Abstract
The association of neurofibromatosis type I with invasive male breast cancer is a rare clinical entity with only one case in literature reported in 1953. Women with NF1 are at risk of developing breast cancer and men also may be at risk but there is scarce data on the risk and association of NF1 with male breast cancer due to its rarity. Established clinical trials in male breast cancer patients are lacking and the results are extrapolated from female breast cancer patients. The treatment of male breast cancer is followed as per the guidelines of premenopausal female breast cancer and tamoxifen is the hormone treatment in them. Mendes et al suggests that silencing of NF1 gene confers resistance to tamoxifen. Our conclusions are that since NF1 is mutated or deleted in one third of sporadic breast cancers, its role as a molecular driver for treatment has to be further explored.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Male breast cancer is a rare disease and accounts for less than 1% of all breast cancers [1]. Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) or Von Recklinghausen disease is an autosomal dominant condition that leads to multiple benign tumors (neurofibromas) and predisposes to several types of malignancies, including breast cancer. To the best of our knowledge, only 1 case of neurofibromatosis in a male patient with breast cancer has been previously reported in the literature [2]. Here we report another case and discuss the potential role of the NF1 gene in the pathogenesis of these cases.
Case description
A 55-year-old male presented to our institution in November 2011 with complaints of multiple skin nodules, brown skin patches since childhood and an enlarging painless lump in the left breast for 2 months. There was no other medical history of relevance including food allergies or drug abuse. There was history of similar skin nodules in his brother and paternal uncle. There was no history of breast, ovary or prostate cancer in the family.
On examination, multiple, soft, sessile to pedunculated, dome shaped, skin colored nodules (Figure 1) with size ranging from 0.5-4 cms and eight well circumscribed brown macular patches distributed all over the body, with size ranging from 0.5-6 cms, were observed. On ophthalmologic examination, the iris and retina were normal. An irregular lump in left breast of size 6 × 2 cms was noted. It was hard in consistency, non-tender, and mobile; axillary lymph nodes were not palpable. Hematological, renal and liver function tests were normal.
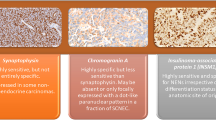
Fine needle aspiration from the lump was suggestive of ductal carcinoma. Genetic analyses could not be conducted for financial/logistics reasons and the diagnosis of NF1 was made based on clinical criteria [3]. Hence a diagnosis of NF1 and breast cancer was made. After staging workup, the patient underwent modified radical mastectomy and axillary lymph node dissection. Histopathological examination revealed invasive ductal carcinoma of Bloom and Richardson histological grade III (Figure 2). The pathological stage was pT3N0M0. On immunohistochemistry, estrogen and progesterone receptors (ER, PgR) were both positive and HER2 was negative (Figure 3).
The patient received 6 cycles of adjuvant FEC (fluorouracil 500 mg/m2 q3w, epirubicin 100 mg/m2 q3w, cyclophosphamide 500 mg/m2 q3w) chemotherapy followed by external beam radiotherapy on a cobalt-60 machine with tangential pairs to chest wall and anterior supraclavicular fields of 50 Gy in 25 fractions with 2 Gy per fraction given once a day for 5 weeks.
At present, the patient is receiving tamoxifen 20 mg once daily and is on follow up since 8 months.
Discussion
NF1 is an autosomal dominant Mendelian syndrome occurring in about 1 in 4000 persons in the general population and has high penetrance but wide variability in expression [4]. It represents a risk factor for the development of various malignancies, including female breast cancer [5].
Neurofibromin 1 (NF1) is a tumor suppressor gene that encodes the neurofibromin protein, a negative regulator of the Ras oncogene. NF1 is located on the pericentromeric region of the long arm of chromosome 17 (which interestingly also houses the BRCA1 gene), and regulates the conversion of the active Ras-GTP to inactive Ras-GDP (Figure 4) [6]. About 28% of sporadic breast cancers in humans are missing at least one copy of NF1 gene, either due to deletion or mutation [7].
According to Knudson’s “two-hit” hypothesis, both alleles have to be inactivated for tumorogenesis to occur. In NF1-associated cancers, the first “hit” is a germline mutation, while the second “hit” is a somatic mutation that occurs either in utero or after birth and results in inactivation of the normal NF1 allele and a consequent loss of neurofibromin function. Both alleles of NF1 need to be inactivated to influence carcinogenesis, but there is emerging evidence that haploinsuficiency or reduced expression may also have a functional impact [8].
Individuals with NF1 are heterozygous for an NF1 mutation. Mutation in the normal copy of the NF1 gene enhances the risk of cancer among NF1 patients but these mutations may also be observed in sporadic tumors [9, 10].
Women with inherited NF1 deficiency have an increased risk of breast cancer [11, 12]. Some reports implicate spontaneous NF1 loss in breast tumorigenesis [13, 14]. A recent report suggests that females with NF1 have a relative risk of 2.3 (95% confidence interval 1.7 to 2.9) for developing breast cancer compared with a reference cohort [5]. Men also may be at risk (as highlighted by this case report) but there is scarce data on the risk and association of NF1 and male breast cancer due to its rarity [15].
Silencing NF1 (or other genes including, BAP1, CDK10, NIPBL, PTEN, RARG, SMC3, and UBA3) have been shown to confer tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer (MCF7) cell lines [16]. Hence tamoxifen, the drug treatment for hormone receptor positive breast cancers, may theoretically be less effective in cancers involving NF1 mutations; however, this needs to be corroborated by clinical evidence.
In conclusion, this report aims to describe a rare presentation of a male patient with NF1 and breast cancer. The NF1 gene is mutated or deleted in a significant proportion of human breast cancers, and its role as a potentially important molecular driver in breast cancers needs to be explored further. One can speculate that drugs blocking the Ras pathway could be useful in breast cancer with NF1 mutations; this hypothesis needs to be tested in a scientifically robust manner.
Consent
Informed consent has been obtained from the patient for publication.
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011, 61: 69–90. 10.3322/caac.20107
Ronchese F: Neurofibromatosis and adenocarcinoma of (male) breast. AMA Arch Derm Syphilol 1953,68(3):359.
Korf BR: Malignancy in Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Oncologist 2000, 5: 477–485. 10.1634/theoncologist.5-6-477
Friedman JM: Epidemiology of neurofibromatosis type 1. Am J Med Genet 1999,89(1):1–6. 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19990326)89:1<1::AID-AJMG3>3.0.CO;2-8
Seminog OO, Goldacre MJ: Risk of benign tumours of nervous system, and of malignant neoplasms, in people with neurofibromatosis: population-based record-linkage study. Br J Cancer 2012. Published online December 20, 2012; doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.535
Xu GF, O’Connell P, Viskochil D, Cawthon R, Robertson M, Culver M, Dunn D, Stevens J, Gesteland R, White R: The neurofibromatosis type 1 gene encodes a protein related to GAP. Cell 1990, 62: 599–608. 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90024-9
Wallace MD, Pfefferle AD, Shen L, McNairn AJ, Cerami EG, Fallon BL, Rinaldi VD, Southard TL, Perou CM, Schimenti JC: Comparative Oncogenomics Implicates the Neurofibromin 1 Gene (NF1) as a Breast Cancer Driver. Genetics 2012, 192: 385–396. 10.1534/genetics.112.142802
Berger AH, Knudson AG, Pandolfi PP: A continuum model for tumour suppression. Nature 2011, 476: 163–169. 10.1038/nature10275
McLendon R, Friedman A, Bigner D, Van Meir EG, Brat DJ, Mastrogianakis GM, Olson JJ, Mikkelsen T, Lehman N, Aldape K, Yung WK, Bogler O, Weinstein JN, VandenBerg S, Berger M, Prados M, Muzny D, Morgan M, Scherer S, Sabo A, Nazareth L, Lewis L, Hall O, Zhu Y, Ren Y, Alvi O, Yao J, Hawes A, Jhangiani S, Fowler G, et al.: Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 2008, 455: 1061–1068. 10.1038/nature07385
Bell D, Berchuck A, Birrer M, Chien J, Cramer D, Dao F, Dhir R, DiSaia P, Gabra H, Glenn P, Godwin A, Gross J, Hartmann L, Huang M, Huntsman D, Iacocca M, Imielinski M, Kalloger S, Karlan B, Levine D, Mills G, Morrison C, Mutch D, Olvera N, Orsulic S, Park K, Petrelli N, Rabeno B, Rader J, Sikic B, et al.: Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature 2011, 474: 609–615. 10.1038/nature10166
Madanikia SA, Bergner A, Ye X, Blakeley JO: Increased risk of breast cancer in women with NF1. Am J Med Genet A 2012,158A(12):3056–60. 10.1002/ajmg.a.35550
Salemis NS, Nakos G, Sambaziotis D, Gourgiotis S: Breast cancer associated with type 1 neurofibromatosis. Breast Cancer 2010, 17: 306–309. 10.1007/s12282-009-0119-7
Guran S, Safali M: A case of neurofibromatosis and breast cancer: loss of heterozygosity of NF1 in breast cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2005, 156: 86–88. 10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2004.04.019
Lee J, Wang M, Torbenson M, Lu Y, Liu QZ, Li S: Loss of SDHB and NF1 genes in a malignant phyllodes tumor of the breast as detected by oligo-array comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2010, 196: 179–183. 10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2009.09.005
Wilson CH, Griffith CD, Shrimankar J, Douglas F: Gynaecomastia, neurofibromatosis and breast cancer. Breast 2004,13(1):77–79. 10.1016/j.breast.2003.08.002
Mendes-Pereira AMD, Sims T, Dexter K, Fenwick K, Assiotis I, Kozarewa I, Mitsopoulos C, Hakas J, Zvelebil M, Lord CJ, Ashworth A: Genome-wide functional screen identifies a compendium of genes affecting sensitivity to tamoxifen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012, 109: 2730–2735. 10.1073/pnas.1018872108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Kuntegowdanahalli Chinnagiriyappa Lakshmaiah, Anil N Kumar, Monika Lamba Saini and Kamal S Saini contributed equally to this work.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Lakshmaiah, K.C., Kumar, A.N., Purohit, S. et al. Neurofibromatosis type I with breast cancer: not only for women!. Hered Cancer Clin Pract 12, 5 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1897-4287-12-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1897-4287-12-5