Abstract
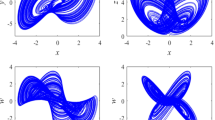
This paper presents a new way of designing a multi-wing chaotic system. The proposed design is based on 3D continuous chaotic system of Lorenz, improved by introducing a saw-tooth and sine functions. The basic proprieties of the proposed system are analyzed using of equilibrium points, phase portrait, Lyapunov exponent, and bifurcation diagram. Furthermore, the modeling of the design is based on Euler method using hardware description language (VHDL) and validated on Xilinx Virtex-II-Pro FPGA platform. Fixed-point arithmetic coding is employed to represented data on 32 bits (16Q16). Finally, the proposed system used to design a new chaos-based TRNG True Random Number Generators by analyzing its chaotic dynamical behavior and FPGA implementation performances. The proposed hardware architecture is based on two stages of pipeline and parallel structure (only 2 clock cycles). Experimental implementation results demonstrate that the design can achieve a maximum operating frequency of 12.649 MHz and a throughput of 202 Mbit/s. Besides, the random bit sequences produced by TRNG have been successfully passed the NIST-800-22 statistical standards tests. The proposed multi-wing attractor presents also complex dynamics and it can be applied in many engineering applications, especially in embedded cryptographic applications.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.M. Cuomo, A.V. Oppenheim, S.H. Strogatz, Synchronization of Lorenz-based chaotic circuits with applications to communications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Anal. Digit. Signal Process. 40(10), 626–633 (1993)
U. Parlitz, L.O. Chua, L. Kocarev, K. Halle, A. Shang, Transmission of digital signals by chaotic synchronization. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2(04), 973–977 (1992)
M. Azzaz, C. Tanougast, S. Sadoudi, A. Dandache, F. Monteiro, Real-time image encryption based chaotic synchronized embedded cryptosystems. In: NEWCAS Conference (NEWCAS), 2010 8th IEEE International (IEEE, 2010), p. 61–64
M.S. Azzaz, C. Tanougast, S. Sadoudi, A. Bouridane, A. Dandache, An FPGA implementation of a feed-back chaotic synchronization for secure communications. In: 7th IEEE, IET International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing (CSNDSP ’10), July 2010. Northumbria University, Newcastle, UK
M.S. Azzaz, C. Tanougast, S. Sadoudi, A. Bouridane, Synchronized hybrid chaotic generators: application to real-time wireless speech encryption. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 18, 2035–2047 (2013)
A. Akgul, H. Calgan, I. Koyuncu, I. Pehlivan, A. Istanbullu, Chaos-based engineering applications with a 3d chaotic system without equilibrium points. Nonlinear Dyn. 84(2), 481–495 (2016)
Q. Lai, X.W. Zhao, K. Rajagopal, G. Xu, A. Akgul, E. Guleryuz, Dynamic analyses, FPGA implementation and engineering applications of multi-butterfly chaotic attractors generated from generalised sprott c system. Pramana 90(1), 6 (2018)
K. Rajagopal, A. Akgul, S. Jafari, A. Karthikeyan, I. Koyuncu, Chaotic chameleon: dynamic analyses, circuit implementation, FPGA design and fractional-order form with basic analyses. Chaos Solitons Fractals 103, 476–487 (2017)
M. Alçın, İ. Pehlivan, İ. Koyuncu, Hardware design and implementation of a novel ANN-based chaotic generator in FPGA. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 127(13), 5500–5505 (2016)
M. Tuna, C.B. Fidan, Electronic circuit design, implementation and FPGA-based realization of a new 3d chaotic system with single equilibrium point. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 127(24), 11786–11799 (2016)
İ. Koyuncu, A.T. Özcerit, The design and realization of a new high speed FPGA-based chaotic true random number generator. Comput. Electr. Eng. 58, 203–214 (2017)
K. Rajagopal, A. Karthikeyan, A. Srinivasan, Dynamical analysis and FPGA implementation of a chaotic oscillator with fractional-order memristor components. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(3), 1491–1512 (2018)
İ. Koyuncu, İ. Şahin, C. Gloster, N.K. Sarıtekin, A neuron library for rapid realization of artificial neural networks on FPGA: a case study of Rössler chaotic system. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 26(01), 1750015 (2017)
M. Anand, R.E. Desrochers, Quantification of restoration success using complex systems concepts and models. Restor. Ecol. 12(1), 117–123 (2004)
M. Dutta, H.E. Nusse, E. Ott, J.A. Yorke, G. Yuan, Multiple attractor bifurcations: a source of unpredictability in piecewise smooth systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83(21), 4281 (1999)
T. Carroll, L. Pecora, Using multiple attractor chaotic systems for communication. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 9(2), 445–451 (1999)
G. Chen, J. Lü, Dynamics of the Lorenz System Family: Analysis, Control and Synchronization (Science Press, Beijing, 2003)
M.H. Lowenberg, Bifurcation analysis of multiple-attractor flight dynamics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 356, 2297–2320 (1998)
J.M.T. Thompson, H.B. Stewart, Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos (Wiley, New York, 2002)
S. Cang, Y. Li, R. Zhang, Z. Wang, Hidden and self-excited coexisting attractors in a Lorenz-like system with two equilibrium points. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(1), 381–390 (2019)
Z. Wang, Y. Sun, B.J. van Wyk, G. Qi, M.A. van Wyk, A 3-d four-wing attractor and its analysis. Braz. J. Phys. 39(3), 547–553 (2009)
W. Sanum, B. Srisuchinwong, Highly complex chaotic system with piecewise linear nonlinearity and compound structures. J. Comput. 7(4), 1041–1047 (2012)
S. Dadras, H.R. Momeni, A novel three-dimensional autonomous chaotic system generating two, three and four-scroll attractors. Phys. Lett. A 373(40), 3637–3642 (2009)
G. Dong, R. Du, L. Tian, Q. Jia, A novel 3d autonomous system with different multilayer chaotic attractors. Phys. Lett. A 373(42), 3838–3845 (2009)
S. ModelSim, User’s Manual, Ver. 6.2 c (Mentor Graphics Corp, Wilsonville, 2006)
Xilinx, Xilinx university program virtex-ii pro development system. Xilinx UG069 (v1.1) (2008)
Xilinx, Integrated software environment (ise) vers 10.1. Xilinx (2008)
NIST, A statistical test suite for random and pseudorandom number generators for cryptographic applications. NIST (2010)
A. Rukhin, J. Soto, J. Nechvatal, M. Smid, E. Barker, A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications (Technical report, Booz-Allen and Hamilton Inc Mclean Va, 2001)
L.G. de la Fraga, E. Torres-Pérez, E. Tlelo-Cuautle, C. Mancillas-Lopez, Hardware implementation of pseudo-random number generators based on chaotic maps. Nonlinear Dyn. 90(3), 1661–1670 (2017)
B. Ramalingam, A. Rengarajan, J.B.B. Rayappan, Hybrid image crypto system for secure image communication: a vlsi approach. Microprocess. Microsyst. 50, 1–13 (2017)
K. Rajagopal, M. Tuna, A. Karthikeyan, İ. Koyuncu, P. Duraisamy, A. Akgul, Dynamical analysis, sliding mode synchronization of a fractional-order memristor hopfield neural network with parameter uncertainties and its non-fractional-order fpga implementation. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 228(10), 2065–2080 (2019)
R. Kaibou, M.S. Azzaz, M. Benssalah, D. Teguig, H. Hamil, A. Merah, M.T. Akrour, Real-time FPGA implementation of a secure chaos-based digital crypto-watermarking system in the dwt domain using co-design approach. J. Real-Time Image Proc. 1–17 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-021-01073-3
M.S. Azzaz, C. Tanougast, A. Maali, M. Benssalah, An efficient and lightweight multi-scroll chaos-based hardware solution for protecting fingerprint biometric templates. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 33(10), e4211 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azzaz, M.S., Fellah, R., Tanougast, C. et al. Design and FPGA implementation of TRNG based on a new multi-wing attractor in Lorenz chaotic system. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 230, 3469–3480 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00234-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00234-6