Abstract
Urinary tract infection attributed to the use of an indwelling urinary catheter is one of the most common infections acquired by patients in health care facilities. As biofilm ultimately develops on all of these devices, the major determinant for development of bacteriuria is duration of catheterization. While the proportion of bacteriuric subjects who develop symptomatic infection is low, the high frequency of use of indwelling urinary catheters means there is a substantial burden attributable to these infections. Catheter-acquired urinary infection is the source for about 20% of episodes of health-care acquired bacteremia in acute care facilities, and over 50% in long term care facilities. The most important interventions to prevent bacteriuria and infection are to limit indwelling catheter use and, when catheter use is necessary, to discontinue the catheter as soon as clinically feasible. Infection control programs in health care facilities must implement and monitor strategies to limit catheter-acquired urinary infection, including surveillance of catheter use, appropriateness of catheter indications, and complications. Ultimately, prevention of these infections will require technical advances in catheter materials which prevent biofilm formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Review
Introduction
Catheter acquired urinary tract infection is one of the most common health care acquired infections[1, 2]; 70–80% of these infections are attributable to use of an indwelling urethral catheter. Recent prevalence surveys report a urinary catheter is the most common indwelling device, with 17.5% of patients in 66 European hospitals having a catheter[1] and 23.6% in 183 US hospitals[2]. In the NHSN 2011 surveillance report, 45–79% of patients in adult critical care units had an indwelling catheter, 17% of those on medical wards, 23% on surgical wards, and 9% on rehabilitation units[3]. Thus, indwelling urethral catheter use is exceedingly common in health care facilities. Prevention of infections attributable to these devices is an important goal of health-care infection prevention programs.
Indwelling urinary catheters are generally considered to be short term if they are in situ for less than 30 days and chronic or long term when in situ for 30 days or more[4]. Indwelling catheter use in acute care facilities is usually short term, while chronic catheters are most common for residents of long term care facilities. Clinical and microbiologic considerations may vary for short and long term catheters. Urinary catheter acquired infection is usually manifested as asymptomatic bacteriuria (CA-ASB). The term catheter associated urinary tract infection (CA-UTI) is used to refer to individuals with symptomatic infection[4]. In early reports, however, asymptomatic and symptomatic catheter-acquired infection were often not differentiated. This review addresses only indwelling urethral catheters, and will not discuss use of intermittent catheters for men or women, or external catheters for men.
Burden of illness
Asymptomatic bacteriuria
Duration of catheterization is the most important determinant of bacteriuria[4]. The daily risk of acquisition of bacteriuria when an indwelling catheter in situ is 3–7%. The rate of acquisition is higher for women and older persons[4]. Bacteriuria is universal once a catheter remains in place for several weeks. Patients with chronic indwelling catheters are assumed to be continuously bacteriuric. From 60–80% of hospitalized patients with an indwelling catheter receive antimicrobials, usually for indications other than urinary tract infection[5]. This intense antimicrobial exposure means antimicrobial resistant organisms are frequently isolated from the urine of catheterized individuals. Statewide surveillance of carbapenemase resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) in Michigan reported 61% of isolates were from urine cultures, and a urinary catheter was present in 48% of these patients[6]. Bacteria colonizing the drainage bags of catheterized patients have been reported to be a source for outbreaks of resistant organisms in acute care facilities[4, 7]. In the nursing home setting, the urine of residents with chronic indwelling catheters is the most common site of isolation of resistant gram negative organisms[8, 9].
Symptomatic urinary tract infection
CA-UTI is the most common adverse event associated with indwelling urinary catheter use (Table 1), although only a small proportion of acute care facility residents with CA-ASB develop symptomatic infection[10]. In the European prevalence survey, 1.3% of patients had urinary infection, representing 17.2% of all healthcare acquired infections, and the third most frequent infection[1]. The presence of any health care acquired infection was independently associated with the number of invasive devices, including indwelling urethral catheters, but the proportion of patients with urinary infections and a catheter was not reported. The recent US point prevalence survey reported urinary tract infection was the fourth most common infection, accounting for 12.9% of health care infections; 67.7% of these patients had a urinary catheter[2]. At one Veteran’s Affairs (VA) hospital, 0.3% of all urinary catheter days involved symptomatic UTI[11]. A comparative British trial evaluating different types of catheters reported rates of CA-UTI of 10.6%-12.6% of catheterized patients, although only 3.2%-5.0% of infections were microbiologically confirmed[12].
CA-UTI rates reported in ICU’s in the NHSN hospitals declined by 18.5%-67% among different adult ICU’s between 1990 – 2007[17] (Table 1). In France, a 66% reduction was reported over a 10-year surveillance period[13]. Some of this decrease is attributable to more intense prevention efforts, but modification of definitions to exclude asymptomatic bacteriuria has also contributed.
In US long term care facilities, 3–10% of residents are managed with chronic indwelling catheters[18]. European surveillance reports describe indwelling catheters being present in 12% of residents in 10 nursing homes in the Netherlands[19], 12.3% in 92 homes in Italy[20], and 10.1% in 40 homes in Germany[21]. The prevalence of chronic indwelling catheters was 7% overall among residents of 78 nursing homes in Sweden, but was 16% for men and only 3% for women[22]. Residents with chronic catheters have an increased risk of symptomatic urinary tract infection. CA-UTI rates of 0–7.3/1,000 catheter days (mean 3.2/1,000) were reported in Idaho long term care facilities[23]. The incidence of fever from a presumed urinary source is 0.7–1.1/100 catheter days, which is three times greater than observed for residents with bacteriuria but without a urinary catheter[24, 25].
Bacteremia
Less than 3% of subjects with CA-ASB develop bacteremia with the urinary isolate[10] but, given the high frequency of indwelling urinary catheter use, CA-UTI is one of the most common causes of secondary bloodstream infection in acute care facilities. During a 3 year period in Quebec, 21% of health care acquired bloodstream infections were from a urinary source, and 71% of these were device associated. The incidence was 1.4 urinary bloodstream infections/10,000 patient days. All cause 30 day mortality in patients with CA-UTI bacteremia was 15%[26].
CA-UTI is the source of over 50% of episodes of bacteremia in long term care facilities[4, 27]. The risk of bacteremia in residents with indwelling catheters in these facilities is 3–36 times that of residents without an indwelling catheter[28].
Other morbidity
Additional infectious complications, usually identified in patients with a chronic indwelling catheter, include urinary catheter obstruction, bladder urolithiasis, purulent urethritis, gland abscesses and, for males, prostatitis[24]. Non-infectious complications attributed to an indwelling urinary catheter include nonbacterial urethral inflammation, urethral strictures, mechanical trauma, and mobility impairment[29, 30]. Prospective daily catheter surveillance in a VA centre identified genitourinary trauma caused by the indwelling catheter on 1.5% of catheter days[11].
Several studies report an association of CA-UTI with increased mortality and prolonged length of stay in acute care facilities. For critical care unit patients, these associations are likely attributable to confounding by unmeasured variables with little, if any, mortality directly attributable to CA-UTI[31]. Long term care facility residents with chronic indwelling catheters have an increased mortality relative to residents without a catheter, but this observation is also attributable to confounding from variable patient characteristics, rather than directly attributable to urinary infection[32].
Pathogenesis of infection
Biofilm
Biofilm formation along the catheter surface is the most important cause of bacteriuria[33]. Biofilm is a complex organic material consisting of micro-organisms growing in colonies within an extra-cellular mucopolysaccharide substance which they produce. Urine components, including Tamm-Horsfall protein and magnesium and calcium ions, are incorporated into this material. Biofilm formation begins immediately after catheter insertion, when organisms adhere to a conditioning film of host proteins which forms along the catheter surface. Both the interior and exterior catheter surfaces are involved. Bacteria usually originate from the periurethral area or ascend the drainage tubing following colonization of the drainage bag. Only about 5% of episodes of CA-ASB follow introduction of periurethral organisms into the bladder at the time of catheter insertion.
Organisms growing in the biofilm are in an environment where they are relatively protected from antimicrobials and host defenses. A single species is usually identified with the initial episode of bacteriuria following insertion of an indwelling catheter. If the catheter remains in situ and a mature biofilm develops, polymicrobial bacteriuria becomes the norm. For individuals with long term indwelling catheters, 3–5 organisms are usually isolated[34, 35]. The microbiology of biofilm on an indwelling catheter is dynamic with continuing turnover of organisms in the biofilm while the catheter remains in situ[36]. Patients continue to acquire new organisms at a rate of about 3–7%/day.
The determinants of CA-UTI are not well described. However, catheter trauma or catheter obstruction are well recognized precipitating events. Risk factors for bloodstream infection from a urinary source in acute care patients are reported to be neutropenia, renal disease and male sex[37]. Bacteremia is not a significant complication of chronic indwelling catheter replacement[28].
Microbiology
The most common infecting organism is Escherichia coli[4]. Other Enterobacteriaceae as well as Enterococci spp, coagulase negative Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, other non-fermenters, and Candida spp are also frequently isolated[24]. Antimicrobial-resistant organisms are common. The urine of patients with indwelling catheters is the major site of isolation of resistant gram negative organisms in both acute and long term care facilities, including extended spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Enterobacteriaceae[8] and CRE[6]. E. coli is usually the most frequent species isolated from bacteremic CA-UTI patients in acute care facilities (Table 2). However, Enterococcus spp (28.4%) and Candida spp (19.7%) were reported to be most common at one US tertiary care academic centre[38].
Proteus mirabilis is an organism of unique importance for patients with chronic indwelling catheters. This species is seldom isolated following initial colonization of the catheterized urinary tract, so it is not common in patients undergoing short term catheterization[42]. The longer a catheter is in place the more likely P. mirabilis will be present. This organism is isolated from about 40% of urine samples collected from patients with chronic indwelling catheters[43]. P. mirabilis produces more copious biofilm than other bacteria, and these strains also tend to persist for longer periods of time[36].
Bacterial species which produce urease may facilitate the formation of a crystalline biofilm[44, 45]. This material is similar to struvite (infection) stones in patients with urolithiasis. Crusts of this material form along the catheter and are the major cause of obstruction of chronic indwelling catheters. About half of patients with chronic indwelling catheters experience catheter blockage at some time, while some patients experience rapid, recurrent obstruction[46, 47]. The urease of P. mirabilis hydrolyzes urea several times faster than the urease produced by other organisms[48]. This species is isolated from 80% of obstructed catheters[49]. Other urease producing species include P. aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Morganella morganii, other Proteus species, some Providencia spp and some strains of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase negative staphylococci. Urease production by many of these species, including M. morganii, K. pneumoniae, and P. aeruginosa, does not generate an alkaline urine, so these strains are seldom associated with appreciable encrustation on catheters[50].
Diagnosis of CA-UTI
Microbiologic diagnosis
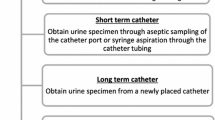
Urine specimens for culture should be collected directly from the catheter or tubing, to maintain a closed drainage system. These may be collected either through the catheter collection port or through puncture of the tubing with a needle[4]. CA-ASB is diagnosed when one or more organisms are present at quantitative counts ≥105 cful/ml from an appropriately collected urine specimen in a patient with no symptoms attributable to urinary infection[4]. Lower quantitative counts may be isolated from urine specimens prior to ≥105 cfu/ml being present, but these lower counts likely reflect the presence of organisms in biofilm forming along the catheter, rather than bladder bacteriuria[5]. A mature biofilm has usually formed once the catheter has been in situ for longer than 2 weeks. Urine collected through these catheters are contaminated by organisms present in the biofilm. There is a greater number of species and quantity of organisms isolated than these specimens compared with bladder urine collected simultaneously. Thus, it is recommended that the catheter be removed and a new catheter inserted, with specimen collection from the freshly placed catheter, before antimicrobial therapy is initiated for symptomatic infection[4]. Organisms isolated with quantitative counts <105 cfu/ml from the replacement catheter tend not to persist[51].
Clinical diagnosis
The diagnosis of symptomatic CA-UTI is often a diagnosis of exclusion[4, 24]. Fever without localizing findings is the usual presentation of CA-UTI. Localizing signs or symptoms such as catheter obstruction, acute hematuria, recent trauma, suprapubic pain, or costovertebral angle pain or tenderness are helpful to identify a urinary source of fever, but are present in only a minority of episodes of presumed symptomatic infection. If localizing genitourinary findings are not present, fever in bacteriuric patients should be attributed to urinary infection only when there are no other potential sources. When the same organism is isolated from both the urine and a simultaneous blood culture, a diagnosis of CA-UTI is presumed in the absence of an alternate source for the bacteremia.
Pyuria
Bacteriuric patients usually have pyuria, irrespective of symptoms. Patients with an indwelling catheter may also have pyuria without bacteriuria, as the catheter itself may cause bladder inflammation[10]. Other potential non-infectious causes of pyuria include renal disease, such as interstitial nephritis. Thus, the presence of pyuria in urine specimens obtained from a patient with an indwelling urinary catheter does not identify symptomatic infection in a bacteriuric subject, nor is it an indication for antimicrobial therapy[4, 28].
Prevention of catheter acquired urinary tract infections
Guidelines
Several evidence-based guidelines provide recommendations for the development and maintenance of prevention programs for CA-UTI[4, 7, 52–54]. Approaches to prevention include avoidance of catheter use, policies for catheter insertion and maintenance, catheter selection, surveillance of CA-UTI and catheter use, and recommendations for quality indicators.
Program implementation
The facility infection prevention and control program should incorporate measures to limit CA-UTI. Improved outcomes following implementation of these programs have been reported[15, 55–57]. The program for a given institution should be individualized to be relevant to local experience, population characteristics, and resources. An essential element of any program is leadership at the senior management level[58].
Infrastructure to support an effective program includes development of policies for catheter indications, catheter selection, and catheter insertion and maintenance[4, 7, 52]. There must be sufficient staffing and staff education, together with access to adequate and appropriate supplies. A means for documentation of urinary catheter use, including indications and dates of insertion and removal, should be established. Where an electronic patient record is used, documentation of catheter use and automatic reminders for removal should be incorporated into this record. The development and implementation of "bundles" for prevention of catheter acquired urinary tract infections has been described. Introduction of a urinary catheter bundle which included education, catheter insertion and management guidelines, and CA-UTI surveillance, in intensive care units in 15 developing countries was followed by a 37% reduction in CA-UTI rate[15]. A state wide initiative in Michigan introduced a CA-UTI bundle with specific practical recommendations addressing implementation under the concepts of "engage and educate", "execute" and "evaluate"[59].
Avoidance of catheter use
The single most important intervention to prevent CA-UTI is to avoid use of an indwelling urinary catheter. There are only a limited number of accepted indications for catheter use[46]:
-
Monitoring of hourly urine output in acutely ill patients.
-
Perioperative use for selected surgical procedures
-
Urologic surgery
-
Surgery on contiguous structures of the genitourinary tract
-
Large volume infusions or diuretics during surgery
-
Requirement for intraoperative monitoring of urine output
-
-
Management of acute urinary retention and urinary obstruction.
-
To facilitate healing of open pressure ulcers or skin grafts in selected patients with urinary incontinence.
-
In exceptional circumstances (e.g. end-of-life care), at patient request to improve comfort.
Alternate voiding management strategies such as intermittent catheterization or, for men, external condom catheters, should be used when possible. Institutional policies should also minimize perioperative catheter use by promoting early post-procedure catheter removal and monitoring of bladder volume with ultrasound bladder scanners, where available, to limit catheter reinsertion for potential urinary retention. When a catheter is indicated, it should be removed promptly once it is no longer required. Patients with indwelling catheters should be identified and reviewed on a continuing basis, preferably at daily rounds, and the catheter removed when no longer indicated. Catheters have been reported to frequently remain in situ beyond necessary, sometimes because health-care personnel are not aware the catheter is present[7, 52]. A systematic review of catheter discontinuation strategies for hospitalized patients reported that the intervention of a "stop order" to facilitate prompt removal of unnecessary catheters reduced the duration of catheter use by 1.06 days, and use of either catheter reminders or stop orders decreased the CA-UTI rate by 53%[60].
Selection of urinary catheter
The smallest gauge catheter possible should be used, to minimize urethral trauma[4, 52]. Infection risks are similar with latex or silicone catheters, and whether or not there is hydrogel coating of the catheter. Residents with chronic catheters have a decreased frequency of obstruction with silicone catheters, but this observation is attributed to the larger bore size of the catheter, rather than the catheter material. The use of silver alloy coated catheters does not decrease the frequency of CA-UTI[12, 61–63]. Nitrofurazone coated catheters have been reported to be associated with a small decrease in CA-UTI[12], but are accompanied by more frequent catheter removal and increased catheter discomfort. Thus, current evidence does not support the routine use of antimicrobial coated catheters[52].
Catheter insertion and maintenance
Recommended practices for catheter insertion and maintenance include[4, 7, 52].These recommendations are primarily based on consensus, but there is strong evidence supporting a decreased rate of acquisition of bacteriuria by maintaining a closed drainage system. There are no benefits with routine daily periurethral cleaning using normal saline, soap, or an antiseptic[52, 64], or with the addition of antiseptics to the drainage bag[52].
-
Catheter insertion:
-
Appropriate hand hygiene
-
Choice of catheter
-
Aseptic techniques/sterile equipment
-
Barrier precautions
-
Antiseptic meatal cleaning
-
-
Catheter maintenance
-
Appropriate hand hygiene
-
Secure catheter
-
Closed drainage system
-
Obtain urine samples aseptically
-
Replace system if breaks in asepsis
-
Avoid irrigation for purpose of prevention of infection
-
Monitoring of infection
The surveillance of catheter use and complications is important to document the facility CA-UTI rate, the effectiveness of interventions, and to allow comparison with benchmark rates[7, 52]. Surveillance with benchmarking was reported, by itself, to decrease infection rates in German intensive care units, although the impact for CA-UTI was not as great as observed for ventilator-associated pneumonia or primary blood stream infections[14]. Standardized surveillance definitions for infection should be used[52]. Core data elements which must be collected to support effective surveillance include recording of catheter indication, catheter insertion and removal dates, urine culture results, and monitoring of bacteremia. Relevant quality indicators are CA-UTI incidence, CA-UTI bacteremia incidence, and the proportion of indwelling catheter use meeting accepted indications.
The outcomes of CA-UTI and bacteremic infection are described using a denominator of device days[52]. However, an effective infection prevention program will minimize catheter use, potentially leading to overall higher device day infection rates as fewer low-risk patients will have catheters[65, 66]. Thus, an outcome based on total patient days, the standardized infection ratio, should also be reported[7]. Surveillance data should be reviewed by appropriate individuals and committees, and observations reported back to caregivers on patient wards[7, 52].
Prevention of CA-UTI in long term care facilities
The prevention of CA-UTI in long term care facilities addresses primarily residents with a chronic indwelling catheter[4, 24, 28]. There should be frequent, systematic review of any resident with a chronic indwelling catheter to determine whether the catheter remains necessary. Bacteriuria in these residents is not avoidable. Interventions should focus on removing the catheter, whenever feasible, minimizing catheter trauma, and early identification of catheter obstruction. Chronic indwelling catheters should not be changed routinely. They should be replaced only if there is obstruction or other malfunction, or prior to initiating antimicrobial therapy when symptomatic urinary infection is treated[52]. Residents with chronic catheters may use a leg bag for drainage to facilitate mobility. Facility policies should address reuse and cleaning or replacement of the leg bags[67]. Antimicrobial therapy for the treatment of bacteriuria in long term care residents with chronic indwelling catheters does not decrease CA-UTI, but there is an increased isolation of resistant organisms with the antimicrobial therapy. Thus, treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria should be avoided[24].
Conclusions
CA-UTI is an important device-associated health care acquired infection. The use of an indwelling urethral catheter is associated with an increased frequency of symptomatic urinary tract infection and bacteremia, and additional morbidity from non-infectious complications. Infection control programs must develop, implement, and monitor policies and practices to minimize infections associated with use of these devices. A major focus of these programs should be to limit the use of indwelling urethral catheters, and to remove catheters promptly when no longer required. Ultimately, however, the avoidance of CA-ASB will likely require development of biofilm resistant catheter materials.
References
Zarb P, Coignard B, Griskevicienne J, Muller A, Vankerckho ven Weist K, Goossens MM, Vaerenberg S, Hopkins S, Catry B, Monnet DL, Goosens H, Suetens C: The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) pilot point prevalence survey of healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use. Euro Surveill. 2012, 17 (46): pil=20316-
Magill SS, Edwards JR, Bamberg W, Beldaus ZG, Dumyati G, Kainer MA, Lynfield R, Maloney M, McAllister-Hollod L, Nadle J, Ray SM, Thompson D, Wilson LE, Fridkin SK: Multistate point-prevalence survey of health care-associated infections. N Engl J Med. 2014, 370: 1198-1208.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Report, Data Summary for 2011, Device-Associated Module, Atlanta: CDC. 2013,http://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/PDFs/dataStat/NHSN-Report-2011-Data-Summary.pdf,
Hooton TM, Bradley SF, Cardenas DD, Colgan R, Geerlings SE, Rice JC, Saint S, Schaeffer AJ, Tambyah PA, Tenke P, Nicolle LE: Diagnosis, prevention and treatment of catheter-associated urinary tract infection in adults; 2009 international clinical practice guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2010, 50: 625-663.
Stark RP, Maki DG: Bacteriuria in the catheterized patient. What quantitative level of bacteriuria is relevant?. N Engl J Med. 1984, 311: 560-564.
Brennan BM, Coyle JR, Marchaim D, Pogue JM, Boehme M, Finks J, Malani AN, Verhec KE, Buckley BO, Mollon N, SUrdin DR, Washer LL, Kaye KS: Statewide surveillance of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Michigan. Infection Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2014, 35: 342-349.
Lo E, Nicolle LE, Coffin SE, Gould C, Maragakis L, Meddings J, Pegues DA, Pettis AM, Saint S, Yokoe DS: Strategies to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infections in acute care hospitals: 2014 update. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2014, 35: 464-479.
Arnoldo L, Migliavasca R, Regastin L, Raglio A, Pagani L, Nucleo E, Spalla M, Vailati F, Agodi A, Mosea A, Zoth C, Tardivo S, Bianco I, Rulli A, Gualdi P, Panetta P, Pasini C, Pedroni M, Brusaferro S: Prevalence of urinary colonization by extended spectrum-beta-lactamase Enterobacteriaceae among catheterized inpatients in Italian long term care facilities. BMC Infect Dis. 2013, 13: 124-
Mody L, Matieshwari S, Galecki A, Kauffman CA, Bradley SF: Indwelling device use and antibiotic resistance in nursing homes: identifying a high-risk group. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007, 55: 1921-1926.
Tambyah PA, Maki DG: Catheter-associated urinary tract infection is rarely symptomatic. Arch Intern Med. 2000, 160: 678-687.
Leuck A-M, Wright D, Ellingson L, Kraemer L, Kuskowski MA, Johnson JR: Complications of Foley catheters – is infection the greatest risk?. J Urol. 2012, 187: 1662-1666.
Pickard R, Lam T, MacLennan G, Starr K, Kilonzo M, McPherson G, Gillies K, McDonald A, Walton K, Buckley B, Glazener C, Boachie C, Burr J, Norrie J, Vale L, Grant A, Nidow J: Types of urethral catheter for reducing symptomatic urinary tact infections in hospitalized adults requiring short-term catheterization: multicenter randomized controlled trial and economic evaluation of antimicrobial- and antiseptic-impregnated urethral catheters (the CATHETER trial). Health Technol Assess. 2012, 16 (47): doi:10.3310/hta16470
Venhems P, Baratin D, Voirin N, Savey A, Caillat-Vallet E, Metzger M-H, Lepape A: Reduction of urinary tract infections acquired in an intensive care unit during a 10-year surveillance program. Eur J Epidemiol. 2008, 23: 641-645.
Gastmeier P, Behnke M, Schwab F, Geffers C: Benchmarking of urinary tract infection rates, experiences from the intensive care unit component of the German national nosocomial infections surveillance system. J Hosp Infect. 2011, 78: 41-44.
Rosenthal VD, Todi SK, Alvarez-Moreno C, Pawar M, Karlekar A, Zeggwagh AA, Mitrev Z, Udwadia FE, Navoa-Ng JA, Chakravarthy M, Salomao R, Sahu S, Dilek A, Kanj SS, Guanche-Garcell H, Cuellar LE, Ersoz G, Nevzat-Yolein A, Jagg N, Madeiros EA, Ye G, Akan DA, Mapp T, Castenada-Sabogal A, Matta-Cortes L, Sirmate IF, Olark N, Torres-Hernandes H, Barahona-Guzman N, Fernandez-Hidalgo R: Impact of a multidimensional infection control strategy on catheter-associated urinary tract infection rates in the adult intensive care units of 15 developing countries: findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium. Infection. 2012, 40: 517-526.
Giks A, Roumbelaki M, Bagatzoumi-Pieridou D, Alexandrou M, Zinseri V, Dimitradis I, Krixtsotaks EI: Device-associated infections in the intensive care units of Cyprus: results of the first national incidence study. Infection. 2010, 38: 165-171.
Burton DC, Edwards JR, Srinivasion A, Fredkin SK, Gould CV: Trends in catheter-associated urinary tract infections in adult intensive care units – United States, 1990–2007. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2011, 32: 748-756.
Crnich CJ, Drinka P: Medical device-associated infections in the long-term care setting. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2012, 26: 143-164.
Eilers R, Veldman-Ariesen MJ, Van Bentham BH: Prevalence and determinants associated with healthcare-associated infections in long-term care facilities in the Netherlands, May to June 2010. Euro Surveill. 2012, 17 (34): pil=20252-
Moro ML, Ricchizzi E, Morsillo F, Marchi M, Purs V, Zotti CM, Prato R, Privitera G, Poli A, Mora I, Fedeli U: Infections and antimicrobial resistance in long term care facilities: a national prevalence study. Ann Ig. 2013, 25: 109-118.
Heudorf L, Boehicke K, Schade M: Healthcare-associated infections in long-term care facilities in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, January to March 2011. Euro Surveill. 2012, 17 (35): pil=20256-
Jonsson K, Loft A-L E, Nasic S, Hedelin H: A prospective registration of catheter life and catheter interventions in patients with long-term indwelling catheters. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2011, 45: 401-403.
Stevenson KB, Moore J, Colwell H, Sleeper B: Standardized infection surveillance in long-term care: interfacility comparisons from a regional cohort of facilities. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2004, 25: 985-994.
Nicolle LE: Urinary catheter associated infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2012, 26: 13.28-
Warren JW, Damron D, Tenney JH, Hoopes JM, Deforge B, Muncie HL: Fever, bacteremia and death as complications of bacteriuria in women with long-term urethral catheters. J Infect Dis. 1987, 155: 1151-1158.
Fortin E, Rocher I, Frenette C, Temblay C, Quach C: Healthcare-associated bloodstream infections secondary to a urinary focus: the Quebec Provincial Surveillance results. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2012, 33: 456-462.
Mylotte JM: Nursing home acquired bloodstream infection. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2005, 26: 838-837.
Nicolle LE: Urinary tract infections in the elderly. Clin Geriatr Med. 2009, 25: 423-436.
Hollingsworth JM, Rogers MA, Krein SL, Hickner A, Kuhn L, Cheng A, Chang R, Saint S: Determining the noninfectious complications of indwelling urethral catheters: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2013, 159: 401-410.
Saint S, Baker PD, McDonald LL, Ossenkop K: Urinary catheters: what type do men and their nurses prefer?. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1999, 47: 1453-1457.
Chant C, Smith DM, Marshall JC, Friedrich JO: Relationship of catheter associated urinary tract infection to mortality and length of stay in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Crit Care Med. 2011, 39: 1167-1173.
Kunin CM, Chin QF, Chambers S: Morbidity and mortality associated with indwelling urinary catheters in elderly patients in a nursing home – confounding due to the presence of associated diseases. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1987, 35: 1001-1006.
Stickler DJ: Bacterial biofilms in patients with indwelling urinary catheters. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2008, 5 (11): 598-608.
Nicolle LE: The chronic indwelling catheter and urinary infection in long term care facility residents. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2001, 22: 316-321.
Warren JW: The catheter and urinary tract infection. Med Clin North Am. 1991, 75: 481-493.
Warren JW, Tenney JH, Hoopes JM, Muncie HL, Anthony WC: A prospective microbiologic study of bacteriuria in patients with chronic indwelling urethral catheters. J Infect Dis. 1982, 146: 719-723.
Greene MT, Chang R, Kuhn L, Rogers MA, Chenoweth CE, Shuman E, Saint S: Predictors of hospital-acquired urinary tract-related bloodstream infection. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2012, 33: 1001-1007.
Chang R, Greene MT, Chenoweth CE, Kuhn L, Shuman E, Rogers NAM, Saint S: Epidemiology of hospital-acquired urinary-tract related blood stream infection at a university hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2011, 32: 1127-1129.
Melzer M, Welch C: Outcomes in UK patients with hospital-acquired bacteremia and the risk of catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Postgrad Med J. 2013, 89: 329-334.
Sader HS, Flamm RK, Jones RN: Frequency of occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Gram-negative bacteremia isolates in patients with urinary tract infection: results from United States and European hospitals (2009–2011). J Chemother. 2014, 26: 133-138.
Ortega M, Marco F, Soriano A, Almela M, Martinez JA, Pitart C, Mensa J: Epidemiology and proynostic determinants of bacteremic catheter acquired urinary tract infection in a single institution from 1991–2010. J Infect. 2013, 67: 282-287.
Matsukawa M, Kunishima Y, Takahashi S, Takeyama K, Tsukamoto T: Bacterial colonization on intraluminal surface of urethral catheter. Urology. 2005, 65: 440-444.
Mobley HT: Virulence of Proteus mirabilis. Urinary tract infections: molecular pathogenesis and clinical management. Edited by: Mobley HL, Warren JW. 1996, Washington DC: ASM Press, 245-270.
Getliffe KA, Mulhall AB: The encrustation of indwelling catheters. Br J Urol. 1991, 67: 337-341.
Stickler DJ, Zimakoff J: Complications of urinary tract infections associated with devices used for long-term bladder management. J Hosp Infect. 1994, 28: 177-194.
Getliffe KA: The characteristics and management of patients with recurrent blockage of long-term urinary catheters. J Adv Nurs. 1994, 20: 140-149.
Kohler-Ockmore J, Feneley RC: Longterm catheterization of the bladder: prevalence and morbidity. Br J Urol. 1996, 77: 347-351.
Jones BD, Mobley HL: Genetic and biochemical diversity of ureases of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella species isolated from urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 1987, 55: 2198-2203.
Jacobsen SM, Stickler DJ, Mobley HL, Shirtliff ME: Complicated catheter-associated urinary tract infections due to Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2008, 21: 26-59.
Stickler D, Morris N, Moreno MC, Sabbaba N: Studies on the formation of crystalline bacterial biofilms on urethral catheters. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998, 17: 649-652.
Tenney JH, Warren JW: Bacteriuria in women with long term catheters: paired comparison of indwelling and replacement catheters. J Infect Dis. 1988, 157: 199-207.
Gould CV, Umscheid CA, Agarwal RK, Kuntz G, Pegues DA: Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC): guideline for prevention of catheter-associated urinary tract infections. 2009,http://www.cdc.gov/hicpac/cauti/011_cauti.html,
Pratt RJ, Pellowe C, Loveday HP, Robinson N, Smith GW, Epic Guideline Development Team: Guidelines for preventing infections associated with the insertion and maintenance of short-term indwelling urethral catheters in acute care. J Hosp Infect. 2001, 47 (suppl): S39-S46.
Pratt RJ, Pellowe CM, Wilson JA, Loveday HP, Harper PJ, Jones SR, McDougall C, Wilcox MH: Epic 2: national evidence-based guidelines for preventing healthcare-associated infections in NHS hospitals in England. J Hosp Infect. 2007, 65 (suppl): S1-S64.
Fakih MG, Watson SR, Green MT, Kennedy EH, Olmsted RN, Krein SL, Saint S: Reducing inappropriate urinary catheter use: a statewide effort. Arch Intern Med. 2012, 172: 255-260.
Marigliano A, Barbadoro P, Pennacchietti L, D’Errico MM, Prospero E: Active training and surveillance: two good friends to reduce urinary catheterization rate. Am J Infect Control. 2012, 40: 692-695.
Titsworth WL, Hester J, Correia T, Reed R, Williams M, Guin P, Layon AJ, Archibald LK, Mocco J: Reduction of catheter-associated urinary tract infections among patients in a neurological intensive care unit: a single institution’s success. J Neurosurg. 2012, 116: 911-920.
Saint S, Kowalski CP, Forman J, Damschroder L, Hofer TP, Kaufman SR, Creswell JW, Krein SL: A multicenter qualitative study on preventing hospital-acquired urinary tract infection in US hospitals. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2008, 29: 333-341.
Saint S, Olmsted RN, Fakih MG, Kowalski CP, Watson SR, Sales AE, Krein SL: Translating health care-associated urinary tract infection prevention research into practice via the bladder bundle. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2009, 35: 449-455.
Meddings J, Rogers MA, Krein SL, Fakih MG, Olmsted RN, Saint S: Reducing unnecessary urinary catheter use and other strategies to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infection: an integrative review. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013, Electronically published ahead of print. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2012-001774
Johnson JR, Roberts PL, Olsen RJ, Moyer KA, Stamm WE: Prevention of catheter-associated urinary tract infection with a silver-oxide-coated urinary catheter: clinical and microbiologic correlation. J Infect Dis. 1990, 162: 1145-1150.
Srinivasan A, Karchmer T, Richards A, Song X, Perl T: A prospective trial of a novel, silicone-based, silver-coated Foley catheter for the prevention of nosocomial urinary tract infection. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2006, 27: 38-43.
Riley DK, Classen DC, Stevens LE, Burke JP: A large, randomized clinical trial of a silver-impregnated urinary catheter: lack of efficacy and staphylococcal superinfection. Am J Med. 1995, 98: 349-356.
Huth TS, Burke JP, Larsen RA, Classen DC, Stevens LE: Randomized trial of meatal care with silver sulfadiazine cream for the prevention of catheter-associated bacteriuria. J Infect Dis. 1992, 165: 14-18.
Fakih MG, Greene MT, Kennedy EH, Meddings JA, Krein SL, Olmsted RN, Saint S: Introducing a population-based outcome measure to evaluate the effect of interventions to reduce catheter-associated urinary tract infection. Am J Infect Control. 2012, 40: 359-364.
Burns AC, Petersen NJ, Garza A, Arya M, Patterson JE, Naik AD, Trautner BW: Accuracy of a urinary catheter surveillance protocol. Am J Infect Control. 2012, 40: 55-58.
Smith P, Bennett G, Bradley S, Drinka P, Lautenbach E, Marx J, Mody L, Nicolle L, Stevenson K: SHEA/APIC Guideline: infection prevention and control in the long-term care facility. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2008, 29: 785-814.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The author declares that she has no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Nicolle, L.E. Catheter associated urinary tract infections. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 3, 23 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-2994-3-23
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-2994-3-23