Abstract
Background
Beliefs of caregivers about patient's pain have been shown to influence assessment and treatment of children's pain, now considered an essential part of cancer treatment. Painful procedures in hematology-oncology are frequently referred by children as the most painful experiences during illness. Aim of this study was to evaluate professionals' beliefs about painfulness of invasive procedures repeatedly performed in Pediatric Hemato-Oncology Units.
Methods
Physicians, nurses, psychologists and directors working in Hemato-Oncology Units of the Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology-Oncology (AIEOP) were involved in a wide-nation survey. The survey was based on an anonymous questionnaire investigating beliefs of operators about painfulness of invasive procedures (lumbar puncture, bone marrow aspirate and bone marrow biopsy) and level of pain management.
Results
Twenty-four directors, 120 physicians, 248 nurses and 22 psychologists responded to the questionnaire. The score assigned to the procedural pain on a 0-10 scale was higher than 5 in 77% of the operators for lumbar puncture, 97.5% for bone marrow aspiration, and 99.5% for bone marrow biopsy. The scores assigned by nurses differed statistically from those of the physicians and directors for the pain caused by lumbar puncture and bone marrow aspiration. Measures adopted for procedural pain control were generally considered good.
Conclusions
Invasive diagnostic-therapeutic procedures performed in Italian Pediatric Hemato-Oncology Units are considered painful by all the caregivers involved. Pain management is generally considered good. Aprioristically opinions about pain depend on invasiveness of the procedure and on the professional role.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Awareness and knowledge about children's pain increased substantially in the last three decades. Many studies have demonstrated that treatment-related pain and procedural pain are often the worst causes of pain in children with cancer[1, 2]. Young patients in fact often refer to lumbar puncture and bone marrow aspiration (procedures repeatedly conducted as part of diagnostic and therapeutic protocols) as the most painful experiences relating to their malignancy[2]. This experience is associated not only with the invasiveness of the procedures, but also with the children's fear of needles[3] and memories of previous procedures, which influence their reaction to subsequent procedures[4–6]. The child's life-long quality of life may be affected by these painful experiences[7].
Therefore procedural pain treatment is now considered an essential part of cancer patient's care, and recommendations were implemented in many nations[8–14].
Beliefs and attitudes of caregivers about patient's pain have been shown to influence assessment and treatment of children's pain[15].
Aim of this study was to estimate the beliefs of healthcare professionals about painfulness of the repeated invasive diagnostic-therapeutic procedures in Pediatric Hemato-Oncology Centers of the AIEOP network (Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology Oncology). A further objective was to evaluate whether or not personal and organizational factors could influence clinical staff's belief about pain. We also evaluated healthcare professionals' opinions about pain management in their own Center and about relevant factors that discourage use of sedation analgesia.
Methods
Participants
We developed a nationwide survey among the Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology-Oncology (AIEOP), which includes the centers treating more than 90% of pediatric cancer patients in Italy. All the healthcare professionals working in each Centers were involved, including physicians, nurses, psychologists and directors.
Questionnaires
The survey focused on the three invasive procedures (lumbar puncture, bone marrow aspiration and bone marrow biopsy) most frequently used in diagnostic and therapeutic protocols. The questionnaire (to be filled in anonymous format) [see additional file 1: The questionnaire] consisted of 4 closed questions:
-
1.
to indicate professional role (physician, nurse, psychologist, director) and working age (under 5 years, 5-10 years, 10 years)
-
2.
to indicate believed painfulness of the three procedures (lumbar puncture, bone marrow aspiration and bone marrow biopsy) on a 0-10 scale (0 = no pain, 10 = the worst pain)
-
3.
to indicate opinion about pain management on a 0-10 scale (0 = the worst control, 10 = the best control)
-
4.
to indicate on a Likert scale format from 0 to 4 (0 no importance, 4 maximum importance) the relevance of: shortage of time, lack of space and equipment, lack of adequate training, shortage of dedicated staff for managing sedation-analgesia, doubts about the safety of sedation-analgesia to determine the decision to perform procedures without sedation-analgesia.
The number of procedures carried out annually at each center (which we used as a dimensional parameter) and the number of physicians, nurses and psychologists on the staff were asked to the Director of each center.
Questionnaires and instructions were sent to Directors of each center in April, 2010. The deadline for returning completed questionnaires by all the healthcare professionals was by September, 30 2010.
Statistics
The results are reported as counts and percentages for the categorical variables (scores globally assigned to the pain and to its control), as quartiles, minimum and maximum for the ordinal ones (distribution of ratings assigned to procedural pain).
The number of lumbar punctures, bone marrow aspirates and biopsies was dichotomized according to median value (respectively 150-150-70); total number of procedures was dichotomized according to clinical consensus (500). The comparison between the number of procedures dichotomized was drawn using the Wilcoxon rank sum test.
The pain scores attributed by the different types of professional and the number of years spent in their professions were compared with the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the pairwise comparison with the Dunn procedure[16] when the test result was statistically significant at the 5% level. The analyses were conducted with the SAS rel. 9.1 for Windows (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
Results
Twenty-four of the 54 centers contacted responded to questionnaire (44.4%).
In these centers the number of procedures handled per year ranged from 50 to 1,565 and 33% of the centers performed more than 500 procedures/year. The responders were the directors of the 24 Centers, 120 physicians, 248 nurses, 22 psychologists, representing respectively: 48% of physicians, 52% of nurses, 42% of psychologists employed in the 24 Centers which responded.
Beliefs about pain
The score assigned on a scale of 0-10 exceeded 5 in 77.2% for the lumbar puncture, 97.5% for the bone marrow aspirate, 99.5% for the bone marrow biopsy [Figure 1].
Physicians, nurses, psychologists and directors scored differently the pain caused by lumbar puncture (p = 0.0001) and bone marrow aspiration (p < 0.0001), while there were no significant differences for bone marrow biopsy (p = 0.1354).
In particular, we found a significant difference (at 5% level) concerning lumbar puncture and bone marrow aspirate comparing nurses with physicians and directors [Figure 2]. Nurses tended to attribute higher score to pain.
Painfulness scored by different professional categories. Distributions of scores assigned by different professional categories on a 0-10 scale to believed painfulness of lumbar puncture (a), bone marrow aspiration (b), and bone marrow biopsy (c) (min, max, quartiles; 0 = no pain, 10 = the worst pain).
A correlation between operators' scoring of pain due to each procedure and the number of corresponding procedures performed annually in their own centers resulted significant for physicians about lumbar puncture and bone marrow aspiration (p = 0,0038 and p = 0,0002), for nurses about bone marrow aspiration (p = 0,0038), for psychologists about lumbar puncture and bone marrow aspiration (p = 0,0069 and p = 0,0212). The operators of centers performing a larger number of procedures tended to attribute lower pain scores whereas the responses of Directors seemed uninfluenced by the dimensions of the center.
Among nurses, a correlation between the pain score attributed to bone marrow biopsy and the number of years spent in the profession resulted statistically significant (p = 0.0005).
Opinions about procedural pain management
The control of procedural pain performed at each center was generally rated highly. However physicians, nurses, psychologists and directors expressed heterogeneous opinions (p = 0.0037): pairwise comparisons demonstrated a statistically significant difference at the 5% level between physicians and nurses [Figure 3].
Operators' opinions were not affected by the number of procedures performed annually at each center (p = 0.3853 for nurses, p = 0.9087 for physicians, p = 0.9169 for psychologists, p = 0.4268 for directors) and by the years of professional experience (p = 0.2398 for nurses, p = 0.3864 for physicians, p = 0.5365 for psychologist).
Opinion about factors discouraging use of sedation-analgesia
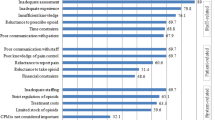
Among all responders, 60% of the nurses, 59% of the physicians, 77% of the psychologists, and 29% of Directors indicated the causes related to the performing the procedures without analgesia. The first relevant factors was the deficiency of dedicated staff for managing sedation-analgesia, relevant for 86% of nurses, 87% of physicians, 70% of psychologist, and 100% of Directors. This factor received the most highest score over all category: 42% of the nurses, 44% of the physicians, 29% of the psychologists, and 43% of the directors; the second most important reason was the doubts about the safety of sedation-analgesia (relevant for 65% of nurses), and following, the lack of space and equipment (relevant for 68% of the physicians and 72% of the directors), and the shortage of time (relevant for 65% of the psychologists).
Discussion
A few studies investigated health professionals' concerns about pain in infants and children with cognitive impairment[17–20]. We would to evaluate hemato-oncology health professionals' beliefs about pediatric procedural pain.
We found that grade of painfulness attributed aprioristically to procedural pain is overall high in the opinion of all the professional categories investigated. Given that a pain scoring more than 4 on scale of 0-10 must necessarily be treated in clinical practice our findings reflect the importance attributed to procedural pain by all the operators involved in patient care. The Italian situation confirms the overall increasing attention to pain in children, which has spread among all operators in the last three decades[21, 22]; a study comparing professionals' and children's opinions even demonstrated a certain tendency for professionals to overestimate pain in the pediatric oncology setting[23].
Painfulness attributed a priori to procedures seem to correlate with their invasiveness: barring a few cases, bone marrow aspiration and bone marrow biopsy were considered more painful than lumbar puncture. In particular, the scores attributed by all responders to the pain caused by bone marrow biopsy were homogeneously distributed around particularly high values (9 or 10/10).
Differences were found in the views expressed by the various professional categories: nurses' scores for pain due to lumbar puncture and bone marrow aspiration differed statistically from those of the physicians and directors, and were generally higher and more homogeneous. A such difference between nurses and physician was been already demonstrated[20, 24]. A possible explanation is the professional different training, and relationships with patients: nurses establish a "caring" relationship with the children, looking after them throughout the course of their disease, spending a lot of time close to patients and their families, so they may have more opportunities to see the children's anxiety and fear, and the side effects of painful procedures. Physicians and directors focus on the patient's "treatment" with a view to achieving their "recovery", a picture in which invasive procedures represent a necessary step in the treatment protocol. Many studies confirmed Nurses' involvement in the "care": workload perceived too great to provide quality patient care appeared the most important cause of stress for nurses following one of their patient's death[25, 26]; nurses administering chemotherapy felt the negative effects of a perceived decrease in their caring role, making them change from "nursing the patient" to "nursing the clinic"[27]. Nurses working routinely with children feel better when the children's pain is well controlled[28], and the amount of action they take on pediatric symptoms and their perceived effectiveness significantly influence nurses' levels of distress[29].
Unlike other experiences[20] pain management was generally considered good. Here again, however, nurses' opinions differed significantly from those of the physicians and psychologists, tending to be less optimistic.
Operators working in the centers performing yearly a great number of procedures attribute on average a lower believed painfulness to lumbar puncture and bone marrow aspirate, even if scores attributed to procedural pain persisted high. On the contrary, operators' opinion about pain management seems not to depend on the dimension of center. It means that an high workload is not perceived as a limit in providing an adequate pain management.
Sedation-analgesia is now globally considered the most important means for ensuring procedures without pain[9, 12]. Opinions expressed by the various professional groups in our study on the reasons for not using sedation-analgesia were fairly homogeneous; in particular, the shortage of staff was generally considered highly relevant and more important than other issues, confirming the relevance of perceived workload in operators' opinions.
Physicians and directors attributed importance to the shortage of space more often than other professional categories, reflecting their attention to the organizational aspects of procedural pain management. Low relevance was attributed by all the professionals except the psychologists to the shortage of time, which prompts two considerations: the need to perform a large number of procedures does not seem to affect the way pain is managed, even though this takes time; psychologists see the shortage of time as a more important problem than the other operators considered because they need to establish a particular relationship with patients, which takes time, closeness and a quiet environment.
Nurses attributed greater relevance to doubts about the safety of sedation-analgesia, confirming their closeness to the children and consequently greater concern about the treatments they receive.
This study has an important bias in the fact it inquires an a priori opinion which could change in the actual situation, when each individual children undergoes the procedure. Nevertheless, we consider this survey an important step to depict state of the art of procedural pain management in Italy, because operators' beliefs about pain could influence pain assessment and treatment and contribute to establish a widespread awareness on pain in children.
A further limit of this study is that we received less answers than expected: less than 50% of contacted Directors sent questionnaires completed by their staff. Probably it could be difficult to collect completed questionnaires from working staff in the overwhelmed context of Pediatric Oncology Units. However the limited number of received responses suggests other substantial questions: had the management of procedural pain reached a so well-defined and widespread organization to be no longer considered an interesting issue? Or, on the contrary, discussion and education on procedural pain control need to continue to increase operators' awareness for the best practice? The importance of operators' continue education in the maintenance of quality standards is demonstrated[30]. So this study could be an opportunity to promote education on procedural pain control in pediatric oncologic field.
Conclusions
In conclusion invasive diagnostic-therapeutic procedures performed in Italian Pediatric Hemato-Oncology Units are considered painful by all the healthcare professionals involved. Pain management is generally considered good.
Aprioristically beliefs about pain depend on invasiveness of the procedure and on the professional role; they are also partially influenced by the dimension of the centers. On the contrary they are not influenced by years of professional experience. Nurses attributed on average higher scores to pain and lower score to pain management, probably because of their main proximity to the child.
Staff shortages are perceived as the most important cause which prevents sedation-analgesia practice for painful procedures. Nurses attribute importance also to doubts about safety of pharmacological sedation.
So that, we want to highlight two possible optimization areas: first of them, a particular support should be assured to nurses who appear more influenced by workload and concerns about the patient in their role of "care". This support could include psychological support, stress management programs, educational programs about sedation-analgesia, and also a farsighted organizational policy (e.g. reducing working hours or time spent in contact with patients, increasing the nurse/patient ratio)[31]. Second, it should be important to educate all the caregivers about the extremely complex psycho-physical nature of pain experience, not necessarily related with the invasiveness of the procedure[32, 33]; they should learn that all available means should be adopted to control every child's anxiety and pain, including both pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments.
References
Miser AW, Dothage JA, Wesley RA, Miser JS: The prevalence of pain in a pediatric and young adult cancer population. Pain. 1987, 29: 73-83. 10.1016/0304-3959(87)90180-1.
Hedstrom M, Haglund K, Skolin L, von Essen L: Distressing events for children and adolescents with cancer: child, parent and nurse perceptions. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs. 2003, 20: 120-32. 10.1053/jpon.2003.76.
Rice LJ: Needle phobia: an anesthesiologist's perspective. J Pediatr. 1993, 122: s9-
Chen E, Zelter LK, Craske MG, Katz ER: Children's memories for painful cancer treatment procedures: implication for distress. Child Dev. 2000, 71: 933-47. 10.1111/1467-8624.00200.
Weisman SJ, Bernstein B, Schechter NL: Consequences of inadequate analgesia during painful procedures in children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1998, 152: 147-49.
Dahlquist LM, Gil KM, Armstrong FD, DeLawyer DD, Greene P, Wuori D: Preparing children for medical examinations: the importance of previous medical experience. Health Psychol. 1986, 5: 249-59.
Pate ME, Blount RL, Cohen LL, Smith AJ: Childhood medical experience and temperament as predictors of adult functioning in medical situations. Children's Heath Care. 1996, 25: 281-98. 10.1207/s15326888chc2504_4.
Zeltzer LK, Altman A, Cohen D, LeBaron S, Munuksela EL, Schechter NL: American Academy of Pediatrics report of the subcommittee on the management of pain associated with procedures in children with cancer. Pediatrics. 1990, 86: 826-31.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Drugs: Guidelines for monitoring and management of pediatric patients during and after sedation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Pediatrics. 1992, 89: 1110-15.
Hoffman GM, Nowakowski R, Troshynski TJ, Berens RJ, Weisman SJ: Risk reduction in pediatric procedural sedation by application of an American Academy of Pediatrics/American Society of Anesthesiologists Process Model. Pediatrics. 2002, 109: 236-43. 10.1542/peds.109.2.236.
Knape JT, Adriaensen H, van Aken H, Blunnie WP, Carlsson C, Dupont M, Pasch T: Board of Anaesthesiology of the European Union of Medical Specialists. Guidelines for sedation and/or analgesia by non-anaesthesiology doctors. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2007, 24: 563-67. 10.1017/S0265021506002092.
Krauss B, Green SM: Primary care: sedation and analgesia for procedures in children. N Engl J Med. 2000, 342: 938-45. 10.1056/NEJM200003303421306.
Meyer S, Grundmann U, Gottschling S, Kleinschmidt S, Gortner L: Sedation and analgesia for brief diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in children. Eur J Pediatr. 2007, 166: 291-302. 10.1007/s00431-006-0356-0.
Lowrie L, Weiss A, Lacombe C: The pediatric sedation unit. A mechanism for pediatric sedation. Pediatrics. 1998, 102: 2-9. 10.1542/peds.102.1.e2.
Hamers JP, Abu-Saad HH, Halfens RJ, Schumacher JN: Factors influencing nurses pain assessment and intervention in children. J Adv Nurs. 1994, 20: 853-60. 10.1046/j.1365-2648.1994.20050853.x.
Dunn OJ: Multiple comparisons using rank sum. Technometrics. 1964, 6: 241-52. 10.2307/1266041.
Porter FL, Wolf CM, Gold J, Lotsoff D, Miller JP: Pain and pain management in newborn infants: a survey of physicians and nurses. Pediatrics. 1997, 100: 626-32. 10.1542/peds.100.4.626.
Breau LM, MacLaren J, McGrath PJ, Camfield CS, Finley GA: Caregivers' beliefs regarding pain in children with cognitive impairment: relation between pain sensation and reaction increases with severity of impairment. Clin J Pain. 2003, 19: 335-44. 10.1097/00002508-200311000-00001.
Breau LM, McGrath PJ, Stevens B, Beyene J, Camfield C, Finley GA, Franck L, Gibbins S, Howlett A, McKeever P, O'Brien K, Ohlsson A: Judgments of pain in the neonatal intensive care setting: a survey of direct care staff's perceptions of pain in infants at risk for neurological impairment. Clin J Pain. 2006, 22: 122-29. 10.1097/01.ajp.0000154045.45402.ec.
Andersen RD, Greve-Isdahl M, Yjlli L: The opinions of clinical staff regarding neonatal procedural pain in two norvegian neonatal intensive care units. Acta Paediatrica. 2007, 96: 1000-1003. 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2007.00190.x.
Schechter NL: The undertreatment of pain in children: an overview. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1989, 36: 781-94.
Rana S: Pain: a subject ignored [Letter]. Pediatrics. 1987, 79: 309-10.
Ljungman G, Kreuger A, Gordh T, Sörensen S: Pain in pediatric oncology: do the experience of children and parents differ from those of nurses and physicians?. Ups J Med Sci. 2006, 111: 87-95. 10.3109/2000-1967-023.
Grosclaude C, Asehnoune K, Demeure D, Millet S, Champin P, Naux E, Malinge M, Lejus C: Opinions of different professional categories about the intensity of procedural pain in adult intensive care units. Annales Françaises d'Anesthésie et de Réanimation. 2010, 29: 884-888.
Hinds PS, Puckett P, Donohoe M, Milligan M, Payne K, Phipps S, Davis SE, Martin GA: The impact of a grief workshop for pediatric oncology nurses on their grief and perceived stress. J Pediatr Nurs. 1994, 9: 388-97.
Emery JE: Perceived sources of stress among pediatric oncology nurses. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs. 1993, 10: 87-92. 10.1177/104345429301000303.
Mcilfatrick S, Sullivan K, McKenna H: Nursing the clinic vs nursing the patient: nurses' experience of a day hospital chemotherapy service. J Clin Nurs. 2006, 15: 1170-8. 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2006.01495.x.
Grulke N, Larbig W, Kächele H, Bailer H: Distress in patients undergoing allogenic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation is correlated with distress in nurses. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2009, 13: 361-67. 10.1016/j.ejon.2009.04.010.
Rheingans JI: Relationship between pediatric oncology nurses' management of patients' symptoms and job satisfaction. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs. 2008, 25: 312-22. 10.1177/1043454208323296.
Moulding NT, Silagy CA, Weller DP: A framework for effective management of change in clinical practice: dissemination and implementation of clinical practice guidelines. Qual Health Care. 1999, 8: 177-83. 10.1136/qshc.8.3.177.
Sherman AC, Edwards D, Simonton S, Mehta P: Caregiver stress and burnout in an oncology unit. Palliat Support Care. 2006, 4: 65-80.
Mc Grath PA: Psychological aspects of pain perception. Pain in infants, children and adolescents. Edited by: Schechter NL, Berde CB, Yaster M. 1993, Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, 39-64.
Schechter NL, Bernstein BA, Beck A, Hart L, Scherzer L: Individual differences in children's response to pain: role of temperament and parental characteristic. Pediatrics. 1991, 87: 171-77.
Acknowledgements
Centers participating to the survey, listed in alphabetical order of corresponding Directors
A. Acquaviva, M.D. Dipartimento di Pediatria, Ostetricia e Medicina della Riproduzione Università degli Studi di Siena;
M. Aricò, M.D, A. Messeri, M.D. Dipartimento AI Oncoematologia Pediatrica e Cure Domiciliari, UO Oncoematologia Pediatrica Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Meyer, Firenze;
L. Battisti, M. D. Pediatria, Ospedale Regionale di Bolzano;
A. Biondi, M.D., D. Longoni, M.D., Clinica Pediatrica dell'Università Milano-Bicocca, Monza;
C. Borgna Pignatti M.D, R. Burnelli M.D. Dipartimento di Medicina Clinica e Sperimentale, Sezione di Pediatria Università di Ferrara;
M. Carli, M.D. Oncoematologia Pediatrica, Dipartimento di Pediatria, Università di Padova, Padova, Italy;
S. Cesaro, M.D. Oncoematologia Pediatrica, Policlinico Rossi, Verona;
C. Consarino, M.D. Unità Operativa di Ematologia ed Oncologia Pediatrica Az. Osp. "Pugliese-Ciaccio", Catanzaro;
D. De Mattia, M.D. N. Santoro, M.D. Dipartimento Biomedicina Età Evolutiva, UO Pediatrica I Policlinico, Bari;
F. Fagioli, M.D. Ospedale Infantile Regina Margherita, Torino;
C. Favre, M.D. Centro di Onco-Ematologia Pediatrica e Trapianto di Midollo Osseo Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Pisana, Ospedale S. Chiara, Pisa;
G. Izzi, M.D. UO di Pediatria e Oncologia Pediatrica, Az. Ospedaliera di Parma Ospedali Riuniti, Parma;
S. Marino, M.D. Divisione Ematologia-Oncologia Pediatrica, Clinica Pediatrica di Catania;
M. Mascarin, M.D. Centro Integrato di Emato-Oncologia pediatrica e dell'adolescenza, IRCCS Centro di Riferimento Oncologico-Aviano, Pordenone;
M. Massimino, M.D. Divisione di Oncologia Pediatrica, Istituto Nazionale Studio e Cura Tumori, Milano;
P. Paolucci, M.D. UO Ematologia,Oncologia e trapianto, Azienda Policlinico di Modena, Modena;
P. Pierani, M.D. Centro Regionale di Oncoematologia pediatrica Ospedale dei Bambini "G.Salesi", Clinica Pediatrica di Ancona;
V. Poggi M.D., F. Borrometi M.D. Dipartimento di Oncologia AO Santobono-Pausilipon, Napoli;
G. Presta M.D., A. Civino M.D. Unità Operativa di Pediatria - U.T.I.N. Az. Ospedaliera "Cardinale G. Panico" Tricase, Lecce;
D. Sperlì, M.D. Unità Operativa di Pediatria Azienda Ospedaliera Annunziata, Cosenza;
P. Tamaro M.D., A. Zanazzo M.D. UO Emato-Oncologia Pediatrica Università degli Studi di Trieste, Ospedale Infantile Burlo Garofolo, Trieste;
R. Targhetta M.D., R. Mura M.D. Ospedale Regionale per le Microcitemie, Cagliari;
M. Zecca M.D. Onco-Ematologia Pediatrica Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, Pavia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
CP wrote the paper. CA and FB supervised the study. CA, LS, FB coordinated the research. SC, LS and CA recruited the responders. CA and CP analyzed the data. MIF, CA, CP, SC and LS discussed the results. ACF provided statistical analysis and results elaboration. The authors confirm they have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Chiara Po', Franca Benini, Laura Sainati, Anna C Frigo, Simone Cesaro, Maria I Farina and Caterina Agosto contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
13052_2011_153_MOESM1_ESM.DOC
Additional files 1: "Questionnaire investigating operators' beliefs about painful procedures". The file is the questionnaire (to be filled in anonymous format) investigating beliefs of operators about painfulness of invasive procedures (lumbar puncture, bone marrow aspirate and bone marrow biopsy) and level of pain management. (DOC 36 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Po', C., Benini, F., Sainati, L. et al. The opinion of clinical staff regarding painfulness of procedures in pediatric hematology-oncology: an Italian survey. Ital J Pediatr 37, 27 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1824-7288-37-27
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1824-7288-37-27