Abstract
Background
Our preliminary work confirmed that, SLC22A7 (solute carrier family 22 member 7), NGFR (nerve growth factor receptor), ARNTL (aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator like) and PPP2R2B (protein phosphatase 2 regulatory subunit Bβ) genes were differentially expressed in dairy cows during different stages of lactation, and involved in the lipid metabolism through insulin, PI3K-Akt, MAPK, AMPK, mTOR, and PPAR signaling pathways, so we considered these four genes as the candidates affecting milk production traits. In this study, we detected polymorphisms of the four genes and verified their genetic effects on milk yield and composition traits in a Chinese Holstein cow population.
Results
By resequencing the whole coding region and part of the flanking region of SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL and PPP2R2B, we totally found 20 SNPs, of which five were located in SLC22A7, eight in NGFR, three in ARNTL, and four in PPP2R2B. Using Haploview4.2, we found three haplotype blocks including five SNPs in SLC22A7, eight in NGFR and three in ARNTL. Single-SNP association analysis showed that 19 out of 20 SNPs were significantly associated with at least one of milk yield, fat yield, fat percentage, protein yield or protein percentage in the first and second lactations (P < 0.05). Haplotype-based association analysis showed that the three haplotypes were significantly associated with at least one of milk yield, fat yield, fat percentage, protein yield or protein percentage (P < 0.05). Further, we used SOPMA software to predict a SNP, 19:g.37095131C > T in NGFR, changed the structure of NGFR protein. In addition, we used Jaspar software to found that four SNPs, 19:g.37113872C > G,19:g.37113157C > T, and 19:g.37112276C > T in NGFR and 15:g.39320936A > G in ARNTL, could change the transcription factor binding sites and might affect the expression of the corresponding genes. These five SNPs might be the potential functional mutations for milk production traits in dairy cattle.
Conclusions
In summary, we proved that SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL and PPP2R2B have significant genetic effects on milk production traits. The valuable SNPs can be used as candidate genetic markers for genomic selection of dairy cattle, and the effects of these SNPs on other traits need to be further verified.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Milk and dairy products have long been regarded as good sources of nutrition, providing proteins, fatty acids, minerals and vitamins. Studies have shown that eating dairy products seems to be good for lowering blood pressure and low density lipoprotein, muscle exercise and preventing tooth decay, diabetes, cancer and obesity [1]. Milk production traits are the most important economic traits for dairy cattle breeding, including 305-day milk yield, fat yield, protein yield, fat percentage and protein percentage [2]. These traits are quantitative traits, controlled by minor polygenes and greatly affected by the environment, so the breeding work is more difficult.
Since the genomic selection (GS) was comprehensively applied in dairy cow breeding in developed countries in 2009, the early and accurate selection of young bulls has been realized, the generation interval has been greatly shortened, and the genetic progress of the population has been accelerated, thus the breeding cost has been significantly reduced. GS uses SNP markers to select target traits. Studies have shown that adding functional gene information with greater genetic effects of target traits to SNP marker data can improve the accuracy of genome breeding value prediction [3,4,5].
Therefore, in recent decades, quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping, candidate gene analysis, genome-wide association analysis and high-throughput sequencing techniques have been widely used in dairy cow breeding to identify the functional elements [6,7,8,9,10]. Moreover, studies have shown that SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) in the gene can significantly affect the milk production traits of dairy cows [11,12,13,14,15].
Previously, we identified a number of genes, miRNAs and lncRNAs that showed differentially expressed patterns in different lactation periods of Holstein, and found 12 genes, including SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL, and PPP2R2B, participating in the lipid metabolism through insulin, PI3K-Akt, MAPK, AMPK, mTOR, and PPAR signaling pathways, which were considered to be the promising candidates for milk production traits in dairy cattle; additionally, the four genes, were regulated by the same lncRNA that is worthy of further verification [16].
SLC22A7 (solute carrier family 22 member 7) is an organic anion transporter, which is involved in the transport of cGMP, niacin and propionic acid [17,18,19,20]. Propionic acid can be effectively converted into glucose, and the gene may regulate cell metabolism through the transport of propionic acid in the kidney and liver, and ultimately affect the milk production traits of dairy cows [21, 22].
It is reported that NGFR (nerve growth factor receptor) is closely associated with fat accumulation and the thickness of subcutaneous fat in pigs [23, 24], and another study has shown that the NGFR gene can regulate the directional differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into skeletal muscle progenitor cells [25].
ARNTL (aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator like, also known as BMAL1) gene, which belongs to the family of transcriptional regulatory factors, is the main transcriptional activator in mammals and plays an important role in regulating circadian rhythm [26, 27]. A study shows that the deletion of ARNTL in the adipocytes can disrupt the energy balance of mice and eventually lead to obesity [28].
The expression product of PPP2R2B (protein phosphatase 2 regulatory subunit Bβ) gene is a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A, which is widely found in neurons throughout the brain [29]. Studies have shown that PPP2R2B is associated with some human diseases, such as spinocerebellar ataxia, breast cancer and autoimmune diseases [30,31,32].
Based on the four candidate genes for milk production traits in dairy cows, the main goal of this study was to identify the SNPs of these four genes, analyze their genetic association with milk yield, fat yield, fat percentage, protein yield, and protein percentage, and evaluate whether they can be used for the genomic selection chip development. In addition, we will predict the potential biological structure and function of the identified SNPs, such as transcription factor binding site (TFBS) and secondary protein structure, and speculate the causal mutation for milk traits in dairy cattle.
Result
SNPs identification
In this study, we found five, eight, three and four SNPs in SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL and PPP2R2B genes, respectively. In SLC22A7, one SNP was located in intron, one in 3′ untranslated region (UTR) and three in 3 ‘flanking region. In NGFR, there were three SNPs located in 5 ‘flanking region, one in intron, one in exon 6, two in 3′ untranslated region and one in 3 ‘flanking region. In ARNTL, one SNP was located in 5 ‘flanking region, and two in intron. In PPP2R2B, two SNPs were located in intron region, one in exon 6, and one in the 3 ‘flanking region (Table 1; Fig. 1).
Location and association with milk yield, fat and protein percentage of SNPs in SLC22A7 (A), NGFR (B), ARNTL (C) and PPP2R2B (D) genes. MY milk yield, FP fat percentage, PP protein percentage. Gray boxes represent exons, and solid black circles represent significant differences in first or second lactation
The SNP of NGFR, 19:g.37095131C > T, was a missense mutation, and when the allele was mutated from C to T, the amino acid changed from cysteine to tyrosine. Additionally, the genotypic and allelic frequencies of all the identified SNPs were summarized in Table 1.
Association analyses between SNPs and the five Milk production traits
We analyzed the association between the 20 SNPs and five milk traits in dairy cows, including milk yield, fat yield, protein yield, fat percentage and protein percentage (Additional file 1; Fig. 1).
In SLC22A7, 23:g.16896145A > G was significantly associated with milk yield, protein yield and protein percentage in the first lactation, and milk yield, fat yield and protein yield in the second lactation. Two SNPs, 23:g.16899640A > G and 23:g.16900723A > T, were significantly associated with milk yield, fat yield and protein yield in the first lactation. The SNP 23:g.16900870G > T had significant associations on milk yield, protein yield in the first lactation, and milk yield, fat yield, protein yield and protein percentage in the second lactation. The 23:g.16901383G > C was significantly associated with milk yield, protein yield in the first lactation, and milk yield, fat yield and protein yield in the second lactation (P < 0.05).
In NGFR, 19:g.37113872C > G, 19:g.37096050G > A, 19:g.37095131C > T and 19:g.37091691C > A had significant associations with fat yield and fat percentage in the second lactation; 19:g.37113157C > T was significantly associated with milk yield, fat yield and fat percentage in the second lactation; and 19:g.37112276C > T had significant genetic effects on fat yield, fat percentage and protein yield in the second lactation (P < 0.05).
In ARNTL, 15:g.39320936A > G was significantly associated with milk yield, protein yield and protein percentage in the first lactation, and milk yield, fat yield and protein percentage in the second lactation; 15:g.39301344 T > C had significant effects on milk yield, fat yield, protein yield in the first and second lactations; and 15:g.39312186 T > C was significantly associated with milk yield, protein percentage in the first lactation, and milk yield, fat yield and protein yield in the second lactation (P < 0.05).
In PPP2R2B, 7:g.58088217C > T was significantly associated with fat yield and protein yield in the first lactation; 7:g.57855248C > T was significantly associated with milk yield, fat yield, protein yield in the first lactation and fat percentage in the second lactation; 7:g.57855119 T > C had significant effects on fat yield, protein yield, protein percentage in the first lactation and fat yield in the second lactation; 7:g.57794491G > T was significantly associated with fat yield in the first lactation, and milk yield and fat yield in the second lactation (P < 0.05).
In addition, the results of additive, dominant and substitution effects were shown in Additional file 2.
Associations between haplotype blocks and the five Milk traits
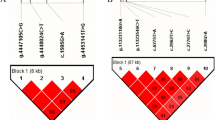
We estimated the degree of linkage disequilibrium (LD) among the 20 identified SNPs in this study using Haploview4.2, and inferred three haplotype blocks, including five, seven and three SNPs of SLC22A7, NGFR, and ARNTL genes, respectively (Fig. 2; Block 1 (SLC22A7): D′ = 0.99–1.00; Block 2 (NGFR): D′ = 0.98–1.00; and Block 3 (ARNTL): D′ = 1).
Linkage disequilibrium estimated between SNPs in SLC22A7, NGFR and ARNTL genes. The blocks indicate haplotype blocks and the text above the horizontal numbers is the SNP names. The values in the red boxes are pair-wise SNP correlations (D′), while bright red boxes without numbers indicate complete LD (D′ = 1)
In Block 1, the frequencies of four haplotypes, H1 (GAATC), H2 (GGTGG), H3 (AAAGG) and H4 (GAAGC), were 45.9, 27.2, 16.3 and 8.9%, respectively. In Block 2, four haplotypes were found, and the frequencies of H1 (CTCGCTC), H2 (ACTACCC), H3 (ACTATCG) and H4 (CTCGCCC), were 47.9, 21.3, 18.8, and 10%, respectively. In Block 3, the frequencies of H1 (TTA), H2 (CCA) and H3 (CTG) haplotypes were 63.5, 21.9 and 14.7%, respectively.
Moreover, we found that the haplotype combinations showed significant associations with 305-day milk yield, fat yield, fat percentage, protein yield, or protein percentage in the two lactations (P < 0.05; Additional file 3). Block 1 of SLC22A7 was strongly associated with milk yield, fat yield, and protein yield in the first lactation, and milk yield and fat yield in the second lactation. Block 2 of NGFR had significant associations with milk yield, fat yield, and protein yield in the first lactation, and fat yield, fat percentage and protein yield in the second lactation. The Block 3 of ARNTL was significantly associated with milk yield, fat yield, protein yield and protein percentage in the first and second lactations.
Functional variation prediction caused by SNPs
We predicted the TFBS changes of the four SNPs (19:g.37113872C > G, 19:g.37113157C > T, 19:g.37112276C > T and 15:g.39320936A > G) in the 5′ promoter region of NGFR and ARNTL genes by Jaspar software (Table 2), and found that all the four SNPs could change TFBSs.
The allele C of 19:g.37113872C > G in NGFR created binding site (BS) for transcription factor SNAI2, and allele G created BS for SPI1 and OSR2. For 19:g.37113157C > T in NGFR, allele T invented BS for STAT3, FEV and ETV6, and allele C invented BS for GATA2 and GATA1. Allele T of 19:g.37112276C > T in NGFR created BS for MXI1, and allele C created BS for NRF1 and SOHLH2.
As for 15:g.39320936A > G in ARNTL, allele G created BS for transcription factors DMRTA2, OSR1, PAX5 and TFAP2C, and allele A created BS for FOXL1, HOXC8, MZF1 and TBX6.
Furthermore, the protein secondary structure variation of the missense mutation in NGFR, 19:g.37095131C > T, was predicted by SOPMA, and the results showed that α-helix varied from 22.61 to 23.78%, β-turn from 2.56 to 1.86%, and random coil from 65.50 to 65.03% when allele A mutated into G.
Discussion
Our previous study considered SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL and PPP2R2B genes to be candidates to affect milk production traits in dairy cows [16]. In this study, we detected the polymorphisms of SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL and PPP2R2B genes, and found that there was a significant genetic association between the SNPs and haplotype blocks of these genes and milk production traits.
Transcription factors can affect gene expression by combining to TFBSs to regulate the transcription of target genes [33]. The SNP located at TFBS may affect the binding of transcription factors, resulting in differences in gene expression among individuals with different genotypes [34, 35]. In this study, we found the changes of TFBSs caused by the SNPs in 5 ‘flanking regions of NGFR and ARNTL genes. For 19:g.37113157C > T in NGFR, allele T invented BS for transcription factors STAT3, FEV and ETV6, and allele C invented BS for GATA2 and GATA1. In 15:g.39320936A > G of ARNTL, allele G created BS for DMRTA2, OSR1, PAX5 and TFAP2C, and allele A created BS for FOXL1, HOXC8, MZF1 and TBX6.
STAT3 is a transcription factor of the STAT family, which can be activated by tyrosine phosphorylation to inhibit the expression of gluconeogenic genes, thereby reducing blood glucose and maintaining blood glucose homeostasis [36]. The change of transcription factor FEV expression can affect the gene expression level of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) neurons in the central nervous system [37]. ETV6 is a transcriptional suppressor, which belongs to the ETS family and is highly conserved [38]. GATA2 inhibits the expression of genes related to cardiac development and up-regulates the important genes of hematopoietic differentiation in an indirect way [39]. GATA1 affects normal platelet production by regulating the expression of NBEAL2 by long-distance enhancers [40]. A study has shown that DMRTA2 may suppress the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2C to regulate spermatogenesis in zebrafish [41]. It has been found that OSR1 can inhibit the transcriptional activity of p53 and then inhibit the expression of oncogenes in renal cancer cells [42]. It is reported that the transcription factor PAX5 suppresses inappropriate genes in B cell lines and activates B cell-specific genes in B lymphocytes [43]. The down-regulation of tumor suppressor gene expression regulated by TFAP2C may be one of the carcinogenic causes of non-small cell lung cancer [44, 45]. FOXL1 can regulate the development of central nervous system by inhibiting the expression of Sonic Hedgehog protein in zebrafish [46]. HOXC8, as a transcriptional activator, induces the expression of transforming growth factor-β-1, which leads to the increase in the proliferation, anchorage-independent growth and migration of non-small cell lung cancer [47]. MZF1 has positive regulation on CDC37 gene transcription by binding the regulatory sites, while MZF1 deletion reduces CDC37 transcription and tumorigenicity of prostate cancer cells [48]. TBX6 is a member of the T-box transcription factor family, which regulates mouse embryonic development by promoting the expression of Dll1 encoding Notch ligands [49].
These transcription factors can cause the activation or inhibition of gene expression, and in this study, they may interact to promote or suppress the expression of NGFR or ARNTL genes. Based on the phenotypic data of milk production traits with different genotypes, we found that the fat yield of genotype TT of 19:g.37113157C > T in NGFR was significantly higher than that of genotype CC, and the milk and protein yields of genotype AA in 15:g.39320936A > G of ARNTL were significantly higher than those of genotype GG. Thus, we speculated that the change of gene expression caused by SNP may be one of the reasons for the phenotypic changes of milk production traits in dairy cows.
In addition, we predicted the change of the protein secondary structure by the missense mutation (19:g.37095131C > T; cysteine (UGC) to tyrosine (UAC)) in exon 6 of the NGFR gene, and found that this missense mutation could change the protein secondary structure of NGFR. Generally speaking, the α-helix is located at the core of the protein and plays an important role in the conformational change of the protein [50]. The results of association analysis showed that this mutation was significantly associated with milk fat yield and fat percentage, so we speculated that this missense mutation, 19:g.37095131C > T, might affect the conformational stability of NGFR protein and ultimately influenced the milk fat traits of dairy cows, yet its biological function needs to be further studied.
Conclusions
This study confirmed the significant genetic effects of SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL and PPP2R2B on milk production traits of Chinese Holstein cattle, and the valuable SNPs can be used as candidate genetic markers for molecular breeding of dairy cattle. Five SNPs were highlighted as the promising functional mutations for milk production traits, of which, 19:g.37113872C > G,19:g.37113157C > T and 19:g.37112276C > T in NGFR and 15:g.39320936A > G in ARNTL, might change the TFBSs to regulate expression of the corresponding gene, and the missense mutation of NGFR, 19:g.37095131C > T, could change the protein secondary structure. This study laid a foundation for further functional verification of SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL and PPP2R2B.
Methods
Animal selection and phenotypic data collection
In this study, we selected 947 daughters from 45 Chinese Holstein sire families in 22 farms of Beijing Shounong Animal Husbandry Development Co. LTD (Beijing, China) as the experimental population. The 45 sires were used for SNP identification and their daughters, 947 cows, were used for association analysis. Each sire family had an average of 21 daughters, and each cow had 3-generation pedigree information and Dairy Herd Improvement (DHI) records for milk yield, protein yield, protein percentage, fat yield and fat percentage (Additional file 4). The cows in each sire family were distributed in various dairy farms and maintained with the same feeding conditions.
We used the phenotypic data of 947 cows in the first lactation and 654 in the second lactation (293 cows merely completed the milking of first lactation) for the association analysis. The individual milk production phenotype of each cow was the data of the whole lactation period of the parity. The 305-day milk yield is calculated by multiplying the actual total milk yield by the corresponding estimated coefficient (Additional file 4). The 305-day milk fat and protein contents were obtained by multiplying the 305-day milk yield by the average milk fat and protein percentages, respectively. The average milk fat and protein percentages were the ratio of total milk fat and protein contents to total milk yield, respectively.
Genomic DNA extraction
Frozen semen of the 45 bulls and blood samples of 947 cows were provided by Beijing Dairy Cattle Center (Beijing, China). We extracted genomic DNAs from the semen using salt-out procedure, and used a TIANamp Blood DNA Kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China) to extract DNAs from the blood. The quantity and quality of extracted DNAs (A260/A280 > 1.8) were determined by a NanoDrop2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Science, Hudson, NH, USA) and gel electrophoresis (1.5%), respectively.
SNP identification and linkage disequilibrium (LD) estimation
We designed primers (Additional file 5) with Primer3 (http://bioinfo.ut.ee/primer3-0.4.0/) to amplify all the coding regions and 2000 bp of 5′ and 3′ flanking regions of SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL and PPP2R2B genes based on the bovine reference genome sequences. Then the primers were synthesized by Beijing Genomics Institute (BGI, Beijing, China). We mixed the genomic DNAs of bull semen with the same amount, and then amplified them by PCR (Additional file 5). We used 2% gel electrophoresis to detect whether the PCR amplification products were qualified, and the qualified PCR products were sequenced.
After sequencing, we compared the sequences with the reference sequences (ARS-UCD1.2) on NCBI-BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm. nih.gov/Blast.cgi) to identify the potential SNP. Subsequently, we genotyped the identified SNPs in 947 cows using Genotyping by Target Sequencing (GBTS) technology by Boruidi Biotechnology Co. Ltd. (Hebei, China). Further we calculated the allele frequency of each site and used the locus with minor allele frequency (MAF) > 0.05 for the following association analysis.
In addition, we used Haploview4.2 (Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA, USA) to estimate the extent of linkage disequilibrium (LD) between the identified SNPs.
Association analyses on Milk production traits
Associations between the SNPs or haplotype blocks and the milk production traits were analyzed using SAS 9.13 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). The additive genetic relationship matrix A was constructed using the SAS, which was computed by tracing the pedigree back to three generations of 2827 involved individuals. Variance components were estimated based on the data of 30,000 Chinese Holstein cows in Beijing area by using the DMU package version 6.0 (University of Aarhus, Foulum, Denmark). Finally, the effects of the SNPs/haplotype blocks on first or second lactation milk production traits were estimated using the mixed procedure of SAS 9.13 software. With the following animal model, each trait was analyzed separately and each polymorphism/block was also fitted separately:
where Y is the phenotypic value of each trait of each cow; μ is the overall mean; hys is the fixed effect of farm (1–22: 22 farms), calving year (1–4: 2012–2015) and calving season (1: April–May; 2: June–August; 3: September–November and 4: December–March); M is the age of calving as a covariant, b is the regression coefficient of covariant M; G is the genotype or haplotype combination effect; a is the individual random additive genetic effect, the distribution is \( \mathrm{N}\ \left(0,\mathbf{A}{\updelta}_a^2\right) \), A is a pedigree-based relationship matrix and the additive genetic variance is \( {\updelta}_a^2 \); and e is random residual, the distribution is \( \mathrm{N}\ \left(0,\mathbf{I}{\updelta}_{\mathrm{e}}^2\right) \), the unit matrix I and the residual variance \( {\updelta}_{\mathrm{e}}^2 \). Bonferroni correction was carried out by multiple tests, the significance level was equal to the original P value divided by the number of genotype or haplotype combinations.
We also calculated the additive (a), dominant (d), and substitution (α) effects as follows: \( a=\frac{AA- BB}{2} \); \( \mathrm{d}= AB-\frac{AA+ BB}{2} \) ; α = a + d(q − p), where, AA, BB, and AB are the least square means of the milk production traits in the corresponding genotypes, p is the frequency of allele A, and q is the frequency of allele B.
Biological function prediction
We used Jaspar software (http://jaspar.genereg.net/) to predict whether SNPs in the 5′ flanking region of NGFR and ARNTL genes changed the TFBS (relative score ≥ 0.80). We used SOPMA (https://prabi.ibcp.fr/htm/site/web/services/secondaryStructurePrediction#SOPMA) software to predict the effect of missense mutation on the secondary structure of protein, including α-helix, β-turn and random coil.
Availability of data and materials
The information of genetic polymorphisms loci can be inquired on European Variation Archive (EVA; https://www.ebi.ac.uk/eva/) using the RS IDs (Table 1). The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the article and its additional files.
Abbreviations
- ARNTL:
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator like
- BS:
-
Binding site
- DHI:
-
Dairy Herd Improvement
- GS:
-
Genomic selection
- GBTS:
-
Genotyping by Target Sequencing
- 5-HT:
-
5-hydroxytryptamine
- NGFR:
-
Nerve growth factor receptor
- PPP2R2B:
-
Protein phosphatase 2 regulatory subunit Bβ
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- SLC22A7:
-
Solute carrier family 22 member 7
- SNPs:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
- TFBS:
-
Transcription factor binding site
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
References
Tunick MH, Van Hekken DL. Dairy products and health: recent insights. J Agric Food Chem. 2015;63(43):9381–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5042454.
Spelman RJ, Coppieters W, Karim L, van Arendonk JA, Bovenhuis H. Quantitative trait loci analysis for five milk production traits on chromosome six in the Dutch Holstein-Friesian population. Genetics. 1996;144(4):1799–808. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/144.4.1799.
Zhang Z, Ober U, Erbe M, Zhang H, Gao N, He J, et al. Improving the accuracy of whole genome prediction for complex traits using the results of genome wide association studies. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e93017. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093017.
Zhang Z, Erbe M, He J, Ober U, Gao N, Zhang H, et al. Accuracy of whole-genome prediction using a genetic architecture-enhanced variance-covariance matrix. G3 (Bethesda). 2015;5(4):615–27.
de Las H-SS, Lopez BI, Moghaddar N, Park W, Park JE, Chung KY, et al. Use of gene expression and whole-genome sequence information to improve the accuracy of genomic prediction for carcass traits in Hanwoo cattle. Genet Sel Evol. 2020;52(1):54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12711-020-00574-2.
Lopdell TJ, Tiplady K, Couldrey C, Johnson TJJ, Keehan M, Davis SR, et al. Multiple QTL underlie milk phenotypes at the CSF2RB locus. Genet Sel Evol. 2019;51(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12711-019-0446-x.
Li Q, Liang R, Li Y, Gao Y, Li Q, Sun D, et al. Identification of candidate genes for milk production traits by RNA sequencing on bovine liver at different lactation stages. BMC Genet. 2020;21(1):72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-020-00882-y.
Vijayakumar P, Bakyaraj S, Singaravadivelan A, Vasanthakumar T, Suresh R. Meta-analysis of mammary RNA seq datasets reveals the molecular understanding of bovine lactation biology. Genome. 2019;62(7):489–501. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2018-0144.
Liu L, Zhou J, Chen CJ, Zhang J, Wen W, Tian J, et al. GWAS-Based Identification of New Loci for Milk Yield, Fat, and Protein in Holstein Cattle. Animals (Basel). 2020;10(11):10(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112048.
Gebreyesus G, Buitenhuis AJ, Poulsen NA, Visker M, Zhang Q, van Valenberg HJF, et al. Multi-population GWAS and enrichment analyses reveal novel genomic regions and promising candidate genes underlying bovine milk fatty acid composition. BMC Genomics. 2019;20(1):178. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5573-9.
Han B, Yuan Y, Liang R, Li Y, Liu L, Sun D. Genetic Effects of LPIN1 Polymorphisms on Milk Production Traits in Dairy Cattle. Genes (Basel). 2019;10(4):10(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10040265.
Clancey E, Kiser JN, Moraes JGN, Dalton JC, Spencer TE, Neibergs HL. Genome-wide association analysis and gene set enrichment analysis with SNP data identify genes associated with 305-day milk yield in Holstein dairy cows. Anim Genet. 2019;50(3):254–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/age.12792.
Dux M, Muranowicz M, Siadkowska E, Robakowska-Hyzorek D, Flisikowski K, Bagnicka E, et al. Association of SNP and STR polymorphisms of insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (IGF2R) gene with milk traits in Holstein-Friesian cows. J Dairy Res. 2018;85(2):138–41. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022029918000110.
Shi L, Han B, Liu L, Lv X, Ma Z, Li C, et al. Determination of Genetic Effects of LIPK and LIPJ Genes on Milk Fatty Acids in Dairy Cattle. Genes (Basel). 2019;10(2):10(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020086.
Shi L, Lv X, Liu L, Yang Y, Ma Z, Han B, et al. A post-GWAS confirming effects of PRKG1 gene on milk fatty acids in a Chinese Holstein dairy population. BMC Genet. 2019;20(1):53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-019-0755-7.
Liang R, Han B, Li Q, Yuan Y, Li J, Sun D. Using RNA sequencing to identify putative competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) potentially regulating fat metabolism in bovine liver. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):6396. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06634-w.
Sun W, Wu RR, van Poelje PD, Erion MD. Isolation of a family of organic anion transporters from human liver and kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;283(2):417–22. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2001.4774.
Cropp CD, Komori T, Shima JE, Urban TJ, Yee SW, More SS, et al. Organic anion transporter 2 (SLC22A7) is a facilitative transporter of cGMP. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;73(4):1151–8. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.107.043117.
Mathialagan S, Bi YA, Costales C, Kalgutkar AS, Rodrigues AD, Varma MVS. Nicotinic acid transport into human liver involves organic anion transporter 2 (SLC22A7). Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;174:113829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113829.
Morita N, Kusuhara H, Nozaki Y, Endou H, Sugiyama Y. Functional involvement of rat organic anion transporter 2 (Slc22a7) in the hepatic uptake of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug ketoprofen. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005;33(8):1151–7. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.104.001552.
Lemosquet S, Delamaire E, Lapierre H, Blum JW, Peyraud JL. Effects of glucose, propionic acid, and nonessential amino acids on glucose metabolism and milk yield in Holstein dairy cows. J Dairy Sci. 2009;92(7):3244–57. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2008-1610.
Islam R, Anzai N, Ahmed N, Ellapan B, Jin CJ, Srivastava S, et al. Mouse organic anion transporter 2 (mOat2) mediates the transport of short chain fatty acid propionate. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008;106(3):525–8. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.SC0070291.
Esteve D, Boulet N, Belles C, Zakaroff-Girard A, Decaunes P, Briot A, et al. Lobular architecture of human adipose tissue defines the niche and fate of progenitor cells. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2549. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09992-3.
Lee YS, Shin D. Genome-wide association studies associated with Backfat thickness in landrace and Yorkshire pigs. Genomics Inform. 2018;16(3):59–64. https://doi.org/10.5808/GI.2018.16.3.59.
Hicks MR, Hiserodt J, Paras K, Fujiwara W, Eskin A, Jan M, et al. ERBB3 and NGFR mark a distinct skeletal muscle progenitor cell in human development and hPSCs. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(1):46–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-017-0010-2.
Huang N, Chelliah Y, Shan Y, Taylor CA, Yoo SH, Partch C, et al. Crystal structure of the heterodimeric CLOCK:BMAL1 transcriptional activator complex. Science. 2012;337(6091):189–94. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222804.
Ray S, Valekunja UK, Stangherlin A, Howell SA, Snijders AP, Damodaran G, et al. Circadian rhythms in the absence of the clock gene Bmal1. Science. 2020;367(6479):800–6. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw7365.
Paschos GK, Ibrahim S, Song WL, Kunieda T, Grant G, Reyes TM, et al. Obesity in mice with adipocyte-specific deletion of clock component Arntl. Nat Med. 2012;18(12):1768–77. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2979.
Mayer RE, Hendrix P, Cron P, Matthies R, Stone SR, Goris J, et al. Structure of the 55-kDa regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A: evidence for a neuronal-specific isoform. Biochemistry. 1991;30(15):3589–97. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00229a001.
Holmes SE, Hearn EO, Ross CA, Margolis RL. SCA12: an unusual mutation leads to an unusual spinocerebellar ataxia. Brain Res Bull. 2001;56(3–4):397–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-9230(01)00596-2.
Li Z, Li Y, Wang X, Yang Q. PPP2R2B downregulation is associated with immune evasion and predicts poor clinical outcomes in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01707-9.
Madera-Salcedo IK, Sanchez-Hernandez BE, Svyryd Y, Esquivel-Velazquez M, Rodriguez-Rodriguez N, Trejo-Zambrano MI, et al. PPP2R2B hypermethylation causes acquired apoptosis deficiency in systemic autoimmune diseases. JCI Insight. 2019;5(16):e126457. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.126457.
Calkhoven CF, Ab G. Multiple steps in the regulation of transcription-factor level and activity. Biochem J. 1996;317(Pt 2):329–42. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3170329.
McDaniell R, Lee BK, Song L, Liu Z, Boyle AP, Erdos MR, et al. Heritable individual-specific and allele-specific chromatin signatures in humans. Science. 2010;328(5975):235–9. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1184655.
Kasowski M, Grubert F, Heffelfinger C, Hariharan M, Asabere A, Waszak SM, et al. Variation in transcription factor binding among humans. Science. 2010;328(5975):232–5. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183621.
Inoue H, Ogawa W, Ozaki M, Haga S, Matsumoto M, Furukawa K, et al. Role of STAT-3 in regulation of hepatic gluconeogenic genes and carbohydrate metabolism in vivo. Nat Med. 2004;10(2):168–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm980.
Krueger KC, Deneris ES. Serotonergic transcription of human FEV reveals direct GATA factor interactions and fate of Pet-1-deficient serotonin neuron precursors. J Neurosci. 2008;28(48):12748–58. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4349-08.2008.
Hollenhorst PC, McIntosh LP, Graves BJ. Genomic and biochemical insights into the specificity of ETS transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80(1):437–71. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.79.081507.103945.
Castano J, Aranda S, Bueno C, Calero-Nieto FJ, Mejia-Ramirez E, Mosquera JL, et al. GATA2 promotes hematopoietic development and represses cardiac differentiation of human mesoderm. Stem Cell Reports. 2019;13(3):515–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.07.009.
Wijgaerts A, Wittevrongel C, Thys C, Devos T, Peerlinck K, Tijssen MR, et al. The transcription factor GATA1 regulates NBEAL2 expression through a long-distance enhancer. Haematologica. 2017;102(4):695–706. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2016.152777.
Xu S, Xia W, Zohar Y, Gui JF. Zebrafish dmrta2 regulates the expression of cdkn2c in spermatogenesis in the adult testis. Biol Reprod. 2013;88(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.112.105130.
Zhang Y, Yuan Y, Liang P, Guo X, Ying Y, Shu XS, et al. OSR1 is a novel epigenetic silenced tumor suppressor regulating invasion and proliferation in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(18):30008–18. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15611.
Schebesta A, McManus S, Salvagiotto G, Delogu A, Busslinger GA, Busslinger M. Transcription factor Pax5 activates the chromatin of key genes involved in B cell signaling, adhesion, migration, and immune function. Immunity. 2007;27(1):49–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2007.05.019.
Pastor WA, Liu WL, Chen D, Ho J, Kim R, Hunt TJ, et al. TFAP2C regulates transcription in human naive pluripotency by opening enhancers. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(5):553−+.
Do H, Kim D, Kang J, Son B, Seo D, Youn H, et al. TFAP2C increases cell proliferation by downregulating GADD45B and PMAIP1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biol Res. 2019;52(1):35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-019-0244-5.
Nakada C, Satoh S, Tabata Y. Arai K-i, Watanabe S: transcriptional repressor foxl1 regulates central nervous system development by suppressing shh expression in Zebra fish. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26(19):7246–57. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00429-06.
Liu H, Zhang M, Xu S, Zhang J, Zou J, Yang C, et al. HOXC8 promotes proliferation and migration through transcriptional up-regulation of TGFβ1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogenesis. 2018;7(2):7(2). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-017-0016-4.
Eguchi T, Prince TL, Tran MT, Sogawa C, Lang BJ, Calderwood SK. MZF1 and SCAND1 Reciprocally Regulate CDC37 Gene Expression in Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2019;11(6):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060792.
White PH, Chapman DL. Dll1 is a downstream target of Tbx6 in the paraxial mesoderm. Genesis. 2005;42(3):193–202.
Jia MW, Luo LF, Liu CQ. Statistical correlation between protein secondary structure and messenger RNA stem-loop structure. Biopolymers. 2004;73(1):16–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.10496.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate Beijing Dairy Cattle Center for providing the phenotypic data.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32072716). The funding body played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BH and DS conceived and designed the experiments, ZM, LL, and YL provided semen and blood samples for this study, RJ prepared the DNA samples for SNP identification and genotyping with the help of YF, LX and HL, RJ and YF analyzed the data, and the manuscript was prepared by RJ and BH. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments were carried out in accordance with Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at China Agricultural University (Beijing, China; permit number: DK996).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1
. Associations of 20 SNPs with milk yield and composition traits in Chinese Holstein cattle during first and second lactations.
Additional file 2: Table S2
. Additive, dominant and allele substitution effects of 20 SNPs in SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL and PPP2R2B genes on milk yield and composition traits in Chinese Holstein cattle during two lactations.
Additional file 3: Table S3
. Haplotypes analyses for SLC22A7, NGFR and ARNTL genes.
Additional file 4: Table S4
. The phenotypic values for milk yield and composition in two lactations and pedigree information.
Additional file 5: Table S5
. Primers and procedures for PCR used in SNPs identification of SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL and PPP2R2B genes.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, R., Fu, Y., Xu, L. et al. Associations between polymorphisms of SLC22A7, NGFR, ARNTL and PPP2R2B genes and Milk production traits in Chinese Holstein. BMC Genom Data 22, 47 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-021-01002-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-021-01002-0