Abstract
Background
Human T lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I)-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) is a chronic myelopathy characterized by motor dysfunction of the lower extremities and urinary disturbance. Immunomodulatory treatments are the main strategy for HAM/TSP, but several issues are associated with long-term treatment. We conducted a clinical trial with prosultiamine (which has apoptotic activity against HTLV-I-infected cells) as a novel therapy in HAM/TSP patients.
Methods
We enrolled 24 HAM/TSP patients in this open-label clinical trial. Prosultiamine (300 mg, orally) was administered once daily for 12 weeks. We monitored changes in the motor function of the lower extremities and urinary function as well as copy numbers of the HTLV-I provirus in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).
Results
Improvement in the motor function of the lower extremities based on a reduction in spasticity (for example, decrease in time required for walking and descending a flight of stairs) was observed. In an urodynamic study (UDS), bladder capacity and detrusor pressure and then maximum flow rate increased significantly. Detrusor overactivity and detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia improved in 68.8% and 45.5% of patients observed at pretreatment, respectively. Improvement in UDS corresponded with improvements in the score of nocturia-quality of life questionnaire. HTLV-I proviral copy numbers in PBMCs decreased significantly (approximately 15.4%) compared with pretreatment levels.
Conclusions
These data suggest that prosultiamine can safely improve motor dysfunction of the lower extremities and urinary disturbance as well as reduce HTLV-I provirus levels in peripheral blood. It therefore has potential as a new therapeutic tool for HAM/TSP patients.
Trial registration
University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trials Registry (UMIN-CTR) number, UMIN000005969.
Please see related commentary: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1741-7015/11/183.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Human T lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) infects approximately 10 to 20 million people worldwide, mainly in large endemic areas such as southern Japan, the Caribbean, Central and South America, the Middle East, Melanesia, and equatorial regions of Africa [1, 2]. HTLV-I is a human retrovirus and the causative agent of adult Tcell leukemia and HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) [3, 4]. HAM/TSP is a chronic progressive myelopathy characterized by bilateral pyramidal tracts involved with sphincteric disturbances [5]. Only a small proportion of HTLV-I-infected individuals develop HAM/TSP. However, the main neurological symptoms (for example, motor dysfunction of the lower extremities accompanied by urinary disturbance) are progressive and lead to a deterioration in the quality of life (QoL) of patients once the myelopathy develops. Therefore, novel and safe therapeutic regimens are needed for HAM/TSP patients to use as treatment, or to prevent disease progression.
The primary neuropathological feature of HAM/TSP is chronic inflammation in the spinal cord caused by high HTLV-I proviral load in peripheral blood. Immunomodulatory therapy such as corticosteroid hormones and interferon (IFN)α has been the main treatment administered to HAM/TSP patients to date [6]. Although these treatments have produced good results in the short term, their overall efficacy is controversial [6, 7]. In addition, it is not known if these treatments can be tolerated as a long-term or lifelong treatment against HAM/TSP, or whether they are necessary in the therapeutic strategy against HAM/TSP. When treating HAM/TSP, the optimal treatment is elimination of HTLV-I-infected cells from peripheral blood because HTLV-I-infected CD4+ T cells are the first responders in the immunopathogenesis of HAM/TSP [8].
(N-[(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl) methyl]-N-[4-hydoxy-1-methyl-2-(propyldithio)-1-butenyl]-formamide) is known as prosultiamine and as Alinamin®. It is a product of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited (Osaka, Japan). Prosultiamine is a homolog of allithiamine, which was originally synthesized from thiol-type vitamin B1 and allicin [9]. For stability in the blood and efficient access of vitamin B1 to tissues, prosultiamine was developed after allyl disulfide derived from allicin was substituted with propyl disulfide in the structure of allithiamine [10]. Importantly, prosultiamine is pharmacologically stable and is readily available for the treatment of Wernicke’s encephalopathy and polyneuropathy induced by deficiency of vitamin B1. Moreover, it has been shown to be safe for use in Japan. Therefore, this drug could be utilized immediately for conducting clinical trials in individuals with HAM/TSP.
Recently, we demonstrated that prosultiamine can induce the caspase-dependent apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected cells through disruption of intracellular redox reactions by a disulfide moiety in its structure [11]. Based on these data, we undertook a clinical trial based on the intravenous administration of prosultiamine in HAM/TSP patients with the purpose of targeting HTLV-I-infected cells [11]. We found that prosultiamine administration for 2 weeks was safe and induced clinical improvement. Examples of such improvement included a decrease in (i) spasticity of the lower extremities and (ii) levels of HTLV-I provirus in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to 30% to 50% of pretreatment levels.
As mentioned above, we do not know if prosultiamine can be tolerated as a long-term treatment against HAM/TSP or indeed if it is necessary in the therapeutic strategy against HAM/TSP. Therefore, in the present study, we administered prosultiamine via the oral route for 12 weeks in subjects with HAM/TSP. We found that such treatment could result in (i) improved motor function in the lower extremities based on a decrease in spasticity, (ii) appreciable amelioration of associated urinary disturbance, and (iii) a decrease in the level of HTLV-I provirus in peripheral blood.
Methods
Ethical approval of the study protocol
This study protocol was approved by the clinical studies review boards of Nagasaki University Hospital (Nagasaki, Japan). The clinical trial was registered in the University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trials Registry (UMIN-CTR) UMIN000005969. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients enrolled in the study for both participation in the study, and for inclusion of personal data as shown in Table 1.
Patients
We enrolled 24 HAM/TSP patients (17 women and 7 men; 31 to 80 years (mean ± SD; 60.1 ± 11.2 years)) who fulfilled criteria described previously [12]. The duration of illness was 3 to 51 years (mean ± SD; 20.9 ± 12.1 years). Motor function scores were rated from 0 to 13 according to the motor disability score described by Osame et al. [13]. Concomitant therapies such as immunomodulators and drugs for the neurogenic bladder were continued on the condition that the dose was kept constant during the study period. Intermittent self-catheterization with regard to voiding was noted except in cases 7, 8, 10, 17, 21, 22, and 24. Patient profiles are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
Study design
Treatment protocol
Prosultiamine was imported from Ildon Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd (Seoul, South Korea). Capsulated prosultiamine (300 mg, orally) was administered once daily for 12 weeks.
Assessment of effect
Neurological assessment
We monitored changes in neurological signs, motor disability scores, time required for walking 10 m, and time required for walking down a flight of stairs at 4-week intervals. Spasticity of the lower extremities was graded using the modified Ashworth scale (MAS) [14].
Urological assessment
Subjective symptoms were evaluated using the scores of the Nocturia Quality of Life (N-QoL) questionnaire [15–17] at 4-week intervals. The N-QoL questionnaire comprised 13 items and dealt with daytime energy, worry, productivity, sleep, and vitality. The total score ranged from 0 (poorest QoL) to 100 (best QoL). The Duet® Logic G2 system (Mediwatch UK Ltd., Rugby, UK) was used for the urodynamic study (UDS). Bladder capacity, detrusor pressure, maximum flow rate, detrusor overactivity (DO) and detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia (DSD) were evaluated by UDS.
Quantification of HTLV-I proviral load
For quantitative analyses of HTLV-I proviral loads, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was carried out in a Light-Cycler® FastStart DNA Master (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) based on fluorescence detection with SYBER® Green, as described previously [11]. Briefly, genomic DNA samples from PBMCs from HAM/TSP patients were prepared using a Genomic DNA Extraction kit (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Osaka, Japan) and were subjected to RT-PCR in a LightCycler PCR system using Tax-specific primers, that is, forward primer (5′- AAACAGCCCTGCAGATACAAAGT-3′) and reverse primer (5′-ACTGTAGAGCTGAGCCGATAACG-3′), as well as β-actin-specific primers, that is, forward primer (5′-GCCCTCATTTCCCTCTCA-3′) and reverse primer (5′-GCTCAGGCAGGAAAGACAC-3′). The PCR condition for Tax was 40 cycles of denaturation (95°C, 15 s), annealing (55°C, 5 s), extension (72°C, 10 s). That for β-actin was 32 cycles of denaturation (95°C, 15 s), annealing (62°C, 5 s), and extension (72°C, 15 s). The HTLV-I proviral load per 10,000 cells was calculated according to the following formula: (copy number of Tax)/(copy number of β-actin/2) × 10,000
Statistical analyses
The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for statistical analyses of the change of HTLV-I proviral copy numbers and on the N-QoL scores or the urodynamic study except for DO and DSD. The McNemar test was used for statistical analyses of improvement of spasticity, DO and DSD. JMP 10 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) was used as the software for statistical analyses. P< 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Improvement of motor function of the lower extremities
Improvement in Osame’s motor function score (OMDS) was observed in three patients during treatment (Table 1). After 12 weeks of treatment, improvement of more than 1 grade of the degree of spasticity (evaluated according to MAS) was observed in 15 of 19 patients in whom spasticity of the lower extremities was observed before treatment (% improvement; 78.9, P = 0.0003, McNemar test) (Table 1). In time required for walking 10 m in 18 ambulatory patients, the decrease ranged from 4.4% to 36.8% was observed in 11 patients although the increase ranged from 4.5% to 52.6% was observed in 7 patients (Table 2). In time required for walking down a flight of stairs in 12 patients, the decrease ranged from 2.3% to 53.2% was observed in 10 patients although the increase of 2.4% or 6.3% was observed in 2 patients (Table 2).
Improvement in urinary function
The conserved overall score of the N-QoL questionnaire was significantly improved, with a significant improvement of subscale scores at 12 weeks post treatment (Table 3). We compared urinary function by UDS at pretreatment with that at 12 weeks after treatment initiation. Bladder capacity and detrusor pressure were significantly increased from 341.3 (SD 127.2) ml to 391.0 (SD 139.9) ml (P = 0.0097), and 16.8 (SD 15.6) cm/H2O to 27.5 (SD 15.3) cm/H2O (P = 0.0001), respectively, by this treatment (Figure 1a,b). As analyzed in 18 patients whose own voiding function was partially reserved, the maximum flow rate was increased significantly from 7.5 (SD 6.2) ml/s to 10.2 (SD 5.6) ml/s (P = 0.0139) (Figure 1c). Moreover, DO improved in 68.8% (11 of 16 patients observed at pretreatment) by this treatment (P = 0.0094, McNemar test) (Table 2). DSD also improved in 45.5% (5 of 11 patients observed at pretreatment) 12 weeks after the start of treatment (P = 0.0736, McNemar test) (Table 2).
Change in bladder function as evaluated by urodynamic study. Bladder capacity (a) and detrusor pressure (b) increased significantly 12 weeks after prosultiamine treatment. Maximum flow rate (c) increased significantly 12 weeks after prosultiamine treatment as assessed in 18 patients whose voiding function alone was partially reserved. Statistical significance was determined by the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Decrease in HTLV-I proviral copy numbers in PBMCs
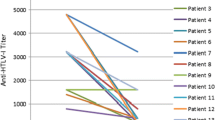
We monitored changes in copy numbers of the HTLV-I provirus in PBMCs at pretreatment as well as 4, 8, and 12 weeks after treatment commencement (Figure 2a). HTLV-I proviral copy numbers in 104 PBMCs decreased gradually from 2,127 (SD 1,932) at pretreatment to 1,961 (SD 1,692) (P = 0.2776, vs pretreatment), 1,845 (SD 1,693) (P = 0.0152, vs pretreatment) and 1,799 (SD 1,676) (P = 0.0207, vs pretreatment) at 4, 8, and 12 weeks after treatment, respectively. The level of HTLV-I proviral copy numbers 12 weeks after treatment decreased significantly (approximately 15.4%) from pretreatment levels. Figure 2b shows the changes in HTLV-I proviral copy numbers in each case between pretreatment and 12 weeks after treatment commencement. A decrease of approximately 30% to 50% in HTLV-I proviral copy numbers was observed in cased 8, 9, 11, 15 and 22.
Change in human T lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) proviral copy numbers in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). (a) HTLV-I proviral copy numbers from 104 PBMCs decreased gradually until 12 weeks after prosultiamine treatment. The level of HTLV-I proviral copy numbers 12 weeks after prosultiamine treatment decreased by 15.4% compared with the time at pretreatment. (b) Changes in HTLV-I proviral copy numbers in each case between pretreatment and 12 weeks after prosultiamine treatment. Statistical significance was determined by the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Adverse effects
There were no serious adverse effects except mild epigastric discomfort rated as ‘2’ evaluated according to the Global Overall Symptom scale [18] in three HAM/TSP patients. This symptom immediately resolved after this clinical trial.
Discussion
Effective therapeutic regimens are needed urgently to treat such myelopathic symptoms of HAM/TSP as spasticity of lower extremities and urinary disturbance. To this end, we administered prosultiamine via the oral route for 12 weeks in subjects with HAM/TSP. This treatment improved (i) the motor ability of the lower extremities by decreasing spasticity, and (ii) urinary function. The mean duration of illness of the patients enrolled in this study was relatively long (approximately 21 years), so the efficacy of this treatment is promising. Indeed, these data suggest that the pathological processes in the spinal cord of HAM/TSP patients are partially reversible and treatable even if the tissues are damaged over a long period of time.
The most striking effect in this clinical trial was the amelioration of urinary disturbance in HAM/TSP patients. The common urodynamic findings in HAM/TSP patients are DO, DSD and detrusor hypoactivity [19]. However, as evaluated by UDS, prosultiamine treatment resulted in a significant increase in detrusor pressure and bladder capacity followed by an increase in maximum flow rate with improved DO. DSD also improved in 45.5% (5 of 11 patients observed at pretreatment) (P = 0.0736). Although this value did not reach statistical significance, it showed a tendency of improvement. This is the first time that the therapeutic effect for urinary dysfunction in HAM/TSP patients was evaluated in detail by UDS. With respect to the effect of urinary conditions on the QoL of HAM/TSP patients, nocturia, urgency, increased frequency of urination and dysuria have been reported to be the main problems [20]. Therefore, we evaluated the change in QoL of patients using N-QoL questionnaires during treatment. The improved UDS corresponded with improvements in the score of N-QoL questionnaires. Concomitant pharmacological therapies for the neurogenic bladder were continued during the present study. However, the efficacy of prosultiamine treatment, even in patients who were not having concomitant therapies (cases 5, 6, 11, 13, 23, and 24), strongly suggested that urological improvement was dependent solely upon prosultiamine treatment (Table 1). Overall, these data suggest that prosultiamine treatment can reverse bladder dysfunction in HAM/TSP patients.
Recently, two reports have focused on targeting HTLV-I in therapeutic trials against HAM/TSP. One study used reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitors, whereas the other used a histone deacetylase enzyme inhibitor for treatment [21, 22]. In the former, the results of combination therapy (zidovudine + lamivudine) in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study suggested that RT inhibitors were not effective for targeting HTLV-I for the treatment of HAM/TSP. In the latter study, long-term treatment using valproic acid did not reduce the number of HTLV-I-infected cells in peripheral blood [22]. A decrease in the HTLV-I provirus in PBMCs was one of the primary endpoints in our recent report [11]. Indeed, oral administration of prosultiamine induced a significant decrease in HTLV-I proviral copy numbers in PBMCs, However, the rate of reduction was not as high as we had expected. This finding might suggest a limitation of the protocol used in the present study. Thus, the remarkable improvement of motor dysfunction and urinary function in the present study cannot be attributed solely to a decrease in HTLV-I proviral copy numbers in PBMCs. The exact mechanism is not known. Prosultiamine was originally developed for efficient access of vitamin B1 to nervous tissues [10]. Although this drug is reduced to a part thiamine and propyl disulfide by the intracellular reducing system after penetration to the cells [10], it is suspected that the disruption of intracellular redox system is induced during reduction of disulfide bond leading to the apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected cells [11]. Therefore, it might be conceivable that, as one of the mechanisms, this drug functions to induce the apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected cells in the spinal cord even if the extent of reduction of the number of HTLV-I-infected cells in PBMCs is relatively small. Further investigations including analysis of cerebrospinal fluid are needed to elucidate the exact mechanism of action of prosultiamine.
Conclusions
In the present work we have demonstrated that oral administration of prosultiamine can safely promote improvement of motor function of the lower extremities based on a reduction of spasticity along with appreciable amelioration of urinary disturbance associated with a decrease in the amount of HTLV-I provirus in peripheral blood. Our results suggest that prosultiamine could be a promising therapeutic tool for HAM/TSP patients. Therefore, further studies are warranted, such as the evaluation of prosultiamine treatment against HAM/TSP in a large-scale, randomized, controlled study.
References
De-Thé G, Bomford R: An HTLV-I vaccine: why, how, for whom?. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993, 9: 381-386.
Hollsberg P, Hafler DA: Pathogenesis of diseases induced by human T-lymphotropic virus type I infection. N Engl J Med. 1993, 328: 1173-1182.
Yoshida M: Multiple viral strategies of HTLV-1 for dysregulation of cell growth control. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001, 19: 475-496.
Osame M, Usuku K, Izumo S, Ijichi N, Amitani H, Igata A, Matsumoto M, Tara M: HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new entity. Lancet. 1986, 8488: 1031-1032.
Osame M, Matsumoto M, Usuku K, Izumo S, Ijichi N, Amitani H, Tara M, Igata A: Chronic progressive myelopathy associated with elevated antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type I and adult T-cell leukemia-like cells. Ann Neurol. 1987, 21: 117-122.
Nakamura T, Nishiura Y, Eguchi K: Therapeutic strategies in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2009, 9: 137-149.
Kira J, Fujihara K, Itoyama Y, Goto I, Hasuo K: Leukoencephalopathy in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: MRI analysis and a 2 year follow-up study after corticosteroid therapy. J Neurol Sci. 1991, 106: 41-49.
Nakamura T: HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP): the role of HTLV-I-infected Th1 cells in the pathogenesis, and therapeutic strategy. Folia Neuropathol. 2009, 47: 182-194.
Fujiwara M, Watanabe H, Matsui K: “Allithiamine” a newly found derivative of vitamine B1. I. discovery of allithiamine. J Biochem (Tokyo). 1954, 41: 29-39.
Matsukawa T, Yurugi S: On the structure of allithiamine. Proc Japan Acad. 1952, 28: 146-149.
Nishiura Y, Nakamura T, Fukushima N, Nakamura H, Ida H, Aramaki T, Eguchi K: Disulfide-mediated apoptosis of human T-lymphotropic virus type-I (HTLV-I)-infected cells in patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Antivir Ther. 2009, 14: 533-542.
Osame M: Review of WHO Kagoshima meeting and diagnostic guidelines for HAM/TSP. Human Retrovirology: HTLV. Edited by: Blattner WA. 1990, New York, NY: Raven, 191-197.
Osame M, Igata A, Matsumoto M: HTLV-I-associated myelopathy (HAM) revisited. HTLV-I and the Nervous System. Edited by: Román GC, Vernant J-C, Osame M. 1989, New York, NY: Alan R, Liss, Inc, 213-223.
Bohannon RW, Smith MB: Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys Ther. 1987, 67: 206-207.
Abraham L, Hareendran A, Mills IW, Martin ML, Abrams P, Drake MJ, MacDonaqh RP, Noble JG: Development and validation of a quality-of-life measure for men with nocturia. Urology. 2004, 63: 481-486.
Yu HJ, Chen FY, Huang PC, Chen THH, Chie WC, Liu CY: Impact of nocturia on symptom-specific quality of life among community-dwelling adults aged 40 years and older. Urology. 2006, 67: 713-718.
Yoshida M, Ikeda S: Development of the Japanese version of the nocturia quality of life questionnaire (N-QOL) [in Japanese]. Jpn J Urol Surg. 2010, 23: 833-838.
Veldhuyzen Van Zanten SJO, Chiba N, Armstrong D, Barkun AN, Thomson ABR, Mann V, Escobedo S, Chakraborty B, Nevin K: Validation of a 7-point global overall symptom scale to measure the severity of dyspepsia symptoms in clinical trials. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006, 23: 521-529.
Oliveira P, Castro NM, Carvalho EM: Urinary and sexual manifestations of patients infected by HTLV-1. Clinics. 2007, 62: 191-196.
Castro NM, Rodrigues W, Freitas DM, Muniz A, Oliveira P, Carvalho EM: Urinary symptoms associated with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I infection: evidence of urinary manifestations in large group of HTLV-I carriers. Urology. 2007, 69: 813-818.
Taylor GP, Goon P, Furukawa Y, Green H, Barfield A, Mosley A, Nose H, Babiker A, Rudge P, Usuku K, Osame M, Bangham CRM, Weber JN: Zidovudine plus lamivudine in human T-lymphotropic virus type-I-associated myelopathy: a randomized trial. Retrovirology. 2006, 3: 63.
Olindo S, Belrose G, Gillet N, Rodriguez S, Boxus M, Verlaeten O, Asquith B, Bangham C, Signaté A, Smadja D, Lezin A, Césaire R, Willems L: Safety of long-term treatment of HAM/TSP patients with valproic acid. Blood. 2011, 118: 6306-6309.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the nurses who supported this study as well as Kaori Furukawa for providing excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by a Health and Labour Sciences Research Grant on Intractable Diseases (‘Clinical research for HAM/TSP toward identification of new biomarkers and establishment of therapeutic strategies’; H22-nanchi-ippan-013) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
TN designed the study, assessed the neurological findings, analyzed data, and wrote the paper. TMatsuo designed the study, analyzed data, and contributed to the urological studies. HSakai contributed to the urological studies. TF and TN-M assessed the neurological findings. TN, TF and SY managed the blood supply and laboratory studies. KY and HSasaki handled the prosultiamine and enclosed it in capsules. IK, TMatsuzaki, YN, KN, HN, KS, and AK were involved in managing the patients. All authors contributed to the manuscript and approved the final version of the report.
Tatsufumi Nakamura, Tomohiro Matsuo contributed equally to this work.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamura, T., Matsuo, T., Fukuda, T. et al. Efficacy of prosultiamine treatment in patients with human T lymphotropic virus type I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: results from an open-label clinical trial. BMC Med 11, 182 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-182
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-182