Abstract
Background
Cassava plants (Manihot esculenta Crantz) have obvious abscission zone (AZ) structures in their leaf pulvinus-petioles. Cassava leaf abscission can be triggered by either 17 days of water-deficit stress or 4 days of ethylene treatment. To date, little is known about cassava AP2/ERF factors, and less is known regarding their roles in regulating abscission zone development.
Results
Here, the cassava and Arabidopsis AP2/ERF genes were compared, finding that the cassava genome contains approximately 1.54-fold more ERF subfamily than the Arabidopsis genome. Microarray analysis was used to identify the AP2/ERF genes that are expressed in cassava leaf pulvinus-petiole abscission zones by comparing the AP2/ERF gene expression profiles of ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission. In total, 99 AP2/ERF genes were identified as expressed in AZs across six time points during both ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission. Comparative expression profile analysis of similar SOTA (Self Organizing Tree Algorithm) clusters at six time points during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission demonstrated that 20 ERF subfamily genes had similar expression patterns in response to both treatments. GO (Gene Ontology) annotation confirmed that all 20 ERF subfamily genes participate in ethylene-mediated signalling. Analysis of the putative ERF promoter regions shown that the genes contained primarily ethylene- and stress-related cis-elements. Further analysis of ACC oxidase activity in AZs across six time points during abscission shown increased ethylene production in response to both ethylene and water-deficit stress; however, the difference was more dramatic for water-deficit stress. Finally, the expression ratios of 20 ERF subfamily genes were analysed in two cassava cultivars, ‘KU50’ and ‘SC5’, that exhibit different levels of leaf abscission when challenged with the same water-deficit stress. The analysis indicated that most of the ERF genes were expressed at higher levels in the precocious abscission ‘KU50’ cultivar than in the delayed abscission ‘SC5’ cultivar.
Conclusion
Ccomparative analysis of both ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission shown that the ERF subfamily functions in the regulation of cassava abscission zone development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Plant cellular and developmental processes are significantly affected by many environmental conditions, e.g. drought, cold, high salinity, flood, submergence, pathogen attack and hormone stress [1, 2], and the processes are regulated by various transcription factors (TFs) [3, 4]. The apetala2/ethylene response factor (AP2/ERF) gene family is one of the most important plant transcription factor families [5]. AP2/ERF genes contain one to two AP2/ERF domains comprising 60–70 conserved amino acid residues [5] and perform important regulatory functions in plant stress defence. In Arabidopsis, 145 AP2/ERF genes have been characterized and are divided among five families [6]: those containing two AP2 domains (AP2), one AP2 domain and an ethylene-responsive factor domain (ERF), one AP2 domain and a dehydration-responsive element-binding protein domain (DREB), one AP2 domain and one B3 domain (RAV), and the Soloists [5]. The AP2/ERF super-family has been recently studied in various plants, e.g. bamboo [5], grape [7], cucumber [8], rice [1], tomato [9], peach [10], sorghum [10], Chinese cabbage [11] and soybean [12].
The AP2/ERF family is known to have important functions in plant growth and development, as well as in abiotic and biotic stress responses [13]. AP2 subfamily members regulate seed abscission zone [14, 15], petal [5], ovule [5], and leaf epidermal cell identity [5], as well as flower development and seed growth [5, 13]. The ERF subfamily has specific functions in the regulation of abscission zone development [14, 16] and biotic stress response [5]. The DREB subfamily is involved in drought [12], cold [5], salinity [5], water-deficit [5], heat and osmotic stress response [5]. The RAV subfamily functions in the ethylene response [5]. Four AP2/ERF genes have been implicated in abscission: SHA1 in rice [14, 15], SlERF.B3 [17] and SlERF52 [16] in tomato, and FUF1 in Arabidopsis [18]. SHA1 and FUF1 both function in AZ development, whereas the two tomato genes function in AZ breakdown.
Cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) is the most important root crop in the world as more than 700 million people depend on cassava for staple food [19]. Cassava plants have obvious abscission zone structures in their leaf pulvinus-petioles [20–22], which facilitate their high drought tolerance as the abscission zones control the inflexible leaf abscission mechanism [22–24]. When subjected to prolonged adverse environmental conditions, cassava adapt to the new environment by shedding some old leaves, resulting in substantially reduced root yield in adverse environments [24]. When water becomes available, the crop can recover by rapidly forming new canopy leaves with substantially increased photosynthetic rates compared with unstressed crops, compensating for yield losses and producing final yields approaching those of well-watered crops [25]. Cassava plants require a flexible leaf abscission mechanism. Many abscission-related AP2/ERF genes have been identified in Arabidopsis [26], tomato [16], rice [15], melon [27] and apple [28, 29]; however, no studies have identified and characterized cassava abscission zone AP2/ERF super-family members.
This study surveyed the AP2/ERF family members using phylogenetic analysis of the 196 cassava AP2/ERF genes, and expression profile analysis indicated that 114 and 103 AP2/ERF genes were expressed during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission, respectively. Comparative analysis of ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission suggested that the expression of 99 AP2/ERF genes in response both treatments resulted in leaf abscission. SOTA clustering indicated that AP2/ERF genes exhibited similar expression patterns during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission, and the putative promoters of the genes were examined for motifs. Additionally, ACC oxidase activities were measured at various time points for both treatments. The important AP2/ERF genes were further studied in two cassava cultivars that exhibit different levels of leaf abscission when subjected to the same stress. Together, the data suggest that ERF subfamily genes regulate the progression of cassava leaf abscission.
Results
Cassava AP2/ERF gene identification
One hundred and ninety-six putative AP2/ERF genes were identified from the Manihot esculenta genome (annotation v.4.1) that were predicted to include one or two complete AP2/ERF domains (Additional file 1: Table S1). The gene set represents approximately (196/34,151) 0.5739 % of the annotated genes in the cassava genome (34,151 genes), which is very similar to the proportion of Arabidopsis genes (0.5481 %), and greater than the proportion of poplar (0.4390 %), foxtail millet (0.4407 %) and rice (0.4315 %) genes [30]. Based on the similarity of the amino acid sequences with the Arabidopsis thaliana AP2/ERF protein family, twenty-nine genes were identified as encoding proteins containing two AP2-domains and thus assigned to the AP2 family. Seven genes were predicted to encode one AP2-domain and one B3-domain and were thus assigned to the RAV family. One hundred and fifty-five genes were found to encode proteins containing a single AP2/ERF domain, and the genes could be further classified into two groups based on the similarity of their amino acid sequences: one hundred genes were found to potentially encode ERF subfamily members, whereas fifty five genes were predicted to encode DREB subfamily members. Two genes were assigned to the Soloist family based on their similarity to the Arabidopsis Soloist (At4g13040) [31]. Three genes were also found to contain one single AP2 domain; however, their homologies were quite low compared with the other AP2/ERF factors and were therefore assigned to the others subfamily (Table 1).
Phylogenetic reconstruction of the cassava AP2/ERF superfamily
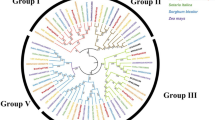
To study the phylogenetic relationships among the cassava AP2/ERF super-family members, a phylogenetic tree were generated using 196 AP2/ERF amino acid sequences. The resulting phylogenetic tree contained 6 groups, termed AP2, RAV, DREB, ERF, Soloist and others. Members of the DREB group were classified into six subgroups: A1, A2, A3, A4, A5 and A6; similarly, the ERF genes were also classified into 6 subgroups: B1, B2, B3, B4, B5 and B6 (Fig. 1).
An unrooted phylogenetic tree of 196 cassava AP2/ERF transcription factors. Cassava AP2/ERF protein sequences were aligned using ClustalW, and the phylogenetic tree was constructed with MEGA 5.0 using the neighbour-joining method, based on the p-distance model with 1000 bootstrap replicates. Each subfamily is represented by a specific colour
Microarray identification of AP2/ERF genes that are expressed in cassava leaf pulvinus-petiole AZs during both ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission
To compare the gene expression profiles during ethylene and water-deficit stress-induced cassava leaf abscission, leaf chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm) values [24] of 0.803, 0.765, 0.726, 0.697, 0.656 and 0.581 were represented as six time points (T1-T6). To verify the reliability and accuracy of differential gene expression profiling, AZs samples were collected with the same Fv/Fm values for both ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission. Then used time course cassava whole genome microarray analysis to examine the AZ gene expression during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission using the T1 time point as a control.
To analyse the AZ gene expression profiles during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission, a cassava whole genome microarray (NimbleGen) containing 41,796 probe sets was constructed, representing the 34,151 JGI database transcripts (http://www.phytozome.net/cassava.php) and the 7645 GenBank transcripts. To identify differences in AP2/ERF gene expression, statistical analysis was used to screen the microarray data for genes that were differentially expressed in the treatment samples (T2-T6) compared with the T1 control. A stringent false discovery rate (FDR, <0.01) and log2T2-T6/T1 (≤0.5 or ≥ 2) values as thresholds were used to estimate the differences in gene expression during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission using three replicates. SOTA clustering performed to analyze the differences in gene expression profiles among the six leaf abscission time points, finding that FDR-corrected P values of <0.01 and significant changes in expression occurred at least one time point for each AP2/ERF gene expressed during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission.
During ethylene-induced leaf abscission, 114 AP2/ERF genes were differentially expressed, whereas 103 AP2/ERF genes were differentially expressed during water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission (Additional file 2: Table S2). Ninety-nine AP2/ERF genes were differentially expressed during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission, whereas 14 were differentially expressed only during ethylene-induced leaf abscission, and 4 were differentially expressed during water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission (Fig. 2 and Additional file 2: Table S2). Of the AP2/ERF genes induced by water-deficit stress treatment, six SOTA clusters (wdS1-wdS6) could be separated into four groups of primary expression patterns (Fig. 3 and Additional file 3: Table S3). The first group, clusters wdS2 and wdS3, was down-regulated throughout the experimental period compared with the control. The second group, cluster wdS1, was up-regulated at the early and middle experimental time points, T2 and T3; whereas the third group, clusters wdS4 and wdS6, was up-regulated at the later experimental time points T4, T5 and T6; and the fourth group, cluster wdS5, was up-regulated at the latest experimental time points, T5 and T6.
SOTA clustering showing the expression profiles of ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission. a SOTA clustering identified six AP2/ERF gene expression clusters among the six leaf abscission time points (114 and 103 AP2/ERF genes for ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission, respectively). The signals are indicated using a red-green colour scale, where red and green represent increased and reduced expression, respectively. b Ethylene signalling GO annotation enrichment of AP2/ERF genes expressed during both ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments among the six SOTA clusters
The six ethylene-induced AP2/ERF gene SOTA clusters (etS1-etS6) were separated into five main expression patterns (Fig. 3 and Additional file 4: Table S4). The first group, clusters etS3 and etS5, was down-regulated throughout the experimental period compared with the control. The second group, cluster etS4, was up-regulated early, at T2; the third group, cluster etS6, was up-regulated at T3 during the middle of the experimental period; and the fourth group, cluster etS2, was up-regulated at the later experimental points T5 and T6. The fifth group, cluster etS1, was up-regulated throughout the experimental period but also exhibited the highest expression levels at T3 and T4 compared with the control.
Comparison of AP2/ERF expression profiles between ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission indicated that ERF subfamily genes are widely expressed in the cassava abscission zone
To identify the AP2/ERF genes that participate in both ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission, the AP2/ERF expression profiles were compared in both treatments using SOTA clustering. Because the expression patterns of AP2/ERF genes were nearly identical between ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission, the similar expression patterns at each time point were compared in both ethylene and water-deficit stress treatment.
The AP2/ERF genes that were up-regulated during the early experimental period (T2) in response to both treatments (Fig. 3a) were first examined. During ethylene treatment-induced leaf abscission, nineteen etS4 cluster AP2/ERF genes exhibited increased expression during the early stages of leaf abscission, and GO annotation indicated that 12 of the genes participate in ethylene-mediated signalling (GO:0009873) (Fig. 3b, Table 2, Additional file 5: Table S5). During water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission, seven wdS1 cluster AP2/ERF genes exhibited increased expression during the early stages of leaf abscission, and GO annotation indicated that five of the genes participate in ethylene-mediated signalling (Fig. 3b, Table 2, Additional file 5: Table S5). Two genes, cassava4.1_025181m and cassava4.1_026705m, were expressed during the early stages of leaf abscission in response to both ethylene and water-deficit stress, and both participate in ethylene-mediated signalling (GO:0009873). Cassava4.1_025181m encodes CRF2, a member of the ethylene response factor (ERF) B-5 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 2.9774 in response to ethylene and 1.6156 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_026705m encodes DREB26, a member of the DREB A-5 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 4.3761 in response to ethylene and 2.1547 to water-deficit stress respectively.
At the middle stage of leaf abscission (T3), the etS6 and wdS1 groups (ethylene and water-deficit stress, respectively) exhibited similar expression patterns (Fig. 3a). Twenty-two AP2/ERF genes exhibited increased expression in response to ethylene treatment, and GO annotation indicated that ten participate in ethylene-mediated signalling (Fig. 3b, Table 2, Additional file 5: Table S5). At the T3 time point during water-deficit stress, seven AP2/ERF genes exhibited increased expression. Two genes, cassava4.1_015499m and cassava4.1_028940m, were expressed during both ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission (Fig. 3b and Additional file 5: Table S5). Cassava4.1_015499m encodes ERF4, a member of the B-1 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 1.5052 in response to ethylene and 1.0759 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_028940m encodes ERF1, a member of the B-3 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 1.1519 in response to ethylene and 1.5544 to water-deficit stress respectively.
Later in leaf abscission (T5 and T6), etS2 and wdS5 (ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments, respectively) exhibited similar expression patterns (Fig. 3a). In response to ethylene treatment, nineteen AP2/ERF genes exhibited increased expression, and GO annotation indicated that fourteen participate in ethylene-mediated signalling (Fig. 3b, Table 2, Additional file 5: Table S5). In response to water-deficit treatment, eight AP2/ERF genes exhibited increased expression, and GO annotation indicated that six participate in ethylene-mediated signalling (Fig. 3b, Table 2, Additional file 5: Table S5). Comparative analysis indicated that three genes, cassava4.1_023899m, cassava4.1_027342m and cassava4.1_030658m, were expressed during both ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission. Cassava4.1_023899m encodes CRF10, a member of the B-6 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 1.7343 in response to ethylene and 2.7688 to water-deficit stress respectively; cassava4.1_027342m encodes EBE, a member of the B-4 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 18.1761 in response to ethylene and 25.1308 to water-deficit stress respectively; and cassava4.1_030658m encodes ESE3, a member B-6 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 2.9389 in response to ethylene and 3.2621 to water-deficit stress respectively.
The etS1, wdS4 and wdS6 groups of genes were up-regulated throughout the experimental period (Fig. 3a). Thirty-one AP2/ERF genes exhibited this expression pattern in response to ethylene treatment, and GO annotation indicated that 16 participate in ethylene-mediated signalling (Fig. 3b, Table 2, Additional file 5: Table S5). Fifty AP2/ERF genes were up-regulated throughout the experimental period in response to water-deficit treatment, and GO annotation indicated that 31 participate in ethylene mediated-signalling (Fig. 3b, Table 2, Additional file 5: Table S5). Seventeen genes, cassava4.1_010068m, cassava4.1_010102m, cassava4.1_010512m, cassava4.1_014721m, cassava4.1_022726m, cassava4.1_023527m, cassava4.1_023697m, cassava4.1_007311m, cassava4.1_007457m, cassava4.1_013880m, cassava4.1_014267m, cassava4.1_014632m, cassava4.1_014695m, cassava4.1_015856m, cassava4.1_017103m, cassava4.1_022781m and cassava4.1_032424m were expressed during both ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission. Cassava4.1_010068m encodes EDF1, a RAV transcription factor family member that contains AP2 and B3 binding domains, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 1.734 in response to ethylene and 4.9585 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_010102m encodes RAP2.4, a DREB A-6 subfamily member of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 1.1817 in response to ethylene and 1.5776 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_010512m encodes CRF11, a member of the ERF B-6 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 1.9445 in response to ethylene and 1.2128 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_014721m encodes ERF4, a member of the ERF B-1 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 3.6437 in response to ethylene and 2.9608 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_022726m encodes CRF11, a member of the ERF B-6 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 1.4961 in response to ethylene and 1.1308 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_023527m encodes RAP2.4, a member of the DREB A-6 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 1.5635 in response to ethylene and 1.2665 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_023697m encodes ERF12, a member of the ERF B-1 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 3.3057 in response to ethylene and 6.3907 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_007311m and cassava4.1_007457m encode a member of the ERF B-4 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, cassava4.1_007311m has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 1.4304 in response to ethylene and 132.6545 to water-deficit stress respectively; cassava4.1_007457m has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 27.6667 in response to ethylene and 23.4243 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_013880m and cassava4.1_014267m both encode RAP2.3, a member of the ERF B-2 subfamily of plant-specific ERF/AP2 transcription factors, cassava4.1_013880m has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 2.5673 in response to ethylene and 1.4501 to water-deficit stress respectively; cassava4.1_014267m has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 2.6542 in response to ethylene and 3.6792 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_014632m encodes RAP2.6 L, a member of the ERF B-4 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 13.188 in response to ethylene and 20.2608 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_014695m encodes CRF9, a member of the ERF B-6 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 1.6535 in response to ethylene and 8.9521 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_015856m, cassava4.1_017103m and cassava4.1_022781m encode ERF1, a member of the ERF B-3 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, cassava4.1_015856m has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 29.6175 in response to ethylene and 9.8903 to water-deficit stress respectively; cassava4.1_017103m has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 13.3218 in response to ethylene and 3.9972 to water-deficit stress respectively; cassava4.1_022781m has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 17.3535 in response to ethylene and 6.7962 to water-deficit stress respectively. Cassava4.1_032424m encodes ERF9, a member of the ERF B-1 subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factors, it has the expression ratio (compared to T1 time-point) of 2.0164 in response to ethylene and 1.6363 to water-deficit stress respectively.
Promoter motif prediction for ERF subfamily genes expressed during both ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission
As described above, twenty-four genes were expressed in response to both ethylene and water-deficit stress, and twenty belonged to the ERF subfamily (Table 3). To further understand the potential functions of the genes in regulating abscission zone development, the promoters of the twenty ERF subfamily genes were analysed to identify cis-elements. For this analysis, 2 kbp sequences of putative promoter regions were examined for potential cis-regulatory elements that are responsive to water-deficit stress and ethylene [5]. Three drought stress response cis-elements, S000415, S000414 and S000176, as well as two ethylene response cis-elements, S000037 and S000457, were frequently identified within the promoter regions of the genes (Additional file 6). Many ERF genes contained more than twenty drought stress elements and more than five ethylene response elements, e.g. cassava4.1_025181m, cassava4.1_014721m, cassava4.1_022726m, cassava4.1_023697m, cassava4.1_007311m, cassava4.1_013880m, cassava4.1_014267m, cassava4.1_015856m, cassava4.1_017103m and cassava4.1_022781m (Additional file 6, Table 2).
ACC oxidase was up-regulated during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission
GO annotation and promoter motif prediction of the twenty ERF subfamily genes expressed during ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments indicated functions in the ethylene response, suggesting that ethylene is an important factor in both ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission. Measurements of ACC oxidase concentration (a key enzyme in ethylene biosynthesis) indicated that ACC oxidase activity gradually increased from T1 to T6. Furthermore, ACC oxidase activity levels were reduced during the early and middle stages of water-deficit stress-induced abscission compared with ethylene treatment. In contrast, ACC oxidase activities later increased sharply during water-deficit stress-induced abscission compared with ethylene treatment (Fig. 4). Together, the results indicate that ethylene was more concentrated in AZs during water-deficit stress than during ethylene treatment.
Validation of comparative gene expression profiles of twenty ERF subfamily genes in two cassava cultivars with differing levels of leaf abscission
To further understand the regulatory function of ERF subfamily genes in leaf abscission, their expression levels were examined in two cassava cultivars, ‘KU50’ and ‘SC5’. Compared to ‘SC5’ and other cultivars, ‘KU50’ is more easily drop off the leaves when met the same stress condition [19, 32, 33]. The expression ratios of the twenty ERF genes were compared between the cultivars at six time points during water-deficit stress, and clustered the ERF gene expression patterns using hierarchical clustering. The analysis indicated that most of the ERF genes (16) were more highly expressed at the middle and later time points (T3, T4, and T5) in the ‘KU50’ cultivar than in ‘SC5’. In particular, six ERF genes, cassava4.1_014267, cassava4.1_014632, cassava4.1_015856, cassava4.1_013880, cassava4.1_007457 and cassava4.1_017103 exhibited increased expression in ‘KU50’ compared with ‘SC5’ during the middle stages (Fig. 5a). At this stage, ‘KU50’ is more susceptible to dropping leaves than ‘SC5’ under the same conditions of water-deficit stress as all ‘KU50’ leaves, but few ‘SC5’ leaves, wither (Fig. 5b). Together, the data indicate that the middle stage is the key stage for determining leaf abscission.
Identification of 20 ERF subfamily genes in two cassava cultivars (‘KU50’ and ‘SC5’) under water-deficit stress. a Heat map of real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) results for 20 ERF subfamily genes in two water-deficit stressed cassava cultivars; three biological and technical replicates were performed. b The water-deficit stress phenotype of two cassava cultivars, ‘KU50’ and ‘SC5’, at the middle stage of leaf abscission. Real-time PCR primer sequences are listed in Additional file 7: Table S7. The expression ratios for each ERF gene at each time point are presented first using T1 as a control for both ‘KU50’ and ‘SC5’, and then to cut ‘KU50’ expression ratios with those of ‘SC5’ at each time point. The heat map depicts the log2-transformed fold change values. The log2 (fold change values) and the colour scale are indicated above the heat map
Discussion
Comparative analysis of cassava and Arabidopsis AP2/ERF genes indicated a greater number of ERF subfamily members in the cassava genome than in the Arabidopsis genome
The AP2/ERF family is one of the most important subfamilies involved in plant development as well as abiotic and biotic stress response [2]. This study is the first to identify and characterize the AP2/ERF family in cassava. Here, one hundred and ninety-six cassava AP2/ERF genes were classified into 6 subfamilies (Table 1 and Fig. 1). Previously, Sakuma et al. (2002) reported the existence of 145 Arabidopsis AP2/ERF genes [6, 34]. We compared the cassava and Arabidopsis families and groups using the available complete genome sequences, finding more ERF and AP2 subfamily members within the cassava genome. Notably, the number of cassava ERF subfamily members (100) far exceeds that of the Arabidopsis genome (65) (Table 1 and Fig. 1). The number of DREB subfamily members is similar between the two genomes; however, the DREB subfamily sizes differ. Four Arabidopsis ERF groups, B1, B3, B4, and B6; and two DREB groups, A3 and A4, contained more members (Table 1). The number of cassava ERF subfamily members far outnumbers that in Arabidopsis, suggesting that this subfamily experienced a gene duplication event during cassava evolution. Gene duplication is considered to be the primary driving force of new gene functions [34]. In the study, more ERF genes were observed to participate in ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced abscission, suggesting that the ERF subfamily plays more important functions in cassava plant development than in other subfamilies.
ERF subfamily genes expressed at various time points function to regulate the progression of cassava leaf abscission
AP2/ERF genes have been shown to play crucial roles in various developmental processes, such as response to various stresses [13], phytohormone signalling [5, 13] and defence [1, 2]. Here, molecular methods were used attemptly to identify the key AP2/ERF genes that regulate cassava leaf abscission in response to ethylene and water-deficit stress. To maintain consistency between the two leaf abscission induction experiments, six Fv/Fm values were selected to serve as time points during leaf abscission for AZ sample collection prior to microarray analysis. To identify the AP2/ERF genes expressed during cassava leaf abscission in response to both treatments, the AP2/ERF gene expression profiles of pulvinus-petiole AZs were used for SOTA clustering. In total, 114 and 103 AP2/ERF genes were detectably expressed during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission, respectively (Fig. 2). Among the AP2/ERF genes, 99 were expressed during both ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission (Additional file 2: Table S2), suggesting that similar genes regulate leaf abscission in response to the stresses. Comparative analysis of AP2/ERF gene expression profiles during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission resulted in the selection of 24 AP2/ERF genes distributed among the different time points, including 20 ERF subfamily genes, 3 DERB subfamily genes, and one RAV subfamily gene (Additional file 5: Table S5), suggesting that ERF subfamily genes play important roles in cassava abscission zone development. During early leaf abscission, high levels of CRF2 expression were detected (Fig. 3a and Additional file 2: Table S2, Additional file 3: Table S3, Additional file 4: Table S4, Additional file 5: Table S5) that mediate the cytokinin response [35], indicating that cassava plant maintained growth and development during the early stages of ethylene and water-deficit stress treatment. Abscission does not occur during the early stages. CRF2 expression decreased during the middle and late stages of abscission, suggesting that abscission occurs within AZs at the stages. The reduced expression this gene type in response to cytokinin may indicate the start of abscission.
During the middle of abscission, ERF4 expression was high (Fig. 3a and Additional file 2: Table S2, Additional file 3: Table S3, Additional file 4: Table S4, Additional file 5: Table S5). ERF4 was shown to direct leaf senescence progression, and transgenic Arabidopsis plants with increased AtERF4 expression exhibited precocious leaf senescence [36]. Gene expression and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays suggested that this gene is involved in regulating the expression of many genes that are involved in leaf senescence progression [36]. High ERF4 expression during the middle stages of cassava abscission suggested that senescence occurred in AZ cells at this stage and that AZ cells underwent precocious senescence in response to external stresses that induced ERF4 expression [36].
Later in abscission, high ESE3 expression levels were detected (Fig. 3a and Additional file 2: Table S2, Additional file 3: Table S3, Additional file 4: Table S4, Additional file 5: Table S5). ESE3 has been suggested to regulate stamen abscission zone development by communicating with components of the HAE pathway within the ethylene-dependent pathway [37]. From this point, both ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments regulate leaf abscission via the ethylene-dependent pathway. The ACC oxidase activity measurements also confirmed that the ethylene contents of AZs increased during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced abscission, although their ethylene contents increased sharply during water-deficit stress treatment (Fig. 4). The data suggest that ethylene is a primary factor that contributes to ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced cassava leaf abscission.
Seventeen AP2/ERF genes were highly expressed between T2 and T6 in response to both ethylene and water-deficit stress treatment (Fig. 3a and Additional file 2: Table S2, Additional file 3: Table S3, Additional file 4: Table S4, Additional file 5: Table S5). The genes that exhibited the expression pattern primarily contributed to cassava leaf abscission. High levels of EDF1 expression at this stage have been reported to promote flower senescence and abscission, as well as activate senescence-associated genes downstream in the ethylene response [18]. Rap2.4a was also highly expressed at this stage; this gene is predicted to act in reactive oxygen species (ROS) signalling by controlling nuclear expression of 2-Cys peroxiredoxin A and other chloroplast antioxidant enzymes. In the previous study, ROS were proved to play an important role in the regulation of cassava leaf abscission [22]; furthermore, ROS are related to ethylene and water-deficit stress [38]. High expression levels of another ERF4 gene were also detected at this stage. RAP2.4 has been implicated in the abiotic stress response, acting to regulate multiple aquaporin genes that were also highly expressed in response to ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments, suggested that water homeostasis is disrupted during cassava leaf abscission [39]. Two RAP2.3 genes, cassava4.1_013880m and cassava4.1_014267m, were also highly expressed at this stage and have been shown to participate in the responses to low oxygen, oxidative and osmotic stress [40]. GO annotation also suggested this gene functions to regulate cell death (Additional file 3: Table S3 and Additional file 4: S4), and comparison of their expression ratios between ‘KU50’ and ‘SC5’ confirmed increased expression in the ‘KU50’ cassava cultivar that exhibited precocious abscission when met the same stress (Fig. 5a). RAP2.6 L has been reported to induce premature senescence by increasing stomatal closure more than the high antioxidant enzyme activity levels that are also detected at that stage. The gene has also been reported to participate in the jasmonic, salicylic, and abscisic acid pathways as well as the ethylene pathway, indicated that many phytohormone pathways are involved in cassava leaf abscission [41]. Furthermore, increased expression levels were also observed in the precocious abscission ‘KU50’ cultivar compared with ‘SC5’ cultivar subjected to the same stress (Fig. 5a). Two ERF1 genes, cassava4.1_015856 and cassava4.1_017103m, are highly expressed at that stage, and this gene has been shown to have early and transient oxidative activity during plant responses to osmotic, ionic, redox and hormonal signalling [42]. Comparison of the ‘KU50’ and ‘SC5’ ERF1 expression ratios further confirmed increased expression in the precocious abscission ‘KU50’ cultivar when subjected to the same stress (Fig. 5a). Together, the data suggest that many signalling pathways are involved in cassava leaf abscission, e.g. hormonal, ROS, water stress, programmed cell death (PCD), and osmotic signalling.
The downstream genes of six ERF genes expressed at higher levels in the precocious abscission ‘KU50’ cultivar
Since six ERF genes, cassava4.1_014267 (RAP2.3), cassava4.1_014632 (RAP2.6 L), cassava4.1_015856 (ERF1), cassava4.1_013880 (RAP2.3), cassava4.1_007457 (ERF-B 4) and cassava4.1_017103 (ERF1), expressed at higher levels in the precocious abscission ‘KU50’ cultivar than in the delayed abscission ‘SC5’ cultivar, suggested the six ERF genes play important regulation roles on abscission when suffered form stress. The analyses of the putative downstream genes of the six genes were examined. Glutathione S-transferase 6 (GST6) can be regulated by RAP2.3, glutathione S-transferase (GST; EC 2.5.1.18) proved to play major roles in oxidative stress metabolism, the levels of GST, can be induced by diverse environmental stimuli, were necessary to maintain cell redox homeostasis and protect plants against oxidative stress [43]. Overexpression RAP2.3 in Arabidopsis have been proved to cause up-regulation of GST6, suggested GST6 act downstream of the RAP2.3 [43]. PDF1.2, a plant defensin gene, related to ROS detoxification, was increased in Arabidopsis lines overexpressing RAP2.3 and ERF1 [43]. Actually, PDF1.2 is a typical downstream gene of the ethylene/jasmonic acid signaling, thus, it is likely that ERF promotes transcription of PDF1.2 through in vivo binding to the GCC-box [43].
WEAK ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE2/ANTHRANILATE SYNTHASE α1 (WEI2/ASA1), encoding a rate-limiting enzyme in tryptophan (Trp) biosynthesis, ASA1 has proved to act downstream of ERF1 [44]. ERF1 can bind to ASA1 promoter and directly up-regulate ASA1 expression [44]. Which also has been examined to have the function of leading to auxin accumulation and ethylene-induced inhibition of plant growth [44], indicated ASA1 regulate the abscission zone separation by regulate the homeostasis of auxin and ethylene. In addition, Arabidopsis nudix hydrolase 7 (AtNUDT7) also proved to act downstream of ERF1 because ERF1 protein has been examined to bind to the GCC-box motif in the AtNUDT7 promoter [45]. AtNUDT7 plays an important role in regulating redox homeostasis during stress/defense signaling [45]. The early responsiveness of AtNUDT7 provides a useful marker especially during oxidative cell death in plants [45], indicated AtNUDT7 may participate in regulating abscission zone development by oxidative cell death pathway.
Many antioxidant enzymes, including APX1 (ascorbate peroxidase 1, EC 1.11.1.11) and FSD1 (Fe-superoxide dismutase 1, EC 1.15.1.1), and the water logging responsive gene ADH1 (alcohol dehydrogenase 1, EC 1.1.1.1), were proved to participate ROS regulation [46]. All these encoded genes of these antioxidant enzymes acted downstream of RAP2.6 L, RAP2.6 L overexpression caused significant increases in the transcripts of these antioxidant enzymes [46], suggesting these antioxidant enzymes participate to regulate abscission zone development by modify the antioxidant system of plants.
The expression profiles of other known genes involved in cassava abscission zone development
Two most important breakthroughs were made in the abscission research, one of the most important breakthrough in abscission research was the identification of INFLORESCENCE DEFICIENT IN ABSCISSION (IDA) to regulate cell separation processes in A. thaliana [47]. The ida mutant proved to fail to undergo floral organ abscission, while overexpression of IDA lead to premature and ectopic abscission [48]. IDA mediates its effect through the two LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT RLKs (LRR-RLKs) HAESA (HAE) and HAESA-LIKE 2 (HSL2), as the double knockout hae hsl2 is phenotypically similar to the ida mutant and overexpression of IDA is not able to rescue this phenotype [47–49]. Another breakthrough in abscission research was the identification of the jointless (j) mutant locus in tomato [50], which causes the plant to fail to develop pedicel AZs. The j locus was isolated by map-based cloning and the wild-type gene encodes a MADS-box transcription factor [51]. In tomato, three MADS-box genes, including JOINTLESS, MACROCAYLYX, and SlMBP21, have been shown to be implicated in development of the flower abscission zone [52], SVP family MADS-Box proteins have also been confirmed the function on abscission regulation, moreover, SVP family MADS-Box proteins have been proved to have the same function as JOINTLESS in abscission regulation, and discovered to interacted with MACROCAYLYX, and SlMBP21, indicating the key regulation role on abscission development [52].
In the cassava abscission zone, IDA expressed both in ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments, the expression patterns in both treatments were confirmed by qPCR in cassava abscission zones, the IDA expression levels had very low at the early stages of abscission in both ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments, however, the expression levels of IDA increased sharply at the later stages of abscission in both ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments, the highest expression ratios increased 275.3248 in ethylene treatment and 64.7765 in water-deficit stress treatment at T6 time point when compared to T1 time point respectively (Fig. 6).
Five MADS-Box proteins have been confirmed to express in abscission in both ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments (Fig. 7). Four MADS-box genes, MADS1, MADS3, MADS4 and MADS5 detected with high expression levels in ethylene treatment, the highest expression ratio of MADS1 and MADS3 appeared at T3 time point and had 3.2 and 2.2 times when compared with T1 time point (Fig. 7); the highest expression ratio of MADS4 and MADS5 appeared at T4 time point with 2.4 and 1.3 times when compared with T1 time point. One MADS-box gene, MADS2 detected with high expression levels in water-deficit stress treatment, the expression ratio of MADS2 had 1.6 times in T5 time point when compared with T1 time point (Fig. 7).
Conclusions
More ERF subfamilies were found in the cassava genome than in the Arabidopsis genome. Comparative analysis of transcriptome expression profiles in response to ethylene and water-deficit stress indicated that most AP2/ERF genes were expressed in response to both treatments, suggested that the same AP2/ERF genes may function in leaf abscission in response to different treatments. Comparisons of AP2/ERF genes that were expressed at the same time points during abscission in response to both treatments indicated that 20 ERF subfamily genes were highly expressed during leaf abscission. Further analysis of promoter cis-elements and ACC oxidase activities confirmed that the ERF subfamily responds to ethylene and regulates cassava abscission zone development. The detection of high expression levels for most ERF subfamily genes in precocious abscission cassava cultivar verified the regulatory function of ERF subfamily genes in cassava abscission zone development.
Methods
Plant materials and treatments
‘SC5’ and ‘KU50’ cassava plants were grown as previously described [53]. In detail, cassava plants were planted in plastic pots at 28 °C under a 16 h light photoperiod (130 μmol · m-2 · s-1) for 3 months in the greenhouse. Three plants were planted in one pot, three pots repeated as a biological replicate. Three-month-old cassava plants with uniform growth statuses were chosen for ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments. Water-deficit stress and ethylene treatments were evaluated using the chlorophyll fluorescence parameter Fv/Fm. For ethylene treatments, leaves were sprayed with 100 μM ethylene, and plants were planted in a pot without water for water-deficit stress treatments. Fv/Fm values were used to select six time points for AZ sample collection.
Samples (approximately 1–2 mm) were cut from each pulvinus-petiole, including the AZs. AZs were collected from the middle of the cassava plants in each pots, three pots as a biological replicate, and repeated 3 times for each time points. AZs that were approximately 1–2 mm in size were frozen in liquid nitrogen for RNA extraction. RNA was purified using the plant RNA reagent from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA) to produce a pure and high-quality RNA preparation as indicated by spectroscopic and gel electrophoresis analysis.
Identification of cassava AP2/ERF family genes
AP2/ERF genes were isolated from the cassava genome (JGI database, version 4.1) using annotation and BLAST. Cassava genome sequences that were suggested to contain an AP2 domain were isolated and identified as candidate AP2/ERF genes using the Arabidopsis genome as a reference [13]. The Arabidopsis AP2/ERF genes were identified using The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) [13]. Each putative cassava AP2/ERF gene was searched against the TAIR database using BLAST to ensure that no additional related genes were selected [13].
Phylogenetic analysis
Phylogenetic analysis was performed using MEGA software, version 5, and the phylogenetic tree was constructed using neighbour-joining. The resulting tree was tested for reliability using bootstrapping with 1,000 replicates and amino acid p-distance parameters [54].
Analysis of cassava ERF subfamily putative promoter region cis-elements
The putative promoter regions were analysed for cis-elements according to Wu et al. [5]. In detail, the 2 kbp putative promoter regions upstream of each ERF subfamily coding DNA sequence were examined for cis-elements using the PLACE website (http://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/PLACE/).
The cassava whole genome microarray: design, hybridization, and data analysis
A time series of whole cassava genome microarray analyses based on the principle of the “loop design” was performed as previously described [55]. For either ethylene or drought treatment, 18 distinct AZ samples (three biological replicates at each of 6 time points) to be compared, the experimental design included 36 two-color microarray slides for both treatments, allowing three technical replicates of each sample to be observed. The cassava microarray was constructed as previously described [22, 55]. In detail, Two public databases were used for cassava microarray construction: the great majority of the ESTs originated from JGI database (http://www.phytozome.net/cassava.php) and the minority based on sequences from NCBI with E <1e-5. Custom-designed 60-mer nimblegen DNA microarrays were synthesized by maskless in situ photolithographic synthesis [22]. The fluorescent dye (Cy3-dCTP)-labeled cassava cDNA was produced as previously described using CapitalBio cRNA Amplification and Labeling Kit (CapitalBio). After completion of double-stranded cDNA (dsDNA) synthesis, the dsDNA products were purified using a PCR NucleoSpin Extract II Kit (MN). The resulting cRNA was labeled according to Nimblegen recommendations. The procedures of Array hybridization, washing, scanning and data analysis were performed at CapitalBio Corporation (Beijing, China) according to the NimbleGen’s Expression user’s guide. The expression data of probes were normalized using quantile normalization and expression data of genes were generated using the Robust Multichip Average (RMA) algorithm [22].
Time course analysis
For comparative analysis, differences in gene expression between samples (T2-T6) and reference (T1) were identified using significant analysis of microarray software (SAM, version 3.02) [56]. Changes in gene expression exceeding a threshold of <0.5 or >2.0-fold change, with a Wilcoxon Rank-Sum test significance level of 0.01 (P < 0.01) and a false discovery rate (FDR) threshold of <1 % in the SAM output were considered to be differentially expressed. Time-dependent differentially expressed genes were classified with self organizing tree algorithm clustering (SOTA) using MeV 4.0 software [57].
GO analysis
GO annotation of gene clusters was performed using BiNGO according to Maere et al. [58]. Significant GO categories were identified using a hypergeometric test with a significance threshold of 0.01 after a Benjamini and Hochberg FDR correction [59]. GO categories were classified by hierarchical clustering using MeV 4.0 software.
Real-time RT-PCR validation of ERF subfamily gene expression in two cassava cultivars
For validation of comparative gene expression profiles of twenty ERF subfamily genes, ‘KU50’ cassava cultivar was chose as the control of the ‘SC5’ cassava cultivar, the two cassava cultivar that were cultivated widely in the south of China, ‘KU50’ was identified as a cassava cultivar with high-starch and different drought-resistance when compared to other cassava cultivars [19, 32, 33]. RNA from three independent biological samples were reverse transcribed and used for real-time qRT-PCR with SYBR Green I (Carlsbad, CA) detection on a STEP-ONE system. The real-time PCR primer sequences are listed in Additional file 7: Table S7. To avoid non-specific amplification from other AP2/ERF family genes, the primers were designed to span intron-exon boundaries or target the untranslated regions and the primer pairs were confirmed using the cassava genome database to ensure their specificity. The expression ratios of ERF genes at each time point are presented using T1 as a control first in both ‘KU50’ and ‘SC5’, and then to cut the ‘KU50’ expression ratios with those of ‘SC5’ at each time point.
ACO measurements for ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments
ACO extractions and assays were performed according to He et al. [60]. Cassava leaf AZ tissue samples (3 g tissue, approximately 30 AZs) were collected at six time points from ethylene- or water-deficit stress-treated plants. The samples were ground in liquid nitrogen and used for extractions and measurements. The T1 sample ACO concentration served as a control.
Abbreviations
AP2/ERF, APETALA2/ethylene response factor; AZs, abscission zones; FDR, false discovery rate; Fv/Fm, chlorophyll fluorescence; GO, gene ontology; SAM, significant analysis of microarray software; SOTA, self organizing tree algorithm.
References
Sharoni AM, Nuruzzaman M, Satoh K, Shimizu T, Kondoh H, Sasaya T, Choi I-R, Omura T, Kikuchi S. Gene structures, classification and expression models of the AP2/EREBP transcription factor family in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011;52(2):344–60.
Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gene Regulatory Mechanisms. 2012;1819(2):86–96.
Dietz K-J, Vogel MO, Viehhauser A. AP2/EREBP transcription factors are part of gene regulatory networks and integrate metabolic, hormonal and environmental signals in stress acclimation and retrograde signalling. Protoplasma. 2010;245(1-4):3–14.
Rashid M, Guangyuan H, Guangxiao Y, Hussain J, Xu Y. AP2/ERF transcription factor in rice: genome-wide canvas and syntenic relationships between monocots and eudicots. Evol Bioinforma. 2012;8:321.
Wu H, Lv H, Li L, Liu J, Mu S, Li X, Gao J. Genome-Wide Analysis of the AP2/ERF Transcription Factors Family and the Expression Patterns of DREB Genes in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0126657.
Xu W, Li F, Ling L, Liu A. Genome-wide survey and expression profiles of the AP2/ERF family in castor bean (Ricinus communis L.). BMC Genomics. 2013;14(1):785.
Licausi F, Giorgi FM, Zenoni S, Osti F, Pezzotti M, Perata P. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily in Vitis vinifera. BMC Genomics. 2010;11(1):719.
Hu L, Liu S. Genome-wide identification and phylogenetic analysis of the ERF gene family in cucumbers. Genet Mol Biol. 2011;34(4):624–34.
Karlova R, Rosin FM, Busscher-Lange J, Parapunova V, Do PT, Fernie AR, Fraser PD, Baxter C, Angenent GC, de Maagd RA. Transcriptome and metabolite profiling show that APETALA2a is a major regulator of tomato fruit ripening. Plant Cell. 2011;23(3):923–41.
Zhang C, Shangguan L, Ma R, Sun X, Tao R, Guo L, Korir N, Yu M. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily in peach (Prunus persica). Genet Mol Res. 2012;11:4789–809.
Li M-Y, Wang F, Jiang Q, Li R, Ma J, Xiong A-S. Genome-wide analysis of the distribution of AP2/ERF transcription factors reveals duplication and elucidates their potential function in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Plant Mol Biol Report. 2013;31(4):1002–11.
Zhang G, Chen M, Li L, Xu Z, Chen X, Guo J, Ma Y. Overexpression of the soybean GmERF3 gene, an AP2/ERF type transcription factor for increased tolerances to salt, drought, and diseases in transgenic tobacco. J Exp Bot. 2009;60(13):3781-96.
Li M-Y, Xu Z-S, Huang Y, Tian C, Wang F, Xiong A-S. Genome-wide analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors in carrot (Daucus carota L.) reveals evolution and expression profiles under abiotic stress. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015;290(6):2049-61.
Hofmann NR. SHAT1, A new player in seed shattering of rice. Plant Cell. 2012;24(3):1034-48.
Zhou Y, Lu D, Li C, Luo J, Zhu B-F, Zhu J, Shangguan Y, Wang Z, Sang T, Zhou B. Genetic control of seed shattering in rice by the APETALA2 transcription factor SHATTERING ABORTION1. Plant Cell. 2012;24(3):1034–48.
Nakano T, Fujisawa M, Shima Y, Ito Y. The AP2/ERF transcription factor SlERF52 functions in flower pedicel abscission in tomato. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(12):3111-9.
Liu M, Pirrello J, Kesari R, Mila I, Roustan JP, Li Z, Latché A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M, Regad F. A dominant repressor version of the tomato Sl‐ERF. B3 gene confers ethylene hypersensitivity via feedback regulation of ethylene signaling and response components. Plant J. 2013;76(3):406–19.
Chen WH, Li PF, Chen MK, Lee YI, Yang CH. FOREVER YOUNG FLOWER Negatively Regulates Ethylene Response DNA-binding Factors (EDFs), by Activating An Ethylene-Responsive Factor (ERF), to Control Arabidopsis Floral Organ Senescence and Abscission. Plant Physiology. 2015; 00433.02015.
Feng B, Xiao Z, Zhou X, Li P, Zhang W, Wang Y, Lindberg Møller B, Zhang P, Luo M, Xiao G. Cassava genome from a wild ancestor to cultivated varieties. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5110. doi:10.1038/ncomms6110.
Rosas C, Cock JH, Sandoval G. Leaf fall in cassava. Exp Agric. 1976;12(04):395–400.
Fakir M, Mostafa M, Karim M, Prodhan A. Prediction of leaf number by linear regression models in cassava. J Bangladesh Agric Univ. 2011;9(1):49–54.
Liao W, Wang G, Li Y, Wang B, Zhang P, Peng M. Reactive oxygen species regulate leaf pulvinus abscission zone cell separation in response to water-deficit stress in cassava. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21542. doi:10.1038/srep21542.
Setter TL, Fregene MA. Recent advances in molecular breeding of cassava for improved drought stress tolerance. In: Jenks MA, Hasegawa PM, Jain SM (ed.). Advances in Molecular Breeding Towards Salinity and Drought Tolerance. New York: Springer; 2007. p. 701–711.
Vandegeer R, Miller RE, Bain M, Gleadow RM, Cavagnaro TR. Drought adversely affects tuber development and nutritional quality of the staple crop cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Funct Plant Biol. 2013;40(2):195–200.
El-Sharkawy MA. Physiological characteristics of cassava tolerance to prolonged drought in the tropics: implications for breeding cultivars adapted to seasonally dry and semiarid environments. Braz J Plant Physiol. 2007;19(4):257–86.
Aharoni A, Dixit S, Jetter R, Thoenes E, van Arkel G, Pereira A. The SHINE clade of AP2 domain transcription factors activates wax biosynthesis, alters cuticle properties, and confers drought tolerance when overexpressed in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2004;16(9):2463–80.
Corbacho J, Romojaro F, Pech JC, Latché A, Gomez-Jimenez MC. Transcriptomic events involved in melon mature-fruit abscission comprise the sequential induction of cell-wall degrading genes coupled to a stimulation of endo and exocytosis. PloS One. 2013;8(3):e58363.
Zhu H, Dardick CD, Beers EP, Callanhan AM, Xia R, Yuan R. Transcriptomics of shading-induced and NAA-induced abscission in apple (Malus domestica) reveals a shared pathway involving reduced photosynthesis, alterations in carbohydrate transport and signaling and hormone crosstalk. BMC Plant Biol. 2011;11(1):138.
Ferrero S, Carretero-Paulet L, Mendes MA, Botton A, Eccher G, Masiero S, Colombo L. Transcriptomic Signatures in Seeds of Apple (Malus domestica L. Borkh) during Fruitlet Abscission. 2015.
Lata C, Mishra AK, Muthamilarasan M, Bonthala VS, Khan Y, Prasad M. Genome-wide investigation and expression profiling of AP2/ERF transcription factor superfamily in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). PLoS One. 2014;9:e86852.
Rao G, Sui J, Zeng Y, He C, Zhang J. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Salix arbutifolia. FEBS Open Bio. 2015;5:132–7.
Yang Z, Zeng CY, Wang B, Yang YY, Lu C, Peng M. Effect of drought stress on K+, Ca2+, and ABA content in Cassava. Chinese journal of tropical crops. 2013;34(9):1725–9.
Zhang D, Fu LL, Peng M, Zhang JM. Real-time PCR analysis of metps1-3 gene under drought stress in cassava. Chinese journal of tropical crops. 2013;34(7):1274–7.
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006;140(2):411–32.
Rashotte AM, Mason MG, Hutchison CE, Ferreira FJ, Schaller GE, Kieber JJ. A subset of Arabidopsis AP2 transcription factors mediates cytokinin responses in concert with a two-component pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(29):11081–5.
Koyama T, Nii H, Mitsuda N, Ohta M, Kitajima S, Ohme-Takagi M, Sato F. A regulatory cascade involving class II ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR transcriptional repressors operates in the progression of leaf senescence. Plant Physiol. 2013;162(2):991–1005.
Cai S, Lashbrook CC. Stamen abscission zone transcriptome profiling reveals new candidates for abscission control: enhanced retention of floral organs in transgenic plants overexpressing Arabidopsis ZINC FINGER PROTEIN2. Plant Physiol. 2008;146(3):1305–21.
Shaikhali J, Heiber I, Seidel T, Ströher E, Hiltscher H, Birkmann S, Dietz K-J, Baier M. The redox-sensitive transcription factor Rap2. 4a controls nuclear expression of 2-Cys peroxiredoxin A and other chloroplast antioxidant enzymes. BMC Plant Biol. 2008;8(1):48.
Rae L, Lao NT, Kavanagh TA. Regulation of multiple aquaporin genes in Arabidopsis by a pair of recently duplicated DREB transcription factors. Planta. 2011;234(3):429–44.
Papdi C, Pérez‐Salamó I, Joseph MP, Giuntoli B, Bögre L, Koncz C, Szabados L. The low oxygen, oxidative and osmotic stress responses synergistically act through the ethylene response factor VII genes RAP2. 12, RAP2. 2 and RAP2. 3. Plant J. 2015;82(5):772–84.
Liu P, Sun F, Gao R, Dong H. RAP2. 6 L overexpression delays waterlogging induced premature senescence by increasing stomatal closure more than antioxidant enzyme activity. Plant Mol Biol. 2012;79(6):609–22.
Ellouzi H, Hamed KB, Hernández I, Cela J, Müller M, Magné C, Abdelly C, Munné-Bosch S. A comparative study of the early osmotic, ionic, redox and hormonal signaling response in leaves and roots of two halophytes and a glycophyte to salinity. Planta. 2014;240(6):1299–317.
Ogawa T, Pan L, Kawai-Yamada M, Yu LH, Yamamura S, Koyama T, Kitajima S, Ohme-Takagi M, Sato F, Uchimiya H. Functional Analysis of Arabidopsis Ethylene-Responsive Element Binding Protein Conferring Resistance to Bax and Abiotic Stress-Induced Plant Cell Death. Plant Physiol. 2005;138:1436–45.
Mao JL, Miao ZQ, Wang Z, Yu LH, Cai XT, Xiang CB. Arabidopsis ERF1 Mediates Cross-Talk between Ethylene and Auxin Biosynthesis during Primary Root Elongation by Regulating ASA1 Expression. PLoS Genet. 2016;12(1):e1005760. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005760.
Muthuramalingam M, Zeng X, Iyer NJ, Klein P, Mahalingam R. A GCC-box motif in the promoter of nudix hydrolase 7 (AtNUDT7) gene plays a role in ozone response of Arabidopsis ecotypes. Genomics. 2015;105(1):31–8.
Krishnaswamy S, Verma S, Rahman MH, Kav NN. Functional characterization of four APETALA2-family genes (RAP2.6, RAP2.6L, DREB19 and DREB26) inArabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol. 2011;75(1-2):107–27.
Aalen RB, Wildhagen M, Stø IM, Butenko MA. IDA: a peptide ligand regulating cell separation processes in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot. 2013;64:5253–61.
Vie AK, Najafi J, Liu B, Winge P, Butenko MA, Hornslien KS, Robert K, Reidunn BA, Atle MB, Tore B. The IDA/IDA-LIKE and PIP/PIP-LIKE gene families in Arabidopsis: phylogenetic relationship, expression patterns, and transcriptional effect of the PIPL3 peptide. J Exp Bot. 2015;66:5351–65. doi:10.1093/jxb/erv285.
Meng XZ, Zhou JG, Tang J, Li B, Oliveira MVV, Chai JJ, He P, Shan LB. Ligand-Induced Receptor-like Kinase Complex Regulates Floral Organ Abscission in Arabidopsis. Cell Rep. 2016;14(6):1330–8.
Liu D, Wang D, Qin Z, Zhang D, Yin L, Wu L, Colasanti J, Li A, Mao L. The SEPALLATA MADS-box protein SLMBP21 forms protein complexes with JOINTLESS and MACROCALYX as a transcription activator for development of the tomato flower abscissionzone. Plant J. 2014;77(2):284–96.
Yasuhiro I, Toshitsugu N. Development and regulation of pedicel abscission in tomato. Front Plant Sci. 2015;6:442.
Nakano T, Kato H, Shima Y, Ito Y. Apple SVP Family MADS-Box Proteins and the Tomato Pedicel Abscission Zone Regulator JOINTLESS have Similar Molecular Activities. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015;56(6):1097–106.
An D, Yang J, Zhang P. Transcriptome profiling of low temperature-treated cassava apical shoots showed dynamic responses of tropical plant to cold stress. BMC Genomics. 2012;13(1):64.
Charfeddine M, Saïdi MN, Charfeddine S, Hammami A, Bouzid RG. Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profiling of the ERF Transcription Factor Family in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Mol Biotechnol. 2015;57(4):348–58.
Breeze E, Harrison E, McHattie S, Hughes L, Hickman R, Hill C, Kiddle S, Kim Y-S, Penfold CA, Jenkins D. High-resolution temporal profiling of transcripts during Arabidopsis leaf senescence reveals a distinct chronology of processes and regulation. Plant Cell. 2011;23(3):873–94.
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(9):5116–21.
Li P, Ponnala L, Gandotra N, Wang L, Si Y, Tausta SL, Kebrom TH, Provart N, Patel R, Myers CR. The developmental dynamics of the maize leaf transcriptome. Nat Genet. 2010;42(12):1060–7.
Maere S, Heymans K, Kuiper M. BiNGO: a Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics. 2005;21(16):3448–9.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B (Methodological). 1995;57(57):289-300.
He C, Finlayson SA, Drew MC, Jordan WR, Morgan PW. Ethylene biosynthesis during aerenchyma formation in roots of maize subjected to mechanical impedance and hypoxia. Plant Physiol. 1996;112(4):1679–85.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Wenquan Wang for providing cassava germplasm.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31471551), the International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of China (grant no. 2013DFA32020), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (grant no. 2012AA101204-2), and the National Basic Research Program (grant no. 2010CB126600).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files.
Authors’ contributions
WBL participated in the study design, performed the microarray analysis and drafted the manuscript. YLY and YYL prepared the cassava material and detected the phenotypes. GW compared the ethylene and water-deficit stress treatment expression profiles. MP helped draft the manuscript and supervised the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional files
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Amino acid sequences of 196 cassava AP2/ERF proteins. (XLS 193 kb)
Additional file 2: Table S2.
Putative AP2/ERF genes expressed during ethylene- and water-deficit stress-induced leaf abscission. (XLS 1472 kb)
Additional file 3: Table S3.
SOTA clustering and annotation of AP2/ERF genes expressed in response to water-deficit stress treatment. (XLS 62 kb)
Additional file 4: Table S4.
SOTA clustering and annotation of AP2/ERF genes expressed in response to ethylene treatment. (XLS 67 kb)
Additional file 5: Table S5.
AP2/ERF genes that exhibited the same expression patterns during ethylene and water-deficit stress treatments. (XLS 19 kb)
Additional file 6: Table S6.
Summary of abiotic stress-inducible cis-elements in cassava ERF subfamily transcription factor promoter regions. (DOC 191 kb)
Additional file 7: Table S7.
Forward and reverse primers used for qRT-PCR analysis of ERF gene expression. (DOC 35 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, W., Li, Y., Yang, Y. et al. Exposure to various abscission-promoting treatments suggests substantial ERF subfamily transcription factors involvement in the regulation of cassava leaf abscission. BMC Genomics 17, 538 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2845-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2845-5