Abstract
Background
Limiting consumption of eggs, which are high in cholesterol, is generally recommended to reduce risk of cardiovascular disease. However, recent evidence suggests that dietary cholesterol has limited influence on serum cholesterol or cardiac risk.
Objective
To assess the effects of egg consumption on endothelial function and serum lipids in hyperlipidemic adults.
Methods
Randomized, placebo-controlled crossover trial of 40 hyperlipidemic adults (24 women, 16 men; average age = 59.9 ± 9.6 years; weight = 76.3 ± 21.8 kilograms; total cholesterol = 244 ± 24 mg/dL). In the acute phase, participants were randomly assigned to one of the two sequences of a single dose of three medium hardboiled eggs and a sausage/cheese breakfast sandwich. In the sustained phase, participants were then randomly assigned to one of the two sequences of two medium hardboiled eggs and 1/2 cup of egg substitute daily for six weeks. Each treatment assignment was separated by a four-week washout period. Outcome measures of interest were endothelial function measured as flow mediated dilatation (FMD) and lipid panel.
Results
Single dose egg consumption had no effects on endothelial function as compared to sausage/cheese (0.4 ± 1.9 vs. 0.4 ± 2.4%; p = 0.99). Daily consumption of egg substitute for 6 weeks significantly improved endothelial function as compared to egg (1.0 ± 1.2% vs. -0.1 ± 1.5%; p < 0.01) and lowered serum total cholesterol (-18 ± 18 vs. -5 ± 21 mg/dL; p < 0.01) and LDL (-14 ± 20 vs. -2 ± 19 mg/dL; p = 0.01). Study results (positive or negative) are expressed in terms of change relative to baseline.
Conclusions
Egg consumption was found to be non-detrimental to endothelial function and serum lipids in hyperlipidemic adults, while egg substitute consumption was beneficial.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
As of the early 1970's, a reduction in consumption of eggs, a concentrated source of cholesterol (one yolk provides ~215 mg of cholesterol), had been widely recommended in an effort to lower blood cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease[1]. In 1973, the American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines specifically advocated exclusion of eggs from the diet, accompanying the advised cholesterol restriction[2]. More recent AHA guidelines no longer advise for or against egg or egg yolk consumption, admitting that there is a lack of scientific evidence for selecting a target level for dietary cholesterol[3]. This is partially due to individual differences in serum cholesterol responses to dietary cholesterol. The recommended intake of daily dietary cholesterol continues to be 300 mg/day or less for healthy adults and less than 200 mg/day for persons with elevated cholesterol or heart disease[3]. Given the widespread nature of this recommendation, there is surprisingly little evidence that egg consumption increases blood cholesterol levels, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk [4].
Data from recent studies show that consumption of one or two eggs per day, when part of a low fat diet, does not adversely affect the lipid profile[5, 6]. In fact, the preclusion of eggs from the diet may represent a potential reduction in overall dietary quality. As an inexpensive functional food with an exceptional nutritional profile[7, 8], eggs are an excellent natural source of folate, riboflavin, selenium, choline, vitamin B12, and fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. Eggs also provide high-quality, bioavailable protein[9, 10] with little total fat. Compared to other animal protein sources, eggs contain proportionately less saturated fat, which has generally been recognized as a strong dietary determinant of elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels and increased risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) [11] although this topic is not without controversy [12].
As a dietary substitute for eggs, egg substitute is comprised of 99% egg whites and provide 12 key vitamins and nutrients, including riboflavin, B12, folate, and pantothenic acid, while excluding the cholesterol contribution of the egg yolk[13]. Although nutritionally similar to eggs, egg substitute contains emulsifiers, stabilizers, and artificial color and are on average three times as expensive as regular eggs.
Endothelial function refers to arterial vasomotor responses mediated predominantly by the release of nitric oxide (vasodilating), and endothelin (vasoconstricting) from the vascular endothelium[14, 15], and plays an important role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes[15–17]. Endothelial dysfunction correlates strongly with both coronary disease and its risk factors[18, 19] and reverses in response to risk modification efforts[15, 20–27]. Endothelial dysfunction has increasingly been viewed as an indicator of coronary risk[19], and its amelioration as an indicator of risk reduction[20, 23].
The relationship of egg consumption to coronary outcomes depends not only on the cholesterol content of eggs themselves, but on the composition of the total diet. It is a common misconception that dietary cholesterol increases serum cholesterol which increases CHD risk[28, 29]; however, research has failed to provide substantial evidence of this assumed relationship[30]. In our previous trial, daily ingestion of eggs did not produce adverse effects on cardiac risk, as indicated by endothelial function and lipid profile, in healthy adults[31]. To the best of our knowledge, no study has ever compared the effects of egg versus egg substitute consumption on cardiovascular risk. Therefore, we performed a randomized cross-over trial to assess the effects of egg or egg substitute consumption on endothelial function and lipid panel in hyperlipidemic adults.
Subjects and Methods
Subjects
Forty adults (16 men and 24 women) with diagnosed hyperlipidemia were recruited from Southwestern Connecticut; largely through mass media print advertisements and posters. Eligible subjects were 35 years of age or older if they were male or post-menopausal and not currently using hormone replacement therapy if they were female. Additionally, eligible subjects were non-smokers, and hyperlipidemic as defined by serum total cholesterol >240 mg/dL, and/or LDL cholesterol >160 mg/dL, and/or a total cholesterol/HDL ratio >5.7. All ethnic and minority groups were equally eligible. Individuals with a current eating disorder, a restricted diet, diagnosed coronary disease, diabetes, or sleep apnea were excluded from the study. Additional exclusion criteria included the regular use of lipid-lowering medication, insulin or glucose sensitizing medication, vasoactive medication or nutriceuticals, high dose vitamin E or C, and fiber supplements.
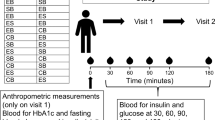
Individuals who responded to recruitment efforts (n = 172) were pre-screened using a semi-structured telephone interview. Those who met initial screening criteria (n = 40) underwent a clinical screening evaluation (weight, height, body mass index (BMI), and blood pressure measurements) performed by a clinical research specialist, along with laboratory testing (fasting total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, and triglycerides levels) (Figure 1).
All participants provided informed consent and were compensated monetarily for their time. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Griffin Hospital (Derby, CT).
Study Design
This study was a randomized, single-blind crossover trial with investigators blinded to treatment assignments. The trial consisted of an acute and a sustained phase. In the acute phase, 40 participants were randomly assigned to consume one of the two sequence permutations of a single dose of breakfast of three medium hardboiled eggs and a sausage/cheese breakfast sandwich (Table 1). In the sustained phase, participants were randomly assigned to one of the two sequence permutations of two medium hardboiled eggs and 1/2 cup of egg substitute breakfast daily for six weeks. Randomization was conducted by the data manager using a SAS (SAS version 9.1; SAS Institute, Cary, NC) algorithm. Each treatment assignment was separated by a four-week washout period. The study participants fasted overnight before undergoing endothelial function assessment. Due to the obvious dietary makeup of each treatment assignment, it was not possible to blind participants to their assignment; however, the ultrasonographer was strictly blinded to participants' treatment assignment.
Outcome Measures
Endothelial Function Assessment
The brachial artery reactivity studies (BARS) methodology employed is comparable to those of other leading labs[16, 32–36], and is described in "Guidelines for ultrasound assessment of endothelial-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery"[16]. Participants were required to lie at rest in the quiet, temperature-controlled, softly lit room for at least 15 minutes before scanning was initiated. The baseline diameter of the brachial artery was measured from two-dimensional ultrasound images using a high frequency, 10-15 MHz, vascular ultrasound transducer (Sonos 4500; Phillips Medical Systems, Andover, MA). Arterial flow-velocity was measured by means of a pulsed Doppler signal at a 70° angle to the vessel, with the range gate in the center of the artery. Flow was determined by multiplying the arterial cross-sectional area (πr2) by the Doppler flow velocity. The timing of each image frame with respect to the cardiac cycle was determined with simultaneous ECG gating during image acquisition via the high-quality mainframe ultrasound system. The arterial diameter was measured at a fixed distance from an anatomical marker, such as a bifurcation, with ultrasonic calipers. Measurements were taken from the anterior to the posterior "m" line in diastole. The brachial artery was imaged at a location 3-7 cm above the antecubital fossa in the longitudinal plane. A segment with clear anterior and posterior intimal interfaces between the lumen and vessel wall was selected for continuous 2D gray scale imaging. The transmit (focus) zone was set to the depth of the near wall because of difficulty in differentiating the near from the far wall "m" line (the interface between media and adventitia)[16, 33]. Images were acquired on videotape and magnetic optical disk for evaluation and analysis subsequent to the examination. Diameter was obtained from m-line to m-line, over a consistent segment of vessel at least 10-15 mm in length.
To create a flow stimulus in the brachial artery, a sphygmomanometer cuff was placed on the upper arm proximal to the transducer. A baseline blood flow and diameter were acquired. Arterial occlusion was created by cuff inflation to 50 mm Hg above the systolic blood pressure. The cuff remains inflated for 5 minutes. This causes ischemia and consequent dilation of downstream resistance vessels via auto-regulatory mechanisms[16]. Cuff deflation induces a brief high-flow state through the brachial artery (reactive hyperemia) to accommodate the dilated resistance vessels. The resulting increase in shear stress causes the normal brachial artery to dilate. A pulsed Doppler signal was obtained within 15 seconds of cuff release to assess hyperemic velocity, and a longitudinal image of the artery was recorded continuously from 20 seconds to 2 minutes after cuff deflation. All images were coordinated with a continuous ECG monitor and obtained at end-diastole. The resultant coefficient of intra observer reliability was 0.9.
Flow-mediated dilation (FMD) was measured as the percent change in brachial artery diameter from pre-cuff inflation to 60-seconds post-cuff release. In addition to brachial diameter at 60 seconds post-cuff release, flow after cuff deflation within the first 15 seconds was used as an indicator of stimulus strength, hyperemic flow being the stimulus for endothelial reactivity. To account for potential variability in stimulus strength, FMD was divided by flow at 15 seconds[16]. post-cuff deflation to create a stimulus-adjusted response measure[31, 37, 38].
Lipid Profile
Serum was drawn for lipid assessments about twenty minutes prior to endothelial function assessment. The lipid profile was determined as follows: Total cholesterol (Tchol), triglycerides (TRIG), and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) were obtained by direct measurements. Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) were obtained by calculation: VLDL = TRIG/5; and LDL = Tchol - (VLDL + HDL) [39].
Body Weight
Body weight was measured for all study participants at the beginning and end of the sustained phase. Body weight was measured to the nearest 0.5 pound using a balance-type medical scale. Participants were measured in the morning, unclothed with the exception of undergarments.
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure was determined with the use of the Datascope Accutorr Plus automatic digital blood pressure device (Datascope Corp, Mahwah, NJ) with the participant supine after a 5-min period of rest. Both systolic and diastolic pressures were calculated as the mean value of 2 readings 5 minutes apart. All measurements were obtained by one investigator.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using SAS software (Version 9.1, SAS Institute, Cary, NC). A two-tailed p-value of ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA, with treatment and time as the main effects, were performed to compare treatment-specific outcome measures responses, accounting for time differences. Within-treatment effects for outcome measures were assessed using paired t-tests. The combined effect of independent variables (age, blood pressure, LDL, BMI and treatment sequence) and treatment assignment on all outcome measures was assessed with generalized linear modeling. All analyses of endpoints were based on the intention-to-treat principle.
Sample size was predicated on 80% power to detect a minimal difference of 3.5% change in FMD between the egg and egg substitute treatments at six weeks. A two-tailed alpha level of 0.05 was set with an allowance for 10% attrition and noncompliance.
Results
Forty hyperlipidemic participants participated in this study. Sixty percent of the participants were female. Participants ranged in age from 35 to 77 years, with a mean age of 60 years (Table 2). Four participants dropped out of the study after the acute phase. One participant dropped out because the participant was unwilling to consume eggs or egg substitute daily for six weeks, another dropped out because of relocation to another state, and two dropped out because they started using lipid lowering medication (statin).
Acute Phase
After a single dose of eggs, endothelial function did not change from baseline as compared to sausage and cheese ( p = 0.99). Accounting for the strength of the stimulus that determines vasodilatations (SARM), our findings on endothelial function persisted (Table 3.)
Sustained Phase
Daily consumption of egg substitute for six weeks improved endothelial function relative to egg consumption ( p < 0.01). These findings persisted controlling for the variation of the strength of the stimulus that causes the vasodilatation (Table 4.)
Daily consumption of egg substitute for six weeks significantly lowered total cholesterol as compared to egg consumption ( p < 0.01) and also lowered LDL as compared to egg consumption ( p = 0.01). However, daily consumption of egg substitute for six weeks did not significantly lowered total cholesterol to HDL ratio as compared to egg consumption ( p = 0.38).
Daily consumption of egg or egg substitute for six weeks did not show significant increase in BMI as compared to egg consumption (p = 0.56)
Discussion
Our findings in this study expand on existing evidence that short-term egg consumption does not adversely affect endothelial function, in a population not previously examined: hyperlipidemic adults. Moreover, we observed that consuming eggs daily did not unfavorably influence serum cholesterol or other measures of the lipid profile. While the subjects demonstrated impaired endothelial function at baseline (i.e. relative to healthy endothelial function), the acute induction of endothelial dysfunction by the test meal high in saturated fat was not observed. Egg substitute, which is made from 99% egg whites, is lower in calories relative to whole eggs, lacks cholesterol and fat, and is fortified with vitamins, also lowered cholesterol and triglyceride levels. In addition, egg substitute led to a decrease in LDL and significantly improved endothelial function, as compared to sustained egg consumption. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to provide evidence that egg or egg substitute consumption does not adversely affect endothelial function in hyperlipidemic adults.
The acute phase findings were consistent with those of the sustained phase. Single, acute doses of egg did not adversely affect endothelial function. The sausage and cheese breakfast sandwich, designed to demonstrate acute dysfunction in the endothelium, surprisingly also did not adversely affect endothelial function. This finding is consistent with the prior study of egg ingestion in healthy adults conducted at our lab[31], but is at odds with the reported literature. This may be explained by differences in gastric transit times for different types of food [31]. Future studies should evaluate postprandial brachial artery dilation at different time points to assess the effect of time. Several studies have examined FMD serially over time following meal ingestion[40, 41].
While rich in cholesterol, eggs are also nutritious. Data from NHANES III reveal that egg consumption is an important nutritional contribution to the average American diet, providing a relatively inexpensive source of amino acids and essential fatty acids[9]. Eggs provide arginine, a precursor to nitric oxide, which in turn plays a central role in endothelial function[42]. Endothelial function is an arterial vasomotor response mediated predominantly by the release of nitric oxide (vasodilating), and endothelin (vasoconstricting) from the vascular endothelium[26]. This system plays an important role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, cardiovascular disease, and other chronic diseases[19, 43].
The relative importance of dietary cholesterol to cardiovascular risk, and the association between dietary and serum cholesterol, are both subject to ongoing debate[44–46]. The association between dietary cholesterol and coronary events and mortality is generally positive but rather weak, and derived largely from ecological and prospective cohort studies with variable follow-up[47–50]. In most of these studies, it is difficult to determine the effects of cholesterol independent of dietary fat. One large prospective cohort followed U.S. male physicians for over 20 years. The study monitored egg consumption and documented new cases of heart failure during follow-up. Results failed to find a correlation between occasional egg consumption and heart failure, although an increased risk of heart failure was related to participants who reported consuming more than one egg per day[49]. Another study found no impact of egg intake on cardiovascular risk, specifically stroke, ischemic stroke, and coronary artery disease. However, Nakamura et al demonstrated significant correlation with serum cholesterol concentrations in women consuming more than two eggs per day [51]. In a recent study by Djoussé et al, egg consumption was associated with increased risk of diabetes [52]. Djoussé et al also linked egg consumption to increased mortality and even more so in diabetics [53]. Overall, scientific studies of the relationship between egg consumption, cardiovascular disease and mortality[30, 54], have thus been somewhat inconsistent.
Little, if any, epidemiological evidence exists supporting a direct link between egg consumption and cardiovascular disease or mortality risk. Previous studies have shown weak positive associations between intake of dietary cholesterol and serum cholesterol, while others failed to find any association[30]. Hu and colleagues analyzed data from two large cohorts, the Health Professional Follow-Up Study and the Nurses' Health Study, to assess the effect of egg consumption on cardiovascular events and deaths[47]. After a mean of 8 years of follow-up, no overall significant association was observed between egg consumption and risk of CHD in both males and females. Hu et al [47] also reported that the relative risk of CHD was the same whether the participants consumed less than, or more than, one egg per week.
While our study provides valuable data regarding egg ingestion in hyperlipidemic adults, it is not without limitations. The study's small sample size almost entirely derived from one community in Southwestern Connecticut may limit the generalization these of results. Furthermore, the duration of egg consumption during this study limits the ability to predict the long-term effects. Variables potentially confounding the correlation between nutrient intakes and endothelial responses included physical activity, vasoactive medication use, and genetic factors. Unmeasured or inaccurately measured dietary intake data could also have confounded results. Three-day food diaries, used to track dietary intake, did not indicate any significant unintended changes in overall dietary pattern, although changes in diet or behavior that were not captured may have impacted findings. Adjustment for potential confounders was managed through application of strict eligibility criteria, randomization, and crossover design. Also of note, the intended provocation of endothelial dysfunction by a single meal high in saturated fat failed to demonstrate a deleterious effect. Finally, endothelial function was measured only one time after treatment assignments and not monitored for a prolonged time.
Conclusions
In light of the persistent uncertainties and lack of observational evidence regarding the effects of egg consumption on serum cholesterol and cardiac risk, the application of this methodology and technology in further studies is appropriate, and very much needed. Short of a randomized controlled trial of egg consumption and cardiovascular events, endothelial function testing offers one of the best available means to evaluate the role of egg ingestion on cardiac risk. To date, the evidence generally mitigates against an association between moderate egg consumption and increased cardiac risk. Further testing in at-risk samples, including individuals with established coronary disease, is now justified to clarify the place of eggs in a judicious and heart-healthy diet.
References
Report of Inter-Society Commission for Heart Disease Resources: Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Primary prevention of the atherosclerotic diseases. Circulation. 1970, 42 (6): A55-95.
American Heart Association: Diet and Coronary Heart Disease. 1973, Dallas, TX: American Heart Association
Krauss RM, Eckel RH, Howard B, Appel LJ, Daniels SR, Deckelbaum RJ, Erdman JWJ, Kris-Ehterton P, Goldberg IJ, Kotchen TA, Lichtenstein AH, Mitch WE, Mullis R, Robinson K, Wylie-Rosett J, St Jeor S, Suttie J, Tribble DL, Bazzarre TL: AHA Dietary Guidelines: Revision 2000: A statement for healthcare professionals from the Nutrition Committee of the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2000, 102 (18): 2284-2299.
Harman NL, Leeds AR, Griffin BA: Increased dietary cholesterol does not increase plasma low density lipoprotein when accompanied by an energy-restricted diet and weight loss. Eur J Nutr. 2008, 47 (6): 287-293. 10.1007/s00394-008-0730-y.
Biostatistical fact sheet -- risk factors; high blood cholesterol and other lipids. http://www.americanheart.org/downloadable/heart/1017696825613chollip.pdf. Accessed December 27, 2002, [http://www.americanheart.org/downloadable/heart/1017696825613chollip.pdf]
American Heart Association: An eating plan for healthy adults. The new 2000 food guidelines. Our American Heart Association diet. Dallas, TX. 2000
USDA: Nutrient Database for Standard Reference. 2009, [http://www.nal.usda.gov/fnic/foodcomp/search/]
Herron KL, Fernandez ML: Are the current dietary guidelines regarding egg consumption appropriate?. J Nutr. 2004, 134 (1): 187-190.
Song WO, Kerver JM: Nutritional contribution of eggs to American diets. J Am Coll Nutr. 2000, 19 (5 Suppl): 556S-562S.
Bowes , Church : Bowes and Church's Food Values of Proteins Commonly Used. 1994, J.B. Lippincott Company, 16
Mente A, de Koning L, Shannon HS, Anand SS: A systematic review of the evidence supporting a causal link between dietary factors and coronary heart disease. Arch Intern Med. 2009, 169 (7): 659-669. 10.1001/archinternmed.2009.38.
Siri-Tarino PW, Sun Q, Hu FB, Krauss RM: Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies evaluating the association of saturated fat with cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 91 (3): 535-546. 10.3945/ajcn.2009.27725.
Vorster HH, Beynen AC, Berger GM, Venter CS: Dietary cholesterol--the role of eggs in the prudent diet. S Afr Med J. 1995, 85 (4): 253-256.
Luscher TF, Barton M: Biology of the endothelium. Clin Cardiol. 1997, 20 (11 Suppl 2): II-3-10.
Vogel RA: Measurement of endothelial function by brachial artery flow-mediated vasodilation. Am J Cardiol. 2001, 88 (suppl): 31E-34E. 10.1016/S0002-9149(01)01764-7.
Corretti MC, Anderson TJ, Benjamin EJ, Celermajer D, Charbonneau F, Creager MA, Deanfield J, Drexler H, Gerhard-Herman M, Herrington D, Vallance P, Vita J, Vogel R: Guidelines for the ultrasound assessment of endothelial-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery. A report of the International Brachial Artery Reactivity Task Force. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002, 16 (2): 257-265. 10.1016/S0735-1097(01)01746-6.
Nash DT: Insulin resistance, ADMA levels, and cardiovascular disease. JAMA. 2002, 287 (11): 1451-1452. 10.1001/jama.287.11.1451.
McVeigh GE, Brennan GM, Johnston GD, McDermott BJ, McGrath LT, Henry WR, Andrews JW, Hayes JR: Impaired endothelium-dependent and independent vasodilation in patients with type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1992, 35 (8): 771-776.
Neunteufl T, Katzenschlager R, Hassan A, Klaar U, Schwarzacher S, Glogar D, et al: Systemic endothelial dysfunction is related to the extent and severity of coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 1997, 129: 111-118. 10.1016/S0021-9150(96)06018-2.
O'Driscoll G, Green D, Taylor RR: Simvastatin, an HMG-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, improves endothelial function within 1 month. Circulation. 1997, 95 (5): 1126-1131.
O'Driscoll G, Green D, Rankin J, Stanton K, Taylor R: Improvement in endothelial function by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1997, 100 (3): 678-684. 10.1172/JCI119580.
Treasure CB, Klein JL, Weintraub WS, Talley JD, Stillabower ME, Kosinski AS, Zhang J, Boccuzzi SJ, Cedarholm JC, Alexander RW: Beneficial effects of cholesterol-lowering therapy on the coronary endothelium in patients with coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 1995, 332 (8): 481-487. 10.1056/NEJM199502233320801.
Anderson TJ, Gerhard MD, Meredith IT, Charbonneau F, Delagrange D, Creager MA, Selwyn AP, Ganz P: Systemic nature of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 1995, 75: 71B-74B. 10.1016/0002-9149(95)80017-M.
Neunteufl T, Heher S, Katzenschlager R, Wolfl G, Kostner K, Maurer G, Weidinger F: Late prognostic value of flow-mediated dilation in the brachial artery of patients with chest pain. Am J Cardiol. 2000, 86 (2): 207-210. 10.1016/S0002-9149(00)00857-2.
Suwaidi JA, Hamasaki S, Higano ST, Nishimura RA, Holmes DR, Lerman A: Long-term follow-up of patients with mild coronary artery disease and endothelial dysfunction. Circulation. 2000, 101 (9): 948-954.
Hutcheson IR, Griffith TM: Central role of intracellular calcium stores in acute flow- and agonist-evoked endothelial nitric oxide release. Br J Pharmacol. 1997, 122 (1): 117-125. 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701340.
Celermajer D, Sorensen KE, Bull C, Robinson J, Deanfield JE: Endothelium-dependent dilation in the systemic arteries of asymptomatic subjects relates to coronary risk factors and their interaction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994, 24 (6): 1468-1474. 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90141-4.
Kritchevsky SB: A review of scientific research and recommendations regarding eggs. J Am Coll Nutr. 2004, 23 (6 Suppl): 596S-600S.
McNamara DJ: Eggs and heart disease risk: perpetuating the misperception. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002, 75 (2): 333-335.
McNamara DJ: The impact of egg limitations on coronary heart disease risk: do the numbers add up?. J Am Coll Nutr. 2000, 19 (5 Suppl): 540S-548S.
Katz DL, Evans M, Nawaz H, Njike V, Chan W, Comerford B, Hoxley M: Egg consumption & endothelial function in healthy adults: A randomized controlled crossover trial. International Journal of Cardiology. 2005, 99 (1): 65-70. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2003.11.028.
Corretti MC, Plotnick GD, Vogel RA: Technical aspects of evaluating brachial artery vasodilatation using high-frequency ultrasound. Am J Physiol. 1995, 268 (4 Pt 2): H1397-1404.
Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Gooch VM, Spiegelhalter DJ, Miller OI, Sullivan ID, Lloyd JK, Deanfield JE: Non-invasive detection of endothelial dysfunction in children and adults at risk of atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1992, 340 (8828): 1111-1115. 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93147-F.
Plotnick GD, Corretti MC, Vogel RA: Effect of antioxidant vitamins on the transient impairment of endothelium-dependent brachial artery vasoactivity following a single high-fat meal. JAMA. 1997, 278 (20): 1682-1686. 10.1001/jama.278.20.1682.
Mannion TC, Vita JA, Keaney JF, Benjamin EJ, Hunter L, Polak JF: Non-invasive assessment of brachial artery endothelial vasomotor function: The effect of cuff position on level of discomfort and vasomotor responses. Vasc Med. 1998, 3 (4): 263-267. 10.1177/1358836X9800300401.
Sorensen KE, Celermajer DS, Spiegelhalter DJ, Georgakopoulos D, Robinson J, Thomas O, Deanfield JE: Non-invasive measurement of human endothelium dependent arterial responses: Accuracy and reproducibility. Br Heart J. 1995, 74: 247-253. 10.1136/hrt.74.3.247.
Faridi Z, Njike V, Dutta S, Ali A, Katz DL: Acute dark chocolate and cocoa ingestion and endothelial function: A randomized, placebo controlled, cross-over trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008, 88 (1): 58-63.
Pyke KE, Tschakovsky ME: Peak vs. total reactive hyperemia: which determines the magnitude of flow-mediated dilation?. J Appl Physiol. 2007, 102 (4): 1510-1519. 10.1152/japplphysiol.01024.2006.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS: Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972, 18 (6): 499-502.
Volek JS, Ballard KD, Silvestre R, Judelson DA, Quann EE, Forsythe CE, Fernandez ML, Kraemer WJ: Effects of dietary carbohydrate restriction versus low-fat diet on flow-mediated dilation. Metabolism. 2009, 58 (12): 1769-1777. 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.06.005.
Tyldum GA, Schjerve IE, Tjonna AE, Kirkeby-Garstad I, Stolen TO, Richardson RS, Wisloff U: Endothelial dysfunction induced by post-prandial lipemia: complete protection afforded by high-intensity aerobic interval exercise. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009, 53 (2): 200-206. 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.09.033.
Preli RB, Klein KP, Herrington DM: Vascular effects of dietary L-arginine supplementation. Atherosclerosis. 2002, 162 (1): 1-15. 10.1016/S0021-9150(01)00717-1.
Anderson TJ, Uehata A, Gerhard MD, Meredith IT, Knab S, Delagrange D, Lieberman EH, Ganz P, Creager MA, Yeung AC: Cardiovascular Division, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA: Close relation of endothelial function in the human coronary and peripheral circulation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995, 26 (5): 1235-1241. 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00327-4.
McNamara D: Cholesterol intake and plasma cholesterol: an update. J Am Coll Nutr. 1997, 16 (6): 530-534.
Beynen AC, Katan MB: Effect of egg yolk feeding on the concentration and composition of serum lipoproteins in man. Atherosclerosis. 1985, 54 (2): 157-166. 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90175-3.
Caggiula AW, Mustad VA: Effects of dietary fat and fatty acids on coronary artery disease risk and total and lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations: epidemiologic studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997, 65 (5 Suppl): 1597S-1610S.
Hu F, Stampfer M, Rimm E, Manson J, Ascherio A, Colditz G, et al: A prospective study of egg consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease in men and women. JAMA. 1999, 281: 1387-1394. 10.1001/jama.281.15.1387.
Gramenzi A, Gentile A, Fasoli M, Negri E, Parazzini F, La Vecchia C: Association between certain foods and risk of acute myocardial infarction in women. Bmj. 1990, 300 (6727): 771-773. 10.1136/bmj.300.6727.771.
Djousse L, Gaziano JM: Egg consumption and risk of heart failure in the Physicians' Health Study. Circulation. 2008, 117 (4): 512-516. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.734210. Epub 2008 Jan 2014
Qureshi AI, Suri FK, Ahmed S, Nasar A, Divani AA, Kirmani JF: Regular egg consumption does not increase the risk of stroke and cardiovascular diseases. Med Sci Monit. 2007, 13 (1): CR1-8. Epub 2006 Dec 2018
Nakamura Y, Okamura T, Tamaki S, Kadowaki T, Hayakawa T, Kita Y, Okayama A, Ueshima H: NIPPON DATA80 Research Group: Egg consumption, serum cholesterol, and cause-specific and all-cause mortality: the National Integrated Project for Prospective Observation of Non-communicable Disease and Its Trends in the Aged, 1980 (NIPPON DATA80). Am J Clin Nutr. 2004, 80: 58-63.
Djousse L, Gaziano JM, Buring JE, Lee IM: Egg consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes in men and women. Diabetes Care. 2009, 32 (2): 295-300. 10.2337/dc08-1271.
Djousse L, Gaziano JM: Egg consumption in relation to cardiovascular disease and mortality: the Physicians' Health Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008, 87 (4): 964-969.
Knopp RH, Retzlaff BM, Walden CE, Dowdy AA, Tsunehara CH, Austin MA, Nguyen T: A double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of the effects of two eggs per day in moderately hypercholesterolemic and combined hyperlipidemic subjects taught the NCEP step I diet. J Am Coll Nutr. 1997, 16 (6): 551-561.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the study participants for taking part in the study. Additionally the technical assistance of Dr. Yuka Yazaki and Mrs. Michelle Pinto-Evans is greatly appreciated.
Funding sources: Funding for this study was provided by the Egg Nutrition Center and the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (Grant#U48-CCU115802).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author contributions
The authors contributions are as follows: DLK served as the Principal Investigator and is responsible for oversight of all study related activities, data analysis and manuscript preparation. VYN was responsible for the protocol development, data analysis, interpretation, manuscript preparation, and critical review of the paper. ZF was responsible for study management, ultrasound reading, data collection, and manuscript preparation. SD contributed to manuscript preparation. AGS contributed to manuscript preparation. All Authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Njike, V., Faridi, Z., Dutta, S. et al. Daily egg consumption in hyperlipidemic adults - Effects on endothelial function and cardiovascular risk. Nutr J 9, 28 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-9-28
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-9-28