Abstract
Introduction
In recent decades, the foreign population in Spain has increased significantly, particularly for Catalonia, an autonomous region of Spain (2.90% in 2000 and 15.95% in 2010) and in particular Girona province (6.18% in 2000 and 21.55% in 2010). Several studies have shown a lower use of family planning methods by immigrants. This same trend is observed in Spain. The objective of this paper is to determine the existence of differences and possible sources of inequity in the use of family planning methods among health service users in Catalonia (Spain) by sex, health status, place of birth and socioeconomic conditions.
Methods
Data were taken from an ad-hoc questionnaire which was compiled following a qualitative stage of individual interviews. Said questionnaire was administered to 1094 Catalan public health service users during 2007. A complete descriptive analysis was carried out for variables related to public health service users’ sociodemographic characteristics and variables indicating knowledge and use of family planning methods, and bivariate relationships were analysed by means of chi-square contrasts. Considering the use (or non-use) of family planning methods as a dependent variable and a set of demographic, socioeconomic and health status variables as explanatory factors, the relationship was modelled using mixed models.
Results
The analysed sample is comprised of 54.3% women and 45.7% men, with 74.3% natives (or from the EU) and 25.7% economic immigrants. 54.8% use some method of family planning, the condom (46.7%) and the pill (28.0%) being the two most frequently used methods. Statistical modelling indicates that those factors which most influence the use of family planning methods are level of education (30.59% and 39.29% more likelihood) and having children over 14 (35.35% more likelihood). With regard to the origin of the user, we observe that patients from North Africa,sub. Saharan Africa and Asia are less likely to use family planning methods (36.68%, 38.59% and 70.51%, respectively).
Conclusions
The use of family planning methods is positively related to a higher level of education and having children over 14. Factors such as sex, age, income and self-perceived health do not appear to influence their use. Furthermore, being a native of this country, the European Union or Central/South America represents a greater likelihood of use than being African or Asian. Although no general differences in use were found between sexes, the difference found in the case of Asian women stands out, with a higher likelihood of use.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
In recent decades, the foreign population in Spain has increased from 1.60% of the total population in 1998 to 12.20% in 2011 [1]. Changes in the annual rates are even greater for Catalonia, an autonomous region of Spain, (2.90% in 2000 and 15.95% in 2010) and in particular Girona province (6.18% in 2000 and 21.55% in 2010) [2].
Inequity in access to and use of different contraceptive methods affects human rights [3]. Although for immigrants from low-income countries or countries with deficient health services migrating may provide a greater opportunity to access sexual and reproductive health services in the host country, it is often the different barriers to access (such as difficulty with the language, dealing with health professionals or lack of information) in addition to structural, social and cultural factors, that determine real opportunities to use said services.
Numerous studies have analysed the situation regarding the use of family planning methods in developing countries [4–13] and developed countries [14–18], and studies also exist on differences between native and immigrant populations of developed countries. However, talking about inequities in the use of family planning methods is more difficult than talking about health inequities in general [19–21], because, in addition to objective factors regarding knowledge of and access to said methods, there is also the influence of moral issues, such as the fear of transgressing certain taboos, cultural factors and even religious impediments. In developing countries, and particularly African countries, it is important to take into account that the attitudes towards and use of contraception may vary due to a multitude of factors, including the quality of the health service and its professionals, availability of and access to family planning methods [22], level of wealth [23], gender roles and the socioeconomic context of the country [20] . Discrepancies have also been found in developing countries with regard to interest in modern family planning methods and their real use. Some results suggest that more support is required to ensure greater prevalence of use, in terms of access to different methods and from an educational and cultural viewpoint [16], as well as greater involvement by health professionals [17].
Research into differences in the use of family planning methods between immigrant and native populations in different countries generally indicates less use by immigrants [24–26], even when they have resided in the host country for some time [21] . This same trend is observed in Spain, with less frequent use of the health service by the immigrant population when it comes to the general health service [27–29] and family planning clinics and the use of different methods of contraception [30, 31], especially for certain groups of immigrants.
The main aim of this study is to detect sources of inequity by analysing factors influencing the use or non-use of family planning methods in a geographical context where there is a high level of relatively recent immigration and a public health system which offers universal cover. The consequences of less access to family planning services are not only a higher number of undesired pregnancies but also increased risk of infections and sexually transmitted diseases, and higher numbers of abortions [14, 15, 25].
Methods
The data used in this study were taken from a questionnaire administered to a sample of Catalan health service users. The health care system in Catalonia has all the powers derived from the Spanish constitution. The Spanish model decentralizes the responsibility for health to autonomous communities.
It is a validated ad-hoc questionnaire with copyright n 02/2010/2833 [32]. The questionnaire was compiled following a qualitative stage involving the conducting of 37 individual interviews to users, health professionals and cultural mediators aimed at drawing out sensitive information and determining opinions regarding the possible existence of access barriers to a public and universal health service such as the one in Spain. The questionnaire was administered to 1094 public health service users at health centres in Girona (ABS Salt and Santa Caterina Hospital), BaixEmpordà (Palamòs Hospital and Palafrugell ABS), Barcelona (Hospital del Mar, Raval Sur ABS, Vila Olímpica ABS and Besòs ABS) and Lleida (Arnau de Vilanova Hospital, RamblaFerran ABS and Eixample ABS) in 2007. Point transect sampling was used in order to ensure the representativeness of the sample [29] . Given the aim of the article, only users aged between 15 and 49 were selected, which meant working with a total of 876 complete questionnaires. Data were weighted in order to correctly reflect the distribution of the population of users according to origin.
Data analysis comprised a complete descriptive analysis of variables relating to the sociodemographic and health status characteristics of public health service users and variables indicating their knowledge and use of family planning methods (Tables 1, 2 and 3). Bivariate relationships were analysed by means of chi-square contrasts between the variable indicating use or non-use of family planning methods and the variable addressing the type of method used and users’ sociodemographic variables and health characteristics (Tables 4 and 5). Finally, considering the use (or non-use) of family planning methods as a dependent variable and a set of demographic, socioeconomic and health status variables as explanatory factors, the relationship was modelled using mixed models.
The model studies factors that have a greater or lesser influence on the likelihood of using family planning methods. Thus, the model to be estimated is specified as follows [eq.(1)]:
where Y is the response variable, that is, use or non-use of family planning methods and Pr(Y=1) refers to the likelihood of using family planning methods and is modelled by a logistic regression. X refers to the group of users’ sociodemographic and health status variables. The special feature offered by this model is that it introduces the heterogeneity associated with the user through a normal random effect, where . This modification allows us to collect the individual effects that are not explained by the explanatory variables of the model (those that depend uniquely on the patient). Due to the multiple advantages it provides within the context of this study, the aforementioned models are estimated using the Bayesian approach [33–35]. All computations were carried out using the interface INLA, running directly in R (version R 2.11.0) [36].
Different effects were tested, both fixed and random, in order to determine the final specification of the model. Models were compared using the DIC (Deviance Information Criterion) and the conditional predictive ordinate (CPO) for each observation (in fact – mean (log(cpo)). CPO is a cross-validated predictive approach, i.e. predictive distributions conditioned on the observed data with a single data point deleted. Asymptotically the CPO statistic has a similar dimensional penalty to AIC. From this perspective, the CPO statistic may be similar to DIC. In both cases, the lower the DIC or the CPO, the better the model. The finally selected model is shown in Table 6.
Results
The main descriptive results shown in Tables 12 and 3 indicate a weighted percentage of 54.3% of women and 45.7% of men. 74.3% are natives or from EU countries, and 25.7% economic immigrants (according to the UNDP country classification [37]). 24.3% state having a low level of education, while 25.2% have studied in higher education. With regard to health status, 27.4% state they have a chronic illness while 20.3% perceive their health to be normal or poor. 54.8% of users in the sample state they regularly use some method of family planning, with the pill (28.9%) and the condom (46.7%) the most common.
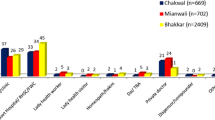
The bivariate relationships shown in Table 4 indicate significant relationships at 95% of confidence regarding the use of family planning methods in the variables age, place of birth (see Figure 1), level of education, basic origin and having children under 14. The relationships indicate that those who use family planning methods less are older people (39 to 49 year-olds), Africans and Asians, people with primary school education (see Figure 2) and those without children. No statistically significant relationships are found with regard to sex, type of family planning methods used, income or perceptions of health.
Table 5 shows statistically significant relationships at 95% confidence with regard to type of family planning methods. No significant differences are found in the type of planning method used with regard to income or basic origin (natives and European Union versus economic immigrants) although differences do stand out when working with different origins of economic immigrants (see Figure 3). Thus, for example, it is worth highlighting that users from sub-Saharan Africa and Asian countries use traditional methods more frequently.
Finally, Table 6 shows the results of the statistical modelling. It is observed that individuals from North Africa, sub-Saharan Africa and Asia are less likely (36.68%, 38.59% and 70.51%, respectively) to use family planning methods than natives. That said, when we analyse this relationship taking into account users’ sex and origin, we observe that women from these geographical regions are more likely to use family planning methods than native men, although only Asian women show a statistically significant relationship in this respect (235% more likelihood than native men). Furthermore, users with secondary and university education have a greater likelihood of using family planning methods (30.59% and 39.29%, respectively) than individuals with primary education. People with children over 14 have a 35.35% more likelihood of using family planning methods than those without children. No significant relationships are detected with regard to perceived health status or chronic illness.
Discussion
The article highlights the difference in use of family planning and contraception among different groups in a geographical region with a high rate of recent immigration where there is universal health cover and analyses the possible existence of sources of inequity in this different use of family planning methods.
Despite the fact that, as we have said, it is difficult to conclude whether the differences detected may be considered solely inequalities, in the sense that they reflect different patterns of behaviour and different preferences in the choice of family model due to sociological and cultural type reasons, we believe that the results do point, as Gillespie et al. [21] suggest, to the inequalities detected in this case being considered sources of inequity. Greater fertility rates among African and Asian populations, which according to the UNDP [37] comprise a proportion of economic immigrants to this country, along with less use of contraceptive methods (Table 7) suggest that the inequalities detected may be considered inequities in contraception in these populations when compared with the native population and populations from other geographical locations.
The main limitations in the interpretation of these results relate to the use of a sample of public health services users during a specific period of time (year 2007) and not a random sample of the population and also are worth mentioning that the questionnaire used not provided detailed information regarding the individual incomes of these users. Despite said limitations, these results provide relevant information for planning improvements in the use of health services in this country.
Conclusion
As follows from this analysis, greater or lesser use of family planning methods is related only to socioeconomic factors and not health status (real or perceived). Level of education, having children over 14 and geographical origin are elements that determine use. Even in Spain, a country with universal health service access, we have found sources of inequity. These results agree with the arguments proposed by Creanga [22], Davis [20], Igbal [19] and Gillespie [21], in the sense that although the use of family planning methods is first and foremost influenced by knowledge of and access to the same, gender roles, moral and/or cultural type reasons and individuals’ socioeconomic context also play an important role in this decision. This inequity is difficult to address from a solely medical point of view, as barriers to accessing family planning methods (difficulty with the language, dealing with health professionals, lack of information, etc.) refer to elements that must also be dealt with from a social viewpoint. Action in this respect would lead to a reduction in the number of undesired pregnancies and abortions, as well as fewer risks of infections and sexually transmitted diseases.
GESIC collaborative group
Mercè Almirall1,2, Andrea Burón3, Xavier Cabré1,2, Dolors Corominas4, Pere Plaja5, Dolors Muñoz6, Marc Saez7,8, Carme Saurina7,8, Catalina Serna9, Laura Serra 7,8, Jorge Soler-González9, Esther Tobías10, Laura Vall-llosera8
1Biomedical Research Institut, Lleida (IRBLLEIDA), Spain
2University Hospital Universitari Arnau de Vilanova, Spain
3Hospital Mar-Parc de Salut MAR, Spain
4Institut d’AssistènciaSanitària de Girona (IAS), Spain
5Figueras Hospital, Spain
6University of Girona, Spain
7CIBER of Epidemiology and Public Health Spain
8 Research Group on Statistics, Econometrics and Health (GRECS), University of Girona, Spain
9 Regional Primary Care Management Office, Catalan Institute of Health, University of Lleida Spain
10 University Foundation of Bages (FUB), Spain
Abbreviations
- ABS:
-
ÁreaBásica de Salud or Local Health Region
- INLA:
-
Integrated Nested Laplace Approximations
- DIC:
-
Deviance Information Criterion
- CPO:
-
conditional Predictive Ordinate
- UNDP:
-
United Nations Development Programme.
References
INE. Instituto Nacional de Estadística: NationalStatisticsInstitute. , www.ine.es
Idescat: Instituto de Estadística de Cataluña. , www.idescat.cat/es
Jain AK: Fertility reduction and the quality of Family Planning Services. Stud Fam Plan. 1989, 1: 1-16.
White JS, Speizer IS: Can family planning outreach bridge the urban–rural divide in Zambia?. BMC Heal Serv Res. 2007, 7: 143-10.1186/1472-6963-7-143. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6963/7/143. 2007 White and Speizer; licensee BioMed Central Ltd
Aliyu AA, Shehu AU, Sambo MN, Sabitu K: Contraceptive knowledge, attitudes and practice among maried women in Samaru community, Zaria, Nigeria. East Afr J Public health. 2010 Dec, 7 (4): 342-344.
Omole-Ohons A, Ashimi A, Attah R: A Review of Family Planning Methods Used in Kano, Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2010, 3: 1-
Bellows B, Warren C, Vonthanak S, Chhorvann C, Sokhom H, Men C, Bajracharya A, Rob U, Rathavy T: Evaluation of the impact of the voucher and accreditation approach on improving reproductive behaviors and status in Cambodia. BMC Publ Health. 2011 Aug 24, 11: 667-10.1186/1471-2458-11-667.
Warren C, Abuya T, Obare F, Sunday J, Njue R, Askew I, Bellows B: Evaluation of the impact of the voucher and accreditation approach on improving reproductive health behaviors and status in Kenya. BMC Publ Health. 2011 Mar 23, 11: 177-10.1186/1471-2458-11-177.
Paul VK, Sachdev HS, Mavalankar D, Ramachandran P, Sankar MJ, Bhandari N, Sreenivas V, Sundararaman T, Govil D, Osrin D, Kirkwood B: Reproductive health, and child health and nutrition in India: meeting the challenge. Lancet. 2011 Jan 22, 377 (9762): 332-349. 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61492-4. Epub 2011 Jan 10
Goicolea I, San Sebastián M, Wulff M: Women’s reproductive rights in the Amazon basin of Ecuador: challenges for transforming policy into practice. Health Hum Rights. 2008, 10 (2): 91-103. 10.2307/20460105.
Kaufman CE: Contraceptive use in South Africa under apartheid. Demography. 1998 Nov, 35 (4): 421-434. 10.2307/3004011.
Gish O: Health and family planning services in Bangladesh: a study in inequality. Int J Health Serv. 1981, 11 (2): 263-281. 10.2190/FEQQ-R9VE-TB3Y-3JNA.
Varga CA: How gender roles influence sexual and reproductive health among South African adolescents. Stud Fam Plann. 2003 Sep, 34 (3): 160-172. 10.1111/j.1728-4465.2003.00160.x.
Rasch V, Gammeltoft T, Knudsen LB, Tobiassen C, Ginzel A, Kempf L: Induced abortion in Denmark: effect of socioeconòmic situation and country of birth. Eur J Public Health. 2008, 18: 144-149.
Van Enk WJ, Gorissen WH, van nk A: Teenage pregnacy and ethnicity in The Netherlands: frequency and obstètric outcome. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2000, 5: 77-84. 10.1080/13625180008500379.
Mikolajczyk RT, Stanford JB, Rauchfuss M: Factors influencing the choice to use modern natural family planning. Contraception. 2003 Apr, 67 (4): 253-258. 10.1016/S0010-7824(02)00490-0.
Păfvăleanu M, Pricop Z, Azoicăi D, Boiculese LV, Cozma A, Pintilie M, Grigoraş RC, Nechita E, Herescu D: Questionnaire regarding the self perception of health status and attitude to family planning of the Roma population in Iaşi county. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2007 Jan-Mar, 111 (1): 265-269.
Becker D, Koenig MA, Mi Kim Y, Cardona K, Sonenstein FL: The Quality of Family Planning Services in the United States: Findings from a Literature Review. Perspect Sex Reprod Heal. 2007, 39: 206-215. 10.1363/3920607.
Iqbal H, Shah , Chandra-Mouli V: Inequity and unwanted fertility in developing countries. Bull World Health Organ. 2007 February, 85 (2): 86-10.2471/BLT.06.037366. World Health Organization (WHO) 2007
Davis J, Lopez-Carr D: The effect of migrant remittances on population-environment dynamics in migrant origen areas: international migration, fertility, and consumption in highland Guatemala. Popul Environ. 2010, 32: 216-237. 10.1007/s11111-010-0128-7.
Gillespie D, Ahmed S, Tsui A, Radloff S: Unwanted fertility among the poor: an inequity?. Bull World Health Organ. 2007, 85 (2): 100-107. 10.2471/BLT.06.033829.
Creanga AA, Gillespie D, Karklins S, Tsui AO: Low use of contraception among poor women in Africa: an equity issue. Bull World Health Organ. 2011 Apr 1, 89 (4): 258-66. 10.2471/BLT.10.083329. Epub 2011 Feb 1
Rahman M, Haque SE, Mostofa MG, Tarivonda L, Shuaib M: Wealth inequality and utilization of reproductive health services in the Republic of Vanuatu: Insights from the Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey, 2007. Int J Equity Health. 2011 Dec 2, 10 (1): 58-10.1186/1475-9276-10-58.
Lamur HE: Characteristics of Caribbean-born women having abortions in an Amsterdam clínic. Genus. 1993, 49: 135-45.
Helstrom L, Zatterstrom C, Odlind V: Abortion rate and contraceptive practices in inmigrant and Swedish adolescents. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2006, 19: 209-13. 10.1016/j.jpag.2006.02.007.
Garces-Palacio IC, Altarac M, Scarinci IC: Contraceptive knowledge and use among low-income Hispanic inmigrant women an non-Hispanic women. Contraception. 2008, 77: 270-5. 10.1016/j.contraception.2007.12.008.
Vall-llosera L, Saurina C, Saez M: Inmigración y salud: necesidades y utilización de los servicios de atención primaria por parte de la población inmigrante en la región sanitaria Girona. Revista Española de Salud Pública. 2009, 83 (2): 291-307.
Saurina C, Vall-llosera L, Saez M: A Qualitative analysis of immigrant population health practices in the Girona Health Region. BMC Publ Health. 2010, 10 (1): 379-10.1186/1471-2458-10-379.
Saurina C, Vall-llosera L, Saez M: Factors determining access to and use of primary health care services in the Girona Health Region (Spain). Eur J HealthEcon. 2012, 13 (4): 419-427.
Zurriaga O, Martinez Beneito M, Peñalver J, Bosch S, García M, Amador : Análisis de las características diferenciales de las inmigraciones atendidas en centros de planificación familiar. Gac Sanit. 2003, 17: 115-
Baraza Cano MP, Lafuente Robres N, Granados Alba A: Identificación de diagnósticos enfermeros en población inmigrante en el distrito Poniente de Almería. Enfermería Comunitaria. 2005, 1: 18-23.
Encuesta de barreras de acceso, estado de salud y utilización de los servicios sanitarios en Catalunya (Soler J, Corominas D, Plaja P, Muñoz-Soler MD, Vall.llosera L, Burón A, Almirall mm, romero ar, saez m, Serna MC, Cabré FJ, Tobias E, Saurina C): Registro de la Propiedad Intelectual (obra literaria). , N 02/2010/2833
Gelfand AE, Dey DK, Chang H: Model determination using predictive distributions with implementation via sampling-based methods (with discussion). Bayesian Statistics 4. Edited by: Bernardo JM, Berger JO, Dawid AP, Smith AFM. 1992, Oxford University Press, Oxford
Geisser S: Predictive Inference: An Introduction. 1993, Chapman and Hall, London
Pettit LI: The conditional predictive ordinate for the normal distribution. J R Stat Soc. Series B 1990, 52 (1): 175-184.
R-INLA project. 2010, URL: http://www.r-inla.org/home
PNUD (Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Desarrollo):http://www.undp.org,
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the FIS (Health Research Fund), Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, project FIS-07/0156.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
CS designed the fieldwork which provided the data and worked on data modelling and drafting the article, MS did the statistical modelling and worked on drafting and revising the article, LV participated in the fieldwork which provided the data, data cleansing and the descriptive analysis of the same, and also worked on drafting and revising the article. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Saurina, C., Vall-llosera, L. & Saez, M. Factors determining family planning in Catalonia. Sources of inequity. Int J Equity Health 11, 35 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-9276-11-35
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-9276-11-35