Abstract
Background
Oxidative Stress contributes to the pathogenesis of many diseases. The NRF2/KEAP1 axis is a key transcriptional regulator of the anti-oxidant response in cells. Nrf2 knockout mice have implicated this pathway in regulating inflammatory airway diseases such as asthma and COPD. To better understand the role the NRF2 pathway has on respiratory disease we have taken a novel approach to define NRF2 dependent gene expression in a relevant lung system.
Methods
Normal human lung fibroblasts were transfected with siRNA specific for NRF2 or KEAP1. Gene expression changes were measured at 30 and 48 hours using a custom Affymetrix Gene array. Changes in Eotaxin-1 gene expression and protein secretion were further measured under various inflammatory conditions with siRNAs and pharmacological tools.
Results
An anti-correlated gene set (inversely regulated by NRF2 and KEAP1 RNAi) that reflects specific NRF2 regulated genes was identified. Gene annotations show that NRF2-mediated oxidative stress response is the most significantly regulated pathway, followed by heme metabolism, metabolism of xenobiotics by Cytochrome P450 and O-glycan biosynthesis. Unexpectedly the key eosinophil chemokine Eotaxin-1/CCL11 was found to be up-regulated when NRF2 was inhibited and down-regulated when KEAP1 was inhibited. This transcriptional regulation leads to modulation of Eotaxin-1 secretion from human lung fibroblasts under basal and inflammatory conditions, and is specific to Eotaxin-1 as NRF2 or KEAP1 knockdown had no effect on the secretion of a set of other chemokines and cytokines. Furthermore, the known NRF2 small molecule activators CDDO and Sulphoraphane can also dose dependently inhibit Eotaxin-1 release from human lung fibroblasts.
Conclusions
These data uncover a previously unknown role for NRF2 in regulating Eotaxin-1 expression and further the mechanistic understanding of this pathway in modulating inflammatory lung disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Oxidative stress in tissues leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species which can interfere with normal cellular function and homeostasis and can contribute to the pathophysiology of many diseases including cancer, atherosclerosis, ischemia reperfusion injury, neurodegenerative disorders and aging [1]. The lung is highly susceptible to oxidant stress since it is exposed to high amounts of oxygen [2] and exogenous oxidants found in environmental pollution such as ozone or diesel exhaust particles [3]. As such, markers of oxidative stress are present in the lungs of people with many pathological conditions including asthma [4, 5], COPD [6] and acute lung injury [7, 8]. There is a large body of evidence from clinical and preclinical studies that this oxidative stress is a key contributor to the disease pathophysiology [9–17] and can modulate responses to pharmacological respiratory therapeutics [18].
Since oxidative stress can have such detrimental effects to the health of the organism, there has evolved an extensive endogenous intracellular and extracellular anti-oxidant system to maintain redox homeostasis [1]. One of the key regulators of this endogenous anti-oxidant system is the transcription factor nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NFE2L2, NRF2). NRF2 is basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor that regulates the expression of numerous genes that encode anti-oxidant and detoxifying phase II enzymes through the binding to cis-acting anti-oxidant response elements (AREs) found in the promoters of these genes. Thus, NRF2 acts as the master regulator of the cellular response to oxidant injury [19]. In order to ensure that the anti-oxidant response is appropriately regulated, under conditions of redox homeostasis NRF2 is sequestered in the cytoplasm by binding through its N-terminal Neh2 domain to Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) [20, 21]. KEAP1 also functions as a substrate adaptor for the cullin-dependent E3 ligase and targets NRF2 for ubiquitination and degradation by the 26S proteasome [22, 23]. Several stimuli including oxidants, toxic agents and electrophilic agents can lead to an oxidation of key sulphydryl groups on KEAP1 leading to the release of NRF2 where it can enter the nucleus and activate the anti-oxidant machinery [24, 25]. In support of this, it has been shown that KEAP1 deficiency results in constitutive activation of NRF2 responsive gene expression [26].
There is significant data suggesting a critical role for NRF2 in preventing lung disease. Studies in COPD patients have shown that NRF2 dependent genes are activated in disease [27], but that as disease progresses there is a defect in this antioxidant response [28]. In preclinical species, there is increased expression of NRF2 regulated genes in cigarette smoke induced models of COPD [29] and in allergic lung models [17] implicating NRF2 as an endogenous regulator of oxidative stress in these models. This critical role has been confirmed in studies using Nrf2 deficient mice. In an allergen-induced model of airway inflammation, loss of Nrf2 has been shown to result in an increase in cellular recruitment to the lung, mucus hypersecretion and airway hyperresponsiveness [30]. Similarly, in cigarette smoke-induced models of COPD, Nrf2 deficiency leads to an increase in inflammation and emphysema [31, 32]. Additionally, Nrf2 deficient mice have also been shown to have increased susceptibility to acute lung injury [33] and Respiratory Syncytial virus infection [34]. Importantly, treatment of mice with pharmacological agents that can activate NRF2 can lead to the inhibition of cigarette smoke [35] and allergen induced pathology in the lung [17]. Thus, there is a clear demonstration of the critical role of the endogenous anti-oxidant response and NRF2 in regulating airway disease.
In order to understand the precise mechanisms of the NRF2 induced anti-oxidant response, researchers have largely turned to expression profiling experiments to determine those genes that mediate NRF2 activity in the tissue or model of interest. Most of these studies have utilized Nrf2 deficient mice or pharmacological treatment of various NRF2 activating compounds to define the NRF2 responsive genes [36–41]. These studies have lead to a well established group of NRF2 regulated genes, however, many novel or differentially regulated genes have been identified suggesting that there are species, tissue and model dependent differences in NRF2 regulated gene expression [42–47].
In this study we have taken a novel approach to define NRF2 dependent gene expression in normal primary human lung fibroblasts. These cells were chosen owing to the known role of oxidative stress pathways in fibroblasts [48], and the known role of fibroblasts to airway remodelling and a source of inflammatory mediators involved in asthma [49–51]. We have utilized siRNA to selectively and robustly knockdown the transcript levels of both NRF2 and KEAP1. Using microarray profiling we have defined a distinct set of anti-regulated genes as well as genes specifically modulated by KEAP1 or NRF2 knockdown. Interestingly, we report the discovery that NRF2 activation by KEAP1 knockdown or by pharmacological activators of NRF2 can specifically inhibit Eotaxin-1/CCL11 expression in human lung fibroblasts independent of several other chemokines further implicating this pathway in asthma pathogenesis.
Methods
Reagents
The IKK-β inhibitor Compound A was synthesized according to previously described methodology [52]. 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO) was synthesized according to previously described methodology [53]. Sulphorafane was purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Cat No. S6317). All siRNA pools were purchased from Sigma Proligo. The siRNA sequences are listed in Additional file 1. Two siRNA pools for KEAP1 and all three pools for NRF2 were comprised of 10 non-redundant siRNAs at low concentration (1 nM each) which has been shown to result in superior specificity while retaining potent target message knockdown compared to less complex pools at higher concentrations (our unpublished observations). The final pool for KEAP1 was generated through the esiRNA technique [54].
siRNA transfection and RNA preparation for microarray
Briefly, endoribonuclease-prepared short interfering RNAs (esiRNA) (KEAP1) or siRNA pools (10 individual siRNAs for each; pool 1: siRNA 1-10, pool 2: siRNA 11-20, pool 3: siRNA 21-30; see Additional file 1) for NRF2 and KEAP1 were incubated with Hiperfect reagent (Qiagen) in basal media (Lonza, # CC-3131) with no serum or antibiotics and allowed to complex for 10 min at room temperature. During this incubation, normal human lung fibroblasts (Lonza, #CC-2512) were plated in T25 flasks (6 × 105 cells/flask) in media containing 2% serum and growth factors but no antibiotics. The complex was then added to the cell suspension of each well (final siRNA pool concentration of 10 nM, 1 nM of each siRNA). Cells were then incubated for 30 hr or 48 hr in a humidified incubator. At the end of the incubation period, the culture medium was removed and the cells were lysed by direct resuspension in Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, CA). Crude total RNA was isolated from Trizol-dissolved samples and purified using the RNAeasy kit (Qiagen) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA concentration was measured using a NanoDrop ND-1000 (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE), and RNA integrity was determined with a 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). Samples displaying a RNA integrity number greater than 8 were used for profiling.
Affymetrix GeneChip experiment
Samples were amplified and labelled using a custom automated version of the RT/IVT protocol and reagents provided by Affymetrix. Hybridization, labelling and scanning were completed following the manufacturer’s recommendations (Affymetrix). For data analysis, we used the mock-transfected sample as the reference to compare with all other time-matched samples to obtain the ratio data. Merck/Affymetrix human custom arrays monitoring 43,737 individual transcripts were used. Raw intensity was normalized using the RMA algorithm. Enrichment for biological processes was performed by comparing each gene signature against the public gene collections Gene Ontology, KEGG, Swissprot and Panther families. Enrichment P values (hypergeometric distribution) were corrected for multiple testing by using Bonferroni correction. Pathway analysis was performed using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) (http://www.ingenuity.com/index.html). Overlap of each gene signature with other publicly available gene signatures was performed by using NextBio libraries (NextBio) (http://nextbio.merck.com/c/nextbio.nb).
NRF2 and KEAP1siRNA transfection for Q-PCR and chemokine/cytokine mesurements
Briefly, siRNA pools for NRF2 and KEAP1 were incubated with Hiperfect reagent (Qiagen, # 301705) in basal media (Lonza, # CC-3131) with no serum or antibiotics and allowed to complex for 10min at room temperature. During this incubation, normal human lung fibroblasts (Lonza, #CC-2512) were plated in 24-well or 96-well plates (Costar # 3524, BD Falcon # 353948), at 4×104 or 2×104 cells/well, respectively, with 2% serum but no antibiotics. The complex was then added to the cell suspension for each well (final siRNA pool concentration of 10 nM). Cells were then incubated for 48 hrs in a humidified incubator. After 48 hrs, cells were challenged with 1 ng/ml of human IL-1β (R+D systems # 201-LB-005) or PBS-0.1% BSA control for 18hrs. After 18 hrs challenge, cells were spun down for RNA isolation and supernatants were removed for cytokine and chemokine measurements.
Real time quantitative PCR
Total RNA was isolated using QIAGEN RNeasy mini tubes according to the manufacturer’s animal cell extraction protocol (QIAGEN # 74106) which included the DNase step (QIAGEN # 79254). All TAQMAN probes were purchased from Applied Biosystems. Reverse transcription was performed in 100 μl of reaction solution using the following reagents per condition (Applied Biosystems # N808-234): 10 μl of 10X reverse transcription buffer, 20 μl of 25 mM MgCl2, 10 μl of 10 mM dNTP mixture (2.5 mM each), 5 μl of 50 μM random hexamer, 5 μl of 20 U/μl RNase inhibitor, 5 μl of 50 U/μl Multiscribe reverse transcriptase and 45 μl of RNase-free H2O/RNA template mix. The RT-PCR reaction conditions 10min incubation at 25°C, 30min at 42°C and 5min at 99°C. The real time PCR reaction was carried out using the Fast TAQMAN PCR apparatus (Applied Biosystems) and the following reagents were used per PCR condition which was carried out in a 20 μl volume (all reagents purchased from Applied Biosystems except the water): 10 μl of 2X master mix, 1 μl of 20X TAQMAN primer-probe mix, 0.2 μl of AmpErase Uracil N-glycosylase, 0.8 μl of sterile water and 8 μl of cDNA template. The amplification conditions were as follows: 2 min at 50°C, 20 sec at 95C, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 1 sec and 60°C for 20 sec. All expression data was normalized for loading using human PPIA.
Cytokine and chemokine measurements
Cells were cultured in the manner described above for siRNA knockdown studies. For studies using compounds, cells were seeded as described above, but in the absence of siRNA transfection. In this case, 1 day following plating, cells were treated with Compound A, Sulphorfane, CDDO or DMSO. 1 hour after compound dosing, cells were challenged with 1 ng/ml human IL-1β, or 10 ng/ml human TNFα R+D systems, # 210-TA), or 10 ng/ml mouse IL-13 or PBS-0.1% BSA control for an additional 24 hrs. Cells were then spun down and supernatants were assayed for cytokine and chemokine using Mesoscale Discovery platform assay plates (#K111AAB-2) according to manufacturer’s protocols.
Statistical analysis
Student’s t test was performed on all data points. All data are represented as mean ± Standard Deviation.
Results
siRNA knockdown of NRF2 and KEAP1in NHLFs
To better understand NRF2/KEAP1 regulated genes in the lung, we chose to employ siRNA knockdown in normal human lung fibroblasts (NHLFs) to specifically modulate this pathway. In this approach, we utilized knockdown of KEAP1, which should result in NRF2 activation [26], to identify those genes regulated by NRF2 activation and utilized knockdown of NRF2 to better define those genes dependent on baseline NRF2 activity. To minimize any confounding effects of potential off-target activity of siRNA [55] we conducted our study using three distinct pools of siRNA for both KEAP1 and NRF2. As shown in Figure 1, significant knockdown (> 80%) of both KEAP1 (Figure 1A) and NRF2 (Figure 1B) mRNA was achieved for all pools tested, as measured by quantitative PCR (QPCR), compared to the negative control firefly luciferase siRNA transfection. To ensure that knockdown of NRF2 and KEAP1 in NHLFs resulted in a significant modulation of classical NRF2 regulated genes we analysed the transcript levels of the ARE-regulated genes MRP2, HMOX-1 and NQO1 following transfection at both time points by (QPCR). KEAP1 knockdown resulted in a significant upregulation of the expression of all of the genes tested at both time points indicating that NRF2 is activated as a result of KEAP1 knockdown (Figure 1C-E). Interestingly, NRF2 knockdown resulted in a decrease in the basal expression of all of these genes (Figure 1C-E) showing that basal activity of NRF2 is required for the expression of these genes in non-stressed conditions. Overall these data indicate that this siRNA approach resulted in significant functional modulation of the KEAP1/NRF2 pathway.
Changes in mRNA expression following NRF2 and KEAP1 gene-specific siRNA transfection in NHLFs. (A,C-E) Cells were transfected with negative control siRNA targeting firefly luciferase (FFL), and 2 pools of 10 siRNAs (KEAP1 pool 1 and pools 2) or an esiRNA preparation targeting KEAP1 (esiRNA KEAP1) and evaluated for KEAP1, MRP2/ABCC-2, HMOX1 and NQO1 mRNA expression by QPCR. (B-E) Cells were transfected with negative control siRNA targeting firefly luciferase (FFL), and 3 pools of 10 siRNAs targeting NRF2 (NRF2 pool 1, pool 2, pool 3) and evaluated for NRF2, MRP2/ABCC-2, HMOX1 and NQO1 mRNA expression by QPCR. Data is expressed as expression levels relative to the FFL transfection. n=4 for each data point. A student’s t-test was performed on each data set relative to the FFL data (*p < 0.5, **p < 0.01). Data are represented as mean ± standard deviation.
Gene expression profiling following NRF2 and KEAP1siRNA knock-down
To define genes regulated by the NRF2/KEAP1 pathway in human lung fibroblasts we conducted microarray mRNA profiling 30 and 48 hours following NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA knockdown. For each siRNA pool, 3 replicates were profiled. ANOVA analyses were then performed to identify genes up- or down-regulated by NRF2 or KEAP1 siRNA at p value of less or equal to 0.01. Data from all three replicates of each siRNA pool were combined and a further filter by absolute fold change of more than or equal to 1.15 was applied. With these filtering criteria, the expression of 2,729 and 2,136 sequences, accounting for 6.2% and 4.9% of the transcriptome probed on our arrays, was significantly modulated by NRF2 and KEAP1 knockdown, respectively. NRF2 siRNA knockdown resulted in the down-regulation of 1,139 sequences and the up-regulation of 1590 sequences. KEAP1 knockdown resulted in the down-regulation of 1175 sequences and the up-regulation of 961 sequences. Figure 2A shows a k-means clustering of the union signature of either NRF2 or KEAP1 siRNA modulated genes. Most of the NRF2 or KEAP1 siRNA modulated genes are up- (clusters 2 and 4, with 754 and 1,184 sequences, respectively) or down-regulated (clusters 1 and 6, with 892 and 834 sequences, respectively) in a consistent manner. Annotation of the up-regulated genes (clusters 2 and 4; total 1,938 sequences) by both NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA indicated an association with multiple developmental processes, including cardiovascular, skeletal, neural and muscular systems; also affected are the cytoskeletal organization, extracellular matrix, apoptosis and WNT signaling pathways (Additional file 2). NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA down-regulated genes (clusters 1 and 6; total 1,726 sequences) are mainly associated with cell cycle progression/regulation, DNA replication and repair (Additional file 3).
K-means clustering of gene signature modulated by either KEAP1 or NRF2 siRNAs. (A) K-means clustering of gene signature modulated by either KEAP1 or NRF2 siRNAs at 48 hours post-transfection. Three replicates were profiled for each siRNA pool. One way ANOVA (NRF2 or KEAP1 siRNA-transfected vs. mock-transfected samples) was performed to identify genes up- or down-regulated by NRF2 or KEAP1 siRNA at p ≤ 0.01. Data from all three replicates of each siRNA pool were combined in silico and further filtered by absolute fold change ≥ 1.15. (B) K-means clustering of the anti-correlated gene signature modulated by KEAP1 and NRF2 siRNAs. The gene signature was obtained by combining anti-correlated genes modulated by KEAP1 and NRF2 siRNAs at 30 hours (308 genes at replicates combined p<=0.05) and 48 hours (893 genes at replicates combined p<=0.05). We further removed a 43 interferon-inducible gene set resulting from a KEAP1-3 siRNA pool to obtain a final signature gene set of 1,045 sequences with 361 sequences down-regulated by NRF2 siRNAs and 684 sequences down-regulated by KEAP1 siRNAs.
With this analysis approach, two gene clusters (e.g. clusters 3 and 5 with 287 and 322 sequences, respectively) are differentially regulated by KEAP1 and NRF2 siRNAs.
Selecting and annotating anti-correlated NRF2 and KEAP1siRNA knock-down genes
To identify those genes whose expression was inversely regulated when comparing NRF2 and KEAP1 knockdown, genes were selected if they were modulated in the opposite direction by NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA with combined p values less than 0.05 at 30 and 48 hours after siRNA transfection. We observed 113 common sequences between 308 and 893 signature sequences obtained from 30 and 48 hour time points; in addition, we removed a 43 gene signature specifically induced by the pool of 3 KEAP1 siRNA which is highly enriched in interferon-responsive genes and is most likely a property of that particular pool of siRNAs. Figure 2B shows a K-means clustering of the resulting 1,045 sequences which met the selection criteria with 361 sequences and 684 sequences down-regulated by NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA, respectively. Lists of most highly down- and up-regulated genes by NRF2 siRNA at 48 hours can be found in Additional file 4.
We then queried the biological processes and pathways associated with the 893 sequences (from 48 hour time point) using resources from GO Biological Process (see Additional file 5) and Ingenuity Pathways. Additional file 6 shows Ingenuity canonical pathway analysis of the gene set derived from anti-correlated genes knocked down by NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA, respectively. Genes involved with the most significant pathways affected by the 2 siRNA treatments (i.e. NRF2-mediated oxidative stress response and Wntβ-catenin signalling) are listed in Table 1. It is interesting to note that several Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway genes were down-regulated by KEAP1 siRNA with the exception of WNT3 which was up-regulated 2.1 fold.
Eotaxin-1 expression is suppressed with KEAP1siRNA knockdown
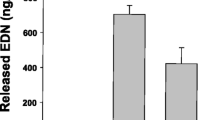
In the microarray profiling, we observed that CCL11/Eotaxin-1 a key chemokine for eosinophil recruitment to the lung [56], is regulated by the KEAP1/NRF2 pathway. Knockdown of KEAP1 led to a suppression of Eotaxin-1 expression, whereas knockdown of NRF2 lead to an increase in Eotaxin-1 levels. Regulation of Eotaxin-1 has not been previously reported in gene expression profiling studies of the NRF2/KEAP1 axis. Therefore to confirm this observation we independently transfected NHLFs with KEAP1 or NRF2 siRNA and indeed confirmed by QPCR (Figure 3A) that upon knockdown of KEAP1 baseline Eotaxin-1 mRNA level was reduced approximately 80% relative to control siRNA transfection. Conversely, upon knockdown of NRF2 baseline Eotaxin-1 mRNA level was increased approximately 50% relative to control siRNA transfection. To determine if these changes resulted in modulation of Eotaxin-1 protein levels secreted from the NHLFs we evaluated levels of Eotaxin-1 protein in the media from these siRNA knockdown experiments. Similar to the changes in Eotaxin-1 mRNA expression, we did find that knockdown of KEAP1 results in a significant decrease of secreted Eotaxin-1 levels from NHLFs, whereas a significant increase in Eotaxin-1 release was observed with NRF2 siRNA transfection (Figure 3B).
Modulation of Eotaxin-1 expression following KEAP1 and NRF2 siRNA knockdown. Cells were transfected with negative control siRNA targeting firefly luciferase (FFL), 1 siRNA pool targeting KEAP1 (KEAP1), and 1 siRNA pool targeting NRF2 (NRF2) and evaluated for (A) mRNA expression and (B) secreted potein levels of Eotaxin-1. Data is expressed levels relative to the FFL transfection. n=4 for each data point. A student’s t-test was performed on each data set relative to the FFL data (*p<0.5, **p<0.01). Data are represented as mean ± standard deviation.
KEAP1knockdown specifically inhibits Eotaxin-1 in NHLFs under inflammatory conditions
In addition to the role of the KEAP1/NRF2 pathway in regulating the anti-oxidant response, it has also been shown that activation of NRF2 can have profound anti-inflammatory effects [57]. We thus sought to evaluate the regulation of Eotaxin-1 by KEAP1/NRF2 under inflammatory conditions. To this end, we challenged NHLFs with IL-1β to induce an inflammatory response and evaluated the secretion of several cytokines and chemokines including Eotaxin-1. Treatment with IL-1β resulted in a significant increase in, Eotaxin-1, IL-2, IL-10. GM-CSF, TNFα, IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1. Interestingly when NHLFs were transfected with KEAP1 siRNA prior to IL-1β challenge very modest increases in IL-6, IL-8 and MCP-1 secretion (Figure 4B) were observed, and a very modest decrease in GM-CSF was observed (Figure 4A). On the other hand a significant reduction of secreted Eotaxin-1 levels were observed (appox. 63%) upon KEAP1 knockdown (Figure 4A). Unlike the effects of NRF2 knockdown observed at baseline, no significant increase of Eotaxin-1 release was observed by NRF2 knockdown upon IL-1β challenge. However, when mRNA expression changes were analysed, a counter regulation of Eotaxin-1 mRNA expression was observed with IL-1β challenge similar to effects at baseline (Figure 4C).
Modulation of IL-1β induced cytokine/chemokine secretion following KEAP1 and NRF2 siRNA knockdown. Cells were transfected with negative control siRNA targeting firefly luciferase (FFL), 1 siRNA pool targeting KEAP1 , and 1 siRNA pool targeting NRF2. (A,B) 24 hours following transfection cells were stimulated with IL-1β and select cytokine and chemokine release was evaluated. Data is expressed as protein levels found in tissue culture supernatants. n=2 for each data point. (C) Eotaxin-1 mRNA expression was also evaluated following IL-1β challenge. Data is expressed as mRNA levels relative to baseline FFL transfection ( see Figure 5). N=4 for each data point. A student’s t-test was performed on each data set relative to the FFL data (*p<0.5, **p<0.01). Data are represented as mean ± standard deviation.
NRF2 activation is thought to lead to the inhibition of NF-κB activity [58]. NF-κB is a broad pro-inflammatory mechanism that can regulate the activity of multiple secreted cytokines and chemokines including Eotaxin-1 [59, 60]. Thus it is possible that the suppression of Eotaxin-1 observed with KEAP1 knockdown is simply mediated by the inhibition of NF-κB activity. To investigate this, we treated NHLFs with a potent and selective IKK-β inhibitor (Compound A) [61] prior to stimulation with IL-1β. Treatment with 1 μM of compound A had profound and robust effects on the secretion of all of the cytokines induced by IL-1β including Eotaxin-1 (Figure 5). The selective inhibition of Eotaxin-1 by KEAP1 knockdown argues that the mechanism by which NRF2 activation is modulating Eotaxin-1 expression is not simply through the inhibition of NF-κB activity.
Modulation of IL-1β induced cytokine/chemokine by the IKK-β inhibitor Compound A [61]. Cells were treated with Compound A for 24 hours prior to IL-1β stimulation. Following IL-1β challenge select cytokine and chemokine release was evaluated. Data is expressed as protein levels found in tissue culture supernatants. n=3 for each data point. A student’s t-test was performed on each data set relative to the untreated data set (*p<0.5, **p<0.01). Data are represented as mean ± standard deviation.
NRF2 activating compounds sulforaphane and CDDO specifically suppress IL-1β, IL-13 and TNFα induced Eotaxin-1 in NHLFs
Several pharmacologic agents have been shown to activate NRF2. These include the dietary isothiocyantes sulforaphane [47] and the synthetic triterpenoid CDDO [62]. Since siRNA can have off-target effects we used these pharmacological modulators of NRF2 activity to evaluate their effect on Eotaxin-1 expression in NHLFs. Similar to siRNA knockdown of KEAP1, treatment with sulforaphane or CDDO resulted in a significant dose-dependent decrease in Eotaxin-1 secretion following IL-1β challenge (Figure 6A). This data provides further confirmation that indeed Eotaxin-1 is specifically inhibited by NRF2 activation in NHLFs. To further explore the role of NRF2 in Eotaxin-1 release under inflammatory conditions, we challenged NHLFs with IL-13 and TNFα following treatment with CDDO and sulforaphane. Similar to IL-1β, IL-13 and TNFα lead to a robust induction of Eotaxin-1 release from fibroblasts (Figure 6B and C). Treatment with CDDO and sulforaphane also led to a dose dependent decrease in Eotaxin-1 release under these conditions (Figure 6B and C). These data suggest that NRF2 activation can inhibit Eotaxin-1 release from lung fibroblasts under diverse inflammatory conditions.
Modulation of IL-1β, TNFα and IL-13 induced Eotaxin-1 release by CDDO and Sulforaphane. Cells were treated with Compound 1 hour prior to stimulation. Secreted Eotaxin-1 was measured 24 hours following challenge. (A) Dose dependent inhibition of IL-1β induced Eotaxin-1 release. (B) Dose dependent inhibition of TNFα induced Eotaxin-1 release. (C) Dose dependent inhibition of IL-13 induced Eotaxin-1 release. Data is expressed as protein levels found in tissue culture supernatants. n=3 for each data point. A student’s t-test was performed on each data set relative to the untreated data set (*p<0.5, **p<0.01). Data are represented as mean ± standard deviation.
Discussion
Here we present our results of microarray profiling of normal human lung fibroblast following siRNA mediated knockdown of NRF2 and KEAP1. We have identified a distinct gene set of anti-correlated genes in this analysis to better define NRF2 regulated genes in a lung specific cellular context.
A comparison of the 1,045 signature sequences differentially modulated by NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA (Figure 2) with other gene expression signatures collected in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) data base indicates a highly significant anti-correlation with a gene signature obtained from primary human lung fibroblast treated with dithiothreitol (DTT) for 24 hours (Overlapping P = 1.7E-99) [63]; and a significant correlation with a gene set from dexamethasone-treated (24 hours) human primary osteoblast-like cells (HOb)(GEO series GSE10311.Overlapping P = 1.0E-46). In addition, we found two cigarette smoke-related gene signatures which are anti-correlated to our gene signature, one from a normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells exposed to a cigarette smoke condensate for 18 hours (Overlapping P = 2.5E-33, data derived from GEO series GSE18235 [64], and the other from a comparison of small airway epithelial cells between smokers and non-smokers (overlapping p = 2.3E-24) [65]. Since DTT and cigarette smoke induce ER stress and oxidative stress, respectively; it appears that NRF2 is activated in both situations to confer cellular protection.
In addition to NRF2 promoting the anti-oxidant response machinery, this pathway also has profound anti-inflammatory effects [57]. Studies with NRF2 deficient mice demonstrate an increased inflammatory response in several inflammatory disease models [58, 66, 67]. In respiratory models, the loss of Nrf2 results in increase eosinophil recruitment in the lungs of allergen challenged animals and the increase in lung macrophages upon hyperoxic lung injury [33]. In models of COPD, Nrf2 deficient mice have increased neutrophil and macrophage recruitment to the lung [31]. In vitro studies have demonstrated a specific effect of the NRF2 regulating cytokine and chemokine expression in neutrophils following LPS challenge [68]. In addition, pharmacological activation of NRF2 with the triterpenoid CDDO can inhibit LPS induced inflammation in neutrophils and PBMCs [68].
In this study we make the novel discovery that Eotaxin-1 is uniquely inhibited by NRF2 activation. While the direct role of NRF2 on Eotaxin-1 regulation has not be reported previously, mice deficient for Nrf2 do have increased eosinphil recruitment to the lung upon allergen challenge associated with increased level of Eotaxin-1 in the BAL fluid [30]. In addition, it has been demonstrated that mice with a deficiency of NADPH oxidase in non-hematopoietic cells have decreased lung eosinophilia during allergen challenge implicating the ROS in the production of Eotaxin-1 in the lung [9]. Interestingly, it has been shown that dietary flavonoids inhibit Eotaxin-1 release from fibroblasts [69, 70]. Flavonoids have various anti-inflammatory properties and are potent inhibitors of NF-κB signalling [71] but are also potent activators of NRF2 [72]. This inhibition of Eotaxin-1 observed is consistent with our study where we show inhibition of Eotaxin-1 with the triterpenoid CDDO. Based on our data with KEAP1 knockdown it can be concluded that the inhibitory effect that these flavonoids have on Eotaxin-1 is likely mediated directly by their activation of NRF2 and not through other anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
As the major eosinophil chemoattractant, Eotaxin-1 plays a critical role in allergic inflammation and asthma [73]. In the lung Eotaxin-1 promotes the influx of eosinophils where activation and release of key mediators of an inflammatory response occurs [56]. The role of the fibroblast in mediating eosinophil recruitment has long been established [74]; where it has been shown that fibroblasts derived from numerous sources secrete a significant amount of Eotaxin-1 in response to several pro-inflammatory stimuli [75–79]. Consistent with this, we have demonstrated in this report that IL-1β, IL-13 and TNFα all have potent effects on Eotaxin-1 secretion in fibroblasts. These factors are key inducers of Eotaxin-1 release and eosinophil recruitment in addition to contributing to fibrotic changes seen in airway disease [75, 79]. It would be of interest to evaluate an NRF2/ Eotaxin-1 relationship in fibroblasts from asthmatics to determine if Eotaxin-1 expression would be equally regulated by NRF2 activation is a disease state.
The mechanism by which Eotaxin-1 is modulated by NRF2 is not known. A detailed promoter study failed to identify a bonafide ARE [80] upstream of the human Eotaxin-1 gene, suggesting that this inhibition may be an indirect consequence of NRF2 activation. One way in which NRF2 has been shown to mediate its anti-inflammatory properties is through the inhibition of NF-κB. NRF2 and NF-κB have been shown to work together to modulate inflammatory gene expression [58, 60] and it has been suggested that NRF2 activation can lead to NF-κB inhibition [58, 81–83]. In addition it has been shown that the NF-κB pathway plays a critical role in Eotaxin-1 regulation in fibroblasts [30, 59]. While it is not clear if this is the case in our study, it is unlikely since we have demonstrated using pharmacological inhibition that all of the chemokines and cytokines induced by IL-1β and TNFα are NF-κB dependent, yet only Eotaxin-1 is inhibited by NRF2 activation.
Another key transcription factor that can mediate Eotaxin-1 expression is STAT6. A STAT6 binding site is present on the Eotaxin-1 promoter along with an NF-κB binding site and it is thought that Eotaxin-1 may be regulated by the concerted activity of NF-κB and STAT6 [84]. STAT6 is of course a key mediator of Eotaxin-1 expression induced by IL-4 [85], but studies in fibroblasts have shown that STAT6 also is required for TNFα induced Eotaxin-1 expression [86]. Thus, it remains feasible that in someway, NRF2 activation inhibits STAT6 activity, thus leading to the inhibition of Eotaxin-1 expression. There is no published data directly linking NRF2 activation to STAT6 activity, however, in one study using the licorice root triterpenoid Glycyrrhizin, it has been demonstrated that inhibition of Eotaxin-1 with this compound is associated with the inhibition of STAT6 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation [87]. This data suggests that perhaps NRF2 does indeed regulate Eotaxin-1 expression through the regulation of STAT6 activity. Another potential mechanisms by which NRF2 may modulate Eotaxin-I expression is through modulation of MAPK signaling as it has been demonstrated that MAPK signaling downstream of TGFβ can synergize with IL-13 to induce Eotaxin-1 expression by interfering with negative feedback loops in the IL-13/STAT6 pathway [51]. Interestingly it has been demonstrated that reactive oxygen species can directly augment the activity of STAT6 [88] raising the possibility that a decrease in reactive oxygen species as a result of NRF2 activation may inhibit STAT6 activity and inhibit Eotaxin-1 expression.
Conclusions
In summary, through gene expression profiling of normal human lung fibroblasts, following siRNA knockdown of NRF2 and KEAP1, we have identified Eotaxin-1 as a novel NRF2 regulated gene. Our data further define the role of this pathway in mediating inflammatory disease in the lungs.
Abbreviations
- NRF2:
-
Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2
- KEAP1:
-
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- CDDO:
-
2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oic acid
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- ARE:
-
Anti-oxidant response elements
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering Ribonucleic acid
- IKK-β:
-
Inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells, kinase beta
- esiRNA:
-
Endoribonuclease-prepared short interfering RNAs
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic acid
- RT/IVT:
-
Reverse transcription/in vitro transcription, reverse transcription/in vitro
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- Q-PCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- NHLFs:
-
Normal human klung fibroblasts
- NHBE:
-
Normal human bronchial epithelial cells
- OVA:
-
Ovalbumin
- IL:
-
Interleukin.
References
Cho HY, Reddy SP, Kleeberger SR: Nrf2 defends the lung from oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006, 8: 76-87. 10.1089/ars.2006.8.76.
Rahman I, Biswas SK, Kode A: Oxidant and antioxidant balance in the airways and airway diseases. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006, 533: 222-239. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.087.
Pope CA: Air pollution and health - good news and bad. N Engl J Med. 2004, 351: 1132-1134. 10.1056/NEJMe048182.
Emelyanov A, Fedoseev G, Abulimity A, Rudinski K, Fedoulov A, Karabanov A, et al: Elevated concentrations of exhaled hydrogen peroxide in asthmatic patients. Chest. 2001, 120: 1136-1139. 10.1378/chest.120.4.1136.
Smith LJ, Shamsuddin M, Sporn PH, Denenberg M, Anderson J: Reduced superoxide dismutase in lung cells of patients with asthma. Free Radic Biol Med. 1997, 22: 1301-1307. 10.1016/S0891-5849(96)00550-3.
Gerritsen WB, Asin J, Zanen P, van den Bosch JM, Haas FJ: Markers of inflammation and oxidative stress in exacerbated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Respir Med. 2005, 99: 84-90. 10.1016/j.rmed.2004.04.017.
Quinlan GJ, Evans TW, Gutteridge JM: 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal levels increase in the plasma of patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome as linoleic acid appears to fall. Free Radic Res. 1994, 21: 95-106. 10.3109/10715769409056561.
Roumen RM, Hendriks T, de Man BM, Goris RJ: Serum lipofuscin as a prognostic indicator of adult respiratory distress syndrome and multiple organ failure. Br J Surg. 1994, 81: 1300-1305. 10.1002/bjs.1800810913.
Abdala-Valencia H, Earwood J, Bansal S, Jansen M, Babcock G, Garvy B, et al: Nonhematopoietic NADPH oxidase regulation of lung eosinophilia and airway hyperresponsiveness in experimentally induced asthma. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007, 292: L1111-L1125. 10.1152/ajplung.00208.2006.
Ciencewicki J, Trivedi S, Kleeberger SR: Oxidants and the pathogenesis of lung diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008, 122: 456-468. 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.08.004.
Diaz-Sanchez D, Jyrala M, Ng D, Nel A, Saxon A: In vivo nasal challenge with diesel exhaust particles enhances expression of the CC chemokines rantes, MIP-1alpha, and MCP-3 in humans. Clin Immunol. 2000, 97: 140-145. 10.1006/clim.2000.4921.
Hao M, Comier S, Wang M, Lee JJ, Nel A: Diesel exhaust particles exert acute effects on airway inflammation and function in murine allergen provocation models. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003, 112: 905-914. 10.1016/j.jaci.2003.07.005.
Kirkham P, Rahman I: Oxidative stress in asthma and COPD: antioxidants as a therapeutic strategy. Pharmacol Ther. 2006, 111: 476-494. 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.10.015.
Li N, Hao M, Phalen RF, Hinds WC, Nel AE: Particulate air pollutants and asthma. A paradigm for the role of oxidative stress in PM-induced adverse health effects. Clin Immunol. 2003, 109: 250-265. 10.1016/j.clim.2003.08.006.
Nel AE, Diaz-Sanchez D, Ng D, Hiura T, Saxon A: Enhancement of allergic inflammation by the interaction between diesel exhaust particles and the immune system. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998, 102: 539-554. 10.1016/S0091-6749(98)70269-6.
Papaiahgari S, Yerrapureddy A, Reddy SR, Reddy NM, Dodd O, Crow MT, et al: Genetic and pharmacologic evidence links oxidative stress to ventilator-induced lung injury in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007, 176: 1222-1235. 10.1164/rccm.200701-060OC.
Whitekus MJ, Li N, Zhang M, Wang M, Horwitz MA, Nelson SK, et al: Thiol antioxidants inhibit the adjuvant effects of aerosolized diesel exhaust particles in a murine model for ovalbumin sensitization. J Immunol. 2002, 168: 2560-2567.
Adcock IM, Barnes PJ: Molecular mechanisms of corticosteroid resistance. Chest. 2008, 134: 394-401. 10.1378/chest.08-0440.
Nguyen T, Sherratt PJ, Pickett CB: Regulatory mechanisms controlling gene expression mediated by the antioxidant response element. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003, 43: 233-260. 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.43.100901.140229.
Kobayashi M, Itoh K, Suzuki T, Osanai H, Nishikawa K, Katoh Y, et al: Identification of the interactive interface and phylogenic conservation of the Nrf2-Keap1 system. Genes Cells. 2002, 7: 807-820. 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2002.00561.x.
Kobayashi M, Yamamoto M: Nrf2-Keap1 regulation of cellular defense mechanisms against electrophiles and reactive oxygen species. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006, 46: 113-140. 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2006.01.007.
Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M, Zenke Y, Chiba T, et al: Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol. 2004, 24: 7130-7139. 10.1128/MCB.24.16.7130-7139.2004.
Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Watai Y, Tong KI, Shibata T, Uchida K, et al: Oxidative and electrophilic stresses activate Nrf2 through inhibition of ubiquitination activity of Keap1. Mol Cell Biol. 2006, 26: 221-229. 10.1128/MCB.26.1.221-229.2006.
Kobayashi M, Yamamoto M: Molecular mechanisms activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway of antioxidant gene regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005, 7: 385-394. 10.1089/ars.2005.7.385.
Kobayashi M, Li L, Iwamoto N, Nakajima-Takagi Y, Kaneko H, Nakayama Y, et al: The antioxidant defense system Keap1-Nrf2 comprises a multiple sensing mechanism for responding to a wide range of chemical compounds. Mol Cell Biol. 2009, 29: 493-502. 10.1128/MCB.01080-08.
Wakabayashi N, Itoh K, Wakabayashi J, Motohashi H, Noda S, Takahashi S, et al: Keap1-null mutation leads to postnatal lethality due to constitutive Nrf2 activation. Nat Genet. 2003, 35: 238-245. 10.1038/ng1248.
Pierrou S, Broberg P, O’Donnell RA, Pawlowski K, Virtala R, Lindqvist E, et al: Expression of genes involved in oxidative stress responses in airway epithelial cells of smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007, 175: 577-586. 10.1164/rccm.200607-931OC.
Malhotra D, Thimmulappa R, Navas-Acien A, Sandford A, Elliott M, Singh A, et al: Decline in NRF2-regulated antioxidants in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease lungs due to loss of its positive regulator, DJ-1. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008, 178: 592-604. 10.1164/rccm.200803-380OC.
Adair-Kirk TL, Atkinson JJ, Griffin GL, Watson MA, Kelley DG, DeMello D, et al: Distal airways in mice exposed to cigarette smoke: Nrf2-regulated genes are increased in Clara cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008, 39: 400-411. 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0295OC.
Rangasamy T, Guo J, Mitzner WA, Roman J, Singh A, Fryer AD, et al: Disruption of Nrf2 enhances susceptibility to severe airway inflammation and asthma in mice. J Exp Med. 2005, 202: 47-59. 10.1084/jem.20050538.
Iizuka T, Ishii Y, Itoh K, Kiwamoto T, Kimura T, Matsuno Y, et al: Nrf2-deficient mice are highly susceptible to cigarette smoke-induced emphysema. Genes Cells. 2005, 10: 1113-1125. 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2005.00905.x.
Rangasamy T, Cho CY, Thimmulappa RK, Zhen L, Srisuma SS, Kensler TW, et al: Genetic ablation of Nrf2 enhances susceptibility to cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice. J Clin Invest. 2004, 114: 1248-1259.
Cho HY, Jedlicka AE, Reddy SP, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Zhang LY, et al: Role of NRF2 in protection against hyperoxic lung injury in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002, 26: 175-182.
Cho HY, Imani F, Miller-DeGraff L, Walters D, Melendi GA, Yamamoto M, et al: Antiviral activity of Nrf2 in a murine model of respiratory syncytial virus disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009, 179: 138-150.
Sussan TE, Rangasamy T, Blake DJ, Malhotra D, El Haddad H, Bedja D, et al: Targeting Nrf2 with the triterpenoid CDDO-imidazolide attenuates cigarette smoke-induced emphysema and cardiac dysfunction in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009, 106: 250-255. 10.1073/pnas.0804333106.
Cho HY, Reddy SP, Debiase A, Yamamoto M, Kleeberger SR: Gene expression profiling of NRF2-mediated protection against oxidative injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005, 38: 325-343. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.10.013.
Lee JM, Calkins MJ, Chan K, Kan YW, Johnson JA: Identification of the NF-E2-related factor-2-dependent genes conferring protection against oxidative stress in primary cortical astrocytes using oligonucleotide microarray analysis. J Biol Chem. 2003, 278: 12029-12038. 10.1074/jbc.M211558200.
Nair S, Xu C, Shen G, Hebbar V, Gopalakrishnan A, Hu R, et al: Toxicogenomics of endoplasmic reticulum stress inducer tunicamycin in the small intestine and liver of Nrf2 knockout and C57BL/6J mice. Toxicol Lett. 2007, 168: 21-39. 10.1016/j.toxlet.2006.10.012.
Purdom-Dickinson SE, Lin Y, Dedek M, Morrissy S, Johnson J, Chen QM: Induction of antioxidant and detoxification response by oxidants in cardiomyocytes: evidence from gene expression profiling and activation of Nrf2 transcription factor. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007, 42: 159-176. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.09.012.
Thompson CA, Burcham PC: Genome-Wide Transcriptional Responses to Acrolein. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008, 21: 2245-2256. 10.1021/tx8001934.
Zhu L, Pi J, Wachi S, Andersen ME, Wu R, Chen Y: Identification of Nrf2-dependent airway epithelial adaptive response to proinflammatory oxidant-hypochlorous acid challenge by transcription profiling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008, 294: L469-L477.
Barve A, Khor TO, Nair S, Lin W, Yu S, Jain MR, et al: Pharmacogenomic profile of soy isoflavone concentrate in the prostate of Nrf2 deficient and wild-type mice. J Pharm Sci. 2008, 97: 4528-4545. 10.1002/jps.21311.
Hu R, Xu C, Shen G, Jain MR, Khor TO, Gopalkrishnan A, et al: Identification of Nrf2-regulated genes induced by chemopreventive isothiocyanate PEITC by oligonucleotide microarray. Life Sci. 2006, 79: 1944-1955. 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.06.019.
Hu R, Xu C, Shen G, Jain MR, Khor TO, Gopalkrishnan A, et al: Gene expression profiles induced by cancer chemopreventive isothiocyanate sulforaphane in the liver of C57BL/6J mice and C57BL/6J/Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Cancer Lett. 2006, 243: 170-192. 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.11.050.
Kwak MK, Wakabayashi N, Itoh K, Motohashi H, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW: Modulation of gene expression by cancer chemopreventive dithiolethiones through the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Identification of novel gene clusters for cell survival. J Biol Chem. 2003, 278: 8135-8145. 10.1074/jbc.M211898200.
Reddy NM, Kleeberger SR, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW, Scollick C, Biswal S, et al: Genetic dissection of the Nrf2-dependent redox signaling-regulated transcriptional programs of cell proliferation and cytoprotection. Physiol Genomics. 2007, 32: 74-81. 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00126.2007.
Thimmulappa RK, Mai KH, Srisuma S, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Biswal S: Identification of Nrf2-regulated genes induced by the chemopreventive agent sulforaphane by oligonucleotide microarray. Cancer Res. 2002, 62: 5196-5203.
Baglole CJ, Sime PJ, Phipps RP: Cigarette smoke-induced expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human lung fibroblasts is regulated by intracellular glutathione. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008, 295: L624-L636. 10.1152/ajplung.90215.2008.
Al Muhsen S, Johnson JR, Hamid Q: Remodeling in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011, 128: 451-462. 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.04.047.
Johnson PR, Burgess JK: Airway smooth muscle and fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2004, 4: 102-108. 10.1007/s11882-004-0054-9.
Zhou X, Hu H, Balzar S, Trudeau JB, Wenzel SE: MAPK regulation of IL-4/IL-13 receptors contributes to the synergistic increase in CCL11/eotaxin-1 in response to TGF-beta1 and IL-13 in human airway fibroblasts. J Immunol. 2012, 188: 6046-6054. 10.4049/jimmunol.1102760.
Murata T, Shimada M, Sakakibara S, Yoshino T, Masuda T, Shintani T, et al: Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel IKK-beta inhibitors. Part 3: Orally active anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004, 14: 4019-4022. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.05.041.
Honda T, Rounds BV, Bore L, Finlay HJ, Favaloro FG, Suh N, et al: Synthetic oleanane and ursane triterpenoids with modified rings A and C: a series of highly active inhibitors of nitric oxide production in mouse macrophages. J Med Chem. 2000, 43: 4233-4246. 10.1021/jm0002230.
Kittler R, Heninger AK, Franke K, Habermann B, Buchholz F: Production of endoribonuclease-prepared short interfering RNAs for gene silencing in mammalian cells. Nat Methods. 2005, 2: 779-784. 10.1038/nmeth1005-779.
Jackson AL, Bartz SR, Schelter J, Kobayashi SV, Burchard J, Mao M, et al: Expression profiling reveals off-target gene regulation by RNAi. Nat Biotechnol. 2003, 21: 635-637. 10.1038/nbt831.
Rothenberg ME, Hogan SP: The eosinophil. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006, 24: 147-174. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.24.021605.090720.
Li N, Nel AE: Role of the Nrf2-mediated signaling pathway as a negative regulator of inflammation: implications for the impact of particulate pollutants on asthma. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006, 8: 88-98. 10.1089/ars.2006.8.88.
Li W, Khor TO, Xu C, Shen G, Jeong WS, Yu S, et al: Activation of Nrf2-antioxidant signaling attenuates NFkappaB-inflammatory response and elicits apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008, 76: 1485-1489. 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.07.017.
Huber MA, Denk A, Peter RU, Weber L, Kraut N, Wirth T: The IKK-2/Ikappa Balpha /NF-kappa B pathway plays a key role in the regulation of CCR3 and eotaxin-1 in fibroblasts. A critical link to dermatitis in Ikappa Balpha -deficient mice. J Biol Chem. 2002, 277: 1268-1275. 10.1074/jbc.M109358200.
Nair S, Doh ST, Chan JY, Kong AN, Cai L: Regulatory potential for concerted modulation of Nrf2- and Nfkb1-mediated gene expression in inflammation and carcinogenesis. Br J Cancer. 2008, 99: 2070-2082. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604703.
Ziegelbauer K, Gantner F, Lukacs NW, Berlin A, Fuchikami K, Niki T, et al: A selective novel low-molecular-weight inhibitor of IkappaB kinase-beta (IKK-beta) prevents pulmonary inflammation and shows broad anti-inflammatory activity. Br J Pharmacol. 2005, 145: 178-192. 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706176.
Liby K, Hock T, Yore MM, Suh N, Place AE, Risingsong R, et al: The synthetic triterpenoids, CDDO and CDDO-imidazolide, are potent inducers of heme oxygenase-1 and Nrf2/ARE signaling. Cancer Res. 2005, 65: 4789-4798. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4539.
Murray JI, Whitfield ML, Trinklein ND, Myers RM, Brown PO, Botstein D: Diverse and specific gene expression responses to stresses in cultured human cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2004, 15: 2361-2374. 10.1091/mbc.E03-11-0799.
Pickett G, Seagrave J, Boggs S, Polzin G, Richter P, Tesfaigzi Y: Effects of 10 cigarette smoke condensates on primary human airway epithelial cells by comparative gene and cytokine expression studies. Toxicol Sci. 2010, 114: 79-89. 10.1093/toxsci/kfp298.
Ammous Z, Hackett NR, Butler MW, Raman T, Dolgalev I, O’Connor TP, et al: Variability in small airway epithelial gene expression among normal smokers. Chest. 2008, 133: 1344-1353. 10.1378/chest.07-2245.
Chen XL, Dodd G, Thomas S, Zhang X, Wasserman MA, Rovin BH, et al: Activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway protects endothelial cells from oxidant injury and inhibits inflammatory gene expression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006, 290: H1862-H1870. 10.1152/ajpheart.00651.2005.
Osburn WO, Yates MS, Dolan PD, Chen S, Liby KT, Sporn MB, et al: Genetic or pharmacologic amplification of nrf2 signaling inhibits acute inflammatory liver injury in mice. Toxicol Sci. 2008, 104: 218-227. 10.1093/toxsci/kfn079.
Thimmulappa RK, Scollick C, Traore K, Yates M, Trush MA, Liby KT, et al: Nrf2-dependent protection from LPS induced inflammatory response and mortality by CDDO-Imidazolide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006, 351: 883-889. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.102.
Jayaprakasam B, Doddaga S, Wang R, Holmes D, Goldfarb J, Li XM: Licorice Flavonoids Inhibit Eotaxin-1 Secretion by Human Fetal Lung Fibroblasts in Vitro. J Agric Food Chem. 2009, 57: 820-825. 10.1021/jf802601j.
Nakajima T, Imanishi M, Yamamoto K, Cyong JC, Hirai K: Inhibitory effect of baicalein, a flavonoid in Scutellaria Root, on eotaxin production by human dermal fibroblasts. Planta Med. 2001, 67: 132-135. 10.1055/s-2001-11532.
Nam NH: Naturally occurring NF-kappaB inhibitors. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2006, 6: 945-951. 10.2174/138955706777934937.
Rahman I, Biswas SK, Kirkham PA: Regulation of inflammation and redox signaling by dietary polyphenols. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006, 72: 1439-1452. 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.07.004.
Garcia-Zepeda EA, Rothenberg ME, Ownbey RT, Celestin J, Leder P, Luster AD: Human eotaxin is a specific chemoattractant for eosinophil cells and provides a new mechanism to explain tissue eosinophilia. Nat Med. 1996, 2: 449-456. 10.1038/nm0496-449.
Minshall EM, Hamid QA: Fibroblasts: a cell type central to eosinophil recruitment?. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000, 30: 301-303. 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2000.00753.x.
Richter A, Puddicombe SM, Lordan JL, Bucchieri F, Wilson SJ, Djukanovic R, et al: The contribution of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 to the epithelial-mesenchymal trophic unit in asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001, 25: 385-391.
Sabatini F, Silvestri M, Sale R, Scarso L, Defilippi AC, Risso FM, et al: Fibroblast-eosinophil interaction: modulation of adhesion molecules expression and chemokine release by human fetal lung fibroblasts in response to IL-4 and TNF-alpha. Immunol Lett. 2002, 84: 173-178. 10.1016/S0165-2478(02)00183-9.
Sato E, Nelson DK, Koyama S, Hoyt JC, Robbins RA: Inflammatory cytokines modulate eotaxin release by human lung fibroblast cell line. Exp Lung Res. 2001, 27: 173-183. 10.1080/019021401750069401.
Terada N, Hamano N, Nomura T, Numata T, Hirai K, Nakajima T, et al: Interleukin-13 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha synergistically induce eotaxin production in human nasal fibroblasts. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000, 30: 348-355. 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2000.00750.x.
Wenzel SE, Trudeau JB, Barnes S, Zhou X, Cundall M, Westcott JY, et al: TGF-beta and IL-13 synergistically increase eotaxin-1 production in human airway fibroblasts. J Immunol. 2002, 169: 4613-4619.
Wasserman WW, Fahl WE: Functional antioxidant responsive elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997, 94: 5361-5366. 10.1073/pnas.94.10.5361.
Kang ES, Kim GH, Kim HJ, Woo IS, Ham SA, Jin H, et al: Nrf2 regulates curcumin-induced aldose reductase expression indirectly via nuclear factor-kappaB. Pharmacol Res. 2008, 58: 15-21. 10.1016/j.phrs.2008.05.009.
Shen G, Jeong WS, Hu R, Kong AN: Regulation of Nrf2, NF-kappaB, and AP-1 signaling pathways by chemopreventive agents. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005, 7: 1648-1663. 10.1089/ars.2005.7.1648.
Yang H, Magilnick N, Lee C, Kalmaz D, Ou X, Chan JY, et al: Nrf1 and Nrf2 regulate rat glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit transcription indirectly via NF-kappaB and AP-1. Mol Cell Biol. 2005, 25: 5933-5946. 10.1128/MCB.25.14.5933-5946.2005.
Hein H, Schluter C, Kulke R, Christophers E, Schroder JM, Bartels J: Genomic organization, sequence, and transcriptional regulation of the human eotaxin gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997, 237: 537-542. 10.1006/bbrc.1997.7169.
Matsukura S, Stellato C, Plitt JR, Bickel C, Miura K, Georas SN, et al: Activation of eotaxin gene transcription by NF-kappa B and STAT6 in human airway epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1999, 163: 6876-6883.
Hoeck J, Woisetschlager M: STAT6 mediates eotaxin-1 expression in IL-4 or TNF-alpha-induced fibroblasts. J Immunol. 2001, 166: 4507-4515.
Matsui S, Sonoda Y, Sekiya T, Aizu-Yokota E, Kasahara T: Glycyrrhizin derivative inhibits eotaxin 1 production via STAT6 in human lung fibroblasts. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6: 369-375. 10.1016/j.intimp.2005.08.025.
Mandal D, Fu P, Levine AD: REDOX regulation of IL-13 signaling in intestinal epithelial cells: usage of alternate pathways mediates distinct gene expression patterns. Cell Signal. 2010, 22: 1485-1494. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.05.017.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Francois Gervais and Dr. Gary O’Neill for critical reading of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
I-M W, DC, AGT and MAC are full time employees of Merck and Co.
Authors’ contributions
MAC, AGT and YB were responsible for experimental design. MAC, JF and I-MW were responsible for data analysis and manuscript preparation. MCM performed all siRNA KD studies. DC conducted TAQman studies. JF and TL conducted experiments assessing Eotaxin expression. ALJ and MAP designed and synthesized esiRNA pools. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12931_2012_1290_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Additional file 1: Sequences of siRNAs. List of siRNA sequences utilized for gene expression knockdown studies. (PDF 13 KB)
12931_2012_1290_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Additional file 2: Upregulated genes by NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA knockdown. List of genes whose expression is increased with NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA knockdown. Genes are group based on annotated biological processes. (PDF 9 KB)
12931_2012_1290_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
Additional file 3: Down-regulated genes by NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA knockdown. List of genes whose expression is decreased with NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA knockdown. Genes are group based on annotated biological processes. (PDF 9 KB)
12931_2012_1290_MOESM4_ESM.pdf
Additional file 4: Most significant NRF2 - and KEAP1 -modulated anti-correlated genes identified in microarray studies. Figure displaying (A) Top 30 genes knockdown by NRF2 siRNAs at 48 hours. Genes were sorted based on their fold change knocked down by NRF2 siRNAs at 48 hours. The corresponding fold changes modulated by NRF2 siRNAs at 30 hours and KEAP1 siRNAs at 48 and 30 hours are also shown. (B) Genes significantly knock down by KEAP1 siRNAs at 48 hours. Genes were sorted based on their fold change knocked down by KEAP1 siRNAs at 48 hours. The corresponding fold changes modulated by NRF2 siRNAs at 30 and 48 hours and KEAP1 siRNAs at 30 hours are also shown. CCL11/eotaxin is included in the Figure as a reference although it is not one of the top 30 KEAP1 siRNAs knock down genes. (PDF 115 KB)
12931_2012_1290_MOESM5_ESM.pdf
Additional file 5: Annotation of anti-correlated NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA knock-down gene set at 48 hours. List of genes whose expression is modulated in an anti-correlated direction with NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA knockdown. Genes are group based on annotated biological processes. (PDF 16 KB)
12931_2012_1290_MOESM6_ESM.pdf
Additional file 6: Ingenuity pathway analysis of anti-correlated genes knock-down by (A) NRF2 siRNAs or (B) KEAP1 siRNAs. Ingenuity pathway analysis of anti-correlated genes knock-down by (A) NRF2 siRNAs or (B) KEAP1 siRNAs. Of the 1,045 anti-correlated signature genes, 361 sequences down-regulated by NRF2 siRNAs and 684 sequences down-regulated by KEAP1 siRNAs were individually up-loaded onto Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) tool for querying canonical pathways associated with the input gene sets (http://www.ingenuity.com). (PDF 60 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Fourtounis, J., Wang, IM., Mathieu, MC. et al. Gene expression profiling following NRF2 and KEAP1 siRNA knockdown in human lung fibroblasts identifies CCL11/Eotaxin-1 as a novel NRF2 regulated gene. Respir Res 13, 92 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-13-92
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-13-92