nutri*, malnutrition, dietary, diet, micronutrients, vitamins, trace elements”. The language of the literature was limited to English and Chinese. To ensure the comprehensiveness of the search, we also screened the references of the retrieved literature.
The inclusion criteria for the literature were: (1) Chinese or English language. (2) Clinical practice guidelines, evidence summaries, best evidence, systematic reviews, expert consensus. (3) Providing guiding opinions on clinical nutrition support. The exclusion criteria for the literature were: (1) Literature with a quality assessment of grade C; (2) Duplicated publications; (3) Literature with unavailable full text; (4) Old guidelines that have been replaced.
Evaluation of the quality of the literature
This study used the evidence-based method of the Australian JBI Evidence-Based Health Care Center (2014), and two people who had received evidence-based course training conducted evidence extraction, analysis and synthesis of the included literature, and prepared a draft of the nutrition support program for middle-aged and elderly ADHF patients during hospitalization. The program included four parts: team organization and management, nutritional assessment, nutritional intervention measures, and outcome evaluation. In case of disagreement, the two people reached a consensus through discussion and consultation.
Expert selection criteria
This study invited experts from Shanghai, Suzhou, and Anhui in China. Experts were selected based on their clinical expertise and previous publications in the field of cardiovascular disease and nutrition. From July to October 2022, the members of the research team conducted expert consultation through email and WeChat. The inclusion criteria for the experts were as follows: (1) Senior specialists with 10 or more years of nursing or clinical experience in cardiovascular medicine, critical care disciplines, and geriatrics; (2) Working years of 10 years or more; (3) Bachelor degree or above, and the title of intermediate or above; (4) Agree to participate in two rounds of inquiry and provide modification suggestions for improving the plan.
Establishing the questionnaire
The questionnaire consists of three parts. (1) Questionnaire instructions: The experts are introduced to the research background, purpose, significance and filling method. (2) Expert basic information: The general information of the experts includes gender, age, working years, professional title, education level, work unit, work field, etc. Experts’ familiarity and judgement basis self-evaluation table: Familiarity is divided into very unfamiliar (0.2), unfamiliar (0.4), generally familiar (0.6), familiar (0.8), and very familiar (1). The judgement basis is classified into four categories: practical experience, theoretical analysis, reference to domestic and foreign literature, and intuition selection. The degree of influence is divided into large, medium, and small, and different quantitative values are assigned accordingly. (3) Expert inquiry form on nutrition support plan for elderly ADHF patients during hospitalization: The importance of the strategy recommendation was rated using the Likert 5-point scoring method: “5” for “extremely important”, “4” for “very important”, “3” for “moderately important”, “2” for “slightly important” and “1” for “unimportant”. In addition, each item has a modification comment column for the experts to modify, delete or add items.
Implementation of an expert consultation
A two-round online Delphi survey was conducted from July to October 2022. After the first round of expert consultation letters were collected, the research team members sorted, counted and analyzed the expert opinions and provided feedback to the experts. According to the item modification principles, they added or deleted relevant item contents and formed the second round of expert consultation letters. Following the same process, they completed the subsequent consultation for the “Nutrition support Plan for Elderly ADHF Patients During Hospitalization” until the expert opinions converged and the consultation was stopped. Based on the importance scores of the items, the principles for modifying the items were formulated in accordance with the clinical work needs. The items with a mean value ≥ 4 and a coefficient of variation ≤ 0.25 were retained. At the same time, to avoid deleting important items, for those items that only had one criterion not met, or that met both criteria but had large deviations in some experts’ opinions, the principles of science and practicality were followed, and the experts’ opinions were respected. The decision to keep or discard the items was made through collective discussion.
Statistics analysis
SPSS 26.0 software is used for data statistics and analysis. The effective recovery rate of the consultation form represents the enthusiasm of the experts. The expert authority coefficient (CR) is calculated based on the average of the expert judgment foundation (Ca) and familiarity (CS) of the research plan, that is, CR=(Ca + CS)/2. The degree of coordination of expert opinions is expressed by Kendall’s harmony coefficient (Kendall´s W) and coefficient of variation CV.
Results
Results of the literature search
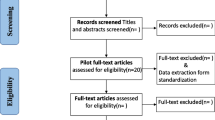
This study retrieved 7732 relevant articles, and after removing duplicates, screening titles and abstracts, 7701 articles were excluded, and 31 articles were preliminarily included. After further reading the full text, 2 articles without recommendation strength, 1 article with an updated version, and 1 article with weak relevance were excluded, and 27 articles [1, 13, 16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] were finally included (Fig. 1). The included articles consisted of 11 guidelines, 10 expert consensuses, 1 systematic review, 2 Mate analysis and 3 evidence summaries.
Flow chart of the process of selecting article for scoping review. SIGN: Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, NICE: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, NGC: National Guideline Clearinghouse, GIN: Guidelines International Network, VIP: China Science and Technology Journal Database, CNKI: China National Knowledge Infrastructure
Basic information of experts
This study invited 15 experts from different fields, including 6 cardiovascular clinicians, 1 clinical nutritionist, 1 clinical dietitian, 6 clinical nursing and management experts in cardiology and 1 rehabilitation therapist. The experts had work experience ranging from 11 to 27 years, with bachelor’s degree or above, and intermediate or above professional titles (Table 1).
Enthusiasm and authority of the experts
The Cr of the experts reflects the reliability of the consultation results. Cr is calculated based on the average of the experts’ judgment foundation (CA) and familiarity (CS) of the research plan. It is generally believed that when Cr ≥ 0.7, the consultation results have a high credibility, and the higher the score, the higher the credibility. The two rounds of Cr in this study were 0.87 and 0.89, respectively, indicating that the expert opinions in this study had a high degree of authority.
Degree of coordination of the expert opinions
After two rounds of consultation, the coefficient of variation CV for each round was between 0.00% and 29.67% (all < 0.25). In addition, the Kendall’s coefficient of concordance Kendall’s W for the first and second round questionnaires were 0.323 and 0.398, respectively, P < 0.05, indicating that the experts had a high degree of consensus on the evaluation results of the indicators, and the evaluation results were reliable.
Selection of indicators
In the first round of expert consultation, 4 items were modified, 3 items were deleted, and 3 items were added. (1) Modifications: The term “nutritional assessment” was revised to “nutritional screening and assessment”. The rationale for this change is that screening and assessment are distinct actions; patients are first subjected to nutritional screening upon admission, and if at risk of malnutrition, they proceed to a comprehensive nutritional assessment. The term “formation of a heart failure nutrition support team: cardiologists, geriatricians, heart failure nurse practitioners, dietitians, cardiac rehabilitators, and counselors form the team” was changed to “mainly by heart failure specialists and dietitians, in collaboration with critical care physicians, geriatricians, heart failure specialist nurses, and cardiac rehabilitation therapists to form a heart failure nutrition support team”. This modification was made to clarify the core members of the multidisciplinary team, facilitating decisive adjustments to the dynamic treatment plan. “Fluid management” was updated to “volume management”, as the former term tends to focus on the intake, infusion, and output of fluids, whereas “volume management” encompasses a broader concept including systemic and pulmonary circulatory volume loads. The “weight loss diet” was revised to “low-calorie diet”, with the reasoning that the former is subjectively aimed at reducing fat or body weight, while the latter is an objective dietary pattern controlling caloric intake due to excess energy and nutrition, aligning more closely with medical interventions. (2) Deletions: The recommendation to “reduce the intake of caffeinated beverages and alcohol for ADHF patients” was removed, as the consumption of coffee and alcohol is not applicable to clinical inpatients. “Cachexia enteral nutrition” was deleted because heart failure patients with cachexia were already excluded from the inclusion criteria, and the significance of nutritional support for patients who have progressed to cachexia remains debatable. The team “eating 30 g of unsalted nuts daily” was also removed, as the high fatty acid content in nuts contradicts the low-fat diet recommended for heart failure patients. (3) Additions: The inclusion of “non-pharmacological measures to alleviate symptoms of dry mouth and thirst” is proposed. The rationale is that patients with cardiac insufficiency commonly experience xerostomia and intense thirst, which contradicts the restrictions on fluid intake. It is recommended to employ non-pharmacological strategies to improve patient comfort and alleviate these symptoms. The creation of “standardized educational materials” is advised. This is due to the observed variability in the understanding and communication of nutritional education among different healthcare professionals. Standardized and unified health education is anticipated to significantly enhance the guidance provided to patients and their families. Furthermore, the outcome indicators focus on nutritional biochemical markers. Experts recommend the inclusion of “prealbumin (PAB)” and ”albumin (ALB)” in the “blood test report” to enhance the sensitivity of these indicators. After discussion by the project team, the experts’ suggestions were adopted.
In the second round of expert consultation, it was recommended to remove the term “plant-based diet”-a regimen predominantly composed of plant-derived foods, encompassing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts, and is often synonymous with a vegan diet [41, 42]. The reasons for this decision stems from clinical observations that plant-based diets frequently induce gastrointestinal bloating. This is particularly pertinent for patients with heart failure, who commonly experience gastrointestinal congestion, as such bloating can impede nutritional absorption. Furthermore, experts proposed an amendment to the “vassessment time within 24 hours”, suggesting it be “completed within the shift or 6 hours” to ensure prompt intervention for patients at nutritional risk. After discussion by the project team, these suggestions were adopted. Furthermore, an expert recommended the removal of “the assessment and supplementation of iron” from the protocol, citing its infrequent application in clinical practice. The research team, after reviewing and discussing relevant literature, concluded that iron deficiency can adversely affect the exercise capacity, quality of life, and functional status of patients with ADHF. Moreover, a report indicated that the prevalence of iron deficiency was 68.6% in male patients with heart failure, and even higher in females, at 75.3% [43]. After careful consideration of the AHA/ACC/HFSA 2022 guidelines [44] and the significance attributed to this indicator, the team has resolved not to incorporate this recommendation. After two rounds of expert consultation, the experts reached a consensus, and finally formed a nutrition support program for ADHF patients, including 4 primary indicators, 7 secondary indicators, and 24 tertiary indicators. The mean and coefficient of variation CV of the importance of each item are shown in Table 2.
Discussion
HF is a common cardiac syndrome. It is estimated that there are 26 million people with HF worldwide, of which about 4 million are in China [45, 46]. HF not only affects the quality of life and life expectancy of patients, but also brings huge economic burden to the health care system [47]. Data from the urban employee medical insurance in China show that HF patients in China are mainly middle-aged and elderly, and the hospitalization rate is increasing year by year, causing a heavy burden on public health in China [48, 49]. Malnutrition is a recognized risk factor for poor prognosis in patients with HF [50, 51]. The clinical manifestations of malnutrition may vary from loss of appetite and/or weight loss, to loss of muscle mass in sarcopenia with sarcopenia, to severe cardiac cachexia [52, 53]. To prevent such adverse outcomes associated with malnutrition, current clinical practice guidelines recommend initiating nutritional support during hospitalization of medical patients at risk for malnutrition [54, 55]. In 2020, the Japanese Heart Failure Society also issued a statement on nutritional management of HF patients, pointing out that nutritional intervention for HF patients, especially ADHF patients, is of great importance [56]. A study of 241 elderly patients with acute HF showed that moderate-to-severe malnutrition is an independent risk of death in patients with acute HF, and that correcting malnutrition is significant in improving the prognosis of HF and in reducing the rate of acute HF recurrence and mortality [57]. Another study also identified underweight status and malnutrition risk as direct predictors of in-hospital mortality among male HF patients [58]. When patients are malnourished, their immunity is low and they are prone to pulmonary infection. Besides, the guidelines for heart failure clearly indicate that infection is the main cause of recurrent acute heart failure [59], and some studies have shown that recurrent acute heart failure may be related to the deficiency of certain nutrients [60]. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor and manage the key nutrients.
This study was based on the relevant clinical guidelines and original literature for middle-aged and elderly ADHF patients, and the recommendation opinions and evidence were analyzed, traced and synthesized. Different types of literature were independently evaluated using the evaluation model of the Australian Joanna Briggs Institute Evidence-Based Health Care Center (2014) [61] to ensure that the evidence included was of high quality. The protocol was developed with the participation of multiple disciplines, and was accepted by the members of the implementation team from various disciplines, and was easy to be applied in clinical practice. The protocol was refined and improved through expert consultation. The experts consulted were from tertiary hospitals in Shanghai, Suzhou, and Anhui, covering various aspects of evidence-based practice, including clinical nursing staff, nursing management staff, clinical doctors, nutritionists, etc. All experts in this study had good disciplinary representation and academic authority, as well as rich clinical experience. The participation rates of the two rounds of expert consultation were 86.7% and 100%, respectively, both > 70%. Specific modification suggestions were proposed by eleven experts and were adopted, indicating that the experts participated actively, the dialectical thinking of the evidence-based expert group was exerted, and the scientificity of the protocol was ensured. In addition, the overall authority coefficients Cr of the two rounds of experts in this study were 0.87 and 0.89, respectively. The expert authority coefficient Cr was an important analysis indicator for the reliability of the results of the Delphi expert consultation method [62]. The higher the Cr value, the higher the authority of the expert [63]. Therefore, the experts sampled in this study had authority and representativeness, and the consultation results were highly reliable.
This study aims to develop a nutrition support therapy protocol based on clinical problem-oriented approach, which has important practical significance. In the process of protocol development, we adopted standardized assessment, implementation, and evaluation procedures, and provided continuous and systematic nutrition support for patients with recurrent acute heart failure from the aspects of volume management, energy management, dietary pattern, and nutrient support. The protocol mainly includes the following measures: First, volume management is to intervene in water intake and fluid replenishment precisely from the admission of the patient, to prevent the occurrence of circulatory congestion from the source, and to reduce the risk of recurrent heart failure. Recurrent acute heart failure is often caused by systemic and pulmonary congestion, and clinically treated with diuretics, coronary vasodilators, sedatives and other drugs. Second, energy management is to estimate the energy requirement reasonably according to the patient’s metabolic status and activity level, and to adjust the energy supply timely according to the monitoring results. Third, dietary pattern is to implement individualized therapeutic diet for different comorbidities, such as Mediterranean diet, DASH diet pattern, etc. Mounting evidence underscores the potential cardiovascular advantages of plant-based diets and dietary patterns, characterized by a high consumption of plant-derived foods and minimal intake of animal products [64]. However, considering that plant-based diets are clinically associated with gastrointestinal bloating—a condition prevalent in patients with heart failure, which can impede nutritional absorption—such diets have not been incorporated into the in-hospital nutritional support protocols for patients with ADHF. Finally, nutrient support is to measure the relevant nutrients regularly according to the patient’s nutrient deficiency and tolerance, and to supplement the deficient nutrients according to the doctor’s orders: high-quality protein, amino acids, unsaturated fatty acids, minerals (potassium, sodium, iron), coenzyme Q10, vitamins, dietary fiber, probiotics, etc. The protocol is based on the guidelines of various countries and combined with the actual situation in China, to optimize and improve the protocol to make it easier to implement. For example, the guidelines recommend that registered dietitians participate in the patient’s nutrition assessment and guidance throughout the process. However, there is a shortage of clinical dietitians in reality, so this study suggests that specialized nutrition nurses complete the task, and consult dietitians when necessary.
Besides, HF patients often have comorbidities such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia or diabetes, which affect the patient’s prognosis and quality of life. Frailty and sarcopenia are two prevalent comorbidities associated with HF, with estimated prevalences in elderly HF patients of 44.5% and 34.0%, respectively [65, 66]. Both conditions are linked to increased mortality and/or hospitalization rates among HF patients [67, 68]. It is postulated that HF, frailty, and sarcopenia share numerous pathophysiological traits, including metabolic dysregulation, systemic inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and elevated levels of interleukin-6 [69]. These endocrine and metabolic disturbances can lead to cardiac changes and a loss of muscle mass and function, creating a vicious cycle of disability. Due to the lack of sufficient evidence supporting the use of nutritional interventions to mitigate the risks of sarcopenia and frailty in HF patients, this study did not adjust the diet specifically for HF-related sarcopenia and frailty, which is a limitation of this research. Further trials are warranted to explore the effects of isolated or combined nutritional sources on muscle mass and physical performance in heart failure patients.
Conclusion
This study developed a nutrition support protocol for hospitalized elderly patients with ADHF, which includes four aspects: team organization and management, nutrition screening and assessment, nutrition intervention measures, and outcome evaluation. The expert consultation was conducted by using the Delphi method, which verified the rationality and scientific basis of the protocol. The research group will further conduct clinical controlled trials to verify the effectiveness and sensitivity of the protocol, and further improve the protocol content according to the actual results, to make it more applicable to clinical practice. In addition, nutrition support also requires the cooperation of the patients and their families, and the nutrition guidance for the patients and their families also needs to be paid attention to in the future.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, Burri H, Butler J, Čelutkienė J, Chioncel O, et al. 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(36):3599–726.
Arrigo M, Jessup M, Mullens W, Reza N, Shah AM, Sliwa K, Mebazaa A. Acute heart failure. Nat Reviews Disease Primers. 2020;6(1):16.
Joseph SM, Cedars AM, Ewald GA, Geltman EM, Mann DL. Acute decompensated heart failure: contemporary medical management. Tex Heart Inst J. 2009;36(6):510.
Peacock W, Hollander J, Diercks D, Lopatin M, Fonarow G, Emerman C. Morphine and outcomes in acute decompensated heart failure: an ADHERE analysis. Emerg Med J. 2008;25(4):205–9.
Masoudi FA, Havranek EP, Krumholz HM. The burden of chronic congestive heart failure in older persons: magnitude and implications for policy and research. Heart Fail Rev. 2002;7:9–16.
Wang C-C, Chang H-Y, Yin W-H, Wu Y-W, Chu P-H, Wu C-C, Hsu C-H, Wen M-S, Voon W-C, Lin W-S. TSOC-HFrEF registry: a registry of hospitalized patients with decompensated systolic heart failure: description of population and management. Acta Cardiol Sinica. 2016;32(4):400.
Mentz RJ, Felker GM. Noncardiac comorbidities and acute heart failure patients. Heart Fail Clin. 2013;9(3):359–67.
Alalawi H, Fida HL, Bokhary OA, Alhuzali MA, Alharbi AF, Alhodian FY, Alsahari MR, Siddiqui AM, Alhuzali Sr M, Alhodian FY. Demographics and characteristics of acutely decompensated heart failure (ADHF) patients in a Tertiary Care Center in Saudi Arabia. Cureus 2023, 15(3).
Kobayashi M, Hayashi M, Yamada R, Ishiguro T, Fujiwara W, Ishii H, Naruse H, Watanabe E, Ozaki Y, Izawa H. Predictors of in-hospital mortality in elderly patients with heart failure treated with tolvaptan. Fujita Med J. 2023;9(2):80–3.
Sze S, Zhang J, Pellicori P, Morgan D, Hoye A, Clark AL. Prognostic value of simple frailty and malnutrition screening tools in patients with acute heart failure due to left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Clin Res Cardiol. 2017;106:533–41.
Yoshihisa A, Kanno Y, Watanabe S, Yokokawa T, Abe S, Miyata M, Sato T, Suzuki S, Oikawa M, Kobayashi A. Impact of nutritional indices on mortality in patients with heart failure. Open Heart. 2018;5(1):e000730.
Kałużna-Oleksy M, Krysztofiak H, Sawczak F, Kukfisz A, Szczechla M, Soloch A, Cierzniak M, Szubarga A, Przytarska K, Dudek M et al. Sex differences in the nutritional status and its association with long-term prognosis in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a prospective cohort study. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2024.
Heidenreich P, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen L, Byun J, Colvin M, Deswal A, Drazner M, Dunlay S, Evers L. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure. J Card Fail. 2022;28(5):e1–167.
Hirose S, Matsue Y, Kamiya K, Kagiyama N, Hiki M, Dotare T, Sunayama T, Konishi M, Saito H, Saito K. Prevalence and prognostic implications of malnutrition as defined by GLIM criteria in elderly patients with heart failure. Clin Nutr. 2021;40(6):4334–40.
Yasumura K, Abe H, Iida Y, Kato T, Nakamura M, Toriyama C, Nishida H, Idemoto A, Shinouchi K, Mishima T, et al. Prognostic impact of nutritional status and physical capacity in elderly patients with acute decompensated heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2020;7(4):1801–8.
Association, HfPCoCMD. Committee NBoCHFS, Cardiomyopathy EBotCJoHFa: Expert consensus on ion management of heart failure patients in China. Chin J Heart Fail Cardiomyopathy. 2020;04(1):16–31.
Cardiovascular Diseases Group GSoCMA, elderly CECoDaTochfit. Chinese Expert Consensus on diagnosis and treatment of Chronic Heart failure in the Elderly (2021). Chin J Geriatr. 2021;40(5):550–61.
Chen Y, Zhu J, Pei H, Pan L, Peng Z. Expert consensus on construction and management of emergency acute heart failure unit in China. Chin J Crit Care Med. 2019;39(6):532–7.
Chiavaroli L, Viguiliouk E, Nishi SK, Blanco Mejia S, Rahelić D, Kahleová H, Salas-Salvadó J, Kendall CW, Sievenpiper JL. DASH dietary pattern and cardiometabolic outcomes: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Nutrients. 2019;11(2):338.
China International Exchange and Promotive Association for Medical and Health, Care EMB, Association EMBCM, Chinese Medical Doctor, Association EPB, Committee PEMP. Chinese guidelines for emergency management of acute heart failure (2022). Chin J Crit Care Med, 42(8):648–70.
Cicero AF, Colletti A, von Haehling S, Vinereanu D, Bielecka-Dabrowa A, Sahebkar A, Toth PP, Reiner Ž, Wong ND, Mikhailidis DP. Nutraceutical support in heart failure: a position paper of the international lipid Expert Panel (ILEP). Nutr Res Rev. 2020;33(1):155–79.
Hollenberg SM, Warner Stevenson L, Ahmad T, Amin VJ, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Davis LL, Drazner MH, Kirkpatrick JN, Peterson PN. 2019 ACC expert consensus decision pathway on risk assessment, management, and clinical trajectory of patients hospitalized with heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(15):1966–2011.
Huixiu H, Chao S, Lingling C, Weijie X, Lei W, Xia W. Summary of the best evidence on the use of discharge preparation services in patients with chronic heart failure. Chin Nurs Manage. 2020;20(10):1557–63.
Jaarsma T, Hill L, Bayes-Genis A, La Rocca HPB, Castiello T, Čelutkienė J, Marques‐Sule E, Plymen CM, Piper SE, Riegel B. Self‐care of heart failure patients: practical management recommendations from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. 2021;23(1):157–74.
Jurgens CY, Goodlin S, Dolansky M, Ahmed A, Fonarow GC, Boxer R, Arena R, Blank L, Buck HG, Cranmer K. Heart failure management in skilled nursing facilities: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association and the Heart Failure Society of America. Circulation: Heart Fail. 2015;8(3):655–87.
Li Q, Li Z, Kang X, Lv R, Zhang F. Practice guidelines for the nursing care of adults with Acute Heart failure. Chin Nurs Manage 2016(9):1179–88.
Marcondes-Braga FG, Moura LAZ, Issa VS, Vieira JL, Rohde LE, Simões MV, Fernandes-Silva MM, Rassi S, Alves SMM, Albuquerque DC, et al. Emerging topics update of the Brazilian heart failure Guideline – 2021. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2021;116(6):1174–212.
McDonald M, Virani S, Chan M, Ducharme A, Ezekowitz JA, Giannetti N, Heckman GA, Howlett JG, Koshman SL, Lepage S, et al. CCS/CHFS heart failure guidelines update: defining a New Pharmacologic Standard of Care for Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Can J Cardiol. 2021;37(4):531–46.
Pranata R, Tondas AE, Yonas E, Vania R, Yamin M, Chandra A, Siswanto BB. Differences in clinical characteristics and outcome of de novo heart failure compared to acutely decompensated chronic heart failure–systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Cardiol. 2021;76(4):410–20.
Prevention CD, Prevention T, Association, CSoCoCM. Association TCoCMD: Chinese guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Zhonghua Xin xue guan bing za zhi. 2020;48(12):1000–38.
Qiujin J, Shichao L, Junping Z. Systematic review of gut microbiota changes in patients with chronic heart failure. Chin J Cardiol. 2021;49(10):1012–9.
Sun G, Yang Y, Liu L, Wang S, Guo C, Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Yang L. Nutrient supplement use scientific consensus. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica. 2018;40(6):521–5.
Tsutsui H, Ide T, Ito H, Kihara Y, Kinugawa K, Kinugawa S, Makaya M, Murohara T, Node K, Saito Y, et al. JCS/JHFS 2021 Guideline focused update on diagnosis and treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart failure. J Card Fail. 2021;27(12):1404–44.
Vest AR, Chan M, Deswal A, Givertz MM, Lekavich C, Lennie T, Litwin SE, Parsly L, Rodgers JE, Rich MW. Nutrition, obesity, and cachexia in patients with heart failure: a consensus statement from the Heart Failure Society of America Scientific Statements Committee. J Card Fail. 2019;25(5):380–400.
Wang H, Liang Y. Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure 2018. Chin J Cardiol. 2018;46(10):760–89.
Wei J, Zhu M, Cui H, Wang Y, Cao W, Chen W, Li Z, Liu X, Jiang H. Guidelines for Parenteral Enteral Nutrition in Elderly patients in China (2020). Chin J Geriatr. 2020;39(2):119–32.
Xu Z, Wei W, Xiaojing Z, Li G, Lin J, Lijuan Y. Summary of the best evidence for the management of access volume in patients with chronic heart failure. Chin J Nurs. 2020;55(3):456–61.
Yamamoto K, Tsuchihashi-Makaya M, Kinugasa Y, Iida Y, Kamiya K, Kihara Y, Kono Y, Sato Y, Suzuki N, Takeuchi H. Japanese heart failure society 2018 scientific statement on nutritional assessment and management in heart failure patients. Circ J. 2020;84(8):1408–44.
Youn JC, Kim D, Cho JY, Cho DH, Park SM, Jung MH, Hyun J, Cho HJ, Park SM, Choi JO, et al. Korean Society of Heart Failure Guidelines for the management of Heart failure: treatment. Int J Heart Fail. 2023;5(2):66–81.
Zhaoyu X, Hua K, Suyun L, Haiyan H, Hua YJ, Jianping C, Xiaowei J. Summary of the best evidence for oral nutritional supplementation in perioperative patients. Chin J Nurs 2021.
Satija A, Hu FB. Plant-based diets and cardiovascular health. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2018;28(7):437–41.
Association P-BF. Certified Plant-Based Claim Certification Program. California, USA 2019.
Cohen-Solal A, Damy T, Terbah M, Kerebel S, Baguet JP, Hanon O, Zannad F, Laperche T, Leclercq C, Concas V, et al. High prevalence of iron deficiency in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2014;16(9):984–91.
Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, Deswal A, Drazner MH, Dunlay SM, Evers LR. 2022 ACC/AHA/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure. J Card Fail. 2022;28(5):e1–167.
Hao G, Wang X, Chen Z, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Wei B, Zheng C, Kang Y, Jiang L, Zhu Z, et al. Prevalence of heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction in China: the China Hypertension Survey, 2012–2015. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019;21(11):1329–37.
Smith SC Jr., Fonarow GC, Zhao D. Measuring and improving the quality of heart failure care globally. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(1):e1918642.
LeMond L, Allen LA. Palliative care and hospice in advanced heart failure. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2011;54(2):168–78.
Wang H, Chai K, Du M, Wang S, Cai JP, Li Y, Zeng P, Zhu W, Zhan S, Yang J. Prevalence and incidence of heart failure among urban patients in China: A National Population-based analysis. Circ Heart Fail. 2021;14(10):e008406.
Hua Wang, Li Y. Chinese Expert Consensus on Comprehensive Management of patients with worsening heart failure 2022. Chin Circulation J. 2022;37(03):215–25.
Bonilla Palomas JL, Gámez López AL, Moreno Conde M, López Ibáñez MC, Castellano García P, Ráez Ruiz CJ. Ruíz Quirós R, Ramiro Ortega E: [Impact of malnutrition on long-term mortality in outpatients with chronic heart failure]. Nutr Hosp. 2017;34(5):1382–9.
Martín-Sánchez FJ, Cuesta Triana F, Rossello X, Pardo García R, Llopis García G, Caimari F, Vidán MT, Ruiz Artacho P, Del González J, Llorens P, et al. Effect of risk of malnutrition on 30-day mortality among older patients with acute heart failure in Emergency Departments. Eur J Intern Med. 2019;65:69–77.
Loncar G, Fülster S, von Haehling S, Popovic V. Metabolism and the heart: an overview of muscle, fat, and bone metabolism in heart failure. Int J Cardiol. 2013;162(2):77–85.
Vest AR, Chan M, Deswal A, Givertz MM, Lekavich C, Lennie T, Litwin SE, Parsly L, Rodgers JE, Rich MW, et al. Nutrition, obesity, and Cachexia in patients with heart failure: a Consensus Statement from the Heart Failure Society of America Scientific Statements Committee. J Card Fail. 2019;25(5):380–400.
Anker SD, John M, Pedersen PU, Raguso C, Cicoira M, Dardai E, Laviano A, Ponikowski P, Schols AM, Becker HF, et al. ESPEN guidelines on Enteral Nutrition: Cardiology and pulmonology. Clin Nutr. 2006;25(2):311–8.
Anker SD, Laviano A, Filippatos G, John M, Paccagnella A, Ponikowski P, Schols AM. ESPEN guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: on cardiology and pneumology. Clin Nutr. 2009;28(4):455–60.
Yamamoto K, Tsuchihashi-Makaya M, Kinugasa Y, Iida Y, Kamiya K, Kihara Y, Kono Y, Sato Y, Suzuki N, Takeuchi H, et al. Japanese heart failure society 2018 Scientific Statement on Nutritional Assessment and Management in Heart failure patients. Circ J. 2020;84(8):1408–44.
Qin Wang H, Gong S, Liao X, Zheng G, Sun, Jinping Tian, Li X. Impact of Nutritional Status on all-cause death in Elderly hospitalized patients with Acute Heart failure. Chin Circulation J. 2020;35(12):1235–40.
Kwaśny A, Uchmanowicz I, Juárez-Vela R, Młynarska A, Łokieć K, Czapla M. Sex-related differences in the impact of nutritional status on in-hospital mortality in heart failure: a retrospective cohort study. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2023;23(2):176–87.
Chen F, Deng Y, Li Y, Mi Y, Shang D, Song J, Wang LSX, Wen W. Guideline for emergency management of acute heart failure in China (2022). J Clin Emerg. 2022;23(08):519–47. Jihong Xing.
Miller TL, Neri D, Extein J, Somarriba G, Strickman-Stein N. Nutrition in pediatric cardiomyopathy. Prog Pediatr Cardiol. 2007;24(1):59–71.
Zhang H, Tian X, Bian W, Li Q, Jin Y, Zeng X, Song G. Brief introduction of the Joanna Briggs Institute. Chin J Evidence-Based Med. 2016;16(12):1477–80.
Wang L, Li B. Application of delphi method in establishing survey index system of medical equipment post-sales service satisfaction. Chin Med Equip. 2012;27(3):88–90.
Chen Y-y, Ni M, Hu X-z. The selection of public welfare evaluation indicators for public medical institutions is based on Delphi expert consultation method [J]. Health Policy Res China. 2012;5(1):6–10.
Key TJ, Appleby PN, Rosell MS. Health effects of vegetarian and vegan diets. Proc Nutr Soc. 2006;65(1):35–41.
Denfeld QE, Winters-Stone K, Mudd JO, Gelow JM, Kurdi S, Lee CS. The prevalence of frailty in heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2017;236:283–9.
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Ni W, Yuan X, Zhang H, Li P, Xu J, Zhao Z. Sarcopenia in heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. ESC Heart Fail. 2021;8(2):1007–17.
Zhang Y, Yuan M, Gong M, Tse G, Li G, Liu T. Frailty and Clinical outcomes in Heart failure: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2018;19(11):1003–e10081001.
Konishi M, Kagiyama N, Kamiya K, Saito H, Saito K, Ogasahara Y, Maekawa E, Misumi T, Kitai T, Iwata K, et al. Impact of Sarcopenia on prognosis in patients with heart failure with reduced and preserved ejection fraction. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2021;28(9):1022–9.
Valdiviesso R, Amaral TF, Moreira E, Sousa-Santos AR, Fernandes M, Aguiar MJV, Martins S, Azevedo LF, Fernandes L, Silva-Cardoso J, et al. Associations of medicine use and ejection fraction with the coexistence of frailty and sarcopenia in a sample of heart failure outpatients: a cross-sectional study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023;23(1):594.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the experts for their effort in participating in the study.
Funding
This study was supported by Shanghai key medical specialty (No. ZK2019C03) and Shanghai Jiading District Central Hospital young and middle-aged backbone training (No. ZQN202103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XDX and RDM: study design, performing the experiments, critical revision of the manuscript. LYL, ZF, DX and TJP: performing the experiments, statistical analysis, interpretation of data, drafting the manuscript. XQ, ZMH and ZW: study design, performing the experiments, interpretation of data, drafted the manuscript. All authors gave their final approval.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhu, F., Ren, D. et al. Establishment of in-hospital nutrition support program for middle-aged and elderly patients with acute decompendated heart failure. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 24, 259 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-024-03887-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-024-03887-y