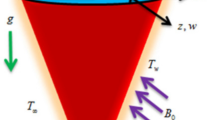
Abstract
The characteristics of heat transport in nanoliquids under the influence of bio-convection (motile microorganism) have significant applications, since nanoliquids have greater capacity to improve heat transport properties than conventional liquids. With these incredible nanoliquid characteristics, the main objective of current research is to examine the impact of the exponential heat source linked to space and the inclined magnetic force on the nano-bioconvective flow between two turntables. The effect of nonlinear thermal radiation, variable thermal conductivity and viscosity aspects are also considered. The complicated nonlinear problem is treated numerically by using Finite difference method. Optimization procedure implemented via Response surface Methodology for the effective parameters thermophoresis parameter, Hartmann number and radiation parameter on the heat transfer rate. The axial velocity is a dwelling function of the inclined angle of the magnetic field, and the variable viscosity parameter. The temperature profile hikes with an exponential space-related heat source and thermal radiation aspects. Also, the heat transport rate is highly sensitive towards nonlinear thermal radiation parameter compared to the thermophoresis effect and Hartmann number.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. U. Choi, J. A. Eastman, No. ANL/MSD/CP-84938, CONF-951135-29, Argonne National Lab., IL United States, (1995)
J. Buongiorno, J. Heat Trans-T ASME. 128, 240 (2006)
M. Sheikholeslami, D.D. Ganji, Powder Technol. 253, 789 (2014)
S. Nadeem, S. Masood, R. Mehmood, M.A. Sadiq, PLoS One 10(6), e0124016 (2015)
Z. Shah, T. Gul, S. Islam, M.A. Khan, E. Bonyah, F. Hussain, M. Ullah, Results Phys. 10, 36 (2018)
B. Mahanthesh, B.J. Gireesha, I.L. Animasaun, T. Muhammad, N.S. Shashikumar, Phys. Scr. 94(8), 085214 (2019)
H.T. Basha, R. Sivaraj, A.S. Reddy, A.J. Chamkha, Eur. Phys. J.-Spec.Top. 228(12), 2531 (2019)
A. Kumar, R. Tripathi, R. Singh, G.S. Seth, Indian J. Phys. 94(3), 319 (2020)
A.V. Kuznetsov, A.A. Avramenko, Int. Commun. Heat Mass. 31(1), 1 (2004)
M.J. Uddin, M.N. Kabir, Y. Alginahi, O.A. Bég, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part C. 233(19–20), 6910 (2019)
N.A. Amirsom, M.J. Uddin, M.F.M. Basir, A. Ismail, O.A. Beg, A. Kadir, Sains Malays. 48(5), 1137 (2019)
P.S. Kumar, B.J. Gireesha, B. Mahanthesh, A.J. Chamkha, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 136(5), 1947 (2019)
L. Zhang, M.B. Arain, M.M. Bhatti, A. Zeeshan, H. Hal-Sulami, H. Appl. Math. Mech-Engl. 41(4), 637 (2020)
J.C. Umavathi, O. Ojjela, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 84, 1 (2015)
D. Mythili, R. Sivaraj, J. Mol. Liq. 216, 466–475 (2016)
B.J. Gireesha, P.S. Kumar, B. Mahanthesh, S.A. Shehzad, F.M. Abbasi, Microgravity Sci. Tec. 30(3), 257 (2018)
R. Sivaraj, A.J. Benazir, S. Srinivas, A.J. Chamkha, Eur. Phys. J.-Spec. Top. 228(1), 35–53 (2019)
S.K. Mondal, D. Pal, J. Comput. Des. Eng. 7(2), 251 (2020)
K.M. Shirvan, M. Mamourian, S. Mirzakhanlari, R. Ellahi, J. Mol. Liq. 220, 888–901 (2016)
M. Akbarzadeh, S. Rashidi, M. Bovand, R. Ellahi, J. Mol. Liq. 220, 1 (2016)
S.M. Vahedi, A.H. Pordanjani, A. Raisi, A.J. Chamkha, Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 134(3), 124 (2019)
K. Thriveni, B. Mahanthesh, Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 135, 459 (2020)
S. Xun, J. Zhao, L. Zheng, X. Zhang, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 111, 1001 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors express their sincere thanks to the Management, CHRIST (Deemed to be University), Bangalore, India for their support to complete this research work. Also, special thanks to the editor and anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BM: Mathematical formulation, solution, proof reading. KT: Formulation, computing the solution, technical writing.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahanthesh, B., Thriveni, K. Significance of inclined magnetic field on nano-bioconvection with nonlinear thermal radiation and exponential space based heat source: a sensitivity analysis. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 230, 1487–1501 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00045-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-021-00045-9