Abstract
Background
Cholangiocarcinoma is one of the deadly disease with poor 5-year survival and poor response to conventional therapies. Previously, we found that p27kip1 nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation confers proliferation potential to cholangiocarcinoma cell line QBC939 and this process is mediated by crm-1. However, no other post-transcriptional regulation was found in this process including sumoylation in cholangiocarcinoma.
Results
In this study, we explored the role of sumoylation in the nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation of p27kip1 and its involvement of QBC939 cells’ proliferation. First, we identified K73 as the sumoylation site in p27kip1. By utilizing plasmid flag-p27kip1, HA-RanBP2, GST-RanBP2 and His-p27kip1 and immunoprecipitation assay, we validated that p27kip1 can serve as the sumoylation target of RanBP2 in QBC939. Furthermore, we confirmed crm-1’s role in promoting nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation of p27kip1 and found that RanBP2’s function relies on crm-1. However, K73R mutated p27kip1 can’t be identified by crm-1 or RanBP2 in p27kip1 translocation process, suggesting sumoylation of p27kip1 via K73 site is necessary in this process by RanBP2 and crm-1. Phenotypically, the overexpression of either RanBP2 or crm-1 can partially rescue the anti-proliferative effect brought by p27kip1 overexpression in both the MTS and EdU assay. For the first time, we identified and validated the K73 sumoylation site in p27kip1, which is critical to RanBP2 and crm-1 in p27kip1 nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation process.
Conclusion
Taken together, targeted inhibition of sumoylation of p27kip1 may serve as a potentially potent therapeutic target in the eradication of cholangiocarcinoma development and relapses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Cholangiocarcinoma, or bile duct cancer, is a gastrointestinal cancer with quite limited response to surgery treatment and other conventional therapies with poor long-term outcome [1,2,3]. Early diagnosis is difficult due to its anatomical and biological characteristics. Therefore, identifying molecular markers and mechanisms that underlie the carcinogenesis in cholangiocarcinoma is critical to the development of diagnostic tools in the early stage, novel potent drugs and effective therapies [1,2,3,4,5,6].
Sumoylation mainly functions at post-translational level affecting lots of cellular functions [7, 8] including nuclear-cytoplasmic transportation, transcription, protein stabilization, stress related processes and cell cycle regulation. It is mainly mediated by SUMO proteins, which is a group of small proteins that can covalently link or unlink to their target proteins to modify their functions [9]. Their function is quite similar to ubiquitin and the whole process is also analogous to the cascade reaction of ubiquitination.
RAN binding protein 2, or RanBP2 is a protein that belong to nucleoporin family that constitutes the nuclear pore complex [10]. RanBP2 has multiple domains, each of which can interact with various kinds of proteins such as importin-β [11], exportin-1/CRM1 [12], cox11 [13], the kinesin-1 [14] and KIF5C [15]. Particularly, exportin-1/CRM1 can utilize the zinc finger cluster domain of RanBP2 as the docking site [12]. By means of these domains, RanBP2 actively participates the protein shuttling program through the nucleomembrane. Cooperatively, there are multiple interactive proteins that help RanBP2 form complex on the nucleus membrane. One of them is the E2 enzyme UBC9 [16]. RanBP2 can promote SUMO1 transfer from UBC9 to the SUMO1 target SP100 [16]. Another protein partner is RanGAP which is the GTPase activating protein for Ran [17]. SUMO-RanGAP interacts with a domain at the carboxyl terminus of RanBP2. Evidence shows that sumoylation at the cytoplasmic filaments of the nuclear pore complex is one of the important activities on the nucleus membrane [18] and suggests that posttranslational sumoylation and nuclear import are tightly connected.
p27kip1, or cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B, is an enzyme inhibitor that can inhibit the activation of cyclin E-CDK2 [19] or cyclin D-CDK4 [20] complexes via binding to these proteins. It mainly helps stop the cell cycle progression at stage G1 [21]. Our previous study proved that crm-1 is enhanced in cholangiocarcinoma and can promote nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation of p27kip1 [22]. Interestingly, p53, a canonical anti-oncogene, was also found to be regulated by CRM-1 in the nucleocytoplasmic translocation and this process is modulated by sumoylation [23]. Also, we found p27kip1 mainly accumulates in the cytoplasm of cholangiocarcinoma cells and acts as a tumor suppressor. However, it is still elusive how this protein is transported to the cytoplasm and the possible epigenetic modification processes as sumoylation contributing in this process. Indeed, only Baldassarre and Schiappacassi et al. reported that K134 of p27kip1 is responsible for its sumoylation before it is transported through nuclear membrane in 293T/17 and Hela cells in response to TGF-β [24]. What’s happened of p27kip1 in the QBC939 and the role of sumoylation in this process is still unknown. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the possible sumoylation sites of p27kip1 and its possible regulatory proteins via immunoprecipitation, GST-pull down assays, MTS assay and EdU assay to evaluate the involvement of sumoylation in p27kip1, together with its clinical significance in cholangiocarcinoma.
Methods
Antibodies, plasmids and reagents
p27kip1 (ZA-0557) mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody, horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled goat-anti-mouse IgG (ZB-2301), streptavidin–peroxidase immunostaining kit and 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) were purchased from Beijing Zhongshan Co. (Beijing, China); rabbit anti-CRM-1 (H-300; sc-5595); SUMO-1 (sc-5308) mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody, His-probe (sc-804) rabbit polyclonal antibody, HA-probe (sc-7392) mouse monoclonal antibody and histone H3 (sc-10809) rabbit polyclonal antibody, CDK-2 (sc-6248) mouse anti-human antibody, p-CDK2 (sc-101656) rabbit anti-human antibody were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Anti-DDDDK tag (or anti-flag tag) (ab1162) rabbit polyclonal antibody was purchased from Abcam (Abcam, MA, USA). Glutathione Agarose (cat#16100) was purchased from Pierce ThermoFisher Scientific Corp. (ThermoFisher, USA). The ECL reagents were purchased from Pierce Chemical Co. (Rockford, IL, USA). Two pair of siRNAs targeting CRM-1 were purchased from Ribobio Corp. (Guangzhou, China) and sequence are listed as follows, siRNA1: GAAGUACUGACACAUUUAA; siRNA2: GGCUGCUGAACUCUAUAGA.
Plasmids for flag-p27kip1-wt, flag-p27kip1-K73R, HA-ranBP2, GST-RanBP2, flag-Crm1 and His-p27kip1 were purchased from Ribobio Corp. (Guangzhou, China).
Cytoplasmic and nuclear protein isolation
The cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins were isolated with the ProteoJET Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Protein Extraction Kit (Fermentas Corp.; Burlington, ON, Canada) by following the manufacturer’s instructions. Tissue samples were gently homogenized in PBS with protease inhibitors after pre-cooled PBS rinsing. The solution was then centrifuged at 250g, 5 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was discarded and 500 μl of cell lysis buffer containing protease inhibitors and DTT was added to 100 mg of tissue, mixed gently by vortexing, and incubated in ice for 10 min. The cytoplasmic fraction was isolated first via centrifugation at 500g, 7 min at 4 °C. The nuclei pellet was set on ice and the supernatant was centrifuged at 20,000g, 15 min at 4 °C to clear the cytoplasmic protein extract. Then it was transferred to a new tube for analysis. At the same time, the nuclei pellet was washed in 500 μl nuclei washing buffer with protease inhibitors and DTT by vortexing briefly, and then incubate in ice for 2 min. After centrifugation at 500g, 7 min at 4 °C, the resultant supernatant was removed. After repeating this wash for another 1–2 times, the volume of the nuclei pellet was estimated and 10 volumes of ice-cold nuclei storage buffer containing protease inhibitors and DTT was used for resuspension. The suspension was transferred to a new tube for centrifugation at 20,000g, 5 min, 150 μl of ice-cold nuclei storage buffer with protease inhibitors and DTT was added to the nuclei pellet. The nuclei were lysed with one tenth of the volume of nuclei lysis reagent. After short vortexing and incubation on a rotating bed (900–1200 rpm), 15 min at 4 °C, the resultant nuclear lysate was processed with centrifugation at 20,000g, 5 min at 4 °C, and the supernatant containing the nuclear protein extract was transferred to a new tube for analysis.
GST-pull down and co-immunoprecipitation assays
GST-pull down was undertaken as mentioned by Sambrook [25]. To investigate protein interactions, co-immunoprecipitation was performed in QBC939 cells. The cells were transfected with different vectors and lysed in NETN buffer. Specific antibody and Protein G Agarose (Roche) were incubated with the cell lysate overnight at 4 °C. The resins were washed four times with buffer NETN. After elution by 1× loading buffer, heated at 95 °C for 5 min, the bound proteins were further analyzed with western blotting.
Western blot analysis
Equal amounts of nuclear or cytoplasmic proteins were examined by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. The proteins were transferred to a PVDF membrane and blocked in blocking buffer (20% skim milk in TBST) for 2 h at 25 °C. The membrane was incubated at 25 °C for 1 h with primary antibodies against SUMO1 (1:1000); flag (1:1000); HA (1:1000); p-CDK2 (Thr 160) (1:1000); CDK-2 (1:2000); His (1:1000); p27kip1 (1:2000); CRM-1 (1:1000); and (1:1000); After further incubation at 4 °C overnight, the membranes were incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:1000) for 2 h at room temperature. The membrane was processed with electrochemical luminescence (ECL) and exposed to X-ray film. The expression level were quantified with a grayscale scanner. H3 (1:2000) was included as loading controls.
Cell viability assay
QBC939 cells were lentiviral infected with flag-p27kip1 and/or HA-RanBP2, HA-Crm1 vector after lentivirus packaging for approximately 24 h. After the treatment, the above two groups together with no treatment QBC939 cells were transferred to 96-well plate with the density of 1000 cells per well. Cell viability was evaluated by MTS assay (Promega, USA) and EdU assay (Ribo, Guangzhou, China) according to manufacturer’s protocol.
In vitro sumoylation assay
This assay was undertaken as described by Lovista et al. [24]. The whole reaction was undertaken in 30 μl reaction system with 50 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM DTT, 2 mM ATP, 270 ng SAE1/SAE2 (Boston Biochem, USA), 300 ng UBC9 (Boston Biochem, USA), 4 µg SUMO1 (Boston Biochem, USA), and 3 µg His-p27 and incubated for 2 h at 30 °C. Then all samples were sent for western blotting analysis.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were repeated three times. Statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS software v. 20.0 (SPSS Inc.; Chicago, IL, USA). Fisher’s exact test was used to determine significant differences between groups of data; Chi square (χ2) test was used to compare protein expression percentage, Spearman’s Rank Correlation test was used to compare pairs of variables. All values are shown as mean ± SEM unless otherwise indicated and one way ANOVA was adopted to examine the difference between the CRM-1 knock-down group, blank group and vector group. All statistical significant results were shown in *** for p < 0.001; ** for p < 0.01 and * for p < 0.05.
Results
p27kip1 can be sumoylated at K73 modification site
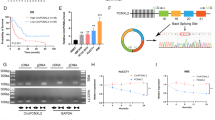
As shown in Fig. 1a, there are five possible sumoylation sites for p27kip1 according to the model developed by Xue and Re [26, 27] at the website of http://sumosp.biocuckoo.org. In order to further validate the sumoylation site for p27kip1, immunoprecipitation were undertaken by using anti-p27kip1, anti-flag and anti-SUMO1 antibodies, together with flag-p27kip1-WT and K73R point mutated form of p27kip1 constructs. Results reveal that K73 is the sumoylation site for p27kip1, as shown in Fig. 1b–d.
p27kip1 can be sumoylated at K73 modification site. a The sites predicted by the model developed by Xue and Ren at the website of http://sumosp.biocuckoo.org. b The immunoprecipitation result with the antibody of SUMO1 as the probe. Also, plasmids expressing 1st–99th amino acid (aa) and 100th–198th aa with or without mutation in potential sumoylation sites fused with flag tag were used for protein immunoprecipitation and purification in QBC939 cells, followed with anti-SUMO1 antibody examination, as shown in c. Also, flag-p27kip1-WT and K73R point mutated form of p27kip1 were constructed and transfected into QBC939 cells, immunoprecipitation with flag antibody reveals that K73 is the sumoylation site for p27kip1 (d)
RanBP2 can increase the sumoylation of p27kip1
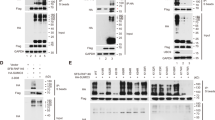
RanBP2-HA plasmid was constructed and transfected to QBC939 cells. Immuno-precipitation with anti-p27kip1 antibody verified that RanBP2 can increase the sumoylation of p27kip1 (Fig. 2a). Also, flag-p27kip1 plasmid was constructed and transfected into either QBC939-RanBP2-HA or QBC939-control cells. Immuno-precipitation with anti-HA antibody proved that p27kip1 can bind with RanBP2 (Fig. 2b). Correspondingly, HA-RanBP2 plasmid was transfected into either QBC939-flag-p27kip1 or QBC939-control cells. Immunoprecipitation result with anti-flag antibody proved that RanBP2 can bind to p27kip1 (Fig. 2c). Moreover, GST-RanBP2 and His-p27kip1 plasmids were constructed for GST-pull down assay. As shown in Fig. 2d, p27kip1 proved to be one of the protein partners of RanBP2. Also, we analyzed the cytoplasmic and nuclear p27kip1 levels and found that p27kip1 in the nucleus is transported through nuclear membrane after RanBP2 is overexpressed (Fig. 2e). In order to further justify the sumoylation of p27kip1 in QBC939 cells, we did an in vitro sumoylation assay (Fig. 2f) and found p27kip1 can be modified via interaction with UBC9, SUMO1 and SAE1/SAE2.
RanBP2 can increase the sumoylation of p27kip1. RanBP2-HA plasmid was constructed and transfected to QBC939 cells. Immuno-precipitation with anti-p27kip1 antibody verified that RanBP2 can increase the sumoylation of p27kip1 (a). Also, flag-p27kip1 plasmid was constructed and transfected into either QBC939-RanBP2-HA or QBC939-control cells. Immuno-precipitation with anti-HA antibody proved that p27kip1 can bind with RanBP2 (b). Correspondingly, HA-RanBP2 plasmid was transfected into either QBC939-flag-p27kip1 or QBC939-control cells. Immunoprecipitation result with anti-flag antibody proved that RanBP2 can bind with p27kip1. c. Moreover, GST-RanBP2 and His-p27kip1 plasmids were constructed for GST-pull down assay. As shown in d, p27kip1 proved to be one of the binding targets of RanBP2. e HA-RanBP2 plasmids and its control vector were transfected into QBC939 cells. Cytoplasmic proteins, nuclear proteins and total cellular proteins were separately extracted from the same batch of cells and sent for WB. Also, RanBP2 was validated to be overexpressed after HA-RanBP2 transfection. f In vitro sumoylation assay was undertaken by his-tagged p27kip1 proteins were incubated with SAE1/SAE2, SUMO1 and UBC9 in increasing doses (**p < 0.01)
Sumoylation p27kip1 is indispensable for its nucleus-cytoplasmic translocation mediated by Crm-1
Nuclear and cytoplasmic protein were separately extracted. Figure 3a shows that p27kip1 expression in the nucleus is reduced after overexpression of Crm-1 in QBC939 cells. Also, as we transfect the HA-RanBP2 plasmid into QBC939 cells, p27kip1 expression in the nucleus was decreased (Fig. 3b). Moreover, when we transfect QBC939-HA-RanBP2 cells with siRNA suppressing Crm-1, p27kip1 level was rescued in the nucleus (Fig. 3b; Additional file 1: Fig. S1). Additionally, immunofluorescence staining with anti-flag antibody also verifies that Crm-1 overexpression can suppress nuclear p27kip1 (Fig. 3c; Additional file 1: Fig. S2) while the level of a K73R point mutated form of p27kip1 in the nucleus cannot be changed by Crm-1 overexpression (Fig. 3c). Further, we found the phosphorylated form of CDK-2 in the nucleus was reduced when Crm-1 overexpressed in QBC939 cells (Fig. 3d).
Sumoylation p27kip1 is indispensable for its nucleus-cytoplasmic translocation mediated by Crm-1. Nuclear and cytoplasmic protein were separately extracted. a shows that p27kip1 expression in the nucleus is reduced after overexpression (OE) of Crm-1 in QBC939 cells. Also, as we transfect the HA-RanBP2 plasmid into QBC939 cells, p27kip1 expression in the nucleus was decreased (b). Moreover, when we transfect QBC939-HA-RanBP2 cells with siRNA suppressing Crm-1, p27kip1 level was rescued in the nucleus (b). Additionally, immunofluorescence staining with anti-flag antibody also verifies that Crm-1 overexpression can suppress nuclear p27kip1 (c) while the level of a K73R point mutated form of p27kip1 in the nucleus cannot be changed by Crm-1 overexpression (c), in which the fluorescence intensity was determined by the red signal/blue signal in each cell’s nuclear area. Further, we found the phosphorylated form of CDK-2 in the nucleus was reduced when Crm-1 overexpressed in QBC939 cells (d)
Sumoylation of p27kip1 promotes the proliferation of cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 cells
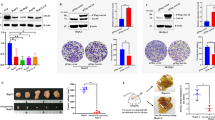
p27kip1 was found to be able to suppress the growth of QBC939 cells when it was artificially overexpressed in QBC939 cells (Fig. 4a). However, this effect can be partially rescued by overexpression of RanBP2 (Fig. 4a). Similar effect was observed when Crm-1 can partially rescue the anti-proliferative effect brought by p27kip1 overexpression (Fig. 4b). Moreover, EdU assay also verifies that both RanBP2 (Fig. 4c) and Crm-1 (Fig. 4d) can partially reverse the effect brought by overexpression of p27kip1 in QBC939 cells (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
Sumoylation of p27kip1 promotes the proliferation of cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 cells. p27kip1 was found to be able to suppress the growth of QBC939 cells when it was artificially overexpressed in QBC939 cells (a). However, this effect can be partially rescued by overexpression of RanBP2 (a). Similar effect was observed when Crm-1 can partially rescue the anti-proliferative effect brought by p27kip1 overexpression (b). Moreover, EdU assay also verifies that both RanBP2 (c) and Crm-1 (d) can partially reverse the effect brought by overexpression of p27kip1 in QBC939 cells (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)
Discussion
SUMO proteins were firstly discovered and validated over a decade ago, when a cellular protein as small as 12 kDa which bears 18% homology to the ubiquitin protein was found. There are four different genes coding for different SUMO proteins [28], including SUMO1, 2, 3 and 4. SUMO 2 and 3 shared 92% common sequences but only 48% identity as compared to SUMO1. Bellail et al. reported that SUMO1 modification can stabilize CDK6 protein and drive the cell cycle and glioblastoma progression [8]. Also, SUMO 1 is said to modify LKB1, which is a major upstream kinase of the energy sensor AMPK, enabling LKB1 to recognize and activate AMPK in energy–stress in cancer microenvironment [7]. However, there’s still a lack of knowledge in sumoylation of p27kip1 in cholangiocarcinoma. Spagnuolo et al. reported that reduction of sumoylation in S100A4 would decrease its nuclear import brought by low dose paclitaxel, leading to halts of tumor invasiveness and hematogenous metastatization [4]. Baldassarre and Schiappacassi et al. reported that K134 of p27kip1 is the sumoylation site in tumor-derived cell in response to TGF-β [24]. There are no other study focusing on the post-translational regulation in cholangiocarcinoma.
p27kip1 is a tumor suppressor gene that actively participate in regulating the cell cycle progression negatively at the G1/S checkpoint via inhibiting CDK2. As shown in Fig. 3d, CDK2 phosphorylation was remarkably enhanced after CRM-1 overexpression. This is consistent with our speculation that CRM-1 controls p27kip1 nucleocytoplasmic translocation thereby eliminating its inhibitory effect on CDK2 and promoting G1/S entry. Aberrant expression or localization of p27kip1 weakens its inhibitory effect in the cell cycle, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and carcinogenesis [29]. Downregulation of p27kip1 and abnormal subcellular localization have been reported in a variety of tumor types [30]. Our previous study shows that p27kip1 nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation also happens in the cholangiocarcinoma and this might due to the enhanced level of crm-1 in this cancer. The downregulation of crm-1 can remarkably reduce the cytoplasmic level of p27kip1, resulting in the improvement of cancer cell proliferation.
In malignancy transformation, p27kip1 is often silenced via synthesis impairment, degradation acceleration, or aberrant cellular localization as we study in the cholangiocarcinoma. P27kip1 silencing generally occur posttranscriptionally brought by the activation of pathways as receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), Ras-mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK). Enhancement of these pathways promoting p27kip1 proteolysis allows cholangiocarcinoma cells to divide and proliferate. Once p27kip1 is phosphorylated by Src at tyrosine 74 or 88, the inhibition to cyclinE-cdk2 would be unchained. Also, in our study, when p27kip1 is sumoylated or tagged by SUMO1 at K73, the transportation of this protein from nucleus to cytoplasm is accelerated with the aid of RanBP2 and crm-1.
Also, evidence shows that RanBP2 mainly functions as SUMO E3 ligase and facilitates protein import or export from the nuclear membrane. Packham et al. [31] reported that the sumoylation of IGF-1R would help its nuclear translocation by RanBP2 and importin-β, leading to the failure of anti-IGF-1R therapy in cancers. However, there are also studies finding that RanBP2 can work as a tumor suppressor gene via sumoylation of different target proteins as Topoisomerase II (TopoII) [32]. Considering our study in the cholangiocarcinoma, together with all the publications concerning RanBP2 and sumoylation, the role of RanBP2 is more likely dependent on its target protein. In our study, the target protein p27kip1 mainly acts as a tumor-suppressor gene in the nucleus, RanBP2 and SUMO1 act as oncogenes by promoting the nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation and debilitate the G1-arrest brought by p27kip1 accumulation in the nucleus. In spite of all the facts we have about the sumoylation regulation in p27kip1, there’re still much more to be discovered including the possible oncogenic effect of other SUMO proteins because of their overlapping and compensatory functions, how the regulatory network of SUMO1, RanBP2, Crm-1, p27kip1 and other cell cycle proteins collaborate in the maintenance of cholangiocarcinoma cells and etc. In spite of these challenges, our investigation in the sumoylation of p27kip1 by RanBP2 and Crm-1 sheds light on the regulation of cancer cell growth in cholangiocarcinoma and offers a novel therapeutic target for the treatment and eradication of this cancer in the future.
Conclusion
According to the results we have, it’s promising that targeted inhibition of sumoylation of p27kip1 may serve as a potentially potent therapeutic target in the eradication of cholangiocarcinoma development and relapses.
Abbreviations
- OE:
-
overexpression
- Crm-1:
-
exportin 1
- RanBP-1:
-
RAN binding protein 1
References
He W, Wang B, Zhuang Y, Shao D, Sun K, Chen J. Berberine inhibits growth and induces G1 arrest and apoptosis in human cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 2012;119(4):341–8.
Luo J, Chen Y-J, Wang W-Y, Zou S-Q. Effect of mutant p27(kip1) gene on human cholangiocarcinoma cell line, QBC(939). World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(34):5344–8.
Shiraso S, Katayose Y, Yamamoto K, Mizuma M, Yabuuchi S, Oda A, Rikiyama T, Onogawa T, Yoshida H, Hayashi H, et al. Overexpression of adenovirus-mediated p27kip1 lacking the Jab1-binding region enhances cytotoxicity and inhibits xenografted human cholangiocarcinoma growth. Anticancer Res. 2009;29(6):2015–24.
Spagnuolo G, Cadamuro M, Sambado L, Indraccolo S, Nardo G, Rosato A, Novelli E, Spirlì C, Strazzabosco M, Fabris L. P0226: reduction in sumoylation-dependent S100A4 nuclear import in cholangiocarcinoma by low dose paclitaxel halts tumor invasiveness and hematogenous metastatization by modulating Rho-A and Cdc42 activities. J Hepatol. 2015;62:S392.
Huether A, Hopfner M, Baradari V, Schuppan D, Scherubl H. Sorafenib alone or as combination therapy for growth control of cholangiocarcinoma. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;73(9):1308–17.
Yabuuchi S, Katayose Y, Oda A, Mizuma M, Shirasou S, Sasaki T, Yamamoto K, Oikawa M, Rikiyama T, Onogawa T, et al. ZD1839 (IRESSA) stabilizes p27Kip1 and enhances radiosensitivity in cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2009;29(4):1169–80.
Ritho J, Arold Stefan T, Yeh Edward TH. A Critical SUMO1 Modification of LKB1 regulates AMPK activity during energy stress. Cell Rep. 2015;12(5):734–42.
Bellail AC, Olson JJ, Hao C. SUMO1 modification stabilizes CDK6 protein and drives the cell cycle and glioblastoma progression. Nature Commun. 2014;5:4234.
Hay RT. SUMO: a history of modification. Mol Cell. 2005;18(1):1–12.
Ferreira PA, Nakayama TA, Pak WL, Travis GH. Cyclophilin-related protein RanBP2 acts as chaperone for red/green opsin. Nature. 1996;383(6601):637–40.
Ben-Efraim I, Gerace L. Gradient of increasing affinity of importin β for nucleoporins along the pathway of nuclear import. J Cell Biol. 2001;152(2):411–8.
Singh BB, Patel HH, Roepman R, Schick D, Ferreira PA. The zinc finger cluster domain of RanBP2 is a specific docking site for the nuclear export factor, exportin-1. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(52):37370–8.
Aslanukov A, Bhowmick R, Guruju M, Oswald J, Raz D, Bush RA, Sieving PA, Lu X, Bock CB, Ferreira PA. RanBP2 modulates Cox11 and hexokinase I activities and haploinsufficiency of RanBP2 causes deficits in glucose metabolism. PLoS Genet. 2006;2(10):e177.
K-i Cho, Yi H, Desai R, Hand AR, Haas AL, Ferreira PA. RANBP2 is an allosteric activator of the conventional kinesin-1 motor protein, KIF5B, in a minimal cell-free system. EMBO Rep. 2009;10(5):480–6.
Cho KI, Cai Y, Yi H, Yeh A, Aslanukov A, Ferreira PA. Association of the kinesin-binding domain of RanBP2 to KIF5B and KIF5C determines mitochondria localization and function. Traffic. 2007;8(12):1722–35.
Werner A, Flotho A, Melchior F. The RanBP2/RanGAP1*SUMO1/Ubc9 complex is a multisubunit SUMO E3 ligase. Mol Cell. 2012;46(3):287–98.
Mahajan R, Delphin C, Guan T, Gerace L, Melchior F. A small ubiquitin-related polypeptide involved in targeting RanGAP1 to nuclear pore complex protein RanBP2. Cell. 1997;88(1):97–107.
Kaminsky R, Denison C, Bening-Abu-Shach U, Chisholm AD, Gygi SP, Broday L. SUMO regulates the assembly and function of a cytoplasmic intermediate filament protein in C. elegans. Dev Cell. 2009;17(5):724–35.
Chu I, Sun J, Arnaout A, Kahn H, Hanna W, Narod S, Sun P, Tan C-K, Hengst L, Slingerland J. p27 phosphorylation by Src regulates inhibition of cyclin E-Cdk2 and p27 proteolysis. Cell. 2007;128(2):281–94.
Larrea MD, Liang J, Da Silva T, Hong F, Shao SH, Han K, Dumont D, Slingerland JM. Phosphorylation of p27(Kip1) regulates assembly and activation of cyclin D1-Cdk4. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(20):6462–72.
Sharma SS, Ma L, Pledger WJ. p27Kip1 inhibits the cell cycle through non-canonical G1/S phase-specific gatekeeper mechanism. Cell Cycle. 2015;14(24):3954–64.
Luo J, Chen Y, Li Q, Wang B, Zhou Y, Lan H. CRM-1 knockdown inhibits extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma tumor growth by blocking the nuclear export of p27Kip1. Int J Mol Med. 2016;38(2):381–90.
Santiago A, Li D, Zhao LY, Godsey A, Liao D. p53 SUMOylation promotes its nuclear export by facilitating its release from the nuclear export receptor CRM1. Mol Biol Cell. 2013;24(17):2739–52.
Lovisa S, Citro S, Sonego M, Dall’Acqua A, Ranzuglia V, Berton S, Colombatti A, Belletti B, Chiocca S, Schiappacassi M, et al. SUMOylation regulates p27Kip1 stability and localization in response to TGFbeta. J Mol Cell Biol. 2016;8(1):17–30.
Sambrook J, Russell DW. Detection of protein–protein interactions using the GST fusion protein pulldown technique. CSH Protoc. 2006;2006(1):pdb-rot3757.
Zhao Q, Xie Y, Zheng Y, Jiang S, Liu W, Mu W, Liu Z, Zhao Y, Xue Y, Ren J. GPS-SUMO: a tool for the prediction of sumoylation sites and SUMO-interaction motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(W1):W325–30.
Xue Y, Zhou F, Fu C, Xu Y, Yao X. SUMOsp: a web server for sumoylation site prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:W254–7.
Park-Sarge O-K, Sarge KD. Detection of sumoylated proteins. Methods Mol Biol. 2005;301:329–38.
Wang Y, Wang Y, Xiang J, Ji F, Deng Y, Tang C, Yang S, Xi Q, Liu R, Di W. Knockdown of CRM1 inhibits the nuclear export of p27(Kip1) phosphorylated at serine 10 and plays a role in the pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014;343(1):6–13.
Pan Y, Zhang Q, Tian L, Wang X, Fan X, Zhang H, Claret FX, Yang H. Jab1/CSN5 negatively regulates p27 and plays a role in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2012;72(7):1890–900.
Packham S, Warsito D, Lin Y, Sadi S, Karlsson R, Sehat B, Larsson O. Nuclear translocation of IGF-1R via p150Glued and an importin-[beta]/RanBP2-dependent pathway in cancer cells. Oncogene. 2015;34(17):2227–38.
Navarro MS, Bachant J. RanBP2: a tumor suppressor with a new twist on TopoII, SUMO, and centromeres. Cancer Cell. 2008;13(4):293–5.
Authors’ contributions
JL and JY design the experiment; JL and YL (Yan) wrote the manuscript; BW and HZL did the sumoylation sites screening. JL did the co-precipitation; YL (Ying) did the statistic work; FC and JZ help revise the manuscript and experiment design. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the technicians in the common equipment room for offering us instructions and assistance in using the instruments in Tongji Hospital, Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Funding
This article was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.: 81672394).
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
12867_2017_100_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Additional file 1. Figure S1. CRM-1 expression in the total cellular protein were validated to be downregulated after siRNA transfection. This is the validation result for CRM-1 knockdown mediated by siRNA. Figure S2. CRM-1 expression in the total cellular protein were validated to be upregulated after flag-CRM1 transfection. This is the validation result for CRM-1 artificial overexpression mediated by flag-CRM1 vector.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Liu, Y., Wang, B. et al. Sumoylation in p27kip1 via RanBP2 promotes cancer cell growth in cholangiocarcinoma cell line QBC939. BMC Molecular Biol 18, 23 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12867-017-0100-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12867-017-0100-5