Abstract
Graphene oxide (GO) sheets exhibit superior adsorption capacity for removing organic dye pollutants from an aqueous environment. In this paper, the facile preparation of GO/polyethylenimine (PEI) hydrogels as efficient dye adsorbents has been reported. The GO/PEI hydrogels were achieved through both hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions between amine-rich PEI and GO sheets. For both methylene blue (MB) and rhodamine B (RhB), the as-prepared hydrogels exhibit removal rates within about 4 h in accordance with the pseudo-second-order model. The dye adsorption capacity of the hydrogel is mainly attributed to the GO sheets, whereas the PEI was incorporated to facilitate the gelation process of GO sheets. More importantly, the dye-adsorbed hydrogels can be conveniently separated from an aqueous environment, suggesting potential large-scale applications of the GO-based hydrogels for organic dye removal and wastewater treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Find the latest articles, discoveries, and news in related topics.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Background
Nowadays, harmful chemical compounds have become the main cause of water pollution. Water pollution exerts negative effects not only on species living in the water but also on the broader biological community. For instance, organic dyes are often discharged with wastewater into the local environment without adequate treatment. Rapid and convenient removal of organic dyes from wastewater has been a challenging issue faced by scientists [1–6]. For example, Kim’s groups achieved excellent systematic works in the relative fields of water remediation by various nanocomposites [1, 2]. In particular, large-scale application requires the potential dye adsorbents to exhibit a high dye removal rate within a relatively short period of time and to be environmentally friendly. For the latter, the adsorbents must be able to be properly separated from an aqueous environment after adsorbing waste dyes. In the past years, graphene oxide (GO) sheets have attracted broad attention as potential dye adsorbents because of their unique conjugated, two-dimensional (2D) structure, which exhibits superior adsorption capacity for various dye molecules through π-π stacking interactions [7–12]. In addition, the negative charges in the GO sheets due to various oxygen-rich functional groups (i.e., carboxy, carbonyl, hydroxyl groups) allow additional strong electrostatic interactions with cationic dye molecules [13–18]. However, GO sheets exhibit a high dispersibility in water, which prevents the efficient separation of dye-adsorbed GO sheets from an aqueous environment. Therefore, various GO-based adsorbent materials have been developed to facilitate the separation of dye-adsorbed GO sheets from aqueous solutions [19–21]. For example, Akhavan et al. successfully reported the preparation and magnetic separation application of superparamagnetic ZnFe2O4/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) composites by hydrothermal reaction method [22]. In addition, their group has also investigated some bacteria bioactivity and interaction with the environment by aggregated graphene nanosheets as an encapsulating material and effective photothermal agent [23]. In addition, depositing magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on GO sheets can allow facile separation of dye-adsorbed composites by applying an external magnetic field [19]. GO-based porous materials have also been used to adsorb organic waste dyes [21]. Alternatively, GO-based hydrogels provide an effective solution for the easy separation of dye-adsorbed materials from water [24].
In this work, the facile preparation of GO/polyethylenimine (PEI) hydrogels as efficient dye adsorbents for wastewater treatment was reported. The GO/PEI hydrogels were obtained through both hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions between amine-rich PEI and GO sheets. PEI was incorporated to facilitate the gelation process of GO sheets, and the dye adsorption capacity of the hydrogel is mainly attributed to the GO sheets. For both methylene blue (MB) and rhodamine B (RhB), the as-prepared hydrogels exhibit removal rates within 4 h in accordance with the pseudo-second-order model. More importantly, the dye-adsorbed hydrogels can be conveniently separated from an aqueous environment, suggesting potential large-scale applications of the GO-based hydrogels for organic dye removal and wastewater treatment.
Methods
The starting materials, PEI (Mw = 600 g·mol−1, Aladdin Reagent, Shanghai, China), RhB (Tianjin Kaitong Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd, Tianjin, China), and MB (Tianjin Kaitong Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China), were used as received. GO sheets were prepared according to the method described by Hummer [25] with some modification [26]. Deionized (DI) water was used in all cases. PEI was first dissolved in DI water to make aqueous stock solutions with different concentrations (1.2, 1.8, 2.4, and 3.0 mg·mL−1). GO powder (24 mg) was dispersed in 10 mL of DI water to give a stock solution (2.4 mg·mL−1). GO/PEI hydrogels were prepared by combining GO and PEI stock solutions with sonication for a few seconds or without sonication for a few minutes to form gels. The detailed formulations are listed in Fig. 1e. The prepared samples of the solution and hydrogels were designated as #1, #2, #3, and #4.
The presently used different xerogels were obtained at −50 °C via a lyophilizer (FD-1C-50, Beijing Boyikang Experimental Instrument Co., Ltd., China) to completely remove water over 2–3 days. The morphology of GO and lyophilized GO/PEI hydrogels was characterized by using both field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, S-4800II, Hitachi, Japan) with an accelerating voltage of 5–15 kV and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, HT7700, Hitachi High-Technologies Corporation) with commercial 300-mesh copper grids. Before SEM investigations, the prepared samples were coated with copper foil fixed by a conductive adhesive tape and covered with gold nanoparticles to make them more conductive. X-ray diffraction study was carried out by using an X-ray diffractometer (SmartLab, Rigaku, Japan) equipped with a conventional Cu Kα X-ray radiation (λ = 1.54 Å) source and a Bragg diffraction setup. Transmission Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra were obtained using a Nicolet iS10 FT-IR spectrophotometer from Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (Waltham, MA, USA) with an average of 16 scans and at a resolution of 4 cm−1 by the conventional KBr disk tablet method. Thermogravimetry-differential scanning calorimetry (TG-DSC) analyses of the samples were conducted in air condition by using a Netzsch STA 409 PC Luxx simultaneous thermal analyzer (Netzsch Instruments Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Germany). Raman spectroscopy was performed using a Horiba Jobin Yvon Xplora PLUS confocal Raman microscope equipped with a motorized sample stage. The wavelength of the excitation laser was 532 nm, and the power of the laser was kept below 1 mW without noticeable sample heating. The intensity of a Raman peak was extracted from the maximum value after baseline subtraction over the corresponding spectral range. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed on Thermo Scientific ESCALAB 250Xi using 200-W monochromated Al Kα radiation. The 500-μm X-ray spot was used for XPS analysis. The base pressure in the analysis chamber was about 3 × 10−10 mbar. Typically, the hydrocarbon C(1s) line at 284.8 eV from adventitious carbon is used for energy referencing. Both survey scan and individual high-resolution scan peaks were recorded.
The adsorption experiments were designed and modified according to the previous reports [27, 28]. In adsorption experiments, about 1 mL of GO/PEI hydrogel (without lyophilizing) was added to 100 mL of either MB (10 mg·L−1) or RhB (4 mg·L−1) solutions. The dye solutions containing gel adsorbents were stirred slowly and continuously at room temperature in a dark condition. The gel samples were then separated by centrifugation at different time intervals, and the supernatant liquid was collected for subsequent analysis using an UV-vis spectrometer (752, Sunny Hengping, Shanghai, China). The absorbance at 662 nm (MB) and 554 nm (RhB) was used to determine the concentration of residual dyes in the supernatant liquid.
Results and discussion
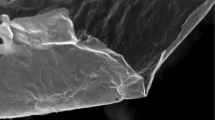
Figure 1 depicts the complete preparation process of GO/PEI hydrogels by combining the GO suspension and the PEI aqueous solution using the formulation listed in Fig. 1e. The prepared samples were designated as #1, #2, #3, and #4. GO sheets are rich in hydrophilic functional groups (e.g., carboxyl, hydroxyl, and epoxides) (Fig. 1a). Functional groups like –OH and –COOH can form hydrogen bonds with amines or amine-containing molecules under appropriate conditions [16, 29, 30]. Therefore, amine-rich PEI (Fig. 1b) was chosen to facilitate the gelation of GO sheets in an aqueous solution. In addition, PEI also exhibits good adsorption and adhesion properties [31]. It was found that the dye adsorption capacity of the above porous materials increases with the amount of PEI content, presumably due to the strong electrostatic attractions between the amine-rich PEI chains and the dye molecules. Therefore, the adsorption capacity of the abovementioned porous materials is essentially attributed to PEI instead to GO. On the other hand, it is well known that in most composite materials, as a kind of functional molecule with multi-amine groups, PEI was used widely as a strong chelating agent and organic intermediate. As for the present as-formed GO-based composite gels, after combination with GO, the formed composites showed very stable self-assembly behaviors by strong hydrogen bonding and electronic interactions, which showed a rare possibility to release PEI to cause secondary waste as dye adsorbents for wastewater treatment. In this study, PEI was only used with a concentration slightly above the critical gelation concentration (i.e., the minimum concentration of the gelator needed for gel formation). The formulation of the GO/PEI gels is shown in Fig. 1e, and photos of the GO/PEI gels are shown in Fig. 1d. The samples possessing good gelation properties are designated as #2, #3, and #4 and were used in the dye adsorption experiments as discussed later in this paper. In addition, the morphology of GO and lyophilized GO/PEI hydrogels was characterized using both FE-SEM and TEM. Figure 2a, a’ shows a typical 2D flake-like morphology of GO sheets. Figure 2b, b’ reveals the porous microstructures of lyophilized GO/PEI gels, suggesting that the GO sheets were cross-linked in the porous PEI networks.
In addition, the strong affiliation between PEI and GO was also evidenced by X-ray diffraction studies. Figure 3a shows the diffraction patterns for the GO and the lyophilized GO/PEI hydrogels. The 2θ values were observed at 11.3° (GO), 8.9° (gel #2), 8.6° (gel #3), and 7.8° (gel #4), corresponding to the d-spacing values of 0.77, 0.98, 1.02, and 1.13 nm, respectively. The X-ray patterns of GO display the presence of a strong peak at 11.3° corresponding to the (001) reflection peak with a layer distance of 0.77 nm [32]. Thus, the regular stacking of GO sheets was significantly altered by PEI chains attached on the surface of the GO sheets, even though the structural features of GO remained largely unchanged. Moreover, Raman spectroscopy provides a useful tool to characterize the carbon-based materials [33], as shown in Fig. 3b. Three characteristic bands of graphene sheets in Raman spectra appeared, including the G band (1601 cm−1) originated from the first-order scattering of the E2g phonons of the sp2-hybridized carbon atoms, the D band (1351 cm−1) caused by a breathing mode of κ-point phonons of A1g symmetry of the defects involved in the sp3-hybridized carbon bonds such as hydroxyl and/or epoxide bonds [34], and the 2D band (2692 cm−1) which is much sensitive to stacking of graphene sheets [35]. It is established that the G and 2D bands of single-layer graphene sheets are usually located at 1585 and 2679 cm−1, while for multi-layer graphene sheets (including 2–6 layers), the positions of the G and 2D bands shift into lower and higher wavenumbers, respectively [36, 37]. Furthermore, the 2D/G ratios of single-, double-, triple-, and multi-layer (>4) graphene sheets are typically >1.6, 0.8, 0.30, and 0.07, respectively [38]. For example, Akhavan achieved excellent research work and reported successfully the 2D/G ratios of the single and bilayer GO sheets in the range of 1.53–1.68 and 0.82–0.89, respectively [39]. In our present work, the 2D/G ratios of the GO sheets and three different composite gels showed the values in the range of 0.12–0.14 (seen in Fig. 3d), suggesting the multi-layer nature of the presently prepared graphene sheets. In addition, due to the origination of the G and D bands, the G/D peak intensity ratio is known as a measure of the sp2 domain size of graphene sheets containing sp3 and sp2 bonds. In our present work, it was found that by forming the composite gels, the D/G ratios (shown in Fig. 3c) shifted from 0.97 to the values of 1.06, 1.19, and 1.20 with increment of PEI concentration, respectively. This change can be attributed to the successful cross-linking of GO in the hydrogel networks and the absence of the C–N bonds formed on the surface of the GO sheets.
The FT-IR spectra of GO and GO/PEI hydrogels are demonstrated in Fig. 4a. In the spectrum of GO, the peak at 3432 cm−1 could be assigned to the –OH vibration stretching. It also showed bands due to carboxyl C=O (1724 cm−1), epoxy C–O (1226 cm−1), and alkoxy C–O (1050 cm−1) groups situated at the edges of the GO nanosheets [16, 29, 30]. In the spectra of GO/PEI gels, an obvious peak could be observed at 1645 cm−1, corresponding to the –NH stretching of polyethylenimine. In addition, the appearance of the bands at 2920 and 2846 cm−1 was also observed, which could be assigned to the methyl stretching in PEI molecules. The obtained FT-IR results clearly indicated that GO-based composite hydrogels have been successfully prepared. In addition, Fig. 4b illustrates the thermograms of GO and GO-based composite hydrogels. The quality of GO declines uniformly from 30 to 150 °C, and the loss of the quality is about 15 %, which is mainly due to the moisture evaporation of the sample. With increment of temperature, the quality of GO declines sharply, especially at 207 °C. This can be due to the pyrolysis of the unstable oxygen-containing functional groups in GO. When the temperature is higher than 450 °C, GO tends to produce further losses. Moreover, according to TG results, GO/PEI hydrogels showed a higher thermal stability compared with the GO sheet, which could be attributed to the higher cross-linking within the network structures in gels. Because of the effect of PEI, it can be found that addition of a low content of PEI can greatly increase the thermal stability of hydrogels, suggesting that a strong interaction exists between GO sheets and PEI even in such a water-abundant hydrogel. It was reported that some GO composites showed different weight retention values at high temperature, probably due to the structural changes from the existence of the carbon net-compound assembly structure in the composites [40–42]. In the present case, the as-formed composite hydrogels enhance the thermal stability of materials to a certain extent.
In order to further investigate the obtained GO/PEI hydrogel, the survey XPS spectra of the lyophilized GO/PEI hydrogel (#2) in Fig. 5a showed the characteristic peaks, such as C(1s), N(1s), and O(1s). In addition, we obtained the relative elemental composition and calculated the O/C ratios of all lyophilized samples (GO sheet, 37.26 %; GO/PEI gel, 36.08 %), respectively, which suggested the decrement of the oxygen element from GO to the nanocomposite. Moreover, the deconvolution of C(1s), N(1s), and O(1s) of XPS peaks for the GO/PEI hydrogel (#2) nanocomposite was demonstrated. Figure 5b shows XPS peak deconvolution of C(1s) core levels of the gel (#2) nanocomposite. The peak centered at 284.9 eV was attributed to the C–C, C=C, and C–H bonds. The other deconvoluted peak located at the binding energies of 286.7 eV was assigned to the C–OH oxygen-containing bonds [43]. The high-resolution N(1s) spectrum in Fig. 5c reveals the presence of amine (399.4 eV), C–N bond (400.6 eV), and N+ species (401.4 eV), suggesting the presence of PEI polymers in the composite, either in their original amine forms or in grafted forms through the covalent bonding and weak interaction force to the GO sheets [44]. In addition, the O(1s) photoelectron peak of the gel (#2) nanocomposite is shown in Fig. 5d. This peak can be deconvoluted into three Gaussian components with identical FWHM after a Shirley background subtraction. The second component at 532.0 eV can be corresponded to the oxygen of the surface OH− bound in nanocomposite [45]. The third deconvoluted O(1s) peak at 532.9 eV was attributed to the oxygen of water molecules existing in the nanostructure or adsorbed on the GO surface. This means that the surface of the gel (#2) nanocomposite was still porous, which can be an advantage for the surface adsorption process.
The dye adsorption capacity was evaluated by placing the as-prepared GO/PEI hydrogels in MB and RhB aqueous solutions. It should be noted that the adsorption process of freeze-dried samples seemed typical and easy to investigate. In the present work, the in situ adsorption behaviors of hydrogels were chosen, which could demonstrate the real adsorption process of GO-based gels for different dyes in wastewater. In addition, graphene oxide has the probability to act as a visible light photocatalyst for degradation of dyes in the adsorption process. So the present adsorption experiments were measured and repeated in a dark condition. The absorbance at 662 nm (Fig. 6a for MB) and 554 nm (Fig. 6b for RhB) was used to determine the concentration of residual dyes for samples collected at different time intervals. The dye removal rates were calculated according to the equation of K = (A 0 − A T)/A 0 × 100 %, where K is the dye removal rate, A 0 is the absorbance of the dye stock solution, and A T is the absorbance of the supernatant liquid collected at different time intervals. Figure 6c shows the calculated dye removal rate versus time plots for both MB and RhB. The dye removal rates can reach nearly 100 % for both MB and RhB within approximately 4 h, suggesting the as-prepared GO/PEI hydrogels as efficient dye adsorbents. In addition, the thermodynamic behaviors of other reduced graphene oxide-based hydrogels for dye adsorption from aqueous solutions were reported and investigated in detail [46]. Now our primary adsorption kinetic experiments of the as-prepared GO/PEI hydrogel (#2) on MB and RhB were performed, and the results are shown in Fig. 7. The hydrogel exhibits a continuous adsorption process, with equilibrium times of approximately 200 min for MB and RhB, respectively. A 200-min equilibrium time is acceptable for efficient photocatalytic applications. Such kinetic behavior can also be associated with the unique nanocomposite structure, i.e., the large three-dimensional network-like nanostructure cross-linked with polyethylenimine by electrostatic attractions and hydrogen bonding, and highly dispersed GO nanosheets as the adsorption sites. In addition, classical kinetic models were employed to describe the above degradation data as follows:
The pseudo-first-order model:
The pseudo-second-order model:
where q e and q t represent the amount of dye adsorbed (mg/g) at equilibrium and time t, respectively, and the k 1 or k 2 values are the kinetic rate constants. The kinetic data (Table 1) can be accurately described by the pseudo-second-order model with a high correlation coefficient (R 2 > 0.994). In addition, it should be noted that only a slightly high concentration of PEI above the gelation condition was chosen and used. Thus, present types of composite materials could not be reused many times with poor recycling ability. The design of stabilized GO-based hydrogel materials and the relative applications are still a challenging problem in the near future.
Considering the obtained experimental results described above, some important points should be proposed and discussed. Firstly, in our recent works about some organogel systems based on organic compounds [47–51], functionalized imide derivatives, with the different substituent groups (such as cholesteryl, azobenzene, or luminol), molecular skeletons, or spacers, can have a profound effect on the gelation abilities and the as-formed nanostructures. In another organogel system based on cationic amphiphile-GO nanocomposites, the headgroups in amphiphiles play a crucial role in the gelation behaviors in various organic solvents [52]. For the present GO/PEI hydrogels, the self-assembly and regular stacking of GO sheets were significantly altered by formulation of PEI attached on the surface of GO sheets. In addition, it should be noted that the present GO/PEI hydrogels are more environmentally friendly than organogels from different organic solvents. Now the drug release behaviors and preparation of nanoparticle-containing hybrid hydrogels generated by the present supramolecular gels are under investigation to display the relationship between the as-formed nanostructures and their applications.
Conclusions
In summary, the facile preparation and dye adsorption capacity of GO/PEI hydrogels have been investigated. PEI was chosen for its abundant amine groups that can form hydrogen bonds with GO. Both the SEM and XRD studies clearly show that the GO sheets were successfully cross-linked in the PEI network. Meanwhile, the Raman spectra suggest that the structural features of GO sheets remain largely unchanged pre- and post-gelation. The as-prepared GO/PEI hydrogels exhibited good removal rates for both MB and RhB in accordance with the pseudo-second-order model. The current research work provides further insight into the applications of GO-based polymer-containing hydrogels as dye adsorbents for wastewater treatment.
References
Georgakilas V, Otyepka M, Bourlinos AB, Chandra V, Kim N, Kemp KC, et al. Functionalization of graphene: covalent and non-covalent approaches, derivatives and applications. Chem Rev. 2012;112:6156–214.
Kemp KC, Seema H, Saleh M, Le NH, Mahesh K, Chandra V, et al. Environmental applications using graphene composites: water remediation and gas adsorption. Nanoscale. 2013;5:3149–71.
Dadfarnia S, Haji Shabani AM, Moradi SE, Emami S. Methyl red removal from water by iron based metal-organic frameworks loaded onto iron oxide nanoparticle adsorbent. Appl Surf Sci. 2015;330:85–93.
Zhang YR, Shen SL, Wang SQ, Huang J, Su P, Wang QR, et al. A dual function magnetic nanomaterial modified with lysine for removal of organic dyes from water solution. Chem Eng J. 2014;239:250–6.
Wang Y, Li Z, He Y, Li F, Liu XQ, Yang JB. Low-temperature solvothermal synthesis of graphene-TiO2 nanocomposite and its photocatalytic activity for dye degradation. Mater Lett. 2014;134:115–8.
Namasivayam C, Sangeetha D. Recycling of agricultural solid waste, coir pith: removal of anions, heavy metals, organics and dyes from water by adsorption onto ZnCl2 activated coir pith carbon. J Hazard Mater. 2006;135:449–52.
Geim AK, Novoselov KS. The rise of graphene. Nature Mater. 2007;6:183–91.
Li D, Kaner RB. Graphene-based materials. Science. 2008;320:1170–1.
Geim AK. Graphene: status and prospects. Science. 2009;324:1530–4.
Huang X, Qi X, Boey F, Zhang H. Graphene-based composites. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41:666–86.
Xu YX, Zhao L, Bai H, Hong WJ, Li C, Shi GQ. Chemically converted graphene induced molecular flattening of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(1-methyl-4-pyridinio) porphyrin and its application for optical detection of cadmium(II) ions. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:13490–7.
Peigney A, Laurent C, Flahaut E, Bacsa RR, Rousset A. Specific surface area of carbon nanotubes and bundles of carbon nanotubes. Carbon. 2001;39:507–14.
Sharma P, Das M. Removal of a cationic dye from aqueous solution using graphene oxide nanosheets: investigation of adsorption parameters. J Chem Eng Data. 2013;58:151–8.
Huang X, Yin ZY, Wu SX, Qi XY, He QY, Zhang QC, et al. Graphene-based materials: synthesis, characterization, properties, and applications. Small. 2011;7:1876–902.
Huang H, Lu S, Zhang X, Shao Z. Glucono-δ-lactone controlled assembly of graphene oxide hydrogels with selectively reversible gel-sol transition. Soft Matter. 2012;8:4609–15.
Sui Z, Zhang X, Lei Y, Luo Y. Easy and green synthesis of reduced graphite oxide-based hydrogels. Carbon. 2011;49:4314–21.
Rao CNR, Sood AK, Subrahmanyam KS, Govindaraj A. Graphene: the new two-dimensional nanomaterial. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;48:7752–77.
Wu S, He Q, Tan C, Wang Y, Zhang H. Graphene-based electrochemical sensors. Small. 2013;9:1160–72.
Geng Z, Lin Y, Yu X, Shen Q, Ma L, Li Z, et al. Highly efficient dye adsorption and removal: a functional hybrid of reduced graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanoparticles as an easily regenerative adsorbent. J Mater Chem. 2012;22:3527–35.
Wang MY, Zhu W, Zhang DE, Li SA, Ma WX, Tong ZW, et al. CeO2 hollow nanospheres decorated reduced graphene oxide composite for efficient photocatalytic dye-degradation. Mater Lett. 2014;137:229–32.
Liu F, Chung S, Oh G, Seo TS. Three-dimensional graphene oxide nanostructure for fast and efficient water-soluble dye removal. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4:922–7.
Meidanchi A, Akhavan O. Superparamagnetic zinc ferrite spinel-graphene nanostructures for fast wastewater purification. Carbon. 2014;69:230–8.
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E, Esfandiar A. Wrapping bacteria by graphene nanosheets for isolation from environment, reactivation by sonication, and inactivation by near-infrared irradiation. J Phys Chem B. 2011;115:6279–88.
Huang YW, Zeng M, Ren J, Wang J, Fan L, Xu Q. Preparation and swelling properties of graphene oxide/poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) super-absorbent hydrogel nanocomposites. Colloids Surf A. 2012;401:97–106.
Hummer WS, Offman RE. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc. 1958;80:1339.
Li D, Muller MB, Gilje S, Kaner RB, Wallace GG. Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nature Nanotechnol. 2008;3:101–5.
Chen B, Liu M, Zhang L, Huang J, Yao J, Zhang Z. Polyethylenimine-functionalized graphene oxide as an efficient gene delivery vector. J Mater Chem. 2011;21:7736–41.
Chandra V, Kim KS. Highly selective adsorption of Hg2+ by a polypyrrole-reduced graphene oxide composite. Chem Commun. 2011;47:3942–4.
Hou CY, Zhang QH, Li YG, Wang HZ. Graphene-polymer hydrogels with stimulus-sensitive volume changes. Carbon. 2012;50:1959–65.
Adhikari B, Biswas A, Banerjee A. Graphene oxide-based hydrogels to make metal nanoparticle-containing reduced graphene oxide-based functional hybrid hydrogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4:5472–82.
Sui ZY, Cui Y, Zhu JH, Han BH. Preparation of three-dimensional graphene oxide-polyethylenimine porous materials as dye and gas adsorbents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:9172–9.
Bose S, Kuila T, Uddin ME, Kim NH, Lau AKT, Lee JH. In-situ synthesis and characterization of electrically conductive polypyrrole/graphene nanocomposites. Polymer. 2010;51:5921–8.
Du X, Guo P, Song HH, Chen XH. Graphene nanosheets as electrode material for electric double-layer capacitors. Electrochim Acta. 2010;55:4812–9.
Perera SD, Mariano RG, Vu K, Nour N, Seitz O, Chabal Y, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of graphene-TiO2 nanotube composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. ACS Catal. 2012;2:949–56.
Balashov T, Takács AF, Wulfhekel W, Kirschner J. Magnon excitation with spin-polarized scanning tunneling microscopy. Phys Rev Lett. 2006;97:187201.
Calizo I, Balandin AA, Bao W, Miao F, Lau CN. Temperature dependence of the Raman spectra of graphene and graphene multilayers. Nano Lett. 2007;7:2645–9.
Kudin KN, Ozbas B, Schniepp HC, Prudhomme RK, Aksay IA, Car R. Raman spectra of graphite oxide and functionalized graphene sheets. Nano Lett. 2008;8:36–41.
Kim KS, Zhao Y, Jang H, Lee SY, Kim JM, Kim KS, et al. Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes. Nature. 2009;457:706–10.
Akhavan O. Bacteriorhodopsin as a superior substitute for hydrazine in chemical reduction of single-layer graphene oxide sheets. Carbon. 2015;81:158–66.
Xue P, Lu R, Chen G, Zhang Y, Nomoto H, Takafuji M, et al. Functional organogel based on a salicylideneaniline derivative with enhanced fluorescence emission and photochromism. Chem Eur J. 2007;13:8231–9.
Konwer S, Boruah R, Dolui SK. Studies on conducting polypyrrole/graphene oxide composites as supercapacitor electrode. J Electron Mater. 2011;40:2248–55.
Sharma A, Kumar S, Tripathi B, Singh M, Vijay YK. Aligned CNT/polymer nanocomposite membranes for hydrogen separation. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2009;34:3977–82.
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E. Self-accumulated Ag nanoparticles on mesoporous TiO2 thin film with high bactericidal activities. Surf Coat Tech. 2010;204:3676–83.
Moulder JF, Stickle WF, Sobol PE, Bomben KD. Hand book of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Eden Prairie, MN: Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Physical Electronics Division; 1992.
Akhavan O, Azimirad R, Moshfegh AZ. Low temperature self-agglomeration of metallic Ag nanoparticles on silica sol-gel thin films. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2008;41:195305.
Tiwari JN, Mahesh K, Le NH, Kemp KC, Timilsina R, Tiwari RN, et al. Reduced graphene oxide-based hydrogels for the efficient capture of dye pollutants from aqueous solutions. Carbon. 2013;56:173–82.
Jiao TF, Wang YJ, Zhang QR, Zhou JX, Gao FM. Regulation of substituent groups on morphologies and self-assembly of organogels based on some azobenzene imide derivatives. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013;8:160.
Jiao TF, Huang QQ, Zhang QR, Xiao DB, Zhou JX, Gao FM. Self-assembly of organogels via new luminol imide derivatives: diverse nanostructures and substituent chain effect. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013;8:278.
Jiao TF, Wang YJ, Gao FQ, Zhou JX, Gao FM. Photoresponsive organogel and organized nanostructures of cholesterol imide derivatives with azobenzene substituent groups. Prog Nat Sci. 2012;22:64–70.
Jiao TF, Gao FQ, Wang YJ, Zhou JX, Gao FM, Luo XZ. Supramolecular gel and nanostructures of bolaform and trigonal cholesteryl derivatives with different aromatic spacers. Curr Nanosci. 2012;8:111–6.
Jiao TF, Gao FQ, Zhang QR, Zhou JX, Gao FM. Spacer effect on nanostructures and self-assembly in organogels via some bolaform cholesteryl imide derivatives with different spacers. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013;8:406.
Jiao TF, Wang YJ, Zhang QR, Yan XH, Zhao XQ, Zhou JX, et al. Self-assembly and headgroup effect in nanostructured organogels via cationic amphiphile-graphene oxide composites. PLoS One. 2014;9:e101620.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 21473153 and 21207112), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (grant no. B2013203108), the Science Foundation for the Excellent Youth Scholars from Universities and Colleges of Hebei Province (grant nos. Y2011113 and YQ2013026), the Support Program for the Top Young Talents of Hebei Province, and the Open Foundation of National Key Laboratory of Biochemical Engineering (Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
TJ, WG, and QZ participated in the analysis and testing of the nanostructures. HG, XY and QP carried out the synthesis of compounds and characterization of nanostructures. TJ and QZ supervised this work, helped in the analysis and interpretation of data, and, together with WG, worked on the drafting and revisions of the manuscript. TJ, XY and QZ conceived of the study and participated in its design and characterization. QP participated in the design of the study and provided analysis instruments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
HG is an MD student. TJ, QP, and XY are professors. QZ and WG are associate professors.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, H., Jiao, T., Zhang, Q. et al. Preparation of Graphene Oxide-Based Hydrogels as Efficient Dye Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment. Nanoscale Res Lett 10, 272 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-0931-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-0931-2