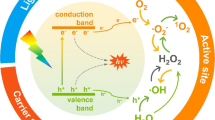
Formaldehyde is one of the most harmful pollutants that endanger occupants' health and the way of its effective removal has become a focus in the field of air quality. This paper studies the static photocatalytic removal of formaldehyde experimentally and finds out that carbon monoxide, which is more harmful to occupants' health than the formaldehyde itself, is one of the by-products in the process of photocatalytic oxidation of formaldehyde. The increase of carbon monoxide concentration should be taken into consideration in the photocatalytic application. The photocatalyst surface at room temperature can weakly adsorb CO and CO2, which can deactivate the photocatalysts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Ye, X., Lian, Z. et al. Experimental study of photocatalytic oxidation of formaldehyde and its by-products. Res Chem Intermediat 32, 9–16 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1163/156856706775012978
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/156856706775012978