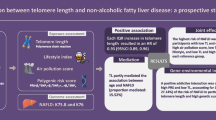
Abstract
Metabolic-dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is a comorbidity that generally increases in people living with HIV (PLWH). This condition is usually accompanied by persistent inflammation and premature immune system aging. In this prospective cohort study, we describe a straightforward methodology for quantifying biomarkers of aging, such as DNA methylation and telomere length, in PLWH and in the context of another relevant condition, such as MAFLD. Fifty-seven samples in total, thirty-eight from PLWH and nineteen from non-PLWH participants with or without MAFLD, were obtained and subjected to DNA extraction from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Global DNA methylation and telomere length quantification were performed using an adapted enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and qPCR, respectively. The quantification results were analysed and corrected by clinically relevant variables in this context, such as age, sex, and metabolic syndrome. Our results show an increased association of these biomarkers in PLWH regardless of their MAFLD status. Thus, we propose including the quantification of these age-related factors in studies of comorbidities. This will allow a better understanding of the effect of comorbidities of HIV infection and MAFLD and prevent their effects in these populations in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
People living with HIV (PLWH) have a high incidence of issues resulting from metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), which can be even more concerning than in other populations [1]
In addition, PLWH faces adverse effects of antiretroviral therapy (ART) and chronic inflammation caused by persistent infection and chronic treatment [2, 3]. Another component associated with HIV infection is acceleration of the biological clock. Biological clocks have been used to understand the effects of various environmental factors on human health. Acceleration of biological age is higher in PLWH than in non-PLWH [4,5,6,7]. This is important because it could bring age-related comorbidities of PLWH forward by up to a decade, thereby decreasing the life expectancy of this population. Aging is an important factor in PLWH, because it increases inflammation and immune activation, and it can be influenced by several components [8,9,10]. Moreover, age-related illnesses in PLWH, including metabolic diseases, are closely related to the associated heightened levels of systemic inflammation and immune activation, known as “inflamm-aging” [11]. A correlation has been shown between metabolic syndromes and the use of antiretrovirals, particularly protease inhibitors (PI) or nucleoside analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI) [12]. For example, Tenofovir has been directly associated with age acceleration by shortening telomere length [13,14,15]. Specifically, the markers that have been shown to be most strongly associated with steatosis and premature aging are mediated by altered tissue homeostasis maintenance in PLWH. This causes systemic inflammatory responses, increasing the levels of several systemic markers of inflammation, including TNF-α and interleukin such as IL-6 and C-reactive protein [10]. Immune dysregulation, immune cell senescence, and chronic inflammation are found even in ART-treated PLWH and have been also described as important mechanisms for aging [11, 16].
Fatty liver disease is a broad term that encompasses two main conditions: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD). Recently, NAFLD has been replaced by MAFLD to highlight the metabolic aspects of the condition [17]. This term aims to encompass a wider range of patients who have fatty liver disease with metabolic risk factors, even if they do not strictly fit the previous criteria used for NAFLD diagnosis. However, metabolic syndrome is not a specific liver condition, but rather a constellation of metabolic abnormalities that can contribute to various health issues, including liver diseases like NAFLD/MAFLD. Metabolic-dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease by itself has become a public health concern, since it is one of the main causes of liver transplants in Western countries [1]. Secondary long-term metabolic complications derived from MAFLD may seriously impact the health and quality of life of patients. Although some non-invasive imaging techniques have been established for the diagnosis of MAFLD, early detection remains challenging [18, 19]. Thus, MAFLD is now considered a health concern, especially in occidental countries, owing to its relationship with metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and high BMI [20]. Furthermore, MAFLD is one of the main comorbidities and mortality factors worldwide in PLWH [21, 22], although studies on MAFLD pathogenesis in PLWH are scarce. There is increasing evidence that the relationship between aging and metabolic dysregulation contributes to fatty liver disease/MAFLD [23,24,25]. The MAFLD condition may influence the aging process through various mechanisms, such as enhancing chronic inflammation [26, 27], establishing metabolic dysfunctions [20, 28, 29], promoting cellular damage, such as the impairment of mitochondrial functions which leads to increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [30,31,32] or by accelerating telomere shortening [33, 34].
One method of analysing the effect of MAFLD on health is the quantification of DNA methylation. An inverse correlation between global DNA methylation and disease progression in individuals with MAFLD has been demonstrated in both mouse and human studies [35,36,37], even describing the role of stress-induced senescence during steatosis development [38]. Other factors, such as mitochondrial DNA damage [32], have been related to MAFLD in animals [24]. In humans, it has been shown that MAFLD patients show epigenetic alterations and age acceleration which can be quantified by analysing cytosine methylation [39, 40]. In addition, studies have investigated how alterations in epigenetics significantly contribute to MAFLD development and have even validated the measurement of DNA methylation as a prognostic marker of aging [41] and liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [36, 42, 43].
Lifestyle, environment, and other factors can influence HIV and MAFLD pathogenesis. Epigenetic modifications in response to environmental exposures have been previously described and their relationship with MAFLD has been recently reviewed [44, 45]. Related to HIV infection, differential DNA methylation has been previously described, and epigenetic clocks have been established to understand this difference in PLWH [6, 26, 46, 47]. Furthermore, as determined previously by our group, there are differences in the plasma-free fatty acid profiles and in some genetic variants of PLWH [48]. Therefore, quantifying these senescence markers should be a priority because of the likelihood of unforeseen events arising in this population.
Different methods have been used to measure telomere length; however, quantitative PCR (qPCR) has proven to be a reliable method that allows the use of small amounts of starting material and large amounts of samples in less time and simpler procedures [49,50,51,52]. Regarding DNA methylation, different methodologies can be used to quantify it. However, most of these methodologies, although they are more informative and can assist in understanding other phenomena, such as biological clocks, are also more complicated to use on a regular basis, especially in locations with limited time and resources.
As both DNA methylation and telomere length are two relevant markers of biological age acceleration [37, 53] and the side effects of HIV infection and MAFLD persistence, we consider that they should be taken into consideration in studies related with these populations. Thus, this study aimed to show the importance of HIV infection in the biological aging process in PLWH with MAFLD by using straightforward methodologies to quantify biomarkers of aging and reinforce their broad study.
Results
Characteristics of the study population
In this study, we analysed samples from 49 participants diagnosed with MAFLD, of whom 30 (61%) were PLWH (MAFLD+ & HIV+) and 19 (39%) were HIV-uninfected (MAFLD+), in addition to 8 control samples from PLWH that were not diagnosed with MAFLD (HIV+).
Participant demographic information is provided in Table 1. In summary,PLWH were younger, with a higher percentage of females, lower BMI, and a lower percentage of diabetes mellitus (DM) and metabolic syndrome. The severity of MAFLD between the group of patients with MAFLD and the group of PLWH was significantly different. There was, however, no difference between PLWH regardless of whether they had MAFLD or not (Table 1). Regarding diet, except for lower dairy consumption and higher alcohol consumption, there were comparable results in PLWH. At inclusion, all PLWH participants were receiving antiretroviral therapy (94% under an integrase-strand-inhibitor-based regimen) for an average of 6 years while maintaining a suppressed viral load (see Table 1).
Cytosine global methylation as a marker of senescence in PLWH with MAFLD
Cytosine methylation is one of the main markers used to quantify DNA methylation which is the main epigenetic parameter related to age, substances, and diseases. In this study, we quantified the total amount of 5-methylcytosine in DNA samples (levels of CpG methylation per sample) using a straightforward approach based on a colorimetric assay. Analysis of the results from 57 samples revealed significant differences, showing the lowest methylation levels in non-PLWH with MAFLD (Fig. 1).
Quantification of cytosine methylation using ELISA assay. Levels of methylation at CpG sites (CpGmet) were measured and calculated as detailed in the Methods section. The calculated results from the duplicates assayed are shown here at each point, and the samples were divided into three groups according to the patient: 19 patients with MAFLD (blue), 8 PLWH (red), and 30 PLWH and MAFLD (purple). The limit of detection was established above the last point of the standard curve (0). Significant differences obtained by linear regression analysis after adjusting by age, sex, and metabolic syndrome (Least Square Mean difference) comparing group to group were significant for the following comparisons: MAFLD vs PLWH (p = 0.005, B0 = 37.81) and MAFLD vs MAFLD + PLWH (p = 0.03, B0 = 22.06) (Figure S1)
Telomere length as a marker of senescence in PLWH with MAFLD
Telomere length has been widely used as a marker of age acceleration. However, different methodologies can be used for this quantification. In this study, we used a previously described qPCR protocol based on the detection of specific sequences in the telomere region. The results showed the greatest differences when comparing the PLWH and MAFLD groups (Fig. 2), although the differences were not statistically significant.
Relative telomere length quantification by qPCR. Telomere length was measured by qPCR and calculated as described in the Methods section. Calculated relative telomere lengths are depicted by dividing the samples into three groups according to the patients: 19 patients with MAFLD (blue), 8 PLWH (red), and 29 PLWH and MAFLD (purple). Differences obtained by linear regression analysis adjusted by age, sex, and metabolic syndrome (Least Square Mean difference) were not significant for any of the group to group comparisons analysed for this quantification (Figure S1)
Further statistical analyses
Different results have been reported in studies on the relationship between methylation and telomere length. In fact, a method to evaluate epigenetic modifications related with telomere length was described [41]. Thus, in our study we aimed to explore whether these two biomarkers of aging were correlated. We fitted the data from both analyses and adjusted them by linear regression. Pearson correlation analysis for methylation data (CpGmet) and telomere length (RTL) showed a moderate correlation (p = 0.0155, r = 0.32) (Fig. 3).
Correlation analysis between methylation data and telomere length data. Linear regression and Pearson correlation was calculated for the 57 samples together since the separated groups had a reduced sample size that could alter the meaning of the statistics. However, the three different groups of the samples have been depicted in different colours (MAFLD, blue; PLWH, red and MAFLD + PLWH, purple) for clarification. The purpose of this analysis is to understand the relationship between the quantification of these two markers in general, but specifically in the context of the methods used in this study
Discussion
In this prospective study, we analysed the effect of HIV and MAFLD in biomarkers of aging, such as DNA methylation and telomere length, by using straightforward methods. Aging has been shown to be clinically relevant for PLWH because it is related to inflammation and immune activation; therefore, the term ‘inflamm-aging’ is used to describe this effect [10, 11]. Telomere length has been widely used as a marker of aging, although its clinical use as the only relevant marker of aging has been questioned. Thus, other factors, such as frailty and epigenetic markers, have been proposed as complementary markers [54, 55]. Epigenetic regulation, such as DNA methylation, has also been linked to the inflammatory status of PLWH [46, 47, 56]. Furthermore, the role of epigenetics in the pathogenesis of MAFLD has been described to explain the effects of lifestyle and environmental factors [45].
Increased methylation in PLWH has been observed within three years after initial HIV infection, although there is some decrease associated with the use of antiretroviral therapy [15, 57]. Furthermore, alterations in DNA methylation have been associated with MAFLD susceptibility [58], although the fact that it may be down- or upregulated depends on the gene being studied [56]. These differences have been addressed by other studies that quantified methylation in CpGs at specific loci [59]. However, these technologies are complex and expensive; therefore, they may not easily be implemented in clinical practice. In this study, we addressed this question by quantifying the level of global DNA methylation using an affordable and straightforward approach. The results showed that CpG methylation levels remained high in the presence of HIV infection, independently of their MAFLD status. Although different associations have been described, previous studies have also pointed to an association between DNA methylation and HIV susceptibility [46, 60, 61]. However, the quantification of global DNA methylation by ELISA, has yielded inconsistent results in PLWH. Some studies have shown an increase [61,62,63] while others have reported a decrease [46, 64] in DNA methylation in PLWH, although it is important to note that these studies used different kits for quantification, making it difficult to compare the results. It has been shown that DNA methylation differs between different immune cell types [65]. In the particular case of HIV, DNA methylation has been related to the CD4/CD8 ratio, viral load and response to treatment [61, 66]. However, more information is needed to take conclusions about this topic and further studies should be performed to understand the effect of aging in PLWH.
Regarding telomeres, only some changes associated with the enzyme Telomerase reverse transcriptase, which is involved in the maintenance of telomeres, have been directly linked to MAFLD-associated conditions [67, 68]. However, in PLWH, shorter telomeres have been previously described, although this has been shown to be controlled by antiretroviral therapy, probably due to the decrease in immune activation [12,13,14, 69]. Here, we decided to study the telomere length relationship with PLWH and MAFLD using relative quantification (qPCR) because it is a feasible technique and can be useful in different contexts. However, following this approach, in our setting, only a trend of increased telomere length without statistical significance was found in PLWH regarding MAFLD status. This could be due to the fact that, although qPCR is one of the main methods used to quantify telomere length because it allows small amounts of DNA to be used, is less labour-intensive, and can be used in high-throughput settings, it also has its limitations. Lacking reference standards, variation between batches, and recognition of mean length measures instead of individual telomeres or ends must be considered in order to interpret the lack of significance when using this technique [50, 52].
Importantly, in this study, some confounding variables related to HIV infection and MAFLD development that could be important for the analysis of DNA methylation and telomere length, were also analysed. In the two PLWH groups, there was a significantly higher number of women, with a lower BMI, hepatic stiffness (KPa), liver steatosis measured by CAP, diabetes mellitus, and prevalence of metabolic syndrome. Furthermore, the two groups of PLWH participants were five years younger on average, although this difference was not significant. Therefore, in addition to adjusting the model for sex and age, we included metabolic syndrome as an adjustment variable, considering it as a proxy for the others, to avoid overfitting and collinearity. In addition, multivariate models were fitted, with similar estimates, adjusting for the presence of DM or arterial hypertension. After adjustment, we can assume that the groups were comparable, as the results were similar to the unadjusted model, except for telomeric length, which did not reach statistical significance, probably due to the small sample size.
DNA methylation and telomere length as biomarkers of aging have shown different levels of correlation when studied previously, especially when adjusted for age [54, 70]. In our study, these factors showed a moderate correlation which could be due to differences in methodologies applied in comparison with previous studies. It has been previously shown that chronic inflammation and immune activation are typically present in PLWH, even if they are under ART, and provoke premature aging, significantly affecting their quality of life [10, 11]. Consequently, our analysis of PLWH showed an increasing trend in DNA methylation and telomere length. A correlation between these two factors using these two specific methods has not been shown previously, and it may be relevant to demonstrate that these techniques can be accessible for daily use.
The limitations of our study include the lack of a control group of healthy patients. However, since this study focused on the methodology applied to understand the role of MAFLD in PLWH, we used samples from patients with MAFLD as a reference group as some other groups have previously done to study hepatic steatosis [71]. Regarding the quantification techniques, limitations are inherent for each method. For telomere length, there is no consensus about the best protocol to perform these quantifications; therefore, we followed the literature and simplified the method as much as possible because we only aimed to determine relative differences. Regarding methylation, there are of course more sophisticated methods of quantification, but these are more complicated and expensive, and this study aimed to find an affordable approach to study these factors and determine their relevance in the clinical setting.
Conclusion
Although this was an exploratory study to test straightforward techniques to quantify DNA methylation and telomere length in a limited number of samples from a very specific population, it provides information about the utility of these facile approaches for testing clinical variables. Furthermore, our findings underline the importance of HIV infection as an accelerating factor for biological aging even if complete virological control has been achieved and independently of other factors or comorbidities, such as MAFLD status.
Materials and methods
Study design and sample collection
This was a prospective cohort study at Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal in Madrid, Spain from January 2018 to December 2018. non-PLWH participants diagnosed with MAFLD were recruited at the Metabolic Liver Disease Clinic. PLWH participants receiving suppressive antiretroviral therapy were recruited at the HIV Clinic. We included those who presented with elevated liver enzymes for at least two determinations, separated by six months. Any transaminase (GGT, ALT, AST) level above the upper limit of normal in our laboratory was considered. PLWH were receiving antiretroviral therapy for at least 1 year with undetectable viremia in the last 6 months. All participants underwent abdominal ultrasound and a screening analysis for liver disease. Based on our previously published data, diagnosis of MAFLD was established by Transient Elastography (CAP), ultrasound confirmation of steatosis, and exclusion of other aetiologies of chronic liver disease. Metabolic syndrome was defined according to the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP)’s third report [72] and the criteria defined by Eslam et al. [73] based on evidence of hepatic steatosis, in addition to one of the following three criteria, namely overweight/obesity, presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus, or evidence of metabolic dysregulation. In addition, diagnosis of MAFLD was screened by non-invasive serological markers (triglyceride and glucose index [TyG], fatty liver index [FLI]) in those participants who met the inclusion criteria [74]. Exclusion criteria included active viral hepatitis; alcohol abuse (defined by > 30 g daily in men and > 20 g daily in women; lower consumption was allowed); cocaine, heroin, or designer drug abuse; other known liver diseases (autoimmune, genetic, drug-related); isolated alkaline phosphatase alteration; recent drug toxicity; the impossibility of cannulating a peripheral bloodline if a liver biopsy was required; pregnancy or desired pregnancy; decompensated liver disease or hepatocarcinoma; and any other comorbidity that, at the investigator’s discretion, could prevent correct compliance with the study protocol. Clinical information was collected through the clinical interview at the baseline visit of the study, together with a review of the patient’s medical history recorded in the electronic medical record. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards of the Carlos III Health Institute, Madrid, Spain (Project PI 17/01717), and by the Ethics Committee at the University Hospital Ramón y Cajal (ceic.hrc@salud.madrid.org, Approval Number 097/17). All patients gave written informed consent before the initiation of the study procedures. All methods were performed following the relevant guidelines and regulations. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patient blood samples collected in EDTA tubes were isolated using Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient (Comercial Rafer S.L., Zaragoza, Spain) and following multiple previously described standard methods.
Methylation analysis
For the determination of the global DNA methylation in the isolated PBMCs from patients, total DNA was extracted by using the commercially available QIAAMP DNA MINI KIT (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer´s instructions. Then, evaluation of the global DNA methylation of liver-derived DNA was performed by measuring the concentration of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) using a commercially available kit (5-mC DNA ELISA Kit, Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Each sample was assayed in duplicate, seeking an equal representation of the study groups. After reading absorbance at 405 nm (OD), a standard curve was generated using a logarithmic curve, and %5-mC values were extrapolated from the curve (in %5-mC). Data obtained from the 0% value of the standard curve were used as negative control and subtracted from all the positive values. Then, to calculate the level of CpG methylation, the observed ODs extrapolated from the logarithmic standard curve were multiplied by the fold difference CpG density between control DNA derived from E. coli (1.00) and the standard human genome hg19 (8.167). Data were provided by the manufacturer of the kit. Final data were represented in a dot-plot comparing the three groups.
Telomere length analysis
For the determination of the average telomere length in total DNA extracted from PBMCs of patients (as indicated previously), we performed a qPCR-based method previously described [21]. After DNA extraction, the purity of DNA was evaluated by detection of the absorbance 260 nm (A260)/absorbance 280 nm (A280) ratio in a NanoVue™ (GE), and concentration was quantified in a Qubit® Fluorometer with a Qubit® dsDNA BR Assay Kit. Then, the qPCR mix was prepared with the following amounts per well: 5ul of SYBR® Green Master Mix from Roche (#0470751600), 10 ng of DNA, and primers at 1uM final concentration. DNA samples were assessed in triplicate in 96-well plates for telomere (T) and housekeeping gene 36B4 (S) primers. The primer sequences (5′ → 3′) were:
-
tel1b CGGTTTGTTTGGGTTTGGGTTTGGGTTTGGGTTTGGGTT;
-
tel2b GGCTTGCCTTACCCTTACCCTTACCCTTACCCTTACCCT;
-
36B4u CAGCAAGTGGGAAGGTGTAATCC;
-
36B4d CCCATTCTATCATCAACGGGTACAA;
-
18S For GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT;
-
18S Rev CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG;
Standard DNA, a positive control (commercially available DNA-Human Genomic DNA, Roche), and a non-template control (NTC) were assessed in parallel.
Relative qPCR was carried out on a LightCycler 480 Roche System. The thermal cycling began with the initial polymerase activation step (10 min at 95 °C) and was followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 1 min. A melting curve analysis was performed to verify the specificity and identity of the products.
For calculations, ∆Ct was calculated for each sample as (Average Ct of 18S)-(Average Ct of telomere) and (Average Ct of 18S)-(Average Ct of 36B4). Since telomeres are present in multiple copies in a cell, as against single-copy genes, ∆Ct value is positive. Then, the relative telomere length (RTL) as ∆∆Ct was calculated by subtracting the ∆Ct for Control DNA (Control DNA Average 36B4 Ct-Control DNA Average Telomere Ct). A higher ∆∆Ct value indicates a longer telomere length. Telomere length has been calculated previously through the measure of the expression of a specific region in the telomere sequence (T) compared to a regular region of a single copy gene (S), based on methods described in previous studies [49,50,51] to obtain the Relative Telomere Length (RTL).
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics of patients with MAFLD, HIV infection, or both were compared with the Wilcoxon rank-sum test for continuous variables and Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables. All contrasts were two-tailed and a p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Differences between the groups were compared with linear regression and adjusted by variables relevant for age acceleration (sex, age, metabolic syndrome) (details in Figure S1A and B). A sensitivity analysis was also conducted to eliminate samples from participants with cured HCV, and obtaining similar estimates (details in Figure S1C). Pearson correlation analysis was performed to evaluate the correlation between the two studied variables (methylation and telomere length). Analyses were performed with Stata v. 17.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA). Figures were created using GraphPad Prism v9.2 (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, USA).
Availability of data and materials
Data are available on request. The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Raza S, Rajak S, Upadhyay A, Tewari A, Anthony Sinha R. Current Treatment Paradigms and Emerging Therapies for NAFLD/NASH. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021;26:206–37. https://doi.org/10.2741/4892.
Manzano‐Nunez, R.; Rivera‐Esteban, J.; Navarro, J.; Bañares, J.; Sena, E.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Lazarus, J.V.; Curran, A.; Pericàs, J.M. Uncovering the NAFLD Burden in People Living with HIV from High‐ and Middle‐income Nations: A Meta‐analysis with a Data Gap from Subsaharan Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2023;26:e26072.https://doi.org/10.1002/jia2.26072.
Navarro J. HIV and Liver Disease. AIDS Rev. 2022;25:87–96. https://doi.org/10.24875/AIDSRev.M22000052.
Liu JCY, Leung JM, Ngan DA, Nashta NF, Guillemi S, Harris M, Lima VD, Um S-J, Li Y, Tam S, et al. Absolute Leukocyte Telomere Length in HIV-Infected and Uninfected Individuals: Evidence of Accelerated Cell Senescence in HIV-Associated Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0124426. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124426
Xu S., Vucic E.A., Shaipanich T., Lam S., Lam W., Montaner J.S., Sin D.D., Paul Man S.F., Leung J.M. Decreased Telomere Length in the Small Airway Epithelium Suggests Accelerated Aging in the Lungs of Persons Living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). Respir Res 2018;19:117. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0821-0.
Horvath S, Levine AJ. HIV-1 Infection Accelerates Age According to the Epigenetic Clock. J Infect Dis. 2015;212:1563–73. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiv277.
Montano M, Oursler KK, Xu K, Sun YV, Marconi VC. Biological Ageing with HIV Infection: Evaluating the Geroscience Hypothesis. The Lancet Healthy Longevity. 2022;3:e194–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-7568(21)00278-6.
Deeks SG. HIV Infection, Inflammation, Immunosenescence, and Aging. Annu Rev Med. 2011;62:141–55. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-042909-093756.
Wing EJ. HIV and Aging. Int J Infect Dis. 2016;53:61–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2016.10.004.
Blanco J-R, Negredo E, Bernal E, Blanco J. Impact of HIV Infection on Aging and Immune Status. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2021;19:719–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/14787210.2021.1848546.
Nasi M, De Biasi S, Gibellini L, Bianchini E, Pecorini S, Bacca V, Guaraldi G, Mussini C, Pinti M, Cossarizza A. Ageing and Inflammation in Patients with HIV Infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016;187:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12814.
Montejano R, Stella-Ascariz N, Monge S, Bernardino JI, Pérez-Valero I, Montes ML, Valencia E, Martín-Carbonero L, Moreno V, González-Garcia J, et al. Impact of Nucleos(t)Ide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors on Blood Telomere Length Changes in a Prospective Cohort of Aviremic HIV–Infected Adults. J Infect Dis. 2018;218:1531–40. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiy364.
Montejano R, Stella-Ascariz N, Monge S, Bernardino JI, Pérez-Valero I, Montes ML, Valencia E, Martín-Carbonero L, Moreno V, González-García J, et al. Impact of Antiretroviral Treatment Containing Tenofovir Difumarate on the Telomere Length of Aviremic HIV-Infected Patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;76:102–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAI.0000000000001391.
Rodríguez-Centeno J, Esteban-Cantos A, Montejano R, Stella-Ascariz N, De Miguel R, Mena-Garay B, Saiz-Medrano G, Alejos B, Jiménez-González M, Bernardino JI, et al. Effects of tenofovir on telomeres, telomerase and t cell maturational subset distribution in long-term aviraemic HIV-infected adults. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022;77:1125–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkab492.
Alejos B, Stella-Ascariz N, Montejano R, Rodriguez-Centeno J, Schwimmer C, Bernardino J, Rodes B, Esser S, Goujard C, Sarmento-Castro R, et al. Determinants of Blood Telomere Length in Antiretroviral Treatment-naïve HIV -positive Participants Enrolled in the NEAT 001/ ANRS 143 Clinical Trial. HIV Med. 2019;20:691–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/hiv.12791.
Aladdin, Ullum, Schjerling, Skov Jensen, Dam Nielsen, Mathiesen, Gerstoft, Skinho J, Klarlund Pedersen Effects of G-CSF on Telomere Lengths in PBMCs from Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Patients: Results From a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Scand J Immunol 2000;52:212–216. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3083.2000.00771.x.
Kim D, Konyn P, Sandhu KK, Dennis BB, Cheung AC, Ahmed A. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease is associated with increased all-cause mortality in the United States. J Hepatol. 2021;75:1284–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2021.07.035.
Piazzolla VA, Mangia A. Noninvasive diagnosis of NAFLD and NASH. Cells. 2020;9:1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041005.
Carrasco I, Olveira A, Lancharro Á, Escosa L, Mellado MJ, Busca C, Montes ML, Díez C, Alcolea-Ruiz S, Navarro ML, et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease using noninvasive techniques among children, adolescents, and youths living with HIV. AIDS. 2022;36:805–14. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0000000000003170.
Sung K-C, Lee MY, Kim Y-H, Huh J-H, Kim J-Y, Wild SH, Byrne CD. Obesity and incidence of diabetes: effect of absence of metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance. Inflammation and Fatty Liver Atherosclerosis. 2018;275:50–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.05.042.
Sherman KE, Peters MG, Thomas D. Human Immunodeficiency virus and liver disease: a comprehensive update. Hepatology Communications. 2017;1:987–1001. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep4.1112.
Tafesh ZH, Verna EC. Managing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients living with HIV. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017;30:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1097/QCO.0000000000000344.
Hu F, Liu F. Targeting tissue-specific metabolic signaling pathways in aging: the promise and limitations. Protein Cell. 2014;5:21–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-013-0002-3.
Moon JH, Kim W, Koo BK, Cho NH. on behalf of the Innovative Target Exploration of NAFLD (ITEN) consortium Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Predicts Long-Term Mortality and Cardiovascular Disease. Gut and Liver. 2022;16:433–42. https://doi.org/10.5009/gnl210167.
Koo, B.K.; Lim, S. Metabolic Syndrome and Metabolic Dysfunction‐Associated Fatty Liver Disease. In Clinical Obesity in Adults and Children; Kopelman, P.G., Caterson, I.D., Dietz, W.H., Armstrong, S., Sweeting, A.N., Wilding, J.P.H., Eds.; Wiley, 2022;159–177 ISBN 978–1–119–69527–1.
Mohan J, Ghazi T, Chuturgoon AA. A critical review of the biochemical mechanisms and epigenetic modifications in HIV- and antiretroviral-induced metabolic syndrome. IJMS. 2021;22:12020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222112020.
Han, W.M.; Apornpong, T.; Chattranukulchai, P.; Siwamogsatham, S.; Lwin, H.M.S.; Boonrungsirisap, J.; Wichiansan, T.; Gatechompol, S.; Ubolyam, S.; Kerr, S.J.; et al. Metabolic‐Associated Fatty Liver Disease ( MAFLD ) Is Associated with Immune Activation, Increased Epicardial Fat Volume, and Steatohepatitis among People with HIV in a Thai Cohort. HIV Medicine 2023;hiv.13499. https://doi.org/10.1111/hiv.13499.
Guaraldi G, Lonardo A, Maia L, Palella FJ. Metabolic concerns in aging HIV-infected persons: from serum lipid phenotype to fatty liver. AIDS. 2017;31:S147–56. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0000000000001483.
Gao Y., Zhang W., Zeng L.-Q., Bai H., Li J., Zhou J., Zhou G.-Y., Fang C.-W.,Wang F., Qin X.-J. Exercise and Dietary Intervention Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced NAFLD and Liver Aging by Inducing Lipophagy. Redox Biol 2020;36:101635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101635.
Brenner C, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Kroemer G. Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation. J Hepatol. 2013;59:583–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.033.
Yang J, Fernández-Galilea M, Martínez-Fernández L, González-Muniesa P, Pérez-Chávez A, Martínez JA, Moreno-Aliaga MJ. Oxidative stress and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: effects of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation. Nutrients. 2019;11:872. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040872.
Xu, L.; Zhou, J.; Che, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, H. Mitochondrial DNA Enables AIM2 Inflammasome Activation and Hepatocyte Pyroptosis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2021;320:G1034–G1044. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00431.2020.
Donati B, Valenti L. Telomeres, NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030383.
Lonardo A, Lugari S, Nascimbeni F. Telomere shortening: an innocent bystander at the crossroad of NASH with Ageing and Cardiometabolic Risk? Liver Int. 2018;38:1730–2. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.13935.
Wang L, Zhang H, Zhou J, Liu Y, Yang Y, Chen X, Zhu C, Zheng R, Ling W, Zhu H. Betaine attenuates hepatic steatosis by reducing methylation of the MTTP promoter and elevating genomic methylation in mice fed a high-fat diet. J Nutr Biochem. 2014;25:329–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.11.007.
Lai Z, Chen J, Ding C, Wong K, Chen X, Pu L, Huang Q, Chen X, Cheng Z, Liu Y, et al. Association of Hepatic Global DNA methylation and serum one-carbon metabolites with histological severity in patients with NAFLD. Obesity. 2020;28:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22667.
Banszerus VL, Vetter VM, Salewsky B, König M, Demuth I. Exploring the relationship of relative telomere length and the epigenetic clock in the lipidcardio cohort. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:E3032. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20123032.
Moustakas II, Katsarou A, Legaki A-II, Pyrina I, Ntostoglou K, Papatheodoridi A-MM, Gercken B, Pateras IS, Gorgoulis VG, Koutsilieris M, et al. Hepatic senescence accompanies the development of NAFLD in non-aged mice independently of obesity. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073446.
Unnikrishnan A, Freeman WM, Jackson J, Wren JD, Porter H, Richardson A. The Role of DNA methylation in epigenetics of aging. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;195:172–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.11.001.
Borowa-Mazgaj B, De Conti A, Tryndyak V, Steward CR, Jimenez L, Melnyk S, Seneshaw M, Mirshahi F, Rusyn I, Beland FA, et al. Gene expression and DNA methylation alterations in the glycine N-Methyltransferase gene in diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-associated carcinogenesis. Toxicol Sci. 2019;170:273–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfz110.
Lee Y, Sun D, Ori APS, Lu AT, Seeboth A, Harris SE, Deary IJ, Marioni RE, Soerensen M, Mengel-From J, et al. Epigenome-wide association study of leukocyte telomere length. Aging. 2019;11:5876–94. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102230.
Loomba R, Gindin Y, Jiang Z, Lawitz E, Caldwell S, Djedjos CS, Xu R, Chung C, Myers RP, Subramanian GM, et al. DNA Methylation Signatures Reflect Aging in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. JCI Insight. 2018;3:e96685. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.96685
Hardy T, Zeybel M, Day CP, Dipper C, Masson S, McPherson S, Henderson E, Tiniakos D, White S, French J, et al. Plasma DNA methylation: a potential biomarker for stratification of liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut. 2017;66:1321–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-311526.
Li D, Li Y, Yang S, Lu J, Jin X, Wu M. Diet-Gut Microbiota-Epigenetics in Metabolic Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113290
Sodum N, Kumar G, Bojja SL, Kumar N, Rao CM. Epigenetics in NAFLD/NASH: Targets and Therapy. Pharmacol Res. 2021;167:105484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105484
Zhang X, Justice AC, Hu Y, Wang Z, Zhao H, Wang G, Johnson EO, Emu B, Sutton RE, Krystal JH, et al. Epigenome-wide differential DNA methylation between HIV-infected and uninfected individuals. Epigenetics. 2016;11:750–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592294.2016.1221569.
Horvath S, Lin DTS, Kobor MS, Zoller JA, Said JW, Morgello S, Singer E, Yong WH, Jamieson BD, Levine AJ. HIV, Pathology and epigenetic age acceleration in different human tissues. GeroScience. 2022;44:1609–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-022-00560-0.
Martínez-Sanz J, Calvo MV, Serrano-Villar S, Montes ML, Martín-Mateos R, Burgos-Santamaría D, Díaz-Álvarez J, Talavera-Rodríguez A, Rosas M, Moreno S, et al. Effects of HIV infection in plasma free fatty acid profiles among people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. JCM. 2022;11:3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133842.
Joglekar MV, Satoor SN, Wong WKMM, Cheng F, Ma RCWW, Hardikar AA. An optimised step-by-step protocol for measuring relative telomere length. Methods and Protocols. 2020;3:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps3020027.
Montpetit AJ, Alhareeri AA, Montpetit M, Starkweather AR, Elmore LW, Filler K, Mohanraj L, Burton CW, Menzies VS, Lyon DE, et al. Telomere length: a review of methods for measurement. Nurs Res. 2014;63:289–99. https://doi.org/10.1097/NNR.0000000000000037.
Lin J, Smith DL, Esteves K, Drury S. Telomere Length measurement by QPCR – summary of critical factors and recommendations for assay design. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019;99:271–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.10.005.
Raschenberger J, Lamina C, Haun M, Kollerits B, Coassin S, Boes E, Kedenko L, Köttgen A, Kronenberg F. Influence of DNA extraction methods on relative telomere length measurements and its impact on epidemiological studies. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25398. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25398.
Vaiserman A., Krasnienkov D. Telomere Length as a Marker of Biological Age: State-of-the-Art, Open Issues, and Future Perspectives. Front. Genet. 2021;11:630186. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.630186.
Breitling LP, Saum K-U, Perna L, Schöttker B, Holleczek B, Brenner H. Frailty is associated with the epigenetic clock but not with telomere length in a german cohort. Clin Epigenet. 2016;8:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-016-0186-5.
Rodriguez-Centeno J, Dronda F, Juan CL, Sánchez-Conde M, Rodriguez-Centeno J, Dronda F, López JC, Jiménez Z, Berenguer J, Pérez-Elías MJ, et al. Frailty phenotype: A clinical marker of age acceleration in the older HIV-infected population. Epigenomics. 2019;11:501–9. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2018-0130.
Titanji B.K., Lee M., Wang Z., Chen J., Hui Q., Lo Re III V., So-Armah K., Justice A.C., Xu K., Freiberg M. et al. Epigenome-Wide Association Study of Biomarkers of Liver Function Identifies Albumin-Associated DNA Methylation Sites among Male Veterans with HIV. Front. Genet. 2022;13:1020871. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.1020871.
Chalouni M., Rodriguez-Centeno J., Samri A., Blanco J., Stella-Ascariz N., Wallet C., Knobel H., Zucman D., Alejos Ferreras B., Autran B., et al. Correlation between Blood Telomere Length and CD4+ CD8+ T-Cell Subsets Changes 96 Weeks after Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy in HIV-1-Positive Individuals. PloS one 2020;15:e0230772. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230772.
Busca C., Arias P., Sánchez-Conde M., Rico M., Montejano R., Martín-Carbonero L., Valencia E., Moreno V., Bernardino J.I., Olveira A. et al. Genetic Variants Associated with Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis in HIV-Infected Patients with NAFLD. Front. Pharmacol. 2022;13:905126. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.905126.
Kim J, Kim K, Kim H, Yoon G, Lee K. Characterization of age signatures of DNA methylation in normal and cancer tissues from multiple studies. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:997. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-997.
Shu C, Jaffe AE, Sabunciyan S, Ji H, Astemborski J, Sun J, Bakulski KM, Mehta SH, Kirk GD, Maher BS. Epigenome-wide association scan identifies methylation sites associated with HIV infection. Epigenomics. 2020;12:1917–27. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2020-0123.
Bogoi RN, De Pablo A, Valencia E, Martín-Carbonero L, Moreno V, Vilchez-Rueda HH, Asensi V, Rodriguez R, Toledano V, Rodés B. Expression profiling of chromatin-modifying enzymes and global DNA methylation in CD4+ T cells from patients with chronic HIV infection at different HIV control and progression States. Clin Epigenet. 2018;10:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-018-0448-5.
Maricato J.T., Furtado M.N., Takenaka M.C., Nunes E.R.M., Fincatti P., Meliso F.M., da Silva I.D.C.G., Jasiulionis M.G., Cecília de Araripe Sucupira M., Diaz R.S. et al. Epigenetic Modulations in Activated Cells Early after HIV-1 Infection and Their Possible Functional Consequences. PLoS One 2015;10:e0119234. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119234.
Desplats P, Dumaop W, Cronin P, Gianella S, Woods S, Letendre S, Smith D, Masliah E, Grant I. Epigenetic Alterations in the Brain Associated with HIV-1 Infection and Methamphetamine Dependence. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e102555. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0102555
Soares LS, Espíndola MS, Zambuzi FA, Galvão-Lima LJ, Cacemiro MC, Soares MR, Santana BA, Calado RT, Bollela VR, Frantz FG. Immunosenescence in Chronic HIV Infected Patients Impairs Essential Functions of Their Natural Killer Cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;84:106568.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106568
Bergstedt J, Azzou SAK, Tsuo K, Jaquaniello A, Urrutia A, Rotival M, Lin DTS, MacIsaac JL, Kobor MS, Albert ML, et al. The immune factors driving DNA methylation variation in human blood. Nat Commun. 2022;13:5895. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33511-6.
Esteban-Cantos A., Rodríguez-Centeno J., Silla J.C., Barruz P., Sánchez-Cabo F., Saiz-Medrano G., Nevado J., Mena-Garay B., Jiménez-González M., De Miguel R. et al. Effect of HIV Infection and Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation on Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Patterns. eBioMedicine 2023;88:104434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104434.
Calado R.T., Regal J.A., Kleiner D.E., Schrump D.S., Peterson N.R., Pons V., Chanock S.J., Lansdorp P.M., Young N.S. A Spectrum of Severe Familial Liver Disorders Associate with Telomerase Mutations. PLoS ONE 2009;4:e7926.https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0007926.
Hartmann D, Srivastava U, Thaler M, Kleinhans KN, N’Kontchou G, Scheffold A, Bauer K, Kratzer RF, Kloos N, Katz S-F, et al. Telomerase gene mutations are associated with cirrhosis formation. Hepatology. 2011;53:1608–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24217.
Stella-Ascariz N, Montejano R, Rodriguez-Centeno J, Alejos B, Schwimmer C, Bernardino JI, Rodes B, Allavena C, Hoffmann C, Gisslén M, et al. Blood telomere length changes after ritonavir-boosted darunavir combined with raltegravir or tenofovir-emtricitabine in antiretroviral-naive adults infected with HIV-1. J Infect Dis. 2018;218:1523–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiy399.
Dong Y, Huang Y, Gutin B, Raed A, Dong Y, Zhu H. Associations between Global DNA methylation and telomere length in healthy adolescents. Sci Rep. 2017;7:4210. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04493-z.
Torgersen J, So-Armah K, Freiberg MS, Goetz MB, Budoff MJ, Lim JK, Taddei T, Butt AA, Rodriguez-Barradas MC, Justice AC, et al. Comparison of the prevalence, severity, and risk factors for hepatic steatosis in hiv-infected and uninfected people. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019;19:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-019-0969-1.
Expert Panel On Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment Of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults Executive Summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA. 2001;285:2486–2497. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.285.19.2486.
Eslam M, Newsome PN, Sarin SK, Anstee QM, Targher G, Romero-Gomez M, Zelber-Sagi S, Wai-Sun Wong V, Dufour J-F, Schattenberg JM, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: an international expert consensus statement. J Hepatol. 2020;73:202–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039.
Busca C., Sánchez-Conde M., Rico M., Rosas M., Valencia E., Moreno A., Moreno V., Martín-Carbonero L., Moreno S., Pérez-Valero I. et al. Assessment of Noninvasive Markers of Steatosis and Liver Fibrosis in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Monoinfected Patients on Stable Antiretroviral Regimens. Open Forum Infect Dis 2022;9:ofac279. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofac279.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge all study participants who made this research possible and Laura Martín Pedraza for her helpful comments.
Informed consent statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, grant number PI17/01717 Plan Estatal de Investigación Científica y Técnica y de Innovación 2013–2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S-C. and E.M.; methodology, M.S-C., E.M., L.L., J.M-S., and S.S-V.; software, J.M-S. and E.M.; validation, E.M. and L.L; formal analysis, J.M-S., E.M., and M.S-C.; investigation, E.M., M.S-C., J.D-A., M.J.V., R.M-M., D.B-S., M.J.P-E., A.M-Z., S.M., and F.D; resources, M.S-C. and R.M-M.; data curation, J.D-A., R.M-M., M.J.V., and D.B-S.; writing—original draft preparation, J.M-S., E.M., and M.S-C.; writing—review and editing, E.M., M.S-C., J.D-A., S.S-V., and J.M-S.; visualization, M.J.V., R.M-M., D.B-S., M.J.P-E., A.M-Z., S.M., F.D., and L.L.; supervision, M.S-C., E.M., and J.M-S.; project administration, M.S-C.; funding acquisition, M.S-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards of the Carlos III Health Institute, Madrid, Spain (Project PI 17/01717), and by the Ethics Committee at the University Hospital Ramón y Cajal (ceic.hrc@salud.madrid.org, Approval Number 097/17). All patients gave written informed consent before the initiation of the study procedures. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
Linear regression analysis tables obtained from STATA.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Moreno, E., Martínez-Sanz, J., Martín-Mateos, R. et al. Global DNA methylation and telomere length as markers of accelerated aging in people living with HIV and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Genomics 24, 567 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-023-09653-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-023-09653-2