Abstract
Background
A recent article by Reeves et al. on the identification and resolution of ambiguities in the 1994 chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) research case definition recommended the Checklist Individual Strength, the Chalder Fatigue Scale, and the Krupp Fatigue Severity Scale for evaluating fatigue in CFS studies. To be able to discriminate between various levels of severe fatigue, extreme scoring on the individual items of these questionnaires must not occur too often.
Methods
We derived an expression that allows us to compute a lower bound for the number of items with the maximum item score for a given study from the reported mean scale score, the number of reported subjects, and the properties of the fatigue rating scale. Several CFS studies that used the recommended fatigue rating scales were selected from literature and analyzed to verify whether abundant extreme scoring had occurred.
Results
Extreme scoring occurred on a large number of the items for all three recommended fatigue rating scales across several studies. The percentage of items with the maximum score exceeded 40% in several cases. The amount of extreme scoring for a certain scale varied from one study to another, which suggests heterogeneity in the selected subjects across studies.
Conclusion
Because all three instruments easily reach the extreme ends of their scales on a large number of the individual items, they do not accurately represent the severe fatigue that is characteristic for CFS. This should lead to serious questions about the validity and suitability of the Checklist Individual Strength, the Chalder Fatigue Scale, and the Krupp Fatigue Severity Scale for evaluating fatigue in CFS research.
Text
Since ambiguities in the 1994 chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) research case definition [1] do indeed contribute to inconsistenties in the identification of cases, I welcome the publication by Reeves et al. [2] and the authors' efforts to resolve these problems. However, I have to express my deepest concerns about the three instruments that the authors have recommend for measuring fatigue in research studies on CFS. Because all three instruments easily reach the extreme ends of their scales on a large number of the individual items, they do not accurately represent the severe fatigue that is required to satisfy any of the published CFS research case definitions [1, 3–5]. This low ceiling effect seriously distorts the fatigue measurements, which will inevitably result in bias and potentially misleading results.
To verify that the three recommended instruments do indeed exhibit low ceiling effects, one can study the mean scale scores that are reported in the literature. The recommended instruments were the Checklist Individual Strength (CIS) [6], the Chalder Fatigue Scale [7], and the Krupp Fatigue Severity Scale [8]. Each of these questionnaires consists of a fixed number of questions or statements. The answer to each question or the degree to which the participant agrees with a statement is scored on a certain scale. A question or statement with its corresponding scale is referred to as an item, and the assigned value corresponding to the participant's answer as the item score. A participant's fatigue rating scale score Y is computed by summing his individual item scores.
We can derive a lower bound L for the number of items with a maximum score for a given study by combining the reported mean fatigue rating scale score with the properties of the scale. Let us denote the reported number of subjects by n and the mean scale score of these subjects by 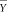 . We consider instruments that consist of N items, with m possible scores for each item. Each item score is an element of the set {S
1, S
2,..., S
m - 1, S
m
}, where S
i- 1 <S
i
. Hence, S
1 and S
m
are respectively the minimum and maximum possible item scores. We count the number of items with a certain score S
i
, and denote this number by k
i
. Because we have n individuals who each answered N questions, the k
i
's add up to nN. Consequently,
. We consider instruments that consist of N items, with m possible scores for each item. Each item score is an element of the set {S
1, S
2,..., S
m - 1, S
m
}, where S
i- 1 <S
i
. Hence, S
1 and S
m
are respectively the minimum and maximum possible item scores. We count the number of items with a certain score S
i
, and denote this number by k
i
. Because we have n individuals who each answered N questions, the k
i
's add up to nN. Consequently,

The sum of the item scores of all individuals together is equal to n
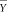 . Moreover, it is also equal to
. Moreover, it is also equal to  . Since S
i- 1 <S
i
, we find that
. Since S
i- 1 <S
i
, we find that

Hence, we find that the lower bound L that we were looking for is given by

If L should be negative, which happens when 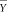 is less than N S
m - 1, then we set L to zero. A lower bound for the percentage of items with the maximum score is
is less than N S
m - 1, then we set L to zero. A lower bound for the percentage of items with the maximum score is  . Note that this percentage is independent of the number of subjects in the study.
. Note that this percentage is independent of the number of subjects in the study.
Lower bounds L for the number of items with the maximum score corresponding to data reported in literature were computed for each of the recommended fatigue rating scales. Because a recent Dutch article [9] recommended the Shortened Fatigue Questionnaire (SFQ) for assessing fatigue in clinical practice, this scale was also included in the analysis. The SFQ is simply a reduced version of the CIS 'fatigue severity' subscale, so the two are closely related.
At least two articles per fatigue rating scale were selected on a rather arbitrary basis. Subjects fulfilled the CDC88-CFS [3], Oxford-CFS [5], CDC94-CFS [1], or CDC94-UCF (unexplained chronic fatigue, i.e. either CFS or idiopathic chronic fatigue) [1] criteria. In particular, the study by Vercoulen et al. [10] was selected because it contains detailed data on the distribution of the scores for each CIS subscale. The study by Alberts et al. [11] was included because it contained normative data for the SFQ. The study by Vermeulen et al. [12] was selected to also include data on the SFQ from another source than the University Medical Centre Nijmegen. The article by Jason et al. [13] was selected because it was specifically concerned with the reliability and validity of a screening instrument for CFS. A recent Cochrane review [14] has investigated the relative effectiveness of exercise therapy and control treatments for CFS. All four studies that were included in that review and that have already been published [15–18] were analyzed here (one study by Moss-Morris et al. that was included in the review was submitted but not yet published). The other studies were selected because they were easily available to the author. Baseline data for Friedberg and Krupp [19] and Deale et al. [20] were read from the graphs presented in the articles. It is remarked that the 'matched ambulant group' in Van der Werf et al. [21] is a subset of the 'total ambulant group' in that study. Furthermore, the 'research participants' in Van der Werf et al. [22] are the same subjects as the 'total ambulant group' in [21].
The lower bounds for the number of items with the maximum score are presented in Table 1. From the lower bounds listed in the last column of the table we see that for several studies the number of items with the maximum score is larger than 40%. It is emphasized that the lower bounds were derived assuming a worse case scenario for the distribution of the item scores, i.e. participants have either the highest or the second highest possible score on each item. Since the worse case distribution is quite unrealistic, in reality the percentages of items with the maximum score are generally (even) higher than the values reported in the table. For example, according to the table it is not possible to conclude that extreme scoring occurred on the 'physical activity' subscale of the CIS in the study by Vercoulen et al. [10]. However, according to additional data listed in that article the 80th percentile of the 'physical activity' subscale is equal to the maximum possible subscale score of 3 × 7 = 21. Thus approximately 20% of the subjects reached the extreme score on all of their items, from which we can infer that extreme scoring occurred on at least 20% of the items.
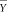 is the reported mean (sub)scale score, and L is the derived lower bound for the number of items with the maximum score. The last column lists a lower bound for the percentage of items with the maximum score based on L. The second highest possible item score S
m - 1 is equal to S
m- 1 for all considered (sub)scales.
is the reported mean (sub)scale score, and L is the derived lower bound for the number of items with the maximum score. The last column lists a lower bound for the percentage of items with the maximum score based on L. The second highest possible item score S
m - 1 is equal to S
m- 1 for all considered (sub)scales.It should be clear that extreme scoring on a large number of items occurred for all scales across several studies. Only the 'concentration' and 'reduced motivation' subscales of the CIS did not show evidence of extreme scoring. That the amount of extreme scoring for a certain scale varies from one study to another suggests heterogeneity in the selected subjects across studies. Since the studies that were analyzed were selected on a rather arbitrary basis and not in a systematic way, the data in Table 1 should not be regarded as a true reflection of the CFS literature as a whole. The main point is that it does prove that abundant extreme scoring occurred for all the recommended fatigue rating scales in at least some of the CFS studies published in literature.
One only needs to glance at the three recommended instruments to understand why extreme scoring occurs so often. The CIS and the Krupp Fatigue Severity Scale consist of statements like "I feel tired" and "I am easily fatigued" that are scored on seven-point scales (from "yes, that is true" to "no, that is not true" for the CIS; from "strongly disagree" to "strongly agree" for the Krupp scale). Thus it does not matter whether a subject feels 'extremely tired,' 'severely tired' or 'just tired,' and is 'easily extremely fatigued,' 'easily severely fatigued' or 'easily fatigued;' he will score on the extreme end of the scale for all these cases. A similar argument applies to the Chalder Fatigue Scale, where the participant has to choose from one of four answers like "less than usual," "no more than usual," "more than usual" and "much more than usual" to questions such as "Do you feel weak?" For the continuous version of the Chalder scale answers are rated from 0 to 3, for the bimodal version the scoring system is {0, 0, 1, 1}. This explains why the binary version performs even worse than the continuous version.
Interestingly, the ceiling effect has been noted before by members of the International CFS Study Group in their individual publications: "The CIS-fatigue score [i.e. the 'fatigue severity' subscale of the CIS] involves an overall rating and in CFS samples easily reaches the extreme end of its scale" [21]; "a ceiling effect in the [Krupp] Fatigue Severity Scale may limit its utility to assess severe fatigue-related disability" [24]. A publication that examined the distribution of the 14 items of the Chalder Fatigue Scale in 136 CFS patients found that "Scores on eight items were normally distributed, but six items ('tiredness,' 'resting more,' 'lacking energy,' 'feeling weak,' 'feeling sleepy or drowsy,' and 'starts things without difficulty but gets weaker as goes on') were highly skewed with the majority of patients reaching the maximum score" [25].
Abundant extreme scoring and the corresponding inability to discriminate between various levels of severe fatigue can lead to misleading results in several ways. For example, van der Werf et al. [21] compared a group of 18 homebound CF(S) patients with a group of 32 matched ambulant CF(S) patients. No significant difference was found when fatigue was measured with the CIS 'fatigue severity' subscale (p = 0.39). But when fatigue was measured with the 'Daily Observed Fatigue' scale that does not exhibit such a strong ceiling effect, it was concluded that the homebound group was significantly more fatigued than the ambulant group (p < 0.01). Another problem occurs when studying the relation between the experienced level of fatigue and another factor such as social support. Then the correlation between the two will certainly be distorted if the fatigue measurement has a low ceiling effect and the other measure has not. The most dangerous situation however arises when a scale with low ceiling is used as a primary outcome measure to evaluate a CFS treatment. Consider five patients with a baseline CIS-fatigue score of 52 (e.g. the mean baseline score in Prins et al. [26] was 52.1). Suppose one patient improves (e.g. CIS-fatigue = 16 at follow-up) and the other four patients become extremely fatigued due to treatment (CIS-fatigue = 56 at follow-up, i.e. the maximum scale score). Then still the overall mean has improved from 52 to 48, even though 80% of the subjects are substantially more fatigued after treatment. In particular, participants who already have the maximum scale score at baseline can never get worse according to the 'recommended' fatigue rating scales. Systematic errors that may result in artificial treatment effects opposite to the true situation should be avoided at all times.
Unfortunately, the reasons for recommending the CIS, the Krupp and the Chalder scales in the main article text are limited to 'they have been used before,' 'normative data have been collected' and 'receiver-operating characteristics have been published.' In the Author's response to reviews (25 July 2003) that is available on the pre-publication site of the article, the authors remark that these are all 'standardized, validated, internationally accepted instruments' without giving any reference to support this statement. Although the recommended fatigue rating scales might indeed be accepted by numerous scientists of various nationalities, the evidence presented here must lead to serious questions about their validity and suitability for CFS research.
Noticeably, the Profile of Fatigue-Related Symptoms (PFRS) that was developed more than a decade ago by Ray et al. [27, 28] is a rating scale that does not has the flaw of low ceiling in CFS samples. It consists of the four subscales 'Emotional Distress,' 'Cognitive Difficulty,' 'Fatigue' and 'Somatic Symptoms.' All subscales have high reliability and showed good convergence with comparison measures. Why was the PFRS not included in the authors' advice? To shed some light on the underlying scientific process that has ultimately led to their recommendations, I would like to ask the authors to make the workshop summaries and the focus group reports available.
Strictly speaking, the CIS, the Krupp Fatigue Severity Scale and the Chalder Fatigue Scale are all able to discriminate between CFS subjects and healthy subjects. Thus all three might indeed be used to improve the precision of CFS case ascertainment for research studies. However, if one really wishes to take CFS research forwards instead of three steps backwards, then it would be wise to abandon these low ceiling fatigue rating scales and start focussing on instruments that accurately represent the severe fatigue that is currently defined to be so characteristic for CFS.
References
Fukuda K, Straus SE, Hickie I, Sharpe MC, Dobbins JG, Komaroff A, the International Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Study Group: The chronic fatigue syndrome: a comprehensive approach to its definition and study. Ann Intern Med. 1994, 121: 953-959.
Reeves WC, Lloyd A, Vernon SD, Klimas N, Jason LA, Bleijenberg G, Evengard B, White PD, Nisenbaum R, Unger ER, the International Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Study Group: Identification of ambiguities in the 1994 chronic fatigue syndrome research case definition and recommendations for resolution. BMC Health Serv Res. 2003, 3: 25-10.1186/1472-6963-3-25.
Holmes GP, Kaplan JE, Gantz NM, Komaroff AL, Schonberger LB, Straus SE, Jones JF, DuBois RE, Cunningham-Rundles C, Pahwa S, Tosato G, Zegans LS, Purtilo DT, Brown N, Schooley RT, Brus I: Chronic fatigue syndrome: a working case definition. Ann Intern Med. 1988, 108: 387-389.
Lloyd AR, Hickie I, Boughton CR, Spencer O, Wakefield D: Prevalence of chronic fatigue syndrome in an Australian population. Med J Aust. 1990, 153: 522-528.
Sharpe MC, Archard LC, Banatvala JE, Borysiewicz LK, Clare AW, David A, Edwards RHT, Hawton KEH, Lambert HP, Lane RJM, McDonald EM, Mowbray JF, Pearson DJ, Peto TEA, Preedy VR, Smith AP, Smith DG, Taylor DJ, Tyrrell DAJ, Wessely S, White PD: A report – chronic fatigue syndrome: guidelines for research. J R Soc Med. 1991, 84: 118-121.
Bültmann U, de Vries M, Beurskens AJHM, Bleijenberg G, Vercoulen JHMM, Kant IJ: Measurement of prolonged fatigue in the working population: determination of a cutoff point for the checklist individual strength. J Occup Health Psychol. 2000, 5: 411-416. 10.1037//1076-8998.5.4.411.
Chalder T, Berelowitz G, Pawlikowska T, Watts L, Wessely S, Wright D, Wallace EP: Development of a fatigue scale. J Psychosom Res. 1993, 37: 147-153. 10.1016/0022-3999(93)90081-P.
Krupp LB, LaRocca NG, Muir-Nash J, Steinberg AD: The fatigue severity scale: application to patients with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Neurol. 1989, 46: 1121-1123.
van Engelen BGM, Kalkman JS, Schillings ML, van der Werf SP, Bleijenberg G, Zwarts MJ: Moeheid bij neuromusculaire aandoeningen. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2004, 148: 1336-1341.
Vercoulen JHMM, Alberts M, Bleijenberg G: De checklist individual strength (CIS). Gedragstherapie. 1999, 32: 131-136.
Alberts M, Smets EMA, Vercoulen JHMM, Garssen B, Bleijenberg G: 'Verkorte vermoeidheidsvragenlijst': een praktisch hulpmiddel bij het scoren van vermoeidheid. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1997, 141: 1526-1530.
Vermeulen RCW, Scholte HR: Chronic fatigue syndrome and sexual dysfunction. J Psychosom Res. 2004, 56: 199-201. 10.1016/S0022-3999(03)00546-4.
Jason LA, Ropacki MT, Santoro NB, Richman JA, Heatherly W, Taylor R, Ferrari JR, Haney-Davis TM, Rademaker A, Dupuis J, Golding J, Plioplys AV, Plioplys S: A screening instrument for chronic fatigue syndrome: reliability and validity. Journal of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. 1997, 3: 39-59.
Edmonds M, McGuire H, Price J: Exercise therapy for chronic fatigue syndrome (Cochrane Review). The Cochrane Library. 2004, Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 3
Wearden AJ, Morriss RK, Mullis R, Strickland PL, Pearson DJ, Appleby L, Campbell IT, Morris JA: Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment trial of fluoxetine and graded exercise for chronic fatigue syndrome. Br J Psychiatry. 1998, 172: 485-490.
Fulcher KY, White PD: Randomised controlled trial of graded exercise in patients with the chronic fatigue syndrome. BMJ. 1997, 314: 1647-1652.
Wallman KE, Morton AR, Goodman C, Grove R, Guilfoyle AM: Randomised controlled trial of graded exercise in chronic fatigue syndrome. Med J Aust. 2004, 180: 444-448.
Powell P, Bentall RP, Nye FJ, Edwards RHT: Randomised controlled trial of patient education to encourage graded exercise in chronic fatigue syndrome. BMJ. 2001, 322: 387-390. 10.1136/bmj.322.7283.387.
Friedberg F, Krupp LB: A comparision of cognitive behavioral treatment for chronic fatigue syndrome and primary depression. Clin Infect Dis. 1994, 18 (Suppl 1): S105-S110.
Deale A, Chalder T, Marks I, Wessely S: Cognitive behavior therapy for chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 1997, 154: 408-414.
van der Werf S, Prins J, Klein-Rouweler E, Alberts M, van der Meer J, Bleijenberg G: Homebound chronic fatigue syndrome patients. Determinants and consequences of experienced fatigue in chronic fatigue syndrome and neurological conditions. PhD thesis. Edited by: van der Werf SP. 2000, Katholieke Universiteit Nijmegen, 31-41. [http://webdoc.ubn.kun.nl/mono/w/werf_s_van_der/deteancoo.pdf]
van der Werf S, Prins J, Jansen T, van der Meer J, Bleijenberg G: Results of a large survey among members of the Dutch ME-Association. Determinants and consequences of experienced fatigue in chronic fatigue syndrome and neurological conditions. PhD thesis. Edited by: van der Werf SP. 2000, Katholieke Universiteit Nijmegen, 15-22. [http://webdoc.ubn.kun.nl/mono/w/werf_s_van_der/deteancoo.pdf]
DeLuca J, Johnson SK, Ellis SP, Natelson BH: Cognitive functioning is impaired in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome devoid of psychiatric disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997, 62: 151-155.
Friedberg F, Jason LA: Selecting a fatigue rating scale. The CFS Research Review. 2002, 35: 7-11. [http://www.cfids.org/archives/2002rr/2002-rr4-article02.asp]
Morriss RK, Wearden AJ, Mullis R: Exploring the validity of the Chalder fatigue scale in chronic fatigue syndrome. J Psychosom Res. 1998, 45: 411-417. 10.1016/S0022-3999(98)00022-1.
Prins JB, Bleijenberg G, Bazelmans E, Elving LD, de Boo TM, Severens JL, van der Wilt GJ, Spinhoven P, van der Meer JWM: Cognitive behaviour therapy for chronic fatigue syndrome: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2001, 357: 841-847. 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04198-2.
Ray C, Weir WRC, Phillips S, Cullen S: Development of a measure of symptoms in chronic fatigue syndrome: the profile of fatigue-related symptoms (PFRS). Psychol Health. 1992, 7: 27-43.
Ray C, Weir WRC, Cullen S, Phillips S: Illness perception and symptom components in chronic fatigue syndrome. J Psychosom Res. 1992, 36: 243-256. 10.1016/0022-3999(92)90089-K.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6963/5/37/prepub
Acknowledgements
The author thanks Dr. Ellen Goudsmit, psychologist, for proofreading the original manuscript and providing valuable information on the various fatigue rating scales.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The author(s) declares that he has no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
BS wrote the paper and performed the analysis.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Stouten, B. Identification of ambiguities in the 1994 chronic fatigue syndrome research case definition and recommendations for resolution. BMC Health Serv Res 5, 37 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-5-37
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-5-37

