Abstract
Background
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is a common complication after cardiac surgery. There are no definite optimal glycemic threshold for pediatric patients receiving open-heart surgery with CPB. The study aimed to investigate the optimal cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) glucose in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.
Methods
We enrolled children with congenital heart disease who underwent surgical repair between June 2012 and December 2020. We included only patients who underwent cardiac surgery with CPB. The primary outcome was severe SIRS. A two-piece-wise regression model was applied to examine threshold effect of CPB glucose on severe SIRS.
Results
A total of 7350 patients were enrolled in the present study, of whom 3895 (52.99%) are female. After potential confounders were adjusted, non-linear relationship was detected between CPB glucose and severe SIRS, whose turning point was 8.1. With CPB glucose < 8.1 mmol/L, the estimated dose–response curve was consistent with a horizontal line. However, the prevalence of severe SIRS increased with increasing glucose up to the turning point (Glucose > 8.1 mmol/L); the odds ratio (OR) of the Glucose was 1.35 (95% CI 1.21, 1.50).
Conclusions
The present study indicates the association of CPB glucose with inflammatory response after pediatric cardiac surgery. The patients might have the best outcomes with the optimal CPB glucose no more than 8.1 mmol/L.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common birth defect occurring in approximately 1% of all live births and affecting millions of individuals internationally [1]. Although surgical techniques had achieved massive breakthroughs, postoperative morbidity and mortality among infants and young children remain relatively high [2]. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) was a frequent complication after pediatric congenital heart surgery; it affects nearly one third of children and prolongs PICU stay significantly [3]. Therefore, identifying modifiable risk factors that could lower the incidence of perioperative SIRS is important for sustained improvement in clinical outcomes of these patients.
Perioperative hyperglycemia is related to cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) [4]. Several clinical studies suggest that hyperglycemia is associated with postoperative morbidity in patients who undergo cardiac surgery [5,6,7]. The perioperative period for congenital heart surgery can be challenging because of the systemic inflammatory response and endocrine metabolic stress associated with these procedures [8].
Improved glycemic control at initiation of CPB in adult patients undergoing cardiac surgery was associated with reduced 30-day mortality [9]. Nevertheless, there are no definite optimal glycemic threshold or reference interval for pediatric patients receiving open-heart surgery with CPB. In this study, we aimed to investigate the association of CPB glucose with severe SIRS in pediatric patients receiving open-heart surgery with CPB. And according to this glycemic threshold, we can reduce the incidence of SIRS and related complications by optimizing glycemic management during CPB.
Methods
Research population
This respective cohort study was conducted in pediatric patients who underwent cardiac surgery at TEDA International Cardiovascular Hospital. We included all patients who underwent cardiac surgery with arrested-heart CPB between June 2012 and December 2020. We excluded patients undergoing a cardiac procedure on a beating heart or required preoperative renal-replacement therapy, mechanical ventilatory support, or mechanical circulatory support. We also excluded those who had missing CPB glucose data or outcome. The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee (Internal Review Board) of TEDA International Cardiovascular Hospital. All the procedures performed in this study involving human participants were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in 2013). All data collection was done anonymously. The requirement of personal consent for this retrospective analysis was waived by the Ethics Committee (Internal Review Board) of TEDA International Cardiovascular Hospital, so there is no confusion regarding prospective consent.
Research exposure
All blood glucose measurements during cardiopulmonary bypass were collected.
In this study, maximum CPB arterial glucose values were retrieved from a local online hospital information system for analysis and further confirmed by independent manual examination of extracorporeal circulation records.
Research covariates
For each patient, those baseline and clinical characteristics, including Gender, Age of surgery (month), Age category of surgery, Body surface area (m2), BMI (kg/m2), Surgery year, Preoperative hemoglobin, Residence altitude, Hemodynamic pathology, Extracardiac malformations, Genetic anomalies, Clinical pathway implementation, Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), Aorta crossclamp time (min), Red Cell need (U) during CPB, Steroids need, Glucose infusion, Insulin need, Aristotle complexity score and level were collected.
Research outcome
The primary outcome variable was severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), which we defined as the time of onset of SIRS from admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), postoperative day 5, or discharge [10]. According to the definition of pediatric SIRS or sepsis, as well as the diagnostic criteria used clinically in our center, severe SIRS is defined by the satisfaction of four criteria below: (1) Body temperature over 38 or under 36 degrees Celsius; (2) Mean heart rate > 2 standard deviations (SD) beyond normal for age; (2) Mean respiratory rate > 2 SD above normal for age; (3) Elevated or reduced age-specific leukocyte count or > 10% immature neutrophils [3, 11, 12]. Secondary outcomes included SIRS length of mechanical ventilation, ICU stay, and all-cause mortality at 30 days postoperatively.
Statistical analysis
All analyses were performed using EmpowerStats (http://www.empowerstats.com). Baseline and clinical materials were grouped by glucose (8.1 mmol/L). Categorical variables are presented as percentages. Continuous variables are reported as medians with interquartile range (IQR). Comparisons between groups were performed using χ2 testing for categorical variables and Kruskal–Wallis testing for continuous variables. Univariate linear regression model was used to evaluate the associations between CPB glucose and severe SIRS. We used used generalized additive model (GAM) to identify the non-linear relationship between glucose and severe SIRS. And we applied a two-piece-wise regression model to examine threshold effect of CPB glucose on severe SIRS. To examine the cumulative incidence of severe SIRS by age at surgery, we used Kaplan–Meier estimates, using age as the time scale [13]. P-value < 0.05 was defined as statistically significant.
Results
Patient characteristics and primary outcome
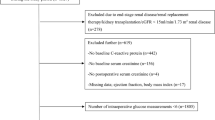
A total of 7350 patients were enrolled in the present study (Fig. 1), of whom 5821 (78.20%) patients had CPB glucose less than 8.1 mmol/L. 3895 (52.99%) are female, 37.5 months (IQR 18.91–69.83) was the median age at the time of surgery, and the median glucose during CPB was 6.40 (IQR 5.3–7.8) mmol/L. Baseline characteristics of patients with low (< 8.1 mmol/L) and high (> 8.1 mmol/L) glucose are shown in Table 1. Low glucose patients were older and congenital heart disease clinical pathways were more frequently implemented (Table 1).
Low glucose patients had a higher frequency of, genetic anomalies and pulmonary hypertension, but had a lower frequency of hemodynamic pathology in comparison to high glucose patients (Table 1). There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of extracardiac malformations (Table 1). The overall incidence of severe SIRS was 21.77%, and the incidence of severe SIRS in low glucose patients and high glucose patients was 17.23% and 39.05% (Table 1).
Secondary outcome
High glucose patients had a significantly longer postoperative length of mechanical ventilation and ICU stay in comparison to low glucose patients (P < 0.01) and a higher incidence of SIRS (P = 0.005) and inpatient mortality (P < 0.001).
Univariate analysis
The results of univariate analysis were shown in Table 2. The results of univariate analysis showed that age of surgery, body surface area, preoperative hemoglobin, cyanotic, clinical pathway implementation, pulmonary arterial hypertension, aorta crossclamp time, red cell need, steroids need, insulin need, aristotle complexity score, aristotle complexity level were correlated with higher severe SIRS. We also found that gender, age category of surgery, BMI, residence altitude, extracardiac malformations, genetic anomalies, were not associated with severe SIRS.
Association of continuous glucose with outcome
Because glucose was continuous variable, the analyses of non-linear relationship are necessary. In the present study (Fig. 2), we found that the relationship between glucose and severe SIRS was non-linear (after adjusting gender, age of surgery, age category of surgery, body surface area, BMI, surgery year, preoperative hemoglobin, residence altitude, hemodynamic pathology, extracardiac malformations, genetic anomalies, clinical pathway implementation, pulmonary arterial hypertension, aorta crossclamp time, red cell need, steroids need glucose infusion, insulin need, aristotle complexity score, aristotle complexity level).
The relationship between CPB glucose and risk probability of severe SIRS. A gradual J-shaped risk curve among total patients. Red dotted lines represent the spline plots of CPB glucose and blue dotted lines represent the 95% CIs of the spline plots. Adjusted for Gender, Age of surgery (month), Age category of surgery, Body surface area (m2), BMI (kg/m2), Surgery year, Preoperative hemoglobin, Residence altitude, Hemodynamic pathology, Extracardiac malformations, Genetic anomalies, Clinical pathway implementation, pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), Aorta crossclamp time (min), Red Cell need (U), Steroids need, Glucose infusion, Insulin need, Aristotle complexity score, Aristotle complexity level
By two-piece-wise linear regression model, we calculated the turning point was 8.1. With a Glucose < 8.1 mmol/L, the estimated dose–response curve was consistent with a horizontal line. However, the prevalence of severe SIRS increased with increasing glucose up to the turning point (Glucose > 8.1 mmol/L); the odds ratio (OR) of the Glucose was 1.35 (1.21, 1.50) < 0.0001 (Table 3). The threshold of glucose would result in a risk probability of roughly0.37 or greater for severe SIRS (Table 3).
Severe SIRS-free probability by age
Figure 3 shows the severe SIRS-free probability by age separately for overall patients. For all patients, this age gradient was steeper for those with glucose > 8.1 mmol/L, and the patients with glucose < 8.1 mmol/L have the lower risk probability (P < 0.001) in overall patients (Fig. 3).
Discussion
This study examines the association between CPB glucose and postoperative severe SIRS in the pediatric cardiac surgical population. These data show that there is an association between an CPB glucose level of greater than 8.1 mmol/L and the development of a postoperative severe SIRS. In our study, Non-linear relationship was detected between CPB glucose and severe SIRS, whose turning point was 8.1 mmol/L. The probability of postoperative severe SIRS increased with elevated CPB glucose up to the turning point (Glucose = 8.1 mmol/L). Using the overall rate of severe SIRS as reference, CPB glucose threshold of SIRS might lower 8.1 mmol/L, which conduce to management of extracorporeal circulation.
Previous studies have suggested that the optimal postoperative glycemic range in children undergoing complex congenital heart surgery was likely to be 6.1–7 mmol/L [9]. Perioperative mean glucose ≤ 8.3 mmol/L may decreased adverse events in infants receiving open cardiac surgery [14]. The recommended threshold is remarkably near to the level at which our data showed significance for the development of postoperative severe SIRS. In the present study (Fig. 2), we found that the relationship between CPB glucose and severe SIRS was non-linear (after adjusting gender, age of surgery, age category of surgery, body surface area, BMI, surgery year, preoperative hemoglobin, residence altitude, hemodynamic pathology, extracardiac malformations, genetic anomalies, clinical pathway implementation, pulmonary arterial hypertension, aorta crossclamp time, red cell need, steroids need, glucose infusion, insulin need, aristotle complexity score, aristotle complexity level). This indicated that CPB glucose was related to severe SIRS after pediatric cardiac surgery. Overall, there was a gradual J-shaped risk curve among total patients (Fig. 2). Previous studies have examined the effect of hyperglycemia on morbidity and mortality in the pediatric population [15]. Intraoperative hyperglycemia was also related to worse hospital outcomes after cardiac surgery, including death [16]. A study showed that strict glycemic control significantly decreased morbidity and mortality in critically ill children [17]. Strict intraoperative and postoperative glycemic control protects the myocardium and reduces the inflammatory response in neonatal cardiac surgery [8].
In the current study, The probability of severe SIRS significantly increased with elevated CPB glucose up to the turning point (Glucose = 8.1 mmol/L). Furthermore, We examined the cumulative incidence of severe SIRS by age at surgery and found that the patients with glucose < 8.1 mmol/L had the lower risk probability (P < 0.001) in overall patients (Fig. 3). These results highlighted that a significant take away maybe to maintain on CPB glucose < 8.1 mmol/L for all patients. Our study indicates that high glucose patients were associated with significantly greater longer postoperative ventilation and ICU stay, and a higher incidence of inpatient mortality in comparison with those low glucose patients, highlighting reasonable CPB glucose control for CHD children in the management of extracorporeal circulation.
Limitations of the study
Our study has several potential limitations. The small set of variables available for covariate-adjusted analyses leaves the possibility of residual confounding. It is the highest arterial glucose that we selected for association analysis in our study that may not be comprehensive enough to reveal the clinical significance of glucose in postoperative inflammatory responses, so further study using the average arterial glucose may more reasonable. This study only studied blood glucose during extracorporeal circulation, and further studies should be conducted in conjunction with postoperative blood glucose.
Conclusion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the optimal CPB glucose in pediatric cardiac surgery. Our study provides evidence supporting that patients might have the best outcomes with the optimal CPB glucose no more than 8.1 mmol/L. These findings can promote to management of CPB glucose.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its Additional file 1.
Abbreviations
- CHD:
-
Congenital heart disease
- CPB:
-
Cardiopulmonary bypass
- SIRS:
-
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- PAH:
-
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- ICU:
-
Intensive care unit
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- SD:
-
Indicated mean
- CI:
-
Confidence Interval
References
Kruszka P. Beaton A The state of congenital heart disease. Am J Med Genet C Sem Med Genet. 2020;184(1):5–6.
O’Brien SM, Clarke DR, Jacobs JP, Jacobs ML, Lacour-Gayet FG, Pizarro C, Welke KF, Maruszewski B, Tobota Z, Miller WJ, et al. An empirically based tool for analyzing mortality associated with congenital heart surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;138(5):1139–53.
Boehne M, Sasse M, Karch A, Dziuba F, Horke A, Kaussen T, Mikolajczyk R, Beerbaum P, Jack T. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome after pediatric congenital heart surgery: Incidence, risk factors, and clinical outcome. J Card Surg. 2017;32(2):116–25.
Doenst T, Wijeysundera D, Karkouti K, Zechner C, Maganti M, Rao V, Borger MA. Hyperglycemia during cardiopulmonary bypass is an independent risk factor for mortality in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;130(4):1144.
Gandhi GY, Nuttall GA, Abel MD, Mullany CJ, Schaff HV, Williams BA, Schrader LM, Rizza RA, McMahon MM. Intraoperative hyperglycemia and perioperative outcomes in cardiac surgery patients. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80(7):862–6.
Yates AR, Dyke PC 2nd, Taeed R, Hoffman TM, Hayes J, Feltes TF, Cua CL. Hyperglycemia is a marker for poor outcome in the postoperative pediatric cardiac patient. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2006;7(4):351–5.
Matsumoto S, Omiya H, Fujinaka W, Morimatsu H. Association between intraoperative hyperglycemia and postoperative end-organ dysfunctions after cardiac surgery: a retrospective observational study. J Anesth. 2021;36:174–84.
Vlasselaers D, Mesotten D, Langouche L, Vanhorebeek I, van den Heuvel I, Milants I, Wouters P, Wouters P, Meyns B, Bjerre M, et al. Tight glycemic control protects the myocardium and reduces inflammation in neonatal heart surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;90(1):22–9.
Polito A, Thiagarajan RR, Laussen PC, Gauvreau K, Agus MS, Scheurer MA, Pigula FA, Costello JM. Association between intraoperative and early postoperative glucose levels and adverse outcomes after complex congenital heart surgery. Circulation. 2008;118(22):2235–42.
Liu H, Hu YJ, Zheng SQ, Chen T, Zeng ZH, Wu DD, Zhao S, Zeng B, Liu ZG, Shao YF. Effect of perfusate oxygenation on inflammatory response in congenital heart disease children from low versus high altitude. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;161(6):2180–90.
Chakraborty RK, Burns B. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome. In: StatPearls. edn. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing LLC; 2022.
Menon K, Schlapbach LJ, Akech S, Argent A, Chiotos K, Chisti MJ, Hamid J, Ishimine P, Kissoon N, Lodha R, et al. Pediatric sepsis definition-a systematic review protocol by the pediatric sepsis definition taskforce. Crit Care Explor. 2020;2(6):e0123.
Qizilbash N, Gregson J, Johnson ME, Pearce N, Douglas I, Wing K, Evans SJW, Pocock SJ. BMI and risk of dementia in two million people over two decades: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3(6):431–6.
Song L, Fan D, Cun L, Jinping L, Ju Z, Zhengyi F. Effects of peri-operative glucose levels on adverse outcomes in infants receiving open-heart surgery for congenital heart disease with cardiopulmonary bypass. Perfusion. 2011;26(2):133–9.
Moorthy V, Sim MA, Liu W, Chew STH, Ti LK. Risk factors and impact of postoperative hyperglycemia in nondiabetic patients after cardiac surgery: a prospective study. Medicine. 2019;98(23):e15911.
Shah NJ, Leis A, Kheterpal S, Englesbe MJ, Kumar SS. Association of intraoperative hyperglycemia and postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery: a multicenter retrospective study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020;20(1):106.
Vlasselaers D, Milants I, Desmet L, Wouters PJ, Vanhorebeek I, van den Heuvel I, Mesotten D, Casaer MP, Meyfroidt G, Ingels C, et al. Intensive insulin therapy for patients in paediatric intensive care: a prospective, randomised controlled study. Lancet. 2009;373(9663):547–56.
Acknowledgements
Thanks for the funding of this study from the Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Construction Project of Tianjin, China.
Funding
This work was supported by TEDA International Cardiovascular Hospital Internal Grant [2020-YJSJJ-01]. The funder had no role in the design of the study; the analysis and interpretation of the data; preparation or review of the manuscript and, decision to submit for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z-ZH, L-ZG and L-XC conceived the study. Z-HZ, Y-XY, L-ZG and L-XC planned the study and contributed to data collection. L-ZG, Z-HZ, L-XC contributed to data analysis. Z-HZ, Y-XY, and L-ZG contributed to writing and preparation of the manuscript. All authors have reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee (Internal Review Board) of TEDA International Cardiovascular Hospital. All the procedures performed in this study involving human participants were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in 2013). All data collection was done anonymously. The requirement of personal consent for this retrospective analysis was waived by the Ethics Committee (Internal Review Board) of TEDA International Cardiovascular Hospital, so there is no confusion regarding prospective consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1
. Data source.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, ZH., Yu, XY., Liu, XC. et al. Effect of CPB glucose levels on inflammatory response after pediatric cardiac surgery. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 22, 222 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-022-02667-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-022-02667-w