Abstract
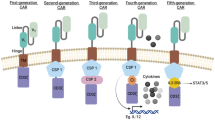
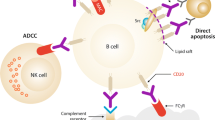
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy has emerged as a widely accepted approach in the management of blood malignancies, enabling specifically trained CAR-T cells to target cancerous cells. Encouraging outcomes have been observed in B-cell lymphoma patients who have exhibited complete responses to CAR-T cell therapy. Ongoing researches are exploring the therapeutic effects of CAR-T cells on various tumors and malignancies, including T cell leukemia. The aim of this study is to present an optimized method for solving the fractional model of CAR-T cell treatment for patients with T-cell leukemia by means of new basis functions, generalized Lerch polynomials (GLPs). The optimization method is performed through the Lagrange multipliers. To observe the correctness, efficiency, competence, and proficiency of the designed computing algorithm, an exhaustive analysis of different parameters, CPU times, and residual function optimal values are presented. Our results predicted a significant decrease in the count of leukemic T-cells after the first dose administration of CAR-T cells to T leukemia patients. Additionally, our mathematical analysis demonstrated that an optimized cure may occur after the second injection of CAR-T cells. These findings underscore the efficacy and potential of our optimized method using GLPs for solving the fractional model of CAR-T cell treatment in patients with T-cell leukemia.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
A. Aureli, B. Marziani, A. Venditti, T. Sconocchia, G. Sconocchia, Acute lymphoblastic Leukemia immunotherapy treatment: now, next, and beyond. Cancers 15(13), 3346 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133346
A. Gavralidis, A.M. Brunner, Novel therapies in the treatment of adult acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 15(4), 294–304 (2020)
D.J. DeAngelo, E. Jabbour, A. Advani, Recent advances in managing acute lymphoblastic Leukemia. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 40, 330–342 (2020)
N. Gokbuget, Treatment of older patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 1, 573–579 (2016)
C.H. Pui, Precision medicine in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Front. Med. 14(6), 689–700 (2020)
K. Sasaki, E. Jabbour, N.J. Short, N. Jain, F. Ravandi, C.H. Pui, H. Kantarjian, Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a population-based study of outcome in the United States based on the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) database, 1980–2017. Am. J. Hematol. 96(6), 650–658 (2021)
B. Samra, E. Jabbour, F. Ravandi, H. Kantarjian, N.J. Short, Evolving therapy of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: state-of-the-art treatment and future directions. J. Hematol. Oncol. 13(1), 1–17 (2020)
R.C. Sterner, R.M. Sterner, CAR-T cell therapy: current limitations and potential strategies. Blood Cancer J. 11(4), 69 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-021-00459-7
X. Xu, S. Huang, X. Xiao, O. Sun, X. Liang, S. Chen, Z. Zhao, Z. Huo, S. Tu, Y. Li, Challenges and clinical strategies of CAR T-cell therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: overview and developments. Front. Immunol. 11, 569117 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.569117
T. Haslauer, R. Greil, N. Zaborsky, R. Geisberger, CAR T-cell therapy in hematological malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22(16), 8996 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168996
P. Lu, Y. Liu, J. Yang, X. Zhang, X. Yang, H. Wang, L. Wang, Q. Wang, D. Jin, J. Li, X. Huang, Naturally selected CD7 CAR-T therapy without genetic manipulations for T-ALL/LBL: first-in-human phase 1 clinical trial. Blood 140(4), 321–334 (2020)
J. Pan, Y. Tan, G. Wang, B. Deng, Z. Ling et al., Donor-derived CD7 chimeric antigen receptor T cells for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: first-in-human, phase I trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 39(30), 3340–3351 (2021)
Z. Avazzadeh, H. Hassani, P. Agarwal, S. Mehrabi, M.J. Ebadi, M.K. Hosseini Asl, Optimal study on fractional fascioliasis disease model based on generalized Fibonacci polynomials. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 46(8), 9332–9350 (2023)
Z. Avazzadeh, H. Hassani, P. Agarwal, S. Mehrabi, M.J. Ebadi, MSh. Dahaghin, An optimization method for studying fractional-order tuberculosis disease model via generalized Laguerre polynomials. Soft. Comput. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08086-z
Y. Nawaz, M.S. Arif, K. Abodayeh, A third-order two-stage numerical scheme for fractional Stokes problems: a comparative computational study. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 17(10), 101004 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4054800
M.S. Arif, K. Abodayeh, A. Ejaz, Stability analysis of fractional-order predator-prey system with consuming food resource. Axioms 12(1), 64 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12010064
Y. Nawaz, M.S. Arif, W. Shatanawi, A new numerical scheme for time fractional diffusive Seair model with non-linear incidence rate: an application to computational biology. Fractal Fract. 6(2), 78 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6020078
M.S. Arif, K. Abodayeh, Y. Nawaz, Numerical schemes for fractional energy balance model of climate change with diffusion effects. Emerging Sci. J. 7(3), 808–820 (2023). https://doi.org/10.28991/ESJ-2023-07-03-011
Y. Nawaz, M.S. Arif, K. Abodayeh, M. Bibi, Finite difference schemes for time-dependent convection q-diffusion problem. AIMS Math. 7(9), 16407–16421 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3934/math.2022897
S.A. Pasha, Y. Nawaz, M.S. Arif, On the nonstandard finite difference method for reaction?Diffusion models. Chaos Solitons Fractals 166, 112929 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2022.112929
P. Veeresha, H.M. Baskonus, D. Prakasha, W. Gao, G. Yel, Regarding new numerical solution of fractional Schistosomiasis disease arising in biological phenomena. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 133, 109661 (2020)
A.S.V.R. Kanth, S. Devi, A computational approach for numerical simulations of the fractal-fractional autoimmune disease model, Chaos. Solitons Fractals 165(2), 112829 (2022)
S.-W. Yao, S. Rashid, M. Inc, E.E. Elattar, On fuzzy numerical model dealing with the control of glucose in insulin therapies for diabetes via nonsingular kernel in the fuzzy sense. AIMS Math. 7(10), 17913–17941 (2022)
S. Rashid, R. Ashraf, Q.-U.-A. Asif, F. Jarad, Novel stochastic dynamics of a fractal-fractional immune effector response to viral infection via latently infectious tissues. MBE 19(11), 11563–11594 (2022)
H.M. Srivastava, S. Deniz, A new modified semi-analytical technique for a fractional-order Ebola virus disease model. RACSAM 115, 137 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13398-021-01081-9
M. AltafKhan, O. Kolebaje, A. Yildirim, S. Ullah, P. Kumam, P. Thounthong, Fractional investigations of zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis disease with singular and non-singular kernel. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 134, 481 (2019)
Q. Haidong, M. ur Rahman, M. Arfan, M. Salimi, S. Salahshour, A. Ahmadian, Fractal-fractional dynamical system of Typhoid disease including protection from infection. Eng. Comput. (2021)
A. Ahmad, M. Farman, P. Ahmad Naik, N. Zafar, A. Akgul, M. Umer Saleem, Modeling and numerical investigation of fractional-order bovine babesiosis disease. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 37(3), 1946–1964 (2021)
C. Maji, D. Mukherjee, D. Kesh, Study of a fractional-order model of chronic wasting disease. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 43(7), 4669–4682 (2020)
P. Kumar, V.S. Erturk, The analysis of a time delay fractional COVID-19 model via Caputo type fractional derivative. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.6935
V.M. Pérez-García, O. León-Triana, M. Rosa, A. Pérez-Martínez, CAR T cells for T-cell leukemias: insights from mathematical models. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 96, 105684 (2021)
I. Podlubny, Geometric and physical interpretation of fractional integration and fractional differentiation. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 5(4), 367–386 (2002)
J.F.G. Aguilar, J.R. García, J.B. Alvarado, M. Guía, Mathematical modelling of the mass-spring-damper system: a fractional calculus approach. Acta Universitaria. 22(5), 5–11 (2012)
K. Diethelm, A fractional calculus based model for the simulation of an outbreak of dengue fever. Nonlinear Dynam. 71, 613–619 (2013)
F.A. Rihan, A.A. Arafa, R. Rakkiyappan, C. Rajivganthi, Y. Xu, Fractional-order delay differential equations for the dynamics of hepatitis C virus infection with IFN-\(\alpha\) treatment. Alex. Eng. J. 60, 4761–4774 (2021)
H. Hassani, J.A. Tenreiro Machado, Z. Avazzadeh, An effective numerical method for solving nonlinear variable-order fractional functional boundary value problems through optimization technique. Nonlinear Dynam. 97, 2041–2054 (2019)
H. Hassani, Z. Avazzadeh, J.A. TenreiroMachado, Numerical approach for solving variable-order space-time fractional telegraph equation using transcendental Bernstein series. Eng. Comput. 36, 867–878 (2020)
G. Estrada-Rodriguez, H. Gimperlein, K.J. Painter, J. Stocek, Space-time fractional diffusion in cell movement models with delay. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 29(1), 65–88 (2019)
S. Cayan, M. Sezer, A novel study based on Lerch polynomials for approximate solutions of pure Neumann problem. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 8, 8 (2022)
V. Kruchinin, D. Kruchinin, Explicit formulas for some generalized polynomials. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 7, 2083–2088 (2013)
Y. Li, Y. Chen, I. Podlubny, Stability of fractional-order non linear dynamic systems: Lyapunov direct method and generalized Mittag–Leffler stability. Comput. Math. Appl. 59, 1810–1821 (2010)
S. Feins, W. Kong, E.F. Williams, M.C. Milone, J.A. Fraietta, An introduction to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell immunotherapy for human cancer. Am. J. Hematol. 94(S1), S3–S9 (2019)
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to each part of this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Avazzadeh, Z., Hassani, H., Ebadi, M.J. et al. Generalized Lerch polynomials: application in fractional model of CAR-T cells for T-cell leukemia. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 1152 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04786-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04786-5