Abstract
Background
We sought to evaluate the effect of mild hypercapnia on brain tissue oxygen tension (Pbto2) and diffusion limitation (impaired ability of oxygen extraction) in a porcine post asphyxial cardiac arrest model.
Methods
In 16 Bama pigs, asphyxial cardiac arrest was induced by endotracheal tube clamping and remained untreated for another 4 min. After return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), animals were randomly assigned to mild hypercapnia (end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2): 45 ~ 50 mmHg) and normocapnia (EtCO2: 35 ~ 40 mmHg) groups for 12 h. Intracranial pressure (ICP), Pbto2, and brain tissue temperature were invasively measured by multimodality monitors. Blood gas analysis, neuron specific enolase (NSE), and S100β were tested at baseline, ROSC 1 h, 6 h, and 12 h. Generalized mixed model with a compound symmetry covariance matrix was used to compare the time-variables of the two groups.
Results
Twelve (75%) pigs had ROSC and 11 pigs survived for the study period, with 6 pigs in mild hypercapnia group and 5 in the normocapnia group. The mean EtCO2 in the mild hypercapnia was significantly higher than normocapnia group (48 vs 38 mmHg, p < 0.001). Compared with normocapnia, mild hypercapnia group had higher Pbto2 (p < 0.001), slightly higher mean arterial pressure (p = 0.012) and ICP (p = 0.009). There were no differences in cerebral perfusion pressure (p = 0.106), gradient of partial pressure of jugular venous bulb oxygen (Pjvo2) and Pbto2 (p = 0.262), difference of partial pressure of jugular venous CO2 and arterial CO2 (p = 0.546), cardiac output (p = 0.712), NSE (p = 0.822), and S100β (p = 0.759) between the two groups.
Conclusions
Short term mild hypercapnia post-resuscitation could improve Pbto2. However, no corresponding improvements in the gradient of Pjvo2 to Pbto2 and biomarkers of neurological recovery were observed in the porcine asphyxial cardiac arrest model.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Cardiac arrest (CA) is one of the major health problems worldwide, with significantly high mortality and morbidity [1,2,3]. Despite the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), a majority of patients die prior to hospital discharge or have severe neurologic injury attributable to the development of post-cardiac arrest syndrome (PCAS) [4, 5]. PCAS, composed of four components: hypoxic brain injury, systemic ischemia reperfusion injury, myocardial dysfunction, and the underlying etiology of CA, is substantially complex to manage [6,7,8].
A number of specific interventions have been demonstrated to improve outcomes of PCAS, of which the management of the partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (Paco2) as a potential therapeutic target receives special attention [9,10,11]. Carbon dioxide is the major physiological regulator of cerebral blood flow (CBF), with higher Paco2 causing increased brain perfusion [12]. Previous studies found mild hypercapnia increased cerebral oxygenation assessed by near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) and attenuated the release of serum neuron specific enolase (NSE) [9, 11, 13]. However, the results were inconsistent and the potential mechanisms are unclear [10, 14, 15]. In addition, NIRS may not accurately reflect the cerebral oxygenation [16].
The present study aimed to investigate the effect of mild hypercapnia on cerebral oxygenation assessed by invasive brain tissue oxygen tension (Pbto2) monitoring probe and diffusion limitation assessed by the gradient of partial pressure of jugular venous bulb oxygen (Pjvo2) and Pbto2 in a porcine asphyxial CA model. We hypothesized that mild hypercapnia might increase Pbto2 and improve diffusion limitation.
Methods
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (No: 201803002) of Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University. All animals received humane care in compliance with the guideline for the care and use of experimental animals by the National Institute of Health [17].
Animal preparation
Sixteen healthy, male Bama miniature pigs (weight 35 ~ 45 kg, mean 39.7 kg), purchased from Beijing Shichuang Minipig Breeding Base were studied. All animals were fasted overnight except for ad libitum access to water. Animals were placed on a heating pad in supine position. Premedication consisted of intramuscular 10 mg/kg ketamine. Anesthesia was induced by ear vein injection of propofol (1–2 mg/kg) and fentanyl (2 μg/kg). Continuous sedation and analgesia consisted of intravenous 4–8 mg/kg/h propofol and 1–5 μg/kg/h fentanyl. Lactated Ringer’s solution (5 ml/kg/h) was administrated as maintenance fluid.
Tracheotomy was performed with a 7 mm cuffed tube. Following securing the airway, animals were mechanically ventilated with a Servo-s ventilator (Maquet, Solna, Sweden) with a tidal volume of 10 ml/kg, respiratory rate (RR) of 16 breaths/min, and inspired oxygen fraction of 21%. The end-tidal carbon dioxide pressure (EtCO2) was monitored by an infrared capnometer (Mindray, BeneVision N19 with module of EtCO2) and EtCO2 of 35 and 40 mmHg was maintained by adjusting the parameters of the ventilator before establishing the asphyxial CA model.
A 7F central venous catheter was placed by surgical cut-down technique via right external jugular vein to the right atrium for fluid infusion, central venous pressure (CVP) measurement and bolus of 10 ml ice-cold saline injections for cardiac output (CO) measurement by transpulmonary thermodilution method. The position was ascertained by the shape of pressure wave in right atrium. A 5F catheter was retrogradely to the cranial direction inserted into the right internal jugular vein reaching an approximated tip location of the jugular bulb for blood collection. Furthermore, the tip location was confirmed by X-rays. Left femoral artery was inserted with a 5F arterial catheter with an integrated thermistor tip (PiCCO, Pulsion Medical Systems, Munich, Germany) for continuous mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) monitoring, arterial blood gas (ABG) sampling, extravascular lung water (EVLW), and CO measurement. Pressure related catheters were connected to transducers (Mindray, BeneVision N19 with module for PiCCO). A conventional electrocardiogram with five adhesive electrodes to the four shaved skin of the proximal limbs and the upper abdomen was continuously monitored.
After the procedures above, animals were turned to left lateral position. A midline incision was performed along the dorsal surface of the head to expose the underlying skull. One burr hole with diameter about 3 mm (mm) approximately 10 mm right and lateral of midline and 10 mm anterior to the coronal suture was drilled. The Pbto2 probe and temperature (Tbt) probe (Licox, INTEGRA, USA) were placed through the same opening hole. The distal tip of the probes were placed into the cortex at a depth of about 10 mm. The Pbto2 and Tbt monitor (Licox, INTEGRA, USA) were connected. Animals were then turned to right lateral position. Another burr hole was drilled at the symmetrical position on the left. An intraparenchymal ICP monitor probe (Codman Microsensor, Raynham, MA, USA) was placed through the hole. The distal tip of the probe was placed into the cortex at a depth of about 10 mm. The probe was connected to the ICP monitor (Codman, Raynham, MA, USA). The urinary catheter (22Fr Foley) was placed through bladder puncture for urine drainage.
Experimental preparation
The animals were allowed to stabilize for 60 min after all the procedures above to achieve a stable resting level and then the baseline parameters were obtained.
Establishment of the CA model
Intravenous rocuronium (0.5 mg/kg) was administrated for muscle relaxation. Asphyxia was induced by clamping the endotracheal tube. CA was confirmed when MAP less than 30 mmHg as previously described [18]. Anesthetic administration was ceased and the endotracheal tube was reopened after CA had been successfully induced.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
After 4 min of untreated CA, CPR was initiated. Mechanical ventilation (volume-controlled ventilation, tidal volume 10 ml/kg, RR 10 breaths/min, Fio2 100%) was resumed. In all animals, chest compressions were performed by the trained investigators at a frequency of 100 compressions/min with equal compression-relaxation duration and compression depth of one third of the anteroposterior diameter of the thorax according to resuscitation guideline [19].
Electrical defibrillation was performed with 150-J biphasic shocks using the defibrillator (Lifepak20e, Medtronic, USA) when ECG showed ventricular fibrillation (VF). If VF waves persisted, CPR was continued, followed by another electrical defibrillation (biphasic 200-J for subsequent attempts). After 2 min of CPR, epinephrine (0.02 mg/kg) was injected through the central venous catheter of external jugular vein. If required, additional doses of epinephrine were administered every 3 min until ROSC was achieved. Within 30 min, the above sequence continued until ROSC was achieved, which was defined as MAP more than 60 mmHg that was continuously sustained for at least 10 min. If ROSC was not achieved within 30 min, CPR was ceased and the animals were regarded as dead.
Randomization and advanced life support
Twelve animals achieved ROSC. After ROSC, animals were randomized into normocapnia (EtCO2 35 ~ 40 mmHg) and mild hypercapnia (EtCO2 45 ~ 50 mmHg) ventilation using a sealed envelope indicating the animal assignment to either the mild hypercapnia group (n = 6) or the normocapnia group (n = 6). The investigators were blinded to the treatment allocation when assessing the outcome.
After ROSC, animals underwent intensive care for 12 h, and advanced life support was followed according to the guidelines [8]. Anesthesia, muscle relaxation, and Lactated Ringer’s solution were maintained. For ventilation, RR was adjusted to obtain an EtCO2 35 ~ 40 mmHg in normocapnia group or EtCO2 45 ~ 50 mmHg in the hypercapnia group when keeping tidal volume 10 ml/kg. For oxygenation, arterial oxygen saturation (Spo2) was titrated as 94% ~ 99%. Hemodynamic goal was set as MAP greater than 65 mmHg and norepinephrine was used when lower than the goal.
The experimental flow chart was summarized in Fig. 1. After intensive care for 12 h, all experimental animals were euthanized with a bolus of propofol 50 mg intravenous and then a bolus 20 ml of 20 mol/L potassium chloride.
Measurements
Hemodynamics (MAP, CVP), electrocardiogram, EtCO2, and Spo2 data were continuously monitored using a patient monitoring system (Mindray, BeneVision N19) and were recorded every half an hour. CO and EVLW were measured at baseline, ROSC 1 h, 6 h, and 12 h with a bolus of 10 ml ice-cold saline injections for three times to obtain mean value, respectively.
Neurological parameters, such as ICP, Pbto2, and Tbt were continuously monitored and were recorded every half an hour until 12 h. Cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) was calculated as MAP minus ICP (CPP = MAP - ICP).
Arterial and jugular venous bulb blood gas (GEM3000, Instrumentation Laboratory, USA) were analyzed with the temperature-corrected measurement at baseline, ROSC 1 h, 6 h, and 12 h. Pressure of arterial oxygen (Pao2), arterial carbon dioxide (Paco2), jugular venous bulb oxygen (Pjvo2), and jugular venous bulb carbon dioxide (Pjvco2), saturation of arterial oxygen (Sao2) and jugular venous bulb oxygen (Sjvo2), lactate of arterial and jugular venous bulb were recorded from the corresponding blood gas results (baseline, ROSC 1 h, 6 h, and 12 h). Gradient of Pjvo2 and Pbto2 was calculated as Pjvo2 minus Pbto2. Arteriojugular oxygen difference (AJDo2), difference of Pjvco2 to Paco2 (ΔPco2), lactate oxygen index (LOI) were calculated with the following equations:
Biomarkers of serum neuron specific enolase (NSE) and central nervous system specific protein (S100β) were measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits (Rapid Bio, USA) at baseline, ROSC 1 h, 6 h, and 12 h, respectively.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were shown as mean and standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile range (IQR). Categorical variables were reported as numbers and percentages. Categorical data were compared with the Chi-square test. Continuous data for normality were checked and compared with the Student’s t-test for the normal distribution and with the Mann-Whitney U test for the non-normal distribution. The EtCO2, MAP, ICP, Pbto2, Tbt, gradient of Pjvo2 and Pbto2, difference of Pjvco2 and Paco2, CO, EVLW, NSE and S100β between hypercapnia and normocapnia group over time were compared using a generalized mixed model with a compound symmetry covariance matrix. We performed all the statistical analyses with R software (version 3.5.1, www.r-project.org). R package “lme4” was used for statistical analyses of generalized mixed model. A two-sided p value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
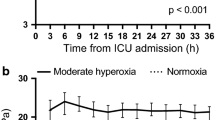
Twelve (75%) of the sixteen pigs were successfully resuscitated and were randomized into the normocapnia (n = 6) and mild hypercapnia (n = 6) group. One of the pigs in the normocapnia group had recurrent CA after ROSC and was not successfully resuscitated. A total of eleven pigs survived during the study period. No significant differences in body weight, MAP, CO, EVLW, ICP, Pbto2, Tbt, hemoglobin, arterial and jugular venous bulb blood gas analyses, NSE, and S100β were observed between the normocapnia and mild hypercapnia groups at baseline (Table 1 and Figs. 2, 3, 4, 5).
End-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2), cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), intracranial pressure (ICP), brain tissue oxygen tension, and brain tissue temperature during the study period between mild hypercapnia group and hypercapnia group. Data were expressed as mean ± SD (error bars). P value were calculated using generalized mixed models
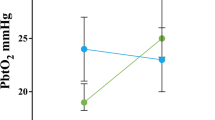
Gradient of jugular venous bulb oxygen tension (Pjvo2) and brain tissue oxygen tension (Pbto2) and difference of jugular venous partial pressure of carbon dioxide (Pjvco2) and arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (Paco2) at baseline, ROSC 1 h, 6 h, and 12 h post-resuscitation. Data were shown as mean ± SD (error bars). P values were calculated using generalized mixed models
During CPR, no significant differences were observed in the duration of asphyxia, duration of CPR, times of shock, and amount of epinephrine use (Table 1). Immediately after resuscitation, there was a transient surge in EtCO2, MAP, ICP, and Pbto2 (Fig. 2). However, they gradually stabilized within 1 h.
After resuscitation, there were significant differences in EtCO2 and Paco2 during the 12 h of treatment. Pigs in the mild hypercapnia group showed a trend toward a lower Pao2 (ROSC 6 h and 12 h) (Table 1). Pbto2, MAP and ICP were significantly higher in the mild hypercapnia group compared to the normocapnia ventilation group using a generalized mixed model with a compound-symmetry covariance matrix. (Fig. 2 and Supplemental Tables 1, 2, 3). The two groups had similar CPP and Tbt during the study period (Fig. 2). No effect of mild hypercapnia ventilation on CO and EVLW were observed (Fig. 4).
There were no significant differences in gradient of Pjvo2 to Pbto2 and ΔPco2 when comparing normocapnia group with mild hypercapnia group (Fig. 3). As for secondary derivatives of metabolism, no differences were observed in AJDo2 and LOI between two groups (Table 1).
There was a significant increase in NSE and S100β over time (p < 0.001 for both biomarkers) (Supplemental Table 4). However, no differences were found between the normocapnia group and mild hypercapnia group (Fig. 5).
Discussion
The present study investigated the effect of mild hypercapnia (EtCO2 45 ~ 50 mmHg) after successful resuscitation, which was obtained by adjusting respiratory rate, on Pbto2, diffusion limitation, and cerebral metabolism. The results showed short term mild hypercapnia post-resuscitation could improve Pbto2; however, mild hypercapnia was associated with higher ICP and was not associated with improved Pjvo2 to Pbto2 gradient. In addition, mild hypercapnia was not associated with attenuation of neurological biomarkers of NSE and S100β in this asphyxial cardiac arrest model. These results may challenge the possible beneficial effect of mild hypercapnia on neurological recovery in hypoxic ischemic brain injury postcardiac arrest.
Respiratory care plays an important role for postcardiac arrest patients; however, no specific target range for Paco2 has been suggested. The resuscitation guidelines recommend normocapnia (EtCO2 30 ~ 40 mmHg or Paco2 35 ~ 45 mmHg) may be a reasonable goal based on inconsistent results [8]. Recently, several studies have investigated the effect of mild hypercapnia on postcardiac arrest care; however, the results were not completely consistent [9,10,11, 13, 15]. The “Carbon Control after Cardiac Arrest (CCC) trial” found mild hypercapnia attenuated the release of NSE compared with normocapnia [11], whereas some experimental and randomized pilot trials did not observe the effect of mild hypercapnia on NSE or S100β [9, 10]. Meanwhile, there was one consistent finding that mild hypercapnia increased regional cerebral tissue oxygen saturation (Scto2) assessed by near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) [9, 13]. The results of the present study were in line with the previous studies. We found no difference in the effect of mild hypercapnia and normocapnia on NSE or S100β; moreover, mild hypercapnia was associated with higher Pbto2 which was monitored by invasive measurement.
Continuous brain oxygenation monitoring had been used both during CPR and post-ROSC with non-invasive cerebral oximetry [20, 21]. Higher Scto2 levels at initiation of resuscitation and during CPR were associated with resuscitation success and may reflect high-quality CPR [21, 22]. However, Scto2 was not found to be predictive of good neurological outcome during the post-arrest period [21]. That partly attributes to Scto2 assessed by NIRS may not correlate with invasively measured Pbto2 values [16, 23]. To the best of our knowledge, this was the first study to report the Pbto2 values between mild hypercapnia and normocapnia ventilation in postcardiac arrest model. Nevertheless, more studies need to be conducted to determine whether a high Pbto2 would increase the likelihood of a favorable neurological outcome.
Hypercapnia could augment Pbto2 in anesthetized rats, by mechanisms which may include incremental increases in CBF and Pao2 [24]. However, in the present study, we found Pao2 was higher in normocapnia than mild hypercapnia ventilation at ROSC 6 h and 12 h, which was not in line with Hare’s study [24]. We induced mild hypercapnia by adjusting the respiratory rate, which decreased the minute ventilation. Lower minute ventilation may cause lower Pao2. The results of the present study showed mild hypercapnia increased Pbto2 but not Pao2, which may suggest the effect of mild hypercapnia on Pbto2 mainly attribute to increased CBF or other potential mechanisms. Previous studies showed Paco2 is the major physiological regulator of CBF and a higher Paco2 could increase CBF [12]. In our study, we did not monitor the CBF, and could not comment on whether there was any difference in CBF between mild hypercapnia and normocapnia in asphyxial CA model. Of note, we found mild hypercapnia had higher MAP, which may be associated with increased CBF.
The increased gradient of Pjvo2 and Pbto2 had been suggested to be associated with diffusion limitation [25, 26]. In the present study, we did not find the difference of gradient of Pjvo2 and Pbto2 between mild hypercapnia and normocapnia. Besides, there were no differences in AJDo2, ΔPco2, and LOI between mild hypercapnia and normocapnia groups. AJDo2 and ΔPco2 had been considered as good indicators of ischemia and hypoperfusion [27,28,29]. LOI levels were also reported to be associated with CBF and related to the outcome of head-injured patients [30, 31]. The findings may suggest that mild hypercapnia does not improve tissue perfusion or diffusion limitation, which could explain the no differences of biomarkers of NSE or S100β between two groups. However, due to the absence of pathologic tissue test or gold standard measures of cerebral metabolism, we were unable to further explore the potential mechanisms.
The side effect of hypercapnia should also need to be mentioned. Hypercapnia increases ICP, with hypocapnia used as a temporizing measure to ameliorate intracranial hypertension [32]. In our study, there was a slightly increased MAP and ICP in mild hypercapnia group. The result of a higher MAP in the mild hypercapnic animals was consistent with previous studies [10, 33]. However, there were studies suggesting no association between hypercapnia and MAP [13, 34]. Hypercapnia may have effects on cardiovascular system, like inhibiting cardiac and vascular muscle contractility; however, the effects could be counterbalanced by an increase in the sympathetic tone [12, 35]. Although the slightly increased ICP in the mild hypercapnia group was expected, CPP was not significantly different between the two groups. In addition, there were no differences in CO and EVLW between the two groups.
There are several limitations to this study. First, we used asphyxial CA model instead of CA of VF model, which was widely used for establishing CA model. Previous studies showed asphyxial CA model causes more severe cerebral metabolism injuries and ischemic brain injury after asphyxial CA appears more severe and more widespread than VF model of the same duration [36, 37]. Second, we defined mild hypercapnia as EtCO2 between 45 and 50 mmHg based on previously published studies [10], which may be arbitrary, since the target EtCO2 levels associated with potential benefit or harm are unknown. Third, we only assessed two different levels of EtCO2 for a period of 12 h. Fourth, Pbto2 is a focal measure, which could not represent the global monitor. The pathophysiology of CA is global cerebral ischemia. Fifth, the observational period was only 12 h in our study. The effect of mild hypercapnia on long-term outcomes may need further investigation. Sixth, the lack of pathology and cerebral blood flow data limited the interpretation of the potential mechanisms. Finally, we did not implement targeted temperature management (TTM) after ROSC, which is strongly recommended by resuscitation guidelines. That may merit further research.
Conclusions
Short term mild hypercapnia post-resuscitation could improve brain tissue oxygen tension. However, no corresponding improvements in the gradient of jugular venous bulb oxygen tension to brain tissue oxygen tension and biomarkers of neurological recovery were observed in the porcine asphyxial cardiac arrest model.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ABG:
-
Arterial blood gas
- AJDo2 :
-
Arteriojugular oxygen difference
- CA:
-
Cardiac arrest
- CBF:
-
Cerebral blood flow
- CO:
-
Cardiac output
- CPP:
-
Cerebral perfusion pressure
- CPR:
-
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- CVP:
-
Central venous pressure
- EtCO2 :
-
End-tidal carbon dioxide
- EVLW:
-
Extravascular lung water
- ICP:
-
Intracranial pressure
- IQR:
-
Median and interquartile range
- LOI:
-
Lactate oxygen index
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial blood pressure
- NIRS:
-
Near infrared spectroscopy
- NSE:
-
Neuron specific enolase
- Paco2 :
-
Partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide
- Pao2 :
-
Pressure of arterial oxygen
- Pbto2 :
-
Brain tissue oxygen tension
- PCAS:
-
Post-cardiac arrest syndrome
- Pjvco2 :
-
Pressure of jugular venous bulb carbon dioxide
- Pjvo2 :
-
Partial pressure of jugular venous bulb oxygen
- ROSC:
-
Return of spontaneous circulation
- Sao2 :
-
Saturation of arterial oxygen
- Scto2 :
-
Regional cerebral tissue oxygen saturation
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- Sjvo2 :
-
Saturation of jugular venous bulb oxygen
- Tbt:
-
Brain tissue temperature
- VF:
-
Ventricular fibrillation
- ΔPco2 :
-
Difference of Pjvco2 to Paco2
References
Berdowski J, Berg RA, Tijssen JG, Koster RW. Global incidences of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and survival rates: systematic review of 67 prospective studies. Resuscitation. 2010;81(11):1479–87.
Andersen LW, Holmberg MJ, Berg KM, Donnino MW, Granfeldt A. In-hospital cardiac arrest: a review. Jama. 2019;321(12):1200–10.
Wissenberg M, Lippert FK, Folke F, Weeke P, Hansen CM, Christensen EF, Jans H, Hansen PA, Lang-Jensen T, Olesen JB, et al. Association of national initiatives to improve cardiac arrest management with rates of bystander intervention and patient survival after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Jama. 2013;310(13):1377–84.
Cronberg T, Lilja G, Horn J, Kjaergaard J, Wise MP, Pellis T, Hovdenes J, Gasche Y, Aneman A, Stammet P, et al. Neurologic function and health-related quality of life in patients following targeted temperature management at 33 degrees C vs 36 degrees C after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2015;72(6):634–41.
Sandroni C, D'Arrigo S, Callaway CW, Cariou A, Dragancea I, Taccone FS, Antonelli M. The rate of brain death and organ donation in patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42(11):1661–71.
Girotra S, Chan PS, Bradley SM. Post-resuscitation care following out-of-hospital and in-hospital cardiac arrest. Heart. 2015;101(24):1943–9.
Hassager C, Nagao K, Hildick-Smith D. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: in-hospital intervention strategies. Lancet (London, England). 2018;391(10124):989–98.
Callaway CW, Donnino MW, Fink EL, Geocadin RG, Golan E, Kern KB, Leary M, Meurer WJ, Peberdy MA, Thompson TM, et al. Part 8: post-cardiac arrest care: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines update for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2015;132(18 Suppl 2):S465–82.
Jakkula P, Reinikainen M, Hastbacka J, Loisa P, Tiainen M, Pettila V, Toppila J, Lahde M, Backlund M, Okkonen M, et al. Targeting two different levels of both arterial carbon dioxide and arterial oxygen after cardiac arrest and resuscitation: a randomised pilot trial. Intensive Care Med. 2018;44(12):2112–21.
Babini G, Ristagno G, Boccardo A, De Giorgio D, De Maglie M, Affatato R, Ceriani S, Zani D, Novelli D, Staszewsky L, et al. Effect of mild hypercapnia on outcome and histological injury in a porcine post cardiac arrest model. Resuscitation. 2019;135:110–7.
Eastwood GM, Schneider AG, Suzuki S, Peck L, Young H, Tanaka A, Mårtensson J, Warrillow S, McGuinness S, Parke R, et al. Targeted therapeutic mild hypercapnia after cardiac arrest: a phase II multi-Centre randomised controlled trial (the CCC trial). Resuscitation. 2016;104:83–90.
Curley G, Laffey JG, Kavanagh BP. Bench-to-bedside review: carbon dioxide. Critical Care (London, England). 2010;14(2):220.
Eastwood GM, Tanaka A, Bellomo R. Cerebral oxygenation in mechanically ventilated early cardiac arrest survivors: the impact of hypercapnia. Resuscitation. 2016;102:11–6.
Ebner F, Harmon MBA, Aneman A, Cronberg T, Friberg H, Hassager C, Juffermans N, Kjærgaard J, Kuiper M, Mattsson N, et al. Carbon dioxide dynamics in relation to neurological outcome in resuscitated out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients: an exploratory Target Temperature Management Trial substudy. Critical care (London, England). 2018;22(1):196.
Zhou D, Li Z, Zhang S, Wu L, Li Y, Shi G. Association between mild hypercapnia and hospital mortality in patients admitted to the intensive care unit after cardiac arrest: a retrospective study. Resuscitation. 2020;149:30–8.
Kerz T, Beyer C, Huthmann A, Kalasauskas D, Amr AN, Boor S, Welschehold S. Continuous-wave near-infrared spectroscopy is not related to brain tissue oxygen tension. J Clin Monit Comput. 2016;30(5):641–7.
National Research Council Committee for the Update of the Guide for the C, Use of Laboratory A. The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health. In: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Washington: National Academies Press (US) 2011, National Academy of Sciences; 2011.
Varvarousi G, Xanthos T, Lappas T, Lekka N, Goulas S, Dontas I, Perrea D, Stefanadis C, Papadimitriou L. Asphyxial cardiac arrest, resuscitation and neurological outcome in a landrace/large-white swine model. Lab Anim. 2011;45(3):184–90.
Kleinman ME, Brennan EE, Goldberger ZD, Swor RA, Terry M, Bobrow BJ, Gazmuri RJ, Travers AH, Rea T. Part 5: adult basic life support and cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines update for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2015;132(18 Suppl 2):S414–35.
Asim K, Gokhan E, Ozlem B, Ozcan Y, Deniz O, Kamil K, Murat Z, Aydin C, Selman Y. Near infrared spectrophotometry (cerebral oximetry) in predicting the return of spontaneous circulation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32(1):14–7.
Ibrahim AW, Trammell AR, Austin H, Barbour K, Onuorah E, House D, Miller HL, Tutt C, Combs D, Phillips R, et al. Cerebral Oximetry as a real-time monitoring tool to assess quality of in-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation and post cardiac arrest care. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015;4(8):e001859.
Parnia S, Yang J, Nguyen R, Ahn A, Zhu J, Inigo-Santiago L, Nasir A, Golder K, Ravishankar S, Bartlett P, et al. Cerebral Oximetry during cardiac arrest: a multicenter study of neurologic outcomes and survival. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(9):1663–74.
Davies DJ, Clancy M, Dehghani H, Lucas SJE, Forcione M, Yakoub KM, Belli A. Cerebral oxygenation in traumatic brain injury: can a non-invasive frequency domain near-infrared spectroscopy device detect changes in brain tissue oxygen tension as well as the established invasive monitor? J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(7):1175–83.
Hare GM, Kavanagh BP, Mazer CD, Hum KM, Kim SY, Coackley C, Barr A, Baker AJ. Hypercapnia increases cerebral tissue oxygen tension in anesthetized rats. Can J Anaesth. 2003;50(10):1061–8.
Menon DK, Coles JP, Gupta AK, Fryer TD, Smielewski P, Chatfield DA, Aigbirhio F, Skepper JN, Minhas PS, Hutchinson PJ, et al. Diffusion limited oxygen delivery following head injury. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(6):1384–90.
Sekhon MS, Ainslie PN, Menon DK, Thiara SS, Cardim D, Gupta AK, Hoiland RL, Gooderham P, Griesdale DE. Brain hypoxia secondary to diffusion limitation in hypoxic ischemic brain injury Postcardiac arrest. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(3):378–84.
Zhang H, Vincent JL. Arteriovenous differences in PCO2 and pH are good indicators of critical hypoperfusion. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;148(4 Pt 1):867–71.
Mekontso-Dessap A, Castelain V, Anguel N, Bahloul M, Schauvliege F, Richard C, Teboul JL. Combination of venoarterial PCO2 difference with arteriovenous O2 content difference to detect anaerobic metabolism in patients. Intensive Care Med. 2002;28(3):272–7.
Stocchetti N, Zanier ER, Nicolini R, Faegersten E, Canavesi K, Conte V, Gattinoni L. Oxygen and carbon dioxide in the cerebral circulation during progression to brain death. Anesthesiology. 2005;103(5):957–61.
Artru F, Dailler F, Burel E, Bodonian C, Grousson S, Convert J, Renaud B, Perret-Liaudet A. Assessment of jugular blood oxygen and lactate indices for detection of cerebral ischemia and prognosis. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2004;16(3):226–31.
Robertson CS, Narayan RK, Gokaslan ZL, Pahwa R, Grossman RG, Caram P Jr, Allen E. Cerebral arteriovenous oxygen difference as an estimate of cerebral blood flow in comatose patients. J Neurosurg. 1989;70(2):222–30.
Carney N, Totten AM, O'Reilly C, Ullman JS, Hawryluk GW, Bell MJ, Bratton SL, Chesnut R, Harris OA, Kissoon N, et al. Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Fourth Edition. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(1):6–15.
Kiely DG, Cargill RI, Lipworth BJ. Effects of hypercapnia on hemodynamic, inotropic, lusitropic, and electrophysiologic indices in humans. Chest. 1996;109(5):1215–21.
Helmerhorst HJ, Roos-Blom MJ, van Westerloo DJ, Abu-Hanna A, de Keizer NF, de Jonge E. Associations of arterial carbon dioxide and arterial oxygen concentrations with hospital mortality after resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Critical care (London, England). 2015;19:348.
Cullen DJ, Eger EI 2nd. Cardiovascular effects of carbon dioxide in man. Anesthesiology. 1974;41(4):345–9.
Zhang Y, Li CS, Wu CJ, Yang J, Hang CC. Comparison of cerebral metabolism between pig ventricular fibrillation and Asphyxial cardiac arrest models. Chin Med J. 2015;128(12):1643–8.
Vaagenes P, Safar P, Diven W, Moossy J, Rao G, Cantadore R, Kelsey S. Brain enzyme levels in CSF after cardiac arrest and resuscitation in dogs: markers of damage and predictors of outcome. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988;8(2):262–75.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This study was supported by ‘Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission-Capital clinical application research’ (Z181100001718068). The sponsor had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, or writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DW Z, GZ S, and JX Z conceived and participated in the design of the study and drafted the manuscript. DW Z, ZM L, L W, SL Z, and YY L participated in the experiments, data collection and statistical analysis. All authors participated in the review and revision of the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University (No: 201803002).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
None of the authors has declared a conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Comparisons of Pbto2 at different time points between mild hypercapnia and normocapnia. Table S2. Comparisons of MAP at different time points between mild hypercapnia and normocapnia. Table S3. Comparisons of ICP at different time points between mild hypercapnia and normocapnia. Table S4. Comparisons of NSE and S100β between mild hypercapnia and normocapnia.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, D., Li, Z., Zhang, S. et al. Mild hypercapnia improves brain tissue oxygen tension but not diffusion limitation in asphyxial cardiac arrest: an experimental study in pigs. BMC Anesthesiol 20, 252 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-020-01162-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-020-01162-z