Abstract
Background
The WOX (WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX) gene family encodes a class of transcription factors that are unique to green plants, where they are involved in regulating the development of plant tissues and organs by determining cell fate. Although the importance of the WOX gene is well known, there are few studies describing their functions in cotton.
Results
In this study, 32 WOX genes were found in Gossypium hirsutum. Phylogenetic analysis showed that WOX proteins of cotton can be divided into three clades: the ancient, intermediate, and WUS clades. The number of WOX proteins in the WUS clade was greater than the sum of the proteins in the other two clades. Our analysis revealed that 20 GhWOX genes are distributed on 16 cotton chromosomes and that duplication events are likely to have contributed to the expansion of the GhWOX family. All GhWOX genes have introns, and each GhWOX protein contains multiple motifs. RNA-seq data and real-time PCR showed that GhWOX13 gene subfamily is specifically expressed at a high level in cotton fibers. We also identified putative GA, NAA, and BR response elements in the promoter regions of the GhWOX13 genes and GhWOX13 transcripts were significantly induced by GA, NAA, and BR.
Conclusions
Our data provides a useful resource for future studies on the functional roles of cotton WOX genes and shows that the GhWOX13 genes may influence cotton fiber development. Our results also provide an approach for identifying and characterizing WOX protein genes in other species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX (WOX) gene family, which encodes one of the largest groups of transcription factors (TFs), is unique to plants, and belongs to a subclade of the homeodomain (HD) superfamily that can form a conserved DNA-binding homeo-domain [1]. Although WOX genes are spatiotemporally expressed during plant development, the number of WOX genes in the genomes of different plant species is not consistent. There are 15, 11, and 21 WOX gene family members in Arabidopsis, sorghum, and maize, respectively [2,3,4]. Phylogenetic analyses of WOX proteins from multiple higher plant species such as Arabidopsis, sorghum, maize, and rice show that they cluster into three clades, known as the WUS clade, the intermediate clade, and the ancient clade. However, the lower plants (green algae and moss) only contain the ancient type of the WOX proteins [5]. In Arabidopsis, 15 WOX proteins can be divided into three phylogenetic clades, AtWOX1–7 and AtWUS belonging to the WUS clade, AtWOX8, AtWOX9, AtWOX11, and AtWOX12 belonging to the intermediate clade, AtWOX10, AtWOX13, and AtWOX14 belonging to the ancient clade [6, 7].
The WOX proteins have been shown to act a pivotal part in numerous developmental processes, such as organ formation, embryo patterning, stem cell maintenance [8,9,10]. AtWOX1 is highly expressed in the initiating vascular primordium of the cotyledons and emerging leaves, and over-expression of AtWOX1 caused small leaves, dwarf plant and low fertility [11, 12]. Ectopically over-expression of TaSF (STENTOFOLIA), the ortholog of AtWOX1, results in transgenic plants with broadened leaves, accelerated flowering and increased chlorophyll content [13]. WOX3 has a highly conserved function during the recruitment of founder cells to form the lateral domains of vegetative and floral organs in Arabidopsis and maize. A loss-of-function AtWOX3 mutant exhibited a degeneration of the lateral stipules and sepals [14]. AtWOX4 is required for auxin-dependent procambium differentiation and/or maintenance, which shows that the WOX gene family influences the auxin-dependent regulation of lateral plant growth [15, 16]. Rice WOX4 is responsible for meristem maintenance and reduction of OsWOX4 expression led to severe malformed leaf primordia [17]. AtWOX5, which is induced by auxin, is a negative factor to regulate IAA homeostasis to maintain stem cells in root apical meristem (RAM) [18]. In Populus, WOX5a was mainly expressed in the adventitious root (AR) tip and lateral root tip. Over-expression of PtoWOX5a led to increased AR number, decreased AR length and leaf number [19]. Also, over-expression of WOX11 and WOX12 significantly increased AR number and decreased ectopic roots in poplar [20]. A homolog of AtWOX11, OsWOX11, interacts with H3K27me3 demethylase JMJ705 to promote the expression of downstream gene during shoot development [21]. In addition, OsWOX11 is also involved in lateral root initiation, root hair formation, and responses to abiotic stresses [22, 23].
Cotton is the important economic crop in the world, which can be used for textile. Cotton fiber is the single seed coat epidermal cell. Quality and yield of fiber depends mainly on three biological processes; fiber initiation, fiber elongation, and secondary cell wall deposition [24,25,26]. Many studies have focused on fiber cell growth in cotton. So far, genome sequences of three cotton species have been completed, including the allotetraploid G. hirsutum. (AADD, 2n = 52) and the two diploid progenitors G. arboreum (AA; 2n = 26) and G. raimondii (DD, 2n = 26) [27,28,29,30,31]. These genome sequences have enabled the identification of WOX genes at a genome-wide scale in cotton.
The roles of WOX proteins have been well-documented in Arabidopsis, rice, and maize, however, the functions of WOX proteins in cotton, especially in fiber development, are largely unknown. In this study, we identified 32 cotton WOX genes and found that they cluster into the previously-known ancient, WUS, and intermediate phylogenetic clades. Chromosomal distribution analysis revealed that 20 GhWOX genes are distributed on 16 cotton chromosomes. Analysis of gene expression patterns showed that GhWOX13 genes are specifically expressed at high levels in the cotton fiber. In addition, we found that all of the GhWOX13 genes had putative GA, NAA, and BR response elements in their promoter regions and can be induced by these hormones. Taken together, the results of our study provide a useful resource for future studies on the functional roles of cotton WOX genes, and demonstrated that the GhWOX13 gene products may act to influence cotton fiber development. We also provide an approach for identifying and characterizing WOX proteins in other plant species.
Results
Identification of WOX gene family proteins in Gossypium
To identify WOX family members in Gossypium, 15 AtWOX protein sequences were used as queries for blast searching of the cotton genome database with the E-value cutoff of 0.001. The candidate GhWOX proteins were manually inspected to ascertain that the candidates contained the conserved DNA-binding homeodomain using the InterPro protein sequence analysis & classification tool. As a result, we identified 32, 18, and 19 WOX protein coding genes in G. hirsutum, G. arboreum, and G. raimondii, respectively (Table 1). We found that the number of WOX genes identified in the tetraploid G. hirsutum was lower than the combined number from its diploid progenitors suggesting some loss after polyploid formation. Compared with Arabidopsis, multiple WOX genes, such as WOX3, WOX4, WOX13 and WUS, were expanded in Gossypium. On the contrary, WOX7 and WOX8 were missing in three cottons, whereas they were found in Arabidopsis, suggesting that WOX7 and WOX8 genes may have been lost in Gossypium after they diverged from the common ancestor of Gossypium and Arabidopsis.
Phylogenetic relationships of the WOX proteins from G. hirsutum, G. arboreum, G. raimondii, and A. thaliana
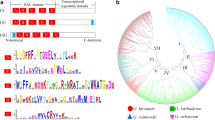
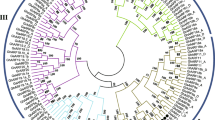
To evaluate the evolutionary and phylogenetic relationships of the WOX gene families among species, a total of 89 WOX protein sequences, including 32 GhWOXs, 18 GaWOXs, 19 GrWOXs, and 15 AtWOXs sequences, were used to construct an unrooted phylogenetic tree based on the alignment using the Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method as implemented in MEGA 6.0 with 1000 bootstrap replicates (Fig. 1). According to the phylogenetic relationship of WOX family, the GhWOX family proteins were also divided into three clades: the WUS clade, the ancient clade and the intermediate clade, The WUS clade, which was the largest clade, contains 23 GhWOX proteins. The ancient clade has six GhWOX proteins. The remaining members belong to the intermediate clade.
An unrooted Neighbor-Joining tree showing phylogenetic relationships among the predicted WOX proteins from Gossypium hirsutum (Gh), Gossypium arboreum (Ga), Gossypium raimondii (Gr) and Arabidopsis thaliana (At). The phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA 6.0, and the WOX proteins from the four plant species group into three clades (ancient, WUS, and intermediate)
Chromosomal locations of the GhWOX genes
We investigated the chromosomal location of the 32 GhWOX genes based on the annotation of the G. hirsutum genome. Genomic localization of the GhWOX genes showed that 20 GhWOX genes map to 16 chromosomes, while 12 GhWOX genes map to scaffold sequences that are not assigned to chromosomes (Fig. 2). Cotton chromosomes At_02, At_09, Dt_08, and Dt_09 harbor two GhWOX genes each, while all other chromosomes have only one. However, no GhWOX genes were found on chromosomes At_06, At_07, At_10, At_12, Dt_04, Dt_06, Dt_07, Dt_12, and Dt_13. We analyzed duplication events in the GhWOX genes mapped to chromosomes, and identified three types of gene duplication: tandem duplication, dispersed duplication, and segmental duplication (Additional file 2: Table S2). Except for GhWOX12_At and GhWUS1b_Dt which were derived from dispersed and tandem duplications, respectively, the other mapped GhWOX genes all resulted from segmental duplications This result indicated that segmental duplications were the main contributors to the expansion of GhWOX genes in G. hirsutum.
GhWOX gene structure and domain analysis
In order to better understand and explore the diversity of the WOX genes in G. hirsutum, we analyzed the conserved motifs and exon/intron structures of the GhWOX genes. The gene structures of GhWOX was generated by aligning the cDNA sequences and corresponding genomic DNA sequences. An unrooted phylogenetic tree was obtained with predicted GhWOX protein sequences (Fig. 3a). Exon/intron structure analysis showed that most GhWOX genes contain two introns, and the others contain no less than one intron, suggesting that GhWOX gene structure is conserved (Fig. 3b). We also analyzed the conserved motifs of the GhWOX proteins using the InterPro protein sequence analysis server, and five distinct conserved motifs were identified. The composition patterns of the motifs tend to be consistent with the phylogenetic tree. Motifs 1 and 2 are present in all GhWOX protein subfamilies, motif 4 is present in 24 GhWOX proteins except for GhWOX9, GhWOX10, GhWOX13, and GhWOX14. Motif 3 is present in GhWOX10, GhWOX13, and GhWOX14, and motif 5 is found only in GhWOX1 and all members of the GhWOX4 subfamily (Fig. 3c). The GhWOX proteins from the ancient clade contain three identical motifs, which could indicate that the proteins in this clade have the same function, and that the functions are redundant. In addition, a new motif was found that is specific to the GhWOX1_At protein, although it shared three identical motifs with GhWOX6A. The two proteins are very close in the phylogenetic tree, suggesting that they may have a shared function. However, a new motif could contribute a novel function to the GhWOX1_At protein.
Phylogenetic relationships, gene structure, and domain compositions of the GhWOX proteins. a A phylogenetic tree was constructed with MEGA 6.0 using the Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method with 1000 bootstrap replicates based on a multiple alignment of the amino acid sequences of the GhWOX proteins. b Exon/intron structures of the GhWOX genes. Exons and introns are represented by blue boxes and black lines, respectively. c Schematic diagram showing the conserved domains in the GhWOX proteins as annotated by InterPro (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ interpro/scan.html). Different color boxes represent different conserved protein motifs
Expression patterns of the GhWOX genes in various tissues
To investigate the tissue-specific expression profiles of 32 GhWOX genes, their relative expression levels in different organs, including young roots, young stems, young leaves, flowers, and 0 dpa ovules were analyzed from RNA-seq data. As shown in Fig. 4, the data indicate that expression of the GhWOX genes varies in the different organs and tissues; GhWOX2, GhWOX4, GhWOX5, GhWOX9, GhWOX11, and GhWOX13b_Dt are highly expressed in young roots, GhWOX4, GhWOX5, GhWOX11, and GhWOX13b_At are highly expressed in young stems, and GhWOX9_At, GhWUSa_At, and GhWUSb_Dt are highly expressed in young leaves, implying that the GhWOX genes have different roles in the growth and development of cotton. These results are consistent with those of previous reports on the function of individual WOX genes, which suggests that WOX gene functions are conserved in different species. Interestingly, all of the GhWOX genes have nearly identical expression levels in the ovules.
We further investigated the expression profiles of GhWOX genes and found that none of them displayed a significant change during the fiber development stage except for GhWOX13a_Dt, GhWOX13b_At, and GhWOX13b_D., which were highly expressed in fibers at 10 and 15 dpa (Fig. 5a). Furthermore, we verified the RNA-seq data using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) experiment. As a result, GhWOX13 were consistent with the RNA-seq data. The transcripts of GhWOX13a_Dt and GhWOX13b_At gradually increased and reached a peak in the fibers at 10 dpa (Fig. 5b). These results indicate that GhWOX13 genes may play an important role in cotton fiber development.
RNA-seq and qRT-PCR analysis of GhWOX genes during different stages of fiber development. a Heat map showing the relative expression levels of the GhWOX genes during different stages of fiber growth based on RNA-seq data. b Expression profiling of the GhWOX13 subfamily genes during cotton fiber development. Gene expression data were obtained from qRT-PCR assays with three independent replicates. The G. hirsutum ubiquitin gene GhUBQ7 was used to normalize the expression of the GhWOX genes
GhWOX13 gene expression is stimulated by GA, BR, and auxin
In order to identify the putative regulatory elements that control expression of the WOX genes in cotton, we analyzed the promoter regions of the GhWOX genes. We found that most of the GhWOX gene promoters contained at least one putative GA-response element (i.e. GARE motif, P-box, and TATC-box) except for GhWOX1_At, GhWOX3a_At, GhWOX3b_At, GhWOX3b_Dt, GhWOX4b_Dt, GhWOX4c_At, GhWOX12_Dt, GhWOX13a_Dt, and GhWOX14_Dt (Additional file 1: Figure S1). We next analyzed the putative BR-response element and found that all GhWOX genes had putative BR-response elements in their promoter regions (Additional file 1: Figure S2). We also searched for putative auxin-related cis-elements in the promoter regions of GhWOX genes, and found that GhWOX3a_Dt, GhWOX4b_Dt, GhWOX4c_At, GhWOX5_Dt, GhWOX9_At, GhWOX13b_At and GhWOX3b_Dt contain a putative auxin response element (AuxRE) in their upstream promoter regions (Additional file 1: Figure S3). Since the GhWOX13 genes are specifically expressed in cotton fibers, we analyzed the promoter regions of the GhWOX13 genes and identified putative GA, NAA, and BR responsive cis-elements in the promoters (Fig. 6a, c and e). In order to determine whether GhWOX13 genes are induced by GA, NAA, and BR, the mRNA levels of GhWOX13a_At, GhWOX13a_Dt, GhWOX13b_At, and GhWOX13b_Dt were evaluated by qRT-PCR after treatment with the three phytohormones. The results showed that the expression of GhWOX13a_Dt and GhWOX13b_Dt was up-regulated after treatment with GA for 48 h, the GhWOX13b_At mRNA level was significantly increased after treatment with GA for 24 h, but the transcription of GhWOX13a_At showed no change in response to GA treatment (Fig. 6b). GhWOX13a_Dt, GhWOX13b_At and GhWOX13b_Dt were up-regulated, with expression peaking after 24 h of BR treatment, while transcription of GhWOX13a_At showed no response to BR (Fig. 6d). Expression of GhWOX13b_At and GhWOX13b_Dt was induced by NAA, while the expression of GhWOX13a_At, GhWOX13a_Dt showed no effect (Fig. 6f). These results indicate that the GhWOX13 genes may play an important role in cotton fiber elongation mediated by plant hormones.
GhWOX13 subfamily gene transcription is induced by gibberellic acid (GA), brassinosteroid (BR), and auxin treatments. a Identification of putative auxin response elements (AuxREs) in the promoter regions of the four GhWOX13 gene family members. b GA-induced transcription in the three GhWOX13 genes with AuxREs in their promoter regions. The promoter of GhWOX13B does not contain an AuxRE. (c) Identification of E-box elements in the promoter regions of GhWOX13a_At/13a_Dt/13b_At/13b_Dt. d Transcription of the four hWOX13 family genes after BR treatment for 6 h, 24 h, and 5 d. e Identification of putative auxin response TGA elements in the promoter regions of the GhWOX13b_At/13b_Dt genes. f Transcription of the four GhWOX13 family genes after treatment with NAA for 12, 24, and 48 h. GhWOX13b_At and GhWOX13b_Dt have putative TGA elements in their promoter regions. Gene expression data were obtained from qRT-PCR assays with three replicates per sample, with each replicate performed using independent materials. The relative expression levels of each gene were determined by normalizing to the expression level in the CK ovules, which was set to 1.0. Statistical significance was determined using one-way analysis of variance combined with Tukey’s test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001
Discussion
Cotton is the one of the most significant economic crops cultivated worldwide, and it is an important source of fiber and oil. Whole genome sequencing of the G. arboreum, G. raimondii, and G. hirsutum genomes has been completed recently, and a number of genes associated with fiber development and leaf formation have been discovered by combining genome analysis with high-throughput transcriptome sequencing. However, the functions of the WOX genes in cotton, especially as they relate to fiber development, are largely unknown. In this study, we identified 32, 18, and 19 WOX genes in G. hirsutum, G. arboreum, and G. raimondii, respectively. Although the total number of WOX genes in G. hirsutum is much higher than in the other two species, the number of genes in the At and Dt genomes of G. hirsutum are less than the numbers in G. arboreum or G. raimondii. Gene copy numbers were largely reduced during the cotton-specific polyploidization event [32,33,34]. Our results are consistent with the finding that the rate of gene loss in allotetraploid cotton was higher than that in the two ancestral diploid species. Previous research has shown that WOX gene family can be divided into three major clades; the ancient clade which is present in green algae and all lineages of land plants, while intermediate and WUS clades are only found in ferns and seed plants [35]. In this study we identified 32 WOX genes representing all three major clades in the allotetraploid cotton species G. hirsutum. Yang et al. identified WOX gene family members in Upland cotton and also found that WOX genes could be naturally classified into three clades [36], which is consistent with our finding. Four of the GhWOXs belonged to the intermediate clade and six belonged to the ancient clade. The number of genes in the WUS clade was much higher than in either the intermediate or ancient clades, which is consistent with a previous report [37]. In A. thaliana, there are 15 AtWOX proteins, including four in the intermediate clade, three in the ancient clade, and eight in the WUS clade.
Gene structure analysis predicted that 15 GhWOX genes contain one intron, 15 GhWOX genes contain two introns, and two GhWOX genes (GhWOX1_At and GhWOX6_Dt) contain three introns. GhWOX1_At and GhWOX6_Dt have nearly identical gene structures within the WOX1/6 subgroup, although the intron phases and lengths differ. Similarly, the Arabidopsis genes AtWOX1 and AtWOX6 are in one phylogenetic clade and share a similar gene structure with three introns. Protein sequence motif analysis revealed that all GhWOX subfamilies contain motifs 1 and 2. Motif 3 is only found in GhWOX10, GhWOX13, and GhWOX14, and these proteins belong to the ancient clade (Fig. 1), indicating that motif 3 is conserved in the most ancient group of WOX proteins. These results suggest that the specific functions of proteins in the different subfamilies may be due to the presence of specific sequence motifs. The patterns of introns and motifs, which correlate well with the phylogenetic clades, strongly support the close evolutionary relationships among the GhWOX genes within each of the subfamilies.
The WOX proteins have been shown to act a pivotal part in numerous developmental processes, such as organ formation, embryo patterning, stem cell maintenance [38, 39]. Our data show that many GhWOX genes have different expression patterns with the homologous genes in Arabidopsis. For example, in contrast to WOX2 expression in the Arabidopsis embryo, we found that GhWOX2a_At/2a_Dt/2b_At/2b_Dt, are specifically expressed in the young root, and exhibit an expression profile similar to that of WOX2 in Populus tomentosa, which is mainly expressed in the roots [40]. We also noted that the duplicated genes show varying expression levels; GhWOX13a_Dt and GhWOX13b_Dt are primarily expressed in flowers, while GhWOX13b_At is expressed at a high level in young stems. These results suggest that some of WOX genes might acquire diverse functions during evolution.
GhWOX13a_Dt, GhWOX13b_At, and GhWOX13b_Dt are highly expressed in the cotton fiber, and their expressions gradually increase during fiber elongation. We analyzed the promoters of the GhWOX13 genes and identified putative GA, NAA, and BR response cis-elements in the promoters; we also found that the GhWOX13 genes are up-regulated after treatment with GA, BR, or NAA. AtWOX13 have high expression levels in inflorescences, floral buds, emerging lateral roots and root tip [41, 42]. The wox13 mutant showed slightly wider fruits with a reduced number of lateral roots in Arabidopsis. Our data indicate that GhWOX13 genes may involved in phytohormone mediating fiber elongation in cotton.
Taken together, our work not only comprehensively identified the WOXs in G. hirsutum, but also found that GhWOX13 transcripts were expressed during cotton fiber development and can be significantly induced by GA, NAA, and BR. Our research provides a clue for further uncovering the precise roles of WOX genes in cotton fiber development.
Conclusions
Gossypium hirsutum contained 32 WOX proteins and can be divided into three clades: the ancient, intermediate, and WUS clades. The number of WOX proteins in the WUS clade was more than that in the remaining two clades. Multiple introns and motifs were found in GhWOX genes. GhWOX13 genes were specifically and highly expressed in cotton fiber cells and they transcripts can be induced by GA, NAA, and BR. Our results also provide an approach for identifying and characterizing WOX genes in other species.
Methods
Databases and sequences
The genome sequence of Arabidopsis thaliana was downloaded from the TAIR database (http://www.arabidopsis.org/). The genome sequences of G. arboreum (A2, CRI-Updated assembly v1.0), Gossypium raimondii (D5, JGI assembly v2.0), and G. hirsutum (AD1, NAU assembly v1.1) were downloaded from the CottonFGD database (https://cottonfgd.org/). We used Ga (G. arboreum), Gr (Gossypium raimondii), Gh (G. hirsutum), and At (A. thaliana) as prefixes in the naming of WOX genes in this study.
Promoter analysis, multiple sequence alignment, and phylogenetic analysis
Sequences of 2000 nucleotides prior to the start codon were extracted from the genomic sequences of the GhWOX genes, and the cis-acting regulatory elements were predicted by the program PlantCARE online (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/). The gene IDs of the WOX genes from the above three species are shown in Additional file 2: Table S1. The full predicted amino acid sequences of the WOX genes from the four plant species were aligned using ClustalW. A Neighbor-Joining (NJ) phylogenetic tree was constructed by MEGA 6.0 software with pairwise deletion option, poisson correction model and uniform rates. Bootstrap test were carried out with 1000 replicates for evaluating the statistical reliability of the phylogenetic tree [43].
Gene structure, protein motif analysis, and genomic location
The Gene Structure Display Server (GSDS, http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/) was used to draw the exon–intron structures of GhWOX genes based on the full-length genomic sequences and the corresponding coding sequences obtained as described above [44]. InterPro, protein sequence analysis & classification (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/scan.html), was used to identify conserved domains in the GhWOX proteins [45]. Chromosomal position information of each GhWOX gene was acquired from the genome annotation, and the relative locations were shown on the respective chromosomes in a top-to-bottom orientation.
Plant materials and hormonal treatments
Gossypium hirsutum (‘Xuzhou 142’) seed was obtained from Institute of Cotton Research of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Anyang, China). Cotton plants were grown in a climate-controlled greenhouse with a 16 h light/8 h dark photoperiod at 30 °C. Fresh cotton seed fibers were harvested from bolls at various days post anthesis (DPA) at the indicated time points and then immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen as previously reported [46].
The plant hormone treatments were performed using previously-described methods [46]. Briefly, self-pollinated cotton flowers were collected at 1 DPA (days post anthesis). Subsequently, bracts, sepals and petals were removed and the ovaries were sterilized using 10% hypochlorous acid for 15 min, and then rinsed with sterile distilled water for seven times. The ovules were carefully dissected from the ovaries under sterile conditions and immediately floated on the liquid medium (0.272 g/L KH2PO4, 6.183 mg/L H3BO3, 0.242 mg/L Na2MoO4·2H2O, 0.441 g/L CaCl2·2H2O, 0.83 mg/L KI, 0.024 mg/L CoCl2·6H2O, 0.493 g/L MgSO4·7H2O, 16.902 mg/L MnSO4·H2O, 8.627 mg/L ZnSO4·7H2O, 0.025 mg/L CuSO4·5H2O, 5.055 mg/L KNO3, 8.341 mg/L FeSO4·7H2O, 11.167 mg/L Na2EDTA, 0.492 mg/L Nicotinic acid, 0.822 mg/L Pyridoxine·HCl, 1.349 mg/L Thiamine·HCl, 0.180 g/L Myo-inositol, 18.016 g/L D-Glucose, 3.603 g/L D-Fructose) containing 1 μM GA (Gibberellic acid), 5 μM BR (Brassinosteroid), or 5 μM NAA (1-Naphthaleneacetic acid) in a conical flask, respectively [46]. Then the ovules were cultured at 30 °C in darkness without agitation. For GA and NAA treatment, ovules incubated for 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h were collected together with fibers because of the difficulty of separating them from each other. For BR treatment, 6 h, 24 h, and 5 d ovules were sampled together with fibers. The samples were frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately after collection and stored at − 80 °C prior to use in the experiments. For each treatment, three individual samples were collected and the analysis was performed on the three biological replicates. GA, BR, and NAA were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
RNA extraction and qRT-PCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted using the E.Z.N.A.® Plant RNA Kit (OMEGA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The tissues were disrupted and homogenized. The column flow-through at the very last step was mixed with the membrane-binding solution and then loaded into the HiBind RNA Mini column. Finally, RNA was washed with RWC buffer and RNA wash buffer to remove proteins, polysaccharides, and salts. The total RNA was treated with DNaseI to remove gDNA contamination. First-strand cDNA was then synthesized using the PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit following the manufacturer’s protocol (TaKaRa, Dalian, China).
The qRT-PCR assays were performed using a Bio-Rad Real Time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad CFX96 Touch) [47]. The SYBR Green qRT-PCR reactions contained 10 μl SYBR® Premix Ex Taq™ II (Takara), 0.5 μl of 10 μM primers, and 2 ng cDNA template. The final volume was adjusted to 20 μl with ddH2O. The PCR cycling conditions were 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 5 s and 60 °C for 30 s. Relative gene expression was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method [47]. The experiment was performed with three biological replicates and each biological replicate was performed with three technical replicates. Primers used for qRT-PCR analysis are shown in Additional file 2: Table S3. The cotton ubiquitin gene GhUBQ7 was used as the internal control for normalization of gene expression in each qRT-PCR experiment.
Availability of data and materials
All of the data and materials supporting our research findings are contained in the methods section of the manuscript. Details are provided in the attached supplementary data.
Abbreviations
- BR:
-
Brassinosteroids
- DPA:
-
Days post anthesis
- GA:
-
gibberellin
- NAA:
-
Naphthaleneacetic Acid
- WOX:
-
WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX
References
Park SO, Zheng Z, Oppenheimer DG, Hauser BA. The PRETTY FEW SEEDS2 gene encodes an Arabidopsis homeodomain protein that regulates ovule development. Development. 2005;132(4):841–9.
Shimizu R, Ji JB, Kelsey E, Ohtsu K, Schnable PS, Scanlon MJ. Tissue specificity and evolution of meristematic WOX3 function. Plant Physiol. 2009;149(2):841–50.
Breuninger H, Rikirsch E, Hermann M, Ueda M, Laux T. Differential expression of WOX genes mediates apical-basal axis formation in the Arabidopsis embryo. Dev Cell. 2008;14(6):867–76.
Suer S, Agusti J, Sanchez P, Schwarz M, Greb T. WOX4 imparts auxin responsiveness to cambium cells in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2011;23(9):3247–59.
Hirakawa Y, Kondo Y, Fukuda H. TDIF peptide signaling regulates vascular stem cell proliferation via the WOX4 homeobox gene in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2010;22(8):2618–29.
Stahl Y, Wink RH, Ingram GC, Simon R. A signaling module controlling the stem cell niche in Arabidopsis root meristems. Curr Biol. 2009;19(11):909–14.
Sarkar AK, Luijten M, Miyashima S, Lenhard M, Hashimoto T, Nakajima K, Scheres B, Heidstra R, Laux T. Conserved factors regulate signalling in Arabidopsis thaliana shoot and root stem cell organizers. Nature. 2007;446(7137):811–4.
Ji J, Strable J, Shimizu R, Koenig D, Sinha N, Scanlon MJ. WOX4 promotes procambial development. Plant Physiol. 2010;152(3):1346–56.
Haecker A, Gross-Hardt R, Geiges B, Sarkar A, Breuninger H, Herrmann M, Laux T. Expression dynamics of WOX genes mark cell fate decisions during early embryonic patterning in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development. 2004;131(3):657–68.
Costanzo E, Trehin C, Vandenbussche M. The role of WOX genes in flower development. Ann Bot-London. 2014;114(7):1545–53.
Zhang Y, Wu R, Qin G, Chen Z, Gu H, Qu LJZDB. Over-expression of WOX1 leads to defects in meristem development and polyamine homeostasis in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol. 2011;53(6):493–506.
Vandenbussche M, Horstman A, Zethof J, Koes R, Rijpkema AS, Gerats T. Differential recruitment of WOX transcription factors for lateral development and organ fusion in Petunia and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2009;21(8):2269–83.
Liu M, Lei L, Miao F, Powers C, Zhang X, Deng J, Tadege M, Carver BF, Yan L. The STENOFOLIA gene from Medicago alters leaf width, flowering time and chlorophyll content in transgenic wheat. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018;16(1):186–96.
Nakata M, Matsumoto N, Tsugeki R, Rikirsch E, Laux T, Okada K. Roles of the middle domain-specific WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX genes in early development of leaves in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2012;24(2):519–35.
Lin H, Niu L, McHale NA, Ohme-Takagi M, Mysore KS, Tadege M. Evolutionarily conserved repressive activity of WOX proteins mediates leaf blade outgrowth and floral organ development in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(1):366–71.
Ji J, Shimizu R, Sinha N, Scanlon MJ. Analyses of WOX4 transgenics provide further evidence for the evolution of the WOX gene family during the regulation of diverse stem cell functions. Plant Signal Behav. 2010;5(7):916–20.
Yasui Y, Ohmori Y, Takebayashi Y, Sakakibara H, Hirano HY. WUSCHEL- RELATED HOMEOBOX4 acts as a key regulator in early leaf development in rice. PLoS Genet. 2018;14(4):e1007365.
Lopez-Moya F, Escudero N, Zavala-Gonzalez EA, Esteve-Bruna D, Blázquez MA, Alabadí D, Lopez-Llorca LV. Induction of auxin biosynthesis and WOX5 repression mediate changes in root development in Arabidopsis exposed to chitosan. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16813.
Li J, Zhang J, Jia H, Liu B, Sun P, Hu J, Wang L, Lu M. The WUSCHEL-related homeobox 5a (PtoWOX5a) is involved in adventitious root development in poplar. Tree Physiol. 2018;38(1):139–53.
Xu M, Xie W, Huang M. Two WUSCHEL-related HOMEOBOX genes, PeWOX11a and PeWOX11b, are involved in adventitious root formation of poplar. Physiol Plant. 2015;155(4):446–56.
Cheng S, Tan F, Lu Y, Liu X, Li T, Yuan W, Zhao Y, Zhou DX. WOX11 recruits a histone H3K27me3 demethylase to promote gene expression during shoot development in rice. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(5):2356–69.
Cheng S, Huang Y, Zhu N, Zhao Y. The rice WUSCHEL-related homeobox genes are involved in reproductive organ development, hormone signaling and abiotic stress response. Gene. 2014;549(2):266–74.
Cheng S, Zhou DX, Zhao Y. WUSCHEL-related homeobox gene WOX11 increases rice drought resistance by controlling root hair formation and root system development. Plant Signal Behav. 2016;11(2):e1130198.
Ruan YL, Llewellyn DJ, Furbank RT. The control of single-celled cotton fiber elongation by developmentally reversible gating of plasmodesmata and coordinated expression of sucrose and K+ transporters and expansin. Plant Cell. 2001;13(1):47–60.
Kim HJ, Triplett BA. Cotton fiber growth in planta and in vitro. Models for plant cell elongation and cell wall biogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2001;127(4):1361–6.
Qin YM, Zhu YX. How cotton fibers elongate: a tale of linear cell-growth mode. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2011;14(1):106–11.
Li FG, Fan GY, Wang KB, Sun FM, Yuan YL, Song GL, Li Q, Ma ZY, Lu CR, Zou CS, et al. Genome sequence of the cultivated cotton Gossypium arboreum. Nat Genet. 2014;46(6):567–72.
Wang KB, Wang ZW, Li FG, Ye WW, Wang JY, Song GL, Yue Z, Cong L, Shang HH, Zhu SL, et al. The draft genome of a diploid cotton Gossypium raimondii. Nat Genet. 2012;44(10):1098–103.
Li FG, Fan GY, Lu CR, Xiao GH, Zou CS, Kohel RJ, Ma ZY, Shang HH, Ma XF, Wu JY, et al. Genome sequence of cultivated upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum TM-1) provides insights into genome evolution. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(5):524–U242.
Zhang TZ, Hu Y, Jiang WK, Fang L, Guan XY, Chen JD, Zhang JB, Saski CA, Scheffler BE, Stelly DM, et al. Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(5):531–7.
Du X, Huang G, He S, Yang Z, Sun G, Ma X, Li N, Zhang X, Sun J, Liu M, et al. Resequencing of 243 diploid cotton accessions based on an updated a genome identifies the genetic basis of key agronomic traits. Nat Genet. 2018;50(6):796–802.
Chen ZJ, Scheffler BE, Dennis E, Triplett BA, Zhang TZ, Guo WZ, Chen XY, Stelly DM, Rabinowicz PD, Town CD, et al. Toward sequencing cotton (Gossypium) genomes. Plant Physiol. 2007;145(4):1303–10.
Wendel JF. New World tetraploid cottons contain old world cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86(11):4132–6.
Wang XY, Guo H, Wang JP, Lei TY, Liu T, Wang ZY, Li YX, Lee TH, Li JP, Tang HB, et al. Comparative genomic de-convolution of the cotton genome revealed a decaploid ancestor and widespread chromosomal fractionation. New Phytol. 2016;209(3):1252–63.
Nardmann J, Reisewitz P, Werr W. Discrete shoot and root stem cell-promoting WUS/WOX5 functions are an evolutionary innovation of angiosperms. Mol Biol Evol. 2009;26(8):1745–55.
Yang Z, Gong Q, Qin W, Yang Z, Cheng Y, Lu L, Ge X, Zhang C, Wu Z, Li F. Genome-wide analysis of WOX genes in upland cotton and their expression pattern under different stresses. BMC Plant Biol. 2017;17(1):113.
Deveaux Y, Toffano-Nioche C, Claisse G, Thareau V, Morin H, Laufs P, Moreau H, Kreis M, Lecharny A. Genes of the most conserved WOX clade in plants affect root and flower development in Arabidopsis. BMC Evol Biol. 2008;8:291.
Nardmann J, Werr W. The invention of WUS-like stem cell-promoting functions in plants predates leptosporangiate ferns. Plant Mol Biol. 2012;78(1):123–34.
Nardmann J, Werr W. The shoot stem cell niche in angiosperms: expression patterns of WUS orthologues in rice and maize imply major modifications in the course of mono- and dicot evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 2006;23(12):2492–504.
Liu B, Wang L, Zhang J, Li J, Zheng H, Chen J, Lu M. WUSCHEL-related Homeobox genes in Populus tomentosa: diversified expression patterns and a functional similarity in adventitious root formation. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:296.
Sakakibara K, Reisewitz P, Aoyama T, Friedrich T, Ando S, Sato Y, Tamada Y, Nishiyama T, Hiwatashi Y, Kurata T, et al. WOX13-like genes are required for reprogramming of leaf and protoplast cells into stem cells in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Development. 2014;141(8):1660–70.
Sun XD, Xiang N, Wang CD, Yang SH, Li X, Yang YQ, Yang YP. Isolation and functional analysis of SpWOX13 from Stipa purpurea. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 2015;33(5):1441–50.
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30(12):2725–9.
Hu B, Jin J, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo J, Gao G. GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(8):1296–7.
Quevillon E, Silventoinen V, Pillai S, Harte N, Mulder N, Apweiler R, Lopez R. InterProScan: protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(Web Server):W116–20.
Shi YH, Zhu SW, Mao XZ, Feng JX, Qin YM, Zhang L, Cheng J, Wei LP, Wang ZY, Zhu YX. Transcriptome profiling, molecular biological, and physiological studies reveal a major role for ethylene in cotton fiber cell elongation. Plant Cell. 2006;18:651–64.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31600223), Hong Kong Scholars Program (XJ2017017), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. GK201803041 and GK201901004), State Key Laboratory of Cotton Biology Open Fund (Grant No. CB2018A03), National Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (Grant No. cx2018143), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Grant No. 2018JZ3006 and 2019JM-491), Shaanxi Youth Entrusted Talents Program (Grant No. 20190205), Shaanxi Postdoctoral Project (Grant No. 2018BSHYDZZ76), and Diligent Research and Innovation Fund Project (Grant No. KY2018YB003). The funding bodies provided the financial support to the research projects, but didn’t involved in study design, data collection, analysis, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.X. and J.Y. designed the research. P.H. and Y.Z. performed the research. H.L., Y.Y., and C.W. analyzed the data. G.X. and P.H. wrote the paper. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Figure S1. Identification of putative GA-related cis-elements in the promoter regions of the GhWOX genes. Figure S2. Putative BR response elements identified in the GhWOX gene promoter regions. Figure S3. Detection of putative auxin-related cis-elements in the GhWOX gene promoter regions. (DOCX 3317 kb)
Additional file 2:
Table S1. Analysis of the G. hirsutum WOX gene family members and their orthologs in the AA and DD genome cotton species. Table S2. Analysis of duplication events in the G. hirsutum WOX genes mapped to chromosomes. Table S3. PCR primers used for analysis of duplication events in the G. hirsutum WOX13 gene family members mapped to chromosomes. (DOC 107 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
He, P., Zhang, Y., Liu, H. et al. Comprehensive analysis of WOX genes uncovers that WOX13 is involved in phytohormone-mediated fiber development in cotton. BMC Plant Biol 19, 312 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1892-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1892-x