Abstract
Purpose
A review of the role of the carotenoids, lutein and zeaxanthin, and their function in altering the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Methods
Medline and Embase search.
Results
Recent evidence introduces the possibility that lutein and zeaxanthin, carotenoids found in a variety of fruits and vegetables may protect against the common eye disease of macular degeneration. This potential and the lack to slow the progression of macular degeneration, has fueled high public interest in the health benefits of these carotenoids and prompted their inclusion in various supplements. The body of evidence supporting a role in this disease ranges from basic studies in experimental animals to various other clinical and epidemiological studies. Whilst some epidemiological studies suggest a beneficial role for carotenoids in the prevention of AMD, others are found to be unrelated to it. Results of some clinical studies indicate that the risk for AMD is reduced when levels of the carotenoids are elevated in the serum or diet, but this correlation is not observed in other studies. Published data concerning the toxicity of the carotenoids or the optimum dosage of these supplements is lacking.
Conclusion
An intake of dietary supplied nutrients rich in the carotenoids, lutein and zeaxanthin, appears to be beneficial in protecting retinal tissues, but this is not proven. Until scientifically sound knowledge is available we recommend for patients judged to be at risk for AMD to: alter their diet to more dark green leafy vegetables, wear UV protective lenses and a hat when outdoors. Future investigations on the role of nutrition, light exposure, genetics, and combinations of photodynamic therapy with intravitreal steroid (triamcinolone-acetonide) injections hold potential for future treatment possibilities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
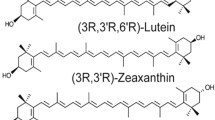
The two major carotenoids in the human macula and retina are lutein and zeaxanthin [1, 2]. Similar to β-carotene, these pigments are found in various coloured fruits and green leafy vegetables. Of the 40 to 50 carotenoids typically consumed in the human diet [3, 4], lutein and zeaxanthin, are deposited at an up to 5 fold higher content in the macular region of the retina [1] as compared to the peripheral retina. Zeaxanthin is preferentially accumulated in the foveal region [2, 5], whereas lutein is abundant in the perifoveal region. These pigments are collectively referred to as the macular pigment (MP). Although the role of the macular pigment remains uncertain, several functions have been hypothesised and these include limitation of the damaging photo-oxidative effects of blue light through its absorption [6–8], reduction of the effects of light scatter and chromatic aberration on visual performance, [9, 10], and protection against the adverse effects of photochemical reactions because of the antioxidant properties of the carotenoids [5, 11, 12].
Age related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of irreversible vision loss in the elderly population in the USA and the Western world. It is estimated that 1.6% of the population in the 50-to 65-year-old age group is affected, rising to 30% in the over-75-year-old age group. As the proportion of the elderly in our population increases, the public health impact of AMD will become even more severe Although the aetiopathogenesis of AMD remains a matter of debate, there is a growing body of evidence to indicate that oxidative damage plays a role [13, 14]. Consequently, the possibility that the absorption characteristics and antioxidant properties of macular pigment confer protection against age-related macular degeneration has been postulated [12, 15] and it has further been hypothesised that dietary supplementation with lutein and / or zeaxanthin might protect the retina and / or delay the progression of age-related macular degeneration [12, 16–18]. Supplementation with foods [19–21] or supplements rich in lutein or zeaxanthin has been reported to increase macular pigment density in most, but not all, human subjects [19, 21, 22]. Yet despite the possible importance of these carotenoids in modulating the course of age-related macular degeneration, critical evidence of beneficial effect has not been found, and the role that these carotenoid supplements play in patients with age-related macular degeneration, or those at risk of developing the disease, remains unproved. In this article we review the current literature present on carotenoids and focus particularly on the controversial evidence that retinal carotenoids are protective against age-related macular degeneration.
Methods
Medline and Embase search.
Results
Age related macular degeneration
Definition and grading
In 1995 the International Age Related Maculopathy (ARM) Study Group published the international classification and grading system for age related maculopathy and age related macular degeneration [23]. In this article all age related macular changes are referred to as age related maculopathy (ARM). ARM is a degenerative disorder involving the retinal pigment epithelium, choriocapillaries and retina which primarily, but not exclusively, affects the macular region. Symptoms of ARM include metamorphosia, impaired light adaptation and decreased central vision. Age related macular degeneration (AMD) is a term reserved for the late stages of ARM [23]. AMD has been categorised in two forms, an exudative form characterised by subretinal haemorrhage, detachment of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), choroidal neovascularization (CNV), or retinal scarring and a "dry" form which includes geographic atrophy. Once patients have reached the late stage of this disease, vision loss cannot be restored [24] and low vision aids are the only known help.
AMD remains the leading cause of legal blindness in the elderly population in the Western world [25–27]. The risk for AMD has been strongly linked to greater age [28], positive family history of AMD [29], smoking [30, 31], female gender [32], and finally the high intake of saturated fat has been demonstrated to be related to early ARM as shown in the Beaver Dam Eye Study [33]. Reports vary on the relationship between light iris colour and the severity of AMD or increase risk of for ARM [34–37]. It is estimated that 1.6% of the population in the 50-to 65-year-old age group is affected, rising to 30% in the over-75 year-old age group [38].
Dietary sources of lutein and zeaxanthin
Lutein is a common carotenoid found in most fruits and vegetables, while zeaxanthin is present only in minute quantities in most fruits and vegetables [39, 40]. Dietary sources of zeaxanthin are limited to greens, certain yellow/ orange fruits and vegetables such as corn, nectarines, oranges, papaya and squash. Orange pepper is recently found to have a high amount of zeaxanthin [40] and the dried fruit of Lycium barbarum (fructus lycii) prescribed by the Chinese herbalist as a therapeutic agent for a number of eye diseases, has been shown to have a high content of zeaxanthin but negligible amount of lutein [41].
The highest mole percentage of both lutein and zeaxanthin can be found in egg yolk and maize [40]. Substantial amounts of lutein are also known to be found in melon, spinach [41], collards, kale [42], and guava. In 1998, the United States department of Agriculture (USDA) updated their Carotenoid database for foods to include the concentrations of lutein and zeaxanthin in the most common fruits and vegetable consumed. http://www.nal.usda.gov/fnic/foodcomp/Data/car98/car98.html.
Pharmaceutical ocular vitamin and mineral supplements – the vitamin/mineral supplement controversy
The pharmaceutical industry also provides patients with various brands of ocular vitamin supplement products all claiming superiority over their competitors. Some of the brands of these ocular vitamins include: I Caps, Maxivision, Ocuguard, Ocuvite, Ocuvite Extra, Ocuvite PreserVision, Ocuvite Lutein, and Vizion. Supplementation with foods rich in lutein and zeaxanthin [19] or with lutein rich supplements [21, 22] increases macular pigment density in most, but not all, human subjects. Nutritional supplements are therefore promoted actively by the vitamin industry in the United States to individuals at risk for AMD. Yet the benefits of ocular antioxidant carotenoid containing vitamin and mineral supplements in patients with ARM, or those at risk of developing the disease remain unproved.
The relation of fasting plasma levels of retinol, ascorbate, alpha-tocopherol, beta-carotene and the use of vitamin supplements has shown that alpha tocopherol, and an antioxidant index including alpha tocopherol, beta-carotene, and ascorbate were protective for ARM [43]. However, no evidence of the protective effect of vitamin supplements was found in this study. In other studies discordant responses of serum and retina to dietary supplementation were observed. Serum lutein increased rapidly after supplementation in individuals, but macular pigment density increased only after several weeks of supplementation [19, 22, 44]. Some studies have shown no effect of supplementation with purified or synthetic beta-carotene on the concentrations of several plasma carotenoids [45–48]. In contrast, other studies have shown that purified or synthetic beta-carotene can diminish concentrations of lutein [49–51]. Hammond et al have reported that out of 13 subjects given supplemental dietary sources of lutein and zeaxanthin 2 subjects were retinal non-responders- that is, they had significant increases in serum lutein, but not in macular pigment density [19]. Recently the evidence of a higher incidence of cancer among cigarette smokers who received beta-carotene supplements in 2 studies [52, 53], was reported. Although beta carotene is considered safe because its conversion to vitamin A is limited [54], the ATBC study reported a significantly higher mortality among treated than non-treated subjects. To our knowledge published data concerning the toxicity of lutein and zeaxanthin or the optimum dosage or combination of these antioxidant vitamin/ mineral supplements is lacking. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS), under the auspices of the National Eye Institute of the National Institutes of Health, is carefully following two large cohorts of patients with AMD – one group is being treated with an Ocuvite formula, the other with a placebo. When the results of this study begin to be released in five to ten years, further guidance may become known.
The impact of zinc and other antioxidants on ARM
There seems to be some support in early clinical and epidemiological studies for the association of zinc and antioxidant nutrients with ARM. In a small clinical trial, high-dose zinc supplementation has been reported to reduce the loss of visual acuity in patients with macular degeneration [55]. Yet other studies were only weakly supportive of the protective effect of zinc on the development of early ARM [56]. More recently, the Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS), research group found a beneficial effect for supplementation with a combination zinc, vitamin E, vitamin C, and beta-carotene in individuals at high risk for disease progression to advanced AMD [57]. Results of this study showed that for patients at high risk of developing advanced stages of AMD, use of the combination of antioxidants and zinc supplements reduced that risk by 25%. For the same group, the risk of vision itself was reduced by 19%. Prospective studies conducted over time, with greater variability in zinc intake in the Beaver Dam population are under way and shall provide further estimates on the protective effect of zinc.
Transport and uptake mechanisms of the carotenoids
The biochemical mechanisms that mediate the selective uptake, concentration, and stabilisation of the of the macular carotenoids are unknown. In lower animals, such as lobsters and cyanobacteria, specialised carotenoid-binding proteins perform these tasks. Much less is known about carotenoid-binding proteins derived from vertebrates, yet it has been hypothesised that comparable carotenoid-binding proteins may have a similar role in the human macula. In the human blood stream, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) is the major carrier of lutein and zeaxanthin, while carotenes are preferentially carried by low-density lipoprotein (LDL) [58]. In the mammalian eye, it has been reported that retinal tubulin binds macular carotenoids [59], possibly as a site for passive deposition in the tissue. Further postulations included the assumption that human macular membranes could be a rich source of specific binding proteins for the macular carotenoids, especially since many plant and invertebrate carotenoid-binding proteins are known to be membrane associated [60, 61]. In a recent report, xanthophyll-binding proteins (XBP) were partially purified and isolated from the human macula and retina and it was shown that lutein and zeaxanthin bind specifically to these proteins [62]. Available evidence further suggests the presence of tissue competition for plasma carotenoids. The concept that adipose tissue and retina may compete for dietary lutein has been suggested [44], and the interactions between carotenoids during intestinal absorption has also been investigated [63]. It has hypothesised that if adipose tissue and liver compete with the retina for dietary lutein as suggested by observations in human subjects [44], macular pigment may be more effectively increased through supplementation with zeaxanthin than with lutein (preferentially absorbed by fat). There is no evidence in literature suggesting that zeaxanthin can be converted to lutein in serum or retina, but the reverse has been proposed by some authors [64, 65]. Dietary lutein may serve as a precursor for the very high concentrations of zeaxanthin found in the primate fovea, [64] and conversion of lutein to mesozeaxanthin has been suggested [66].
Controversial evidence on the beneficial effects of carotenoids and other antioxidant vitamins in modulating the course of AMD
Epidemiological evidence
Some epidemiological evidence suggest a beneficial role for carotenoids and antioxidant vitamins in the prevention of AMD [31, 67, 68]. In contrast, in a case control study consisting of subjects with late AMD, exudative AMD, and retinal pigment abnormalities with the presence of drusen, and an equal number of control subjects, the serum concentrations of lutein and zeaxanthin were found to be unrelated to the risk of incidence of AMD [69]. Lower risk for macular degeneration has been associated with the consumption of food sources of these carotenoids [70], with overall level of lutein and zeaxanthin in the diet [68, 71], or with higher levels of these carotenoids in the blood [31]. However, in several studies, these associations were not observed [56, 72] or were observed only in population subgroups [71]. Other epidemiological studies have reported a protective effect against lung cancer of foods rich in beta-carotene [73]. This finding has been contradicted in two recent studies in which supranutritional doses of beta-carotene (25–50 mg/day) supplemented to smokers during 6 y had a higher incidence of lung cancer than did the placebo-treated control subjects [52, 74]. Please see table 1, additional file 1.
Experimental evidence
The body of evidence available from studies in laboratory animals that supports associations between the intake of antioxidant nutrients and ARM is inconsistent. Several antioxidant nutrients known to affect retinal degeneration in animals have not been found to consistently correlate with macular degeneration in humans. In macaque monkeys fed diets devoid of all sources of carotenoid pigment, levels of these pigments in the macula disappear and retinal abnormalities (drusen formation), an early sign of ARM appear [75]. In contrast, inverse associations with several carotenoids in the serum [43, 69] or diet and early ARM have not been documented in studies in humans.
In a recent study done on rhesus monkeys serum levels and macular density of zeaxanthin was raised by feeding monkeys a carotenoid-containing fraction of fructus lycii also known as Gou Qi Zi [76]. This was contrary to the study by Snodderly et al [77] where no change in the concentration of serum lutein was noted after supplementation of zeaxanthin in squirrel monkeys.
A potential animal model in which to study the protective effects of these carotenoids is the quail. The quail retina has been shown to selectively accumulate lutein and zeaxanthin [78, 79] and quail retina has been shown to exhibit age-related loss of photoreceptors [80]. Preliminary studies indicate an inverse correlation between the level of zeaxanthin in quail retina and light-induced cell death [81, 82]. Further studies report that quail fed for 6 months on zeaxanthin-supplemented diets have an almost 5-fold elevation in retinal zeaxanthin, and a more than 45-fold increase in zeaxanthin concentrations in serum, liver and fat [79].
Reports on other antioxidant vitamins are also controversial. Supplementation of rats with vitamin C has been reported to reduce retinal damage due to intense light exposure [83]. However, several other human studies that have examined levels of vitamin C in the serum [43, 67] or foods [68, 70] have found similar statistically significant associations. Reports have shown that animals with diets deficient in vitamin E have increased retinal damage [84], although supplementation with this nutrient does not protect against light damage [85]. In human studies, one study [43], but not 3 others [67, 69, 86], have found low levels of this nutrient in the serum to be associated with lower risk for various forms of ARM.
Clinical evidence
Of the hypothesis that macular pigment protects against AMD was a study in which risk factors for AMD namely, age and advanced disease in the fellow eye, were shown to be associated with a relative absence of macular pigment [87]. Recently an autopsy study has reported that eyes from donors with a history of AMD had lower levels of macular carotenoids than eyes without a known history of AMD [88], although studies relying on post mortem analysis and retrospective reviews of clinical records after death have substantial limitations.
In some studies MP density was changed by dietary modification or through lutein supplementation [21, 22]. In another study, some subjects failed to show a change in MP density after increasing their dietary intake of lutein and zeaxanthin [19]. Evidence in favour of changing the dietary intake of fat soluble vitamins to protect against AMD has been contradicted by some authors [89]. Reports have also been made on the influence of factors such as sex, and smoking on the relation between MP density and serum concentrations of lutein and zeaxanthin [90, 91], yet these associations were evaluated in small study samples. Please see table 2, additional file 2.
Effect of light and genetic influence on ARM
It has been suggested that the exposure of the retina to light can promote the development of macular degeneration [92]. Increased risk for late AMD was associated with increased exposure to blue and visible light in a case control study of Chesapeake watermen [93, 94] and with increased exposure to sunlight in the Beaver Dam Eye Study [95]. Light exposure can also increase the production of free radicals in the lens and retina [96]. Epidemiological data to support a damaging role of light in macular degeneration is inconsistent [97], although the difficulty in capturing actual light exposure over many years in the participants studied must be taken into account.
Several results on genetic studies with ARM have been published. First-degree relatives of ARM patients are between 2 to 4 times greater at risk of developing ARM in comparison to controls [98]. Twin studies have shown high levels of concordance of the disease among monozygous sibs [99, 100]. Careful segregation analyses on a large study of 564 families suggest that a single major gene accounts for 89–97% of the genetic variability or 55–57% of the total variability [101]. Even so, relatively little is known about identified genetic risk factors for ARM and controversial reports exist supporting genetic variations [102, 103].
Treatment options for ARM and future hopes
Some of the clinical approaches to treating AMD include novel laser therapies (photodynamic laser therapy, PDT), surgery (submacular and macular translocation surgery), chemotherapeutic agents (angiogenesis inhibitors such as thaliomide, interferon, vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors), radiation (external beam/ teletherapy or episcleral plaque/bracytherapy), transplantation of retinal pigment epithelium and photoreceptors, and gene therapy.
One of the more promising therapies is photodynamic therapy (PDT). A light activated drug is administered intravenously, followed by a waiting period of several minutes to allow the neovascular network of vessels to bind and absorb the drug. Laser light is then applied to the now pharmacologically-sensitised target tissues resulting in precise demise of the microvascular network. This process spares the overlying elements, whereas surgery and radiation could cause retinal scar formation.
Recently, a combination of PDT along with intravitreal steroid (triamcinolone-acetonide) injections has been introduced. Steroid compounds are well known antiangiogenic agents which have been suggested as treatment for the choroidal neovascular membranes that cause visual loss in ARM [104, 105]. We hope to release the results of the study done on a cohort of patients treated with triamcinolone and PDT, along with a control group of patients treated with PDT, within one year. Much of our hope for successful future treatments also lies in the areas of suppression or modification of neovascular response with novel anti-antiogenic factors and gene therapy.
Discussion
The information available provides an indication that the carotenoids, lutein and zeaxanthin, may play a role in modulating the course of AMD, yet critical evidence of the beneficial effect has not been found, and crucial information for the most effective design of clinical trials is needed [106]. For the clinician it is clear that this area of research is only beginning to evolve and further research is indicated. There is no doubt that any scientific support for the use of these carotenoids and /or other vitamins or minerals with antioxidant properties will boost the supply of these supplements on pharmacy shelves, despite the unproved benefits. As of yet the long-term physiological consequences of taking ocular vitamin supplements are unknown, and until the optimum combination and dosage of these ocular antioxidant vitamins and minerals has been proven and their long-term safety established, the routine prescription of vitamin/mineral supplements cannot be justified.
We finally suggest that clinicians inform their patients that there is no agreement among scientists and doctors to the benefit of supplementation and we urge them to be cautious when prescribing ocular vitamin/mineral supplements. However, patients with ARM or at risk of developing the disease, should be encouraged to eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and in particular they should be informed by they clinician on the dietary sources rich in these carotenoids. We further recommend patients to wear UV protective lenses and a hat or cap when outdoors and suggest they see their primary care physician to treat any hypertension, hypercholesterolemia or potentially compromising vascular disease. We truly hope that future investigations on the role of nutrition, light exposure and genetics help reduce the incidence of this debilitating disease.
References
Handelman GJ, Dratz EA, Reay CC, van Kuijk JG: Carotenoids in the human macula and whole retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988, 29: 850-5.
Bone RA, Landrum JT, Fernandez L, Tarsis SL: Analysis of the macular pigment by HPLC: retinal distribution and age study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988, 29: 843-9.
Khachik F, Beecher GR, Goli MB, Lusby WR, Daitch CE: Seperation and quantification of carotenoids in human plasma. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 213: 205-219.
Khachik F, Beecher GR, Goli MB, Lusby WR: Seperation and quantification of carotenoids in foods. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 213: 347-359.
Snodderly DM, Handelman GJ, Adler AJ: Distribution of individual macular pigment carotenoids in the central retina of macaque and squirrel monkeys. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991, 32: 268-279.
Dichtburn RW: Eye movements and visual perception. Oxford: Claredon Press. 1973
Bone RA, Landrum JT: Macular pigment in Henle fiber membranes: a model for Haidinger's brushes. Vis Res. 1984, 24: 103-8. 10.1016/0042-6989(84)90094-4.
Kirschfeld K: Carotenoid pigments: their possible role in protecting against photooxidation in eyes and photoreceptor cells. Proc R Soc Lond. 1982, 216: 71-85.
Nussbaum JJ, Pruett RC, Delori FC: Macular yellow pigment. The first 200 years. Retina. 1981, 1: 296-310.
Reading VM, Weale RA: Macular pigment and chromatic aberration. J Optom Soc Am. 1974, 64: 231-4.
Foote CS, Chang YC, Denny RW: Chemistry of singlet oxygen. X: Carotenoid quenching parallels biological protection. J Am Chem Soc. 1970, 92: 5216-18.
Snodderly DM: Evidence for protection against age-related macular degeneration by carotenoids and antioxidant vitamins. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995, 62 (suppl): 1448s-60s.
Young RW: Solar radiation and age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol. 1988, 32: 252-69.
De La Paz MA, Anderson RE: Regional and age-dependent variation in susceptibility of the human retina to lipid peroxidation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992, 33: 3497-9.
Landrum JT, Bone RA, Kilburn MD: The macular pigment : a possible role in protection from age-related macular degeneration. Adv Pharm. 1997, 38: 537-56.
Moeller SM, Jaques PF, Blumberg JB: The potential role of dietary xanthophylls in cataract and age-related macular degeneration. J Am Coll Nutr. 2000, 19: 522S-527S.
Pratt S: Dietary prevention of age-related macular degeneration. J Am Optom Assoc. 1999, 70: 39-47.
Jaques PF: The potential preventive effects of vitamins for cataract and age-related macular degeneration. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 1999, 69: 198-205.
Hammond Br, Johnson EJ, Russel RM, Krinsky NI, Yeum KJ, Edwards RB, et al: Dietary modification of human macular pigment density. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997, 38: 1795-1801.
Handelman GJ, Nightingale ZD, Lichtenstein AH, Schaefer EJ, Blumberg JB: Lutein and zeaxanthin concentrations in plasma after dietary supplementation with egg yolk. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999, 70: 247-251.
Landrum JT, Bone RA, Joa H, Kilburn MD, Moore LL, Sprague KE: A one year study of the macular pigment: the effect of 140 days of a lutein supplement. Exp Eye Res. 1997, 65: 57-62. 10.1006/exer.1997.0309.
Berendschot TTJM, Goldbohm RA, Klopping WAA, van Norel J, van Norren D: Influence of lutein supplementation on macular pigment, assessed with two objective techniques. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000, 41: 3322-6.
The International ARM Epidemiological Study Group: An international classification and grading system for grading system for age-related maculopathy and age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol. 1995, 39: 367-74.
Macular Photocoagulation Study Group: Laser photocoagulation for juxtafoveal choroidal neovascularization. Five-year results for randomized clinical trials. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994, 112: 500-9.
Ghafour IM, Allan D, Foulds WS: Common causes of visual handicap in the west of Scotland. Br J Ophthalmol. 1983, 67: 209-13.
Ferris FL: Senile macular degeneration: review of epidemiological features. Am J Epidemiol. 1983, 118: 132-51.
Bressler NM, Bressler SB, Fine SL: Age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol. 1988, 32: 375-413.
Age-Related Eye Disease Study Report Number 3: Risk factors associated with age-related macular degeneration: a case-control study in the age-related eye disease study. Ophthalmology. 2000, 107: 2224-2232. 10.1016/S0161-6420(00)00409-7.
Klein ML, Mauldin WM, Stoumbos VD: Hereditory and age-related macular degeneration: observations in monozygotic twins. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994, 112: 932-937.
Smith W, Assink J, Klein R, Mitchell P, Klaver CC, Klein BE, et al: Risk factors for age-related macular degeneration: pooled findings from three continents. Ophthalmology. 2001, 108: 697-704. 10.1016/S0161-6420(00)00580-7.
Eye Disease Case-Control Study Group: Risk factors for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 1992, 110: 1701-1708.
Klein R, Rowland MR, Harris MI: Racial/ethnic differences in age-related maculopathy. Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Ophthalmology. 1995, 102: 371-8.
Mares-Perlman JA, Brady WE, Klein R, VandenLangenberg GM, Klein BEK, Palta M: Dietary fat and age-related maculopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995, 113: 743-748.
Holz FG, Piguet B, Minassian DC, Bird AC, Weale RA: Decreasing stromal iris pigmentation as a risk factor for age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994, 117: 19-23.
Sandberg MA, Gaudio AR, Miller S, Weiner A: Iris pigmentation and extent of disease in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994, 35: 2734-40.
Blumenkranz MS, Russel SR, Robey MG, Kott-Blumenkranz Penneys N: Risk factors in age-related maculopathy complicated by choroidal neovascularization. Ophthalmology. 1986, 93: 552-6.
Gibson JM, Shaw DE, Rosenthal AR: Senile cataract and senile macular degeneration. An investigation into possible risk-factors. Trans Ophthalmol Soc UK. 1986, 105: 463-9.
Votruba M, Zdenek G: Neovascular age-related macular degeneration: present and future treatment options. Eye. 2001, 15: 424-429.
Mangels AR, Holden JM, Beecher GR, Forman MR, Lanza E: Carotenoid content of fruits and vegetables:an evaluation of analytic data. J Am Diet Assoc. 1993, 93: 284-296.
Sommerburg O, Keunen JEE, Bird AC, van Kuijk FJGM: Fruits and vegetables that are sources of lutein and zeaxanthin: the macular pigment in human eye. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998, 82: 907-910.
Leung IYF, Ngai J, Lam KW, Tso MOM: Absorption of zeaxanthin in rats after feeding with purified zeaxanthin or a traditional Chinese medicine, gou chi zi. [ARVO abstract]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999, 40 (4): S608-Abstract nr 3196
Schalch W: Carotenoids in the retina: a review of their possible role in preventing or limiting damage caused by light and oxygen. In: Free radicals and ageing. Edited by: Emerit I, Chase B. 1992, Basel:Birkhauser
West S, Vitale S, Hallfrisch J, Munoz B, Muller D, Bressler S, et al: Are antioxidants or supplements protective for age-related macular degeneration?. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994, 112: 222-7.
Johnson EJ, Hammond BR, Yeum KJ, Qin J, Wang XD, Castaneda C, et al: Relation among serum and tissue concentrations of lutein and zeaxanthin and macular pigment density. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000, 71: 1555-1562.
Canfield LM, Giuliano AR, Neilson EM, Yap HH, Graver EJ, Cu HA, et al: Beta-carotene in breast milk and serum is increased after a single beta-carotene dose. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997, 66: 52-61.
Nierenberg DW, Dain BJ, Mott LA, Baron JA, Greenberg ER: Effects of 4 y of oral supplementation with beta-carotene on serum concentrations of retinol, tocopherol, and five carotenoids. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997, 66: 315-9.
Fotouhi N, Meydani M, Santos MS, Meydani SN, Hennekens CH, Gaziano JM: Carotenoid and tocopherol concentrations in plasma, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and red blood cells after long-term supplementation in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996, 63: 533-8.
Ribaya-Mercado JD, Ordovas JM, Russell RM: Effect of beta-carotene supplementation on the concentrations and distribution of carotenoids, vitamin E, vitamin A and cholesterol in plasma lipoprotein and non-lipoprotein fractions in healthy older women. J Am Coll Nutr. 1995, 14: 614-20.
Micozzi MS, Brown ED, Edwards BK, Bieri JG, Taylor PR, Khachik F, et al: Plasma carotenoid response to chronic intake of selected foods and beta-carotene supplements in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992, 55: 1120-5.
Albanes D, Virtamo J, Taylor PR, Rautalahti M, Pietinen P, Heinonen OP: Effects of supplemental beta-carotene, cigarette smoking, and alcohol consumption on serum carotenoids in the Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta-carotene Cancer Prevention Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997, 66: 366-72.
Faulks RM, Hart DJ, Scott KJ, Southon S: Changes in plasma carotenoid and vitamin E profile during supplementation with oil palm fruit carotenoids. J Lab Clin Med. 1998, 132: 507-11.
The Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta Carotene Cancer Prevention Study Group: The effect of vitamin E and beta-carotene on the incidence of lung cancer and other cancers in male smokers. N Engl J Med. 1994, 330: 1029-1035. 10.1056/NEJM199404143301501.
Peterson K: 'Natural' cancer prevention trial halted. Science. 1996, 271: 441-
Bendich A: The safety of beta-carotene. Nutr Cancer. 1988, 11: 207-14.
Newsome DA, Swartz M, Leone NC, Elston RC, Miller E: Oral zinc in macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988, 106: 192-198.
Mares-Perlman JA, Klein R, Klein BE, Greger JL, Brady WE, Palta M, Ritter LL: Association of zinc and antioxidant nutrients with age-related maculopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996, 114: 991-997.
AREDS report Nn. 8: A randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of high-dose supplementation with vitamins C and E, beta carotene, and zinc for age-related macular degeneration and vision loss. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001, 119: 1417-36.
Clevidence BA, Bieri JG: Association of carotenoids with human plasma lipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1993, 214: 33-46.
Bernstein PS, Balashov NA, Tsong ED, Rando RR: Retinal tubulin binds macular carotenoids. Inv Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997, 38: 167-75.
Lakshman Mr, Okoh C: Carotenoid-protein compexes. Methods Enzymol. 1993, 214: 74-86.
Reddy KJ, Bullerjahn GS, Sherman LA: Characteristics of membrane-associated carotenoid-binding proteins in cyanobacteria and prochlorophytes. Methods Enzymol. 1993, 214: 390-401.
Yemelyanov AYU, Katz NB, Bernstein PS: Ligand-binding characterization of xantophyll carotenoids to solubilized membrane proteins derived from human retina. Exp Eye Res. 2001, 72: 381-392. 10.1006/exer.2000.0965.
van den Berg H: Carotenoid interactions. Nutr Rev. 1999, 57: 1-10.
Bone RA, Landrum JT, Friedes LM, Gomez CM, Kilburn MD, Menendez E, et al: Distribution of lutein and zeaxanthin stereoisomers in the human retina. Exp Eye Res. 1997, 64: 211-218. 10.1006/exer.1996.0210.
Khachik F, Bernstein PS, Garland DL: Identification of lutien and zeaxanthin oxidation products in human and monkey retinas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997, 38: 1802-1811.
Bone RA, Landrum JT, Hime GW, Cains A, Zamor J: Stereochemistry of the human macular carotenoids. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993, 34: 2033-2040.
The Eye-Disease Case Control Study Group: Antioxidant status and neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993, 111: 104-109.
Seddon JM, Ajani UA, Sperduto RD, Hiller R, Blair N, Burton TC, et al: Dietary carotenoids, vitamin A, C, and E, and advanced age-related macular degeneration. JAMA. 1994, 272: 1413-1420. 10.1001/jama.272.18.1413.
Mares-Perlman JA, Brady WE, Klein R, Klein BE, Bowen P, Stacewicz-Sapuntzakis M, et al: Serum antioxidants and age-related macular degeneration in a population-based case control study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995, 113: 1518-1523.
Goldberg J, Flowerdew J, Smith E, Brody JA, Tso MOM: Factors associated with age-related macular degeneration: an analysis of data from the First National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Epidemiol. 1988, 128: 700-710.
Mares-Perlman JA, Fisher A, Klein R, Palta M, Block G, Millen AE, Wright JD: Lutein and zeaxanthin in the diet and serum and their relation to age-related maculopathy in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Epidemiol. 2001, 153: 424-432. 10.1093/aje/153.5.424.
Vandenlangenberg GM, Mares-Perlman JA, Klein R, Klein BEK, Brady WE, Palta M: Associations between antioxidant and zinc intake and the 5-year incidence of early age-related maculopathy in the Beaver Dam Eye Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1988, 148: 204-214.
Ziegler RG, Colavito EA, Hartge P, Mc Adams MJ, Schoenberg JB, Mason TJ, et al: Importance of alpha-carotene, beta-carotene, and other phytochemicals in the etiology of lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996, 88: 612-5.
Omenn GS, Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, Balmes J, Cullen MR, Glass A, et al: Effects of a combination of beta-carotene and vitamin A on lung cancer and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 1996, 334: 1150-5. 10.1056/NEJM199605023341802.
Malinow MR, Feeney-Burns L, Peterson LH, Klein ML, Neuringer M: Diet-related macular anomalies in monkeys. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1980, 19: 857-863.
Leung IYF, Tso MOM, Li WWY, Lam TT: Absorption and tissue distribution of zeaxanthin and lutein in rhesus monkeys after taking fructus lycii (Gou Qi Zi) extract. 2001, 42: 466-471.
Snodderly DM, Shen B, Land RI, Krinsky NI: Dietary manipulation of plasma carotenoid concentrations of squirrel monkeys (Saimiri Sciureus). JNutr. 1997, 127: 122-9.
Toyoda Y, Sapunztkis M, Nichols C, Cheng K, Dorey C: Preferential accumulation of lutein and zeaxanthin in the quail retina, an experimental model of the primate macula [ARVO Abstract]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996, 36 (3): S802-Abstract nr 3692
Toyoda Y, Thomson L, Langner A, Craft NE, Garnett KM, Nichols CR, et al: Effect of dietary zeaxanthin on tissue distribution of zeaxanthin and lutein in quail. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002, 43: 1210-1221.
Fite KV, Bengston L: Aging and sex-related changes in the outer retina of the Japanese quail. Curr Eye Res. 1989, 8: 1039-1048.
Goldsmith TH, Collins JS, Licht S: The cone oil droplets of avian retinas. Vision Res. 1984, 24: 1661-1671. 10.1016/0042-6989(84)90324-9.
Thomsom LR, Toyoda Y, Langner A, Delori FC, Garnett KM, Craft N, et al: Elevated retinal zeaxanthin and prevention of light-induced photoreceptor cell death in quail. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002, 43: 3538-49.
Organisciak DT, Want HM, Li Z, Tso MOM: The protective effect of ascorbate in retinal light damage of rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1985, 26: 1580-88.
Leure-duPree AE, Mc Clain CJ: The effect of severe zinc deficiency on the morphology of the rat retinal pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1982, 23: 425-434.
Ursin G, Ziegler RG, Subar AF, Graubard BI, Haile RW, Hoover R: Dietary pattern associated with low-fat diet in the national health examination follow-up study: identification of potential confounders for epidemiologic analyses. Am J Epidemiol. 1993, 137: 916-27.
Sanders TAB, Haines AP, Wormald R, Wright LA, Obeid O: Essential fatty acids, plasma cholesterol, and fat soluble vitamins in subjects with age-related maculopathy and matched control subjects. Am J Clinc Nutr. 1993, 57: 428-433.
Beatty S, Murray IJ, Henson DB, Carden D, Koh HH, Boulton ME: Macular pigment and risk for age-related macular degeneration in subjects from a Northern European population. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001, 42: 439-446.
Bone RA, Landrum JT, Mayne ST, Gomez CM, Tibor SE, Tweiska EE: Macular pigment in donor eyes with and without AMD: a case-control study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001, 42: 235-240.
Sanders TAB, Haines AP, Wormald R, Wright LA, Obeid O: Essential fatty acids, plasma cholesterol, and fat soluble vitamins in subjects with age-related maculopathy and matched control subjects. Am J Clinc Nutr. 1993, 57: 428-433.
Hammond BR, Curran-Celentano J, Judd S, Fuld K, Krinsky NI, Wooten BR, et al: Sex differences in macular pigment optical density: relation to plasma carotenoid concentrations and dietary patterns. Vision Res. 1996, 36: 2001-12. 10.1016/0042-6989(95)00290-1.
Hammond BR, Wooten BR, Snodderly DM: Cigarette smoking and retinal carotenoids: implications for age-related macular degeneration. Vision Res. 1996, 36: 3003-9. 10.1016/0042-6989(96)00008-9.
Borges J, Li ZY, Tso MOM: Effects of repeated public exposures on the monkey macula. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990, 108: 727-733.
West SK, Rosenthal FS, Bressler NM, Bressler SB, Munoz B, Fine SL, et al: Exposure to sunlight and other risk factors for age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989, 107: 875-859.
Taylor HR, West S, Munoz B, et al: The long-term effects of visible light on the eye. Arch Ophthalmol. 1992, 110: 99-104.
Cruickshanks KJ, Klein R, Klein BE: Sunlight and age-related macular degeneration. The Beaver Dam Eye Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993, 111: 514-518.
Dayhow-Barker P: Ocular photosensitization. Photochem Photobiol. 1986, 46: 1051-55.
McCarty C, Taylor HR: Light and risk for age-related eye diseases. In: Nutritional and environmental influences on the eye. Edited by: Taylor A. 1999, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 135-160.
Seddon AJ, Ajani UA, Mitchell BD: Familial aggregation of age-related maculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997, 123: 199-206.
Gottfredsdottir MS, Sverrisson T, Musch DC, Steffanson E: Age-related macular degeneration in monozygotic twins and their spouses in Iceland. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1999, 77: 422-425.
Meyers SM, Greene T, Gutman FA: A twin study of age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995, 120: 757-766.
Heiba IM, Elston RC, Klein BE, Klein R: Sibling correlations and segregation analysis of age-related maculopathy: the Beaver Dam Eye Study. Genet Epidemiol. 1994, 11: 51-67.
Allikmets R, Shroyer NF, Singh N, Seddon JM, Lewis RA, Bernstein PS, et al: Mutation of the Stargate disease (ABCR) in age-related macular degeneration. Science. 1997, 277: 1805-7. 10.1126/science.277.5333.1805.
Stone EM, Webster AR, Vandenburg K, Streb LM, Hockey RR, Lotery AJ, et al: Allelic variation in ABCR associated with Stargate disease but not age-related macular degeneration. Nat Genet. 1998, 20: 328-9. 10.1038/3798.
Danis R, Bingaman DP, Yang Y, Ladd B: Inhibition of preretinal and optic nerve head neovascularization in pigs by intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide. Ophthalmology. 1996, 103: 2099-2104.
Ciulla TA, Criswell MH, Danis RP, Hill TE: Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide inhibits choroidal neovascularization in a laser-treated rat model. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001, 119: 399-404.
Mares-Perlman JA: Too soon for lutein supplements. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999, 70: 431-432.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12937_2003_24_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Additional File 1: Summary of major epidemiological studies suggesting or contradicting a beneficial role of the carotenoids or other antioxidants in altering the pathogenesis of macular degeneration. (DOC 83 KB)
12937_2003_24_MOESM2_ESM.doc
Additional File 2: Summary of major clinical studies suggesting or contradicting a beneficial role of the carotenoids or other antioxidants in altering the pathogenesis of macular degeneration. (DOC 74 KB)
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Mozaffarieh, M., Sacu, S. & Wedrich, A. The role of the carotenoids, lutein and zeaxanthin, in protecting against age-related macular degeneration: A review based on controversial evidence. Nutr J 2, 20 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-2-20
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-2-20