Abstract
Background
Antimicrobial catheters have been utilized to reduce risk of catheter colonization and infection. We aimed to determine if there is a greater than expected risk of microorganism-specific colonization associated with the use of antimicrobial central venous catheters (CVCs).
Methods
We performed a meta-analysis of 21 randomized, controlled trials comparing the incidence of specific bacterial and fungal species colonizing antimicrobial CVCs and standard CVCs in hospitalized patients.
Results
The proportion of all colonized minocycline-rifampin CVCs found to harbor Candida species was greater than the proportion of all colonized standard CVCs found to have Candida. In comparison, the proportion of colonized chlorhexidine-silver sulfadiazine CVCs specifically colonized with Acinetobacter species or diphtheroids was less than the proportion of similarly colonized standard CVCs. No such differences were found with CVCs colonized with staphylococci.
Conclusion
Commercially-available antimicrobial CVCs in clinical use may become colonized with distinct microbial flora probably related to their antimicrobial spectrum of activity. Some of these antimicrobial CVCs may therefore have limited additional benefit or more obvious advantages compared to standard CVCs for specific microbial pathogens. The choice of an antimicrobial CVC may be influenced by a number of clinical factors, including a previous history of colonization or infection with Acinetobacter, diphtheroids, or Candida species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Central venous catheters (CVCs) have become essential in the management of critically ill patients, as well as other patient populations requiring acute or long-term medical care. Intravascular catheters can become colonized by microbial pathogens following an extraluminal or intraluminal route of endemic infection emanating from the insertion site and catheter connector/hub, respectively [1]. Meta-analyses have been published demonstrating a reduced risk of CVC colonization and CVC-related bloodstream infection with some of the currently marketed antimicrobial CVCs [2–4]. However, there are no publications that have systematically reviewed prospective, randomized clinical trials comparing antimicrobial CVCs with non-antimicrobial CVCs to determine if there are differences in the incidence of species-specific CVC colonization that might suggest a lack of efficacy for specific pathogens. We hypothesized that some currently marketed antimicrobial CVCs may lack activity against specific microbial pathogens, and as such, may select for colonization and eventual bloodstream infection caused by such pathogens. We analyzed available data to determine if there is a proven benefit at the species-specific level for use of antimicrobial CVCs and to determine if some of these CVCs may have any vulnerability in their antimicrobial spectra. We studied CVC colonization rather than CVC-related bloodstream infection since endemic CVC infections start with microbial colonization prior to the development of CVC-related bloodstream infection. Additionally, most studies have shown a 2 to 10-fold increase in episodes of CVC colonization compared to CVC-related bloodstream infection [2]. Thus, the greatest likelihood of uncovering any potential gaps in the spectrum of activity of antimicrobial CVCs would best be done by assessing CVC colonization.
Materials and methods
We reviewed prospective, randomized clinical trials comparing antimicrobial CVCs to non-antimicrobial control CVCs. Inclusion criteria were as previously described [2]. In brief, we performed a search in Cochrane, MEDLINE, and EMBASE databases of randomized controlled trials from 1995 to current with the following strings: “central venous catheter”, “colonization”, “catheter colonization”, “bloodstream infection”, “bacteremia”, “chlorhexidine”, “benzalkonium chloride”, “rifampicin”, “minocycline”, “silver”, and “miconazole”. We chose to search from 1995 onwards as this was when the first study was published in those included in our first meta-analysis [2]. Catheter colonization was defined as at least 15 CFUs of microbial growth by semi-quantitative culture [5], or at least 1000 CFUs after quantitative vortex culture [6], or at least 100 CFUs after vortexing and sonication [6]. All statistical analyses were performed with MetAnalysis 1.0 software. Gart odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs were calculated for each study that met entry criteria. For each antimicrobial CVC, we analyzed the number of antimicrobial CVCs colonized with a specific microorganism or related group of microorganisms as a fraction of all colonized antimicrobial CVCs of the same type. This fraction was compared with non-antimicrobial CVCs used in the same studies analyzed in the same way.
The rate of CVC colonization for each microorganism was analyzed separately and various pooled odds ratios (ORs) were calculated by both the Gart fixed-effects models (FEMs) and the DerSimonian-Laird random-effects models (REMs). The Cochran Q statistics and I2 test were used to assess heterogeneity. I2 values of 0% indicates no observed heterogeneity, whereas larger values indicated increasing heterogeneity. Results of the Gart FEM are quoted unless substantial heterogeneity was found, in which case the results of the DerSimonian-Laird REM are stated. We only included trials meeting our previously published criteria. Additionally, we only included those studies in which species-specific rates of colonization were delineated or those studies in which we were able to contact the authors directly to obtain species-specific colonization rates for antimicrobial and non-antimicrobial CVC groups. Our final analysis included an assessment for rates of CVC colonization for specific microbial species if available. If authors used the terms ‘coliforms’ or ‘diphtheroids’, we analyzed colonization rates but we did not combine these results with species-specific data. If the information regarding CVC colonization was insufficient, we attempted to contact the study corresponding author. We requested additional information from eleven authors; three authors responded before the final analysis was completed. As such, these latter studies [7–9] were included in the final analysis.
Results
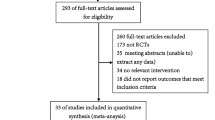
Twenty-one randomized, controlled trials met our inclusion criteria [5, 7–26] (Figure 1; Tables 1 and 2). Combining all antimicrobial CVCs, there was no significant difference in the proportion of colonized antimicrobial CVCs that were colonized by Staphylococcus aureus or coagulase-negative staphylococci compared to the corresponding fractions of colonized control CVCs (Figures 2 and 3). Similarly, the proportion of S. aureus or coagulase-negative staphylococci colonized chlorhexidine-silver sulfadiazine, minocycline-rifampin, or silver antimicrobial CVCs was similar to the total proportion of colonized control CVCs. The proportion of miconazole-rifampin CVCs colonized with coagulase-negative staphylococci was less than the standard CVCs. However, this reflected the results of a single study [23].
Horizontal lines represent 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) of CVC colonization with coagulase-negative staphylococci in different trials. They express the likelihood of test vs. control catheter colonization in relation to the vertical line that represents the null hypothesis of no difference between test and control catheters. For every type of catheter tested, the data from available trials was pooled and graphed as Gart fixed-effects model (FEM). If substantial heterogeneity was present, DerSimonian-Laird random-effects model (REM) results were used instead. *Coagulase-negative staphylococci colonized control CVCs/All colonized control CVCs. #Coagulase-negative staphylococci colonized test CVCs/All colonized test CVCs.
Horizontal lines represent 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) of CVC colonization with S. aureus in different trials. They express the likelihood of test vs. control catheter colonization in relation to the vertical line that represents the null hypothesis of no difference between test and control catheters. For every type of catheter tested, the data from available trials was pooled and graphed as Gart fixed-effects model (FEM). If substantial heterogeneity was present, DerSimonian-Laird random-effects model (REM) results were used instead. *S. aureus colonized control CVCs/All colonized control CVCs. #S. aureus colonized test CVCs/All colonized test CVCs.
The findings also demonstrated that there was no significant difference in the proportion of antimicrobial CVCs specifically colonized with Acinetobacter species compared to the proportion of Acinetobacter colonized control CVCs (Figure 4). Among those antimicrobial CVCs, the chlorhexidine-silver sulfadiazine CVCs colonized with Acinetobacter species were significantly less frequent, compared to corresponding colonized control CVCs (OR 0.16 [95%CI 0.04-0.64]). However, publication bias was detected (P=0.01).
Horizontal lines represent 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) of CVC colonization with Acinetobacter in different trials. They express the likelihood of test vs. control catheter colonization in relation to the vertical line that represents the null hypothesis of no difference between test and control catheters. For every type of catheter tested, the data from available trials was pooled and graphed as Gart fixed-effects model (FEM). If substantial heterogeneity was present, DerSimonian-Laird random-effects model (REM) results were used instead. *Acinetobacter colonized control CVCs/All colonized control CVCs. #Acinetobacter colonized test CVCs/All colonized test CVCs.
The proportion of antimicrobial CVCs that were colonized with diphtheroids was less than that of colonized control CVCs (OR 0.45 [95%CI 0.25-0.79]). The proportion of colonized chlorhexidine-silver sulfadiazine CVCs that were colonized by diphtheroids was less than that of colonized standard control CVCs (OR 0.43 [95%CI 0.23-0.82]).
Combining all antimicrobial CVCs, the proportion of colonized CVCs that were colonized by coliforms was greater than that of standard CVCs (OR 2.38 [95%CI 1.10-5.15]). The proportion of coliform-colonized silver CVCs and minocycline-rifampin CVCs was greater than that of standard control CVCs (Figure 5). However, these findings each represented only a single clinical trial [20, 22].
Horizontal lines represent 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) of CVC colonization with coliform bacteria in different trials. They express the likelihood of test vs. control catheter colonization in relation to the vertical line that represents the null hypothesis of no difference between test and control catheters. For every type of catheter tested, the data from available trials was pooled and graphed as Gart fixed-effects model (FEM). If substantial heterogeneity was present, DerSimonian-Laird random-effects model (REM) results were used instead. *Coliforms colonized control CVCs/All colonized control CVCs. #Coliforms colonized test CVCs/All colonized test CVCs.
Combining all antimicrobial CVCs, there was no significant difference in the proportion of colonized antimicrobial CVCs colonized with Candida species compared to colonized standard CVCs (Figure 6). However, the proportion of colonized minocycline-rifampin CVCs colonized with Candida species was greater than that of colonized standard CVCs (OR 13.6 [95%CI 4.2-43.4]).
Horizontal lines represent 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) of CVC colonization with Candida species in different trials. They express the likelihood of test vs. control catheter colonization in relation to the vertical line that represents the null hypothesis of no difference between test and control catheters. For every type of catheter tested, the data from available trials was pooled and graphed as Gart fixed-effects model (FEM). If substantial heterogeneity was present, DerSimonian-Laird random-effects model (REM) results were used instead. *Candida species colonized control CVCs/All colonized control CVCs. #Candida species colonized test CVCs/All colonized test CVCs.
Discussion
Antimicrobial-coated CVCs were developed in an effort to mitigate risk of serious CVC-related infections. Meta-analyses have shown that chlorhexidine-silver sulfadiazine CVCs, and particularly minocycline-rifampin CVCs, reduce the risk of CRBSI in prospective, randomized trials [2–4]. We compared data regarding colonization of antimicrobial and standard CVCs with known microorganisms that can cause CRBSI with an aim to investigate any potential vulnerability in the spectrum of antimicrobial activity. We found that chlorhexidine-silver sulfadiazine CVCs may have unique activity in reducing risk of colonization by Acinetobacter species and diphtheroids, but the former finding needs to be confirmed since we detected publication bias. Single study findings suggest that the miconazole-rifampin CVC may reduce the risk of colonization by coagulase-negative staphylococci, while the silver CVC and minocycline-rifampin CVC may be more vulnerable to coliform colonization, but these observations need to be confirmed by future studies. We identified a significant increase in the proportion of Candida species colonization among colonized minocycline-rifampin CVCs. Published clinical trials have not found an increased incidence of CVC-related bloodstream infections due to Candida species but these studies are underpowered to detect such a difference.
Our findings regarding minocycline-rifampin CVC colonization with Candida species, as well as coliforms, support the observations of other investigators [22, 27–29]. Some investigators found significantly less microbial adherence of Enterobacter aerogenes, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and C. albicans to chlorhexidine-silver sulfadiazine CVCs compared to non-antimicrobial CVCs but no such difference when minocycline-rifampin CVCs or silver CVCs were tested [28]. Additionally, they found increased microbial adherence of C. albicans to minocycline-rifampin CVCs compared to control CVCs in an in vitro model.
Our study has important limitations. We looked at CVC colonization rather than CVC-related bloodstream infection. However, as previously stated, for endemic intravascular CVC infections, CVC colonization is a prerequisite for bloodstream infection. As such, we feel that our findings have clinical relevance. We were unable to assess differences in CVC colonization based on the anatomic site of CVC insertion as this information was unavailable in the majority of the studies included in our analysis. Another potential weakness was the variable reported use of neutralizers when cultures of antimicrobial CVCs were performed.
Prospective studies and the ensuing meta-analyses have demonstrated the attributes of antimicrobial CVCs. However, we were interested in further understanding potential unintended consequences of widespread use of such devices. The data presented herein suggest that some antimicrobial CVCs may not reduce risk of CVC infections due to Candida or coliforms compared to uncoated CVCs despite showing overall benefit in clinical trials. As such, clinicians should weigh potential risks and benefits when contemplating use of specific antimicrobial CVCs in patients with prior colonization or infection due to these pathogens or when the patients are located in clinical areas where these microorganisms are endemic. Novel CVCs combining components of previously studied catheters have been demonstrated to have broader antimicrobial coverage and may well be less prone to colonization with select microorganisms as demonstrated in our investigation [30].
References
Mermel LA: What is the predominant source of intravascular catheter infections?. Clin Infect Dis. 2011, 52: 211-212. 10.1093/cid/ciq108.
Casey AL, Mermel LA, Nightingale P, Elliott TSJ: Antimicrobial central venous catheters in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008, 8: 763-776. 10.1016/S1473-3099(08)70280-9.
Hockenhull JC, Dwan K, Boland A, Smith G, Bagust A, Dündar Y, Gamble C, McLeod C, Walley T, Dickson R: The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of central venous catheters treated with anti-infective agents in preventing bloodstream infections: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2008, 12: 1-154.
Wang H, Huang T, Jing J, Jin J, Wang P, Yang M, Cui W, Zheng Y, Shen H: Effectiveness of different central venous catheters for catheter-related infections: a network meta-analysis. J Hosp Infect. 2010, 76: 1-11. 10.1016/j.jhin.2010.04.025.
Maki DG, Stolz SM, Wheeler S, Mermel LA: Prevention of central venous catheter-related bloodstream infection by use of an antiseptic-impregnated catheter. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1997, 127: 257-266.
Cleri DJ, Corrado ML, Seligman SJ: Quantitative culture of intravenous catheters and other intravascular inserts. J Infect Dis. 1980, 141: 781-786. 10.1093/infdis/141.6.781.
Heard SO, Wagle M, Vijayakumar E, McLean S, Brueggemann A, Napolitano LM, Edwards LP, O'Connell FM, Puyana JC, Doern GV: Influence of triple-lumen central venous catheters coated with chlorhexidine and silver sulfadiazine on the incidence of catheter-related bacteremia. Arch Intern Med. 1998, 158: 81-87.
Rupp ME, Lisco SJ, Lipsett PA, Perl TM, Keating K, Civetta JM, Mermel LA, Lee D, Dellinger EP, Donahoe M, Giles D, Pfaller MA, Maki DG, Sherertz R: Effect of a second-generation venous catheter impregnated with chlorhexidine and silver sulfadiazine on central catheter-related infections: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2005, 143: 570-580.
Raad I, Darouiche R, Dupuis J, Abi-Said D, Gabrielli A, Hachem R, Wall M, Harris R, Jones J, Buzaid A, Robertson C, Shenaq S, Curling P, Burke T, Ericsson C: Central venous catheters coated with minocycline and rifampin for the prevention of catheter-related colonization and bloodstream infections. A randomized, double-blind trial. The Texas Medical Center Catheter Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1997, 127: 267-274.
Goldschmidt H, Hahn U, Salwender HJ, Haas R, Jansen B, Wolbring P, Rinck M, Hunstein W: Prevention of catheter-related infections by silver coated central venous catheters in oncological patients. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. 1995, 283: 215-223. 10.1016/S0934-8840(11)80203-3.
Bach AA, Schmidt HH, Böttiger BB, Schreiber BB, Böhrer HH, Motsch JJ, Martin EE, Sonntag HGH: Retention of antibacterial activity and bacterial colonization of antiseptic-bonded central venous catheters. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996, 37: 315-322. 10.1093/jac/37.2.315.
Ciresi DL, Albrecht RM, Volkers PA, Scholten DJ: Failure of antiseptic bonding to prevent central venous catheter-related infection and sepsis. Am Surg. 1996, 62: 641-646.
van Heerden PV, Webb SA, Fong S, Golledge CL, Roberts BL, Thompson WR: Central venous catheters revisited–infection rates and an assessment of the new Fibrin Analysing System brush. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1996, 24: 330-333.
Bach A, Eberhardt H, Frick A, Schmidt H, Böttiger BW, Martin E: Efficacy of silver-coating central venous catheters in reducing bacterial colonization. Crit Care Med. 1999, 27: 515-521. 10.1097/00003246-199903000-00028.
Collin GR: Decreasing catheter colonization through the use of an antiseptic-impregnated catheter: a continuous quality improvement project. Chest. 1999, 115: 1632-1640. 10.1378/chest.115.6.1632.
Hannan M, Juste RN, Umasanker S, Glendenning A, Nightingale C, Azadian B, Soni N: Antiseptic-bonded central venous catheters and bacterial colonisation. Anaesthesia. 1999, 54: 868-872. 10.1046/j.1365-2044.1999.01000.x.
Marik PE, Abraham G, Careau P, Varon J, Fromm RE: The ex vivo antimicrobial activity and colonization rate of two antimicrobial-bonded central venous catheters. Crit Care Med. 1999, 27: 1128-1131. 10.1097/00003246-199906000-00034.
Sheng WH, Ko WJ, Wang JT, Chang SC, Hsueh PR, Luh KT: Evaluation of antiseptic-impregnated central venous catheters for prevention of catheter-related infection in intensive care unit patients. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000, 38: 1-5. 10.1016/S0732-8893(00)00166-8.
Jaeger K, Osthaus A, Heine J, Ruschulte H, Kuhlmann C, Weissbrodt H, Ganser A, Karthaus M: Efficacy of a benzalkonium chloride-impregnated central venous catheter to prevent catheter-associated infection in cancer patients. Chemotherapy. 2001, 47: 50-55. 10.1159/000048501.
Corral L, Nolla-Salas M, Ibañez-Nolla J, León MA, Díaz RM, Cruz Martín M, Iglesia R, Catalan R: A prospective, randomized study in critically ill patients using the Oligon Vantex catheter. J Hosp Infect. 2003, 55: 212-219. 10.1016/j.jhin.2003.07.001.
Brun-Buisson C, Doyon F, Sollet J-P, Cochard J-F, Cohen Y, Nitenberg G: Prevention of intravascular catheter-related infection with newer chlorhexidine-silver sulfadiazine-coated catheters: a randomized controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30: 837-843. 10.1007/s00134-004-2221-9.
León C, Ruiz-Santana S, Rello J, La Torre De MV, Vallés J, Alvarez-Lerma F, Sierra R, Saavedra P, Alvarez-Salgado F: Cabaña Study Group: benefits of minocycline and rifampin-impregnated central venous catheters. A prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled, multicenter trial. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30: 1891-1899. 10.1007/s00134-004-2378-2.
Yücel N, Lefering R, Maegele M, Max M, Rossaint R, Koch A, Schwarz R, Korenkov M, Beuth J, Bach A, Schierholz J, Pulverer G, Neugebauer EAM: Reduced colonization and infection with miconazole-rifampicin modified central venous catheters: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004, 54: 1109-1115. 10.1093/jac/dkh483.
Dünser MW, Mayr AJ, Hinterberger G, Flörl CL, Ulmer H, Schmid S, Friesenecker B, Lorenz I, Hasibeder WR: Central venous catheter colonization in critically ill patients: a prospective, randomized, controlled study comparing standard with two antiseptic-impregnated catheters. Anesth Analg. 2005, 101: 1778-1784.
Osma S, Kahveci SF, Kaya FN, Akalin H, Ozakin C, Yilmaz E, Kutlay O: Efficacy of antiseptic-impregnated catheters on catheter colonization and catheter-related bloodstream infections in patients in an intensive care unit. J Hosp Infect. 2006, 62: 156-162. 10.1016/j.jhin.2005.06.030.
Kalfon P, de Vaumas C, Samba D, Boulet E, Lefrant J-Y, Eyraud D, Lherm T, Santoli F, Naija W, Riou B: Comparison of silver-impregnated with standard multi-lumen central venous catheters in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 2007, 35: 1032-1039. 10.1097/01.CCM.0000259378.53166.1B.
Sampath LA, Tambe SM, Modak SM: In vitro and in vivo efficacy of catheters impregnated with antiseptics or antibiotics: evaluation of the risk of bacterial resistance to the antimicrobials in the catheters. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2001, 22: 640-646. 10.1086/501836.
Gaonkar TA, Modak SM: Comparison of microbial adherence to antiseptic and antibiotic central venous catheters using a novel agar subcutaneous infection model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003, 52: 389-396. 10.1093/jac/dkg361.
Yorganci K, Krepel C, Weigelt JA, Edmiston CE: Activity of antibacterial impregnated central venous catheters against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Intensive Care Med. 2002, 28: 438-442. 10.1007/s00134-002-1243-4.
Raad I, Mohamed JA, Reitzel RA, Jiang Y, Raad S, Al Shuaibi M, Chaftari AM, Hachem RY: Improved antibiotic-impregnated catheters with extended- spectrum activity against resistant bacteria and fungi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012, 56: 935-941. 10.1128/AAC.05836-11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
Dr. Mermel has had research funding from Astrellas and he has served as a consultant for Angiotech, Bard, Catheter Connections, Fresenius, ICU Medical, Semprus, and Teleflex. Dr. Elliott has received research funding from Carefusion, 3M and Becton Dickinson and has served on an advisory board for 3M. Drs. Novikov, Lam, Casey and Nightingale have no competing interest.
Authors’ contributions
This project was initiated by LAM. AN, MYL, and ALC assisted in the meta-analysis; ALC and PN carried out statistical analysis; AN and MYL drafted the initial manuscript; ALC, TSE, PN, and LAM reviewed and amended the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Novikov, A., Lam, M.Y., Mermel, L.A. et al. Impact of catheter antimicrobial coating on species-specific risk of catheter colonization: a meta-analysis. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 1, 40 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-2994-1-40
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-2994-1-40