Abstract
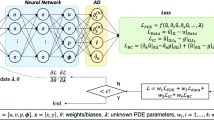
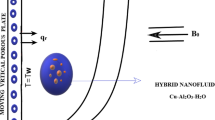
The presented work examines the dynamics of convective Eyring–Powell magneto-nanofluid model (CEP-MNFM) with a stretching cylinder by using stupendous knacks of supervised stochastic Levenberg–Marquardt intelligent networks (SSLMINs). The partial differential equations governing the CEP-MNFM are reduced into coupled ODEs by incorporating the similarity transformations. The dataset of the proposed SSLMINs approach is generated with state-of-the-art Adam numerical method for seven different scenarios of CEP-MNFM including variation of radiation, Brownian diffusivity, and thermophoresis parameter, as well as, Biot, Schmidh, and Prandtl numbers. The reference dataset is further utilized for numerical calculation of various physical quantities on CEP-MNFM by applying the AI based methods via SSLMINs. The precision and accuracy of the designed SSLMINs approach is efficaciously substantiated through the negligible level of mean squared error with magnitude around 10–8 to 10–10, histograms with maximum instances error range 10–5, very near to the optimum correlation/regression measures.






























Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
No data are associated with this manuscript.
Abbreviations
- \(u\) , \(v\) , \(x\), \(r\) :
-
Components of velocity
- \(\rho_{f}\) :
-
Liquid density
- \(l\) :
-
Characteristic length
- \(\nu\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- \(\beta\), \(c\) :
-
Material variables
- \(R_{1}\) :
-
Radius of cylinder
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Liquid electrical conductivity
- \(B_{0}\) :
-
Magnetic field potency
- \(c_{p}\) :
-
Specific heat
- \(k^{ * }\) :
-
Mean-absorption coefficient
- \(\left( {D_{B} ,\,D_{T} } \right)\) :
-
Coefficient of Brownian diffusion & thermophoretic
- \(\sigma^{ * }\) :
-
Stefan-Boltzmann constant
- \(Q_{0}\) :
-
Heat sink/source coefficient
- \({\left(\rho c\right)}_{f}\) :
-
Liquid heat capacity
- \({\left(\rho c\right)}_{p}\) :
-
Nano-particles effective heat capacity
- \({S}_{2}\) :
-
Solutal stratification parameter
- \({S}_{1}\) :
-
Thermal stratification parameter
- \({\gamma }_{2}\) :
-
Solutal biot number
- \({\gamma }_{1}\) :
-
Thermal biot number
- \(Re\) :
-
Reynolds number
- \(\hbar_{f} ,\) \(\hbar_{\theta }\), \(\hbar_{\varphi }\) :
-
Auxiliary constraints
- EPFM:
-
Eyring–Powell fluid model
- SSLMINs:
-
Supervised stochastic Levenberg–Marquardt intelligent networks
- \(f,g\) :
-
Dimensionless velocities
- \(\theta \) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(\phi \) :
-
Dimensionless concentration
- \({q}_{r}\) :
-
Radiative heat flux
- ANNs:
-
Artificial neural networks
- \(C\) :
-
Concentration
- \(T\) :
-
Temperature
- \(\left( {h_{2} ,\,h_{1} } \right)\) :
-
Dimensional constants
- \({U}_{w}\) :
-
Stretching velocity
- \({U}_{o}\) :
-
Reference velocity
- \({C}_{f}\left(x\right)\) :
-
Convective liquid concentration
- \({T}_{f}\left(x\right)\) :
-
Convective liquid temperature
- \(a,b,c,d\) :
-
Dimensional constants
- \({C}_{\infty }\left(x\right)\) :
-
Wall mass transport coefficients
- \({T}_{\infty }\left(x\right)\) :
-
Wall heat transport coefficients
- \(\tau = \tfrac{{\left( {\rho c} \right)_{{_{p} }} }}{{\left( {\rho c} \right)_{{_{f} }} }}\) :
-
Ratio of heat capacity
- \(\varepsilon ,\lambda \) :
-
Material variables
- \(S\) :
-
Suction/injection
- \(\gamma \) :
-
Curvature parameter
- \({H}_{a}\) :
-
Hartmann number
- \({P}_{r}\) :
-
Prandtl number
- \({N}_{b}\) :
-
Brownian diffusion factor
- \({N}_{t}\) :
-
Thermophoretic factor
- \(Sc\) :
-
Schmidt number
- \(R\) :
-
Radiation variable
- \(\delta \) :
-
Heat source
- ODE:
-
Ordinary differential equation
- CEP-MNFM:
-
Convective Eyring–Powell magneto-nanofluid model
- EP:
-
Eyring-Powell
- \({D}_{B}\) :
-
Coefficient of Brownian diffusion
- \({D}_{T}\) :
-
Coefficient of Brownian thermophoretic
- ɳ :
-
Dimensionless variable
References
S.U. Choi, J.A. Eastman, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles (No. ANL/MSD/CP-84938; CONF-951135–29) (1995), Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States).
O.D. Makinde, I.L. Animasaun, Thermophoresis and Brownian motion effects on MHD bioconvection of nanofluid with nonlinear thermal radiation and quartic chemical reaction past an upper horizontal surface of a paraboloid of revolution. J. Mol. Liq. 221, 733–743 (2016)
L. Yang, W. Ji, M. Mao, J.N. Huang, An updated review on the properties, fabrication and application of hybrid-nanofluids along with their environmental effects. J. Clean. Prod. 257, 120408 (2020)
M. Waqas, Z. Asghar, W.A. Khan, Thermo-solutal Robin conditions significance in thermally radiative nanofluid under stratification and magnetohydrodynamics. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 230(5), 1307–1316 (2021)
A.H. Pordanjani, S. Aghakhani, M. Afrand, M. Sharifpur, J.P. Meyer, H. Xu, H.M. Ali, N. Karimi, G. Cheraghian, Nanofluids: physical phenomena, applications in thermal systems and the environment effects-a critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 320, 128573 (2021)
M. Imran, M. Naveed, B. Iftikhar, Z. Abbas, Heat transfer analysis in a curvilinear flow of hybrid nanoliquid across a curved oscillatory stretched surface with nonlinear thermal radiation. ZAMM-J. Appl. Math. Mech./Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik 20, 220–0600 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.202200600
M. Ali, F. Sultan, W.A. Khan, M. Shahzad, H. Arif, Important features of expanding/contracting cylinder for cross magneto-nanofluid flow. Chaos Solit. Fract. 133, 109656 (2020)
K.S. Tshivhi, O.D. Makinde, Magneto-nanofluid coolants past heated shrinking/stretching surfaces: dual solutions and stability analysis. Results Eng. 10, 100229 (2021)
A.S. Alshomrani, M.Z. Ullah, S.S. Capizzano, W.A. Khan, M. Khan, Interpretation of chemical reactions and activation energy for unsteady 3D flow of Eyring–Powell magneto-nanofluid. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 579–589 (2019)
Y. Akbar, S. Huang, M.U. Ashraf, K.S. Nisar, M.M. Alam, Electrothermal analysis for reactive Powell Eyring nanofluid flow regulated by peristaltic pumping with mass transfer. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 44, 102828 (2023)
A. Shafiq, A.B. Çolak, T.N. Sindhu, Significance of EMHD graphene oxide (GO) water ethylene glycol nanofluid flow in a Darcy-Forchheimer medium by machine learning algorithm. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138(3), 213 (2023)
N.M. Sakan, I. Traparic, V.A. Sreckovic, M. Ivkovic, The usage of perceptron, feed and deep feed forward artificial neural networks on the spectroscopy data: astrophysical & fusion plasmas. Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 52(3), 97–104 (2022)
A. Jahani, S. Allahverdi, M. Saffariha, A. Alitavoli, S. Ghiyasi, Environmental modeling of landscape aesthetic value in natural urban parks using artificial neural network technique. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 8, 1–10 (2021)
Z. Fu, Y. Shen, S. Wang, W. Jiang, J. Li, G. Bin, B. Hu, Asymmetric Bouc-Wen hysteresis modeling for MFC actuator via hybrid APSO-TRR identification algorithm. Sens. Actuators A 346, 113830 (2022)
C. Ma, J. Mou, F. Yang, H. Yan, A fractional-order hopfield neural network chaotic system and its circuit realization. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135(1), 100 (2020)
Y. Liu, L. Liu, F. Lombardi, J. Han, An energy-efficient and noise-tolerant recurrent neural network using stochastic computing. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 27(9), 2213–2221 (2019)
I. Khan et al., Design of neural network With Levenberg-Marquardt and Bayesian Regularization backpropagation for solving pantograph delay differential equations. IEEE Access 8, 137918–137933 (2020)
E. Fol, R. Tomás, G. Franchetti, Supervised learning-based reconstruction of magnet errors in circular accelerators. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136(4), 365 (2021)
A. Jafarian, M. Mokhtarpour, D. Baleanu, Artificial neural network approach for a class of fractional ordinary differential equation. Neural Comput. Appl. 28(4), 765–773 (2017)
A. Jafarian, S.M. Nia, A.K. Golmankhaneh, D. Baleanu, On artificial neural networks approach with new cost functions. Appl. Math. Comput. 339, 546–555 (2018)
A. Jafarian, D. Baleanu, Application of ANNs approach for wave-like and heat-like equations. Open Phys. 15(1), 1086–1094 (2017)
R.P. Sharma, J.K. Madhukesh, S. Shukla, B.C. Prasannakumara, Numerical and Levenberg–Marquardt backpropagation neural networks computation of ternary nanofluid flow across parallel plates with Nield boundary conditions. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138(1), 63 (2023)
F. Nasirzadehroshenin, M. Sadeghzadeh, A. Khadang, H. Maddah, M.H. Ahmadi, H. Sakhaeinia, L. Chen, Modeling of heat transfer performance of carbon nanotube nanofluid in a tube with fixed wall temperature by using ANN–GA. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135(2), 217 (2020)
M. Umar, F. Amin, H.A. Wahab, D. Baleanu, Unsupervised constrained neural network modeling of boundary value corneal model for eye surgery. Appl. Soft Comput. 85, 105826 (2019)
M. Umar et al., Stochastic numerical technique for solving HIV infection model of CD4+ T cells. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135(6), 403 (2020)
A. Mehmood et al., Design of neuro-computing paradigms for nonlinear nanofluidic systems of MHD Jeffery-Hamel flow. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 91, 57–85 (2018)
J. Shlomi, P. Battaglia, J.R. Vlimant, Graph neural networks in particle physics. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 2(2), 021001 (2020)
A.Y.T. Wang, R.J. Murdock, S.K. Kauwe, A.O. Oliynyk, A. Gurlo, J. Brgoch, K.A. Persson, T.D. Sparks, Machine learning for materials scientists: an introductory guide toward best practices. Chem. Mater. 32(12), 4954–4965 (2020)
A. Mehmood et al., Design of nature-inspired heuristic paradigm for systems in nonlinear electrical circuits. Neural Comput. Appl. 32, 1–17 (2019)
I. Ahmad et al., Novel applications of intelligent computing paradigms for the analysis of nonlinear reactive transport model of the fluid in soft tissues and microvessels. Neural Comput. Appl. 31(12), 9041–9059 (2019)
J. Rabault, M. Kuchta, A. Jensen, U. Réglade, N. Cerardi, Artificial neural networks trained through deep reinforcement learning discover control strategies for active flow control. J. Fluid Mech. 865, 281–302 (2019)
C.H. Martin, M.W. Mahoney, Implicit self-regularization in deep neural networks: evidence from random matrix theory and implications for learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 22(1), 7479–7551 (2021)
G. Rajput, V. Logashree, K.N. Biyani, S.K. Vishvakarma, Clock gating-based effectual realization of stochastic hyperbolic tangent function for deep neural hardware accelerators. Circuit Syst. Signal Proc. 42, 1–23 (2023)
F. Shahzad, S.A. Shehzad, W.A. Khan, M. Waqas, M. Manzur, M. Zubair, Convective stratified flow of magnetized Eyring–Powell (EP) nanofluid by a stretching cylinder. Appl. Nanosci. 10, 5401–5408 (2020)
J. Buongiorno, Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transfer. 128, 240–250 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, Z., Raja, M.A.Z., Shoaib, M. et al. Supervised stochastic Levenberg–Marquardt intelligent netwoks for dynamics of convective Eyring–Powell magneto-nanofluid model. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 139, 173 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04852-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04852-y