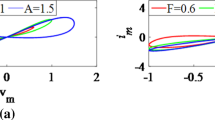
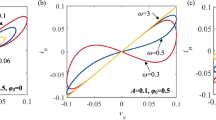
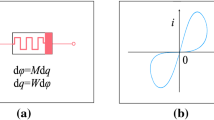
Abstract
In this paper, a discrete memristor-coupled heterogeneous neural network (MCHNN) by coupling KTz neuron and tabu learning neurons with a locally active discrete memristor is constructed. Firstly, rationale of the proposed discrete MCHNN is presented. Then, taking the memristor initial state and coupling weight as variables, the abundant dynamical behaviors of the coupled neuron network are systematically analyzed, as well as the multi-stability of the discrete bi-neuron network are proved. Particularly, the six different firing cases and three types infinite multi-structure hyperchaotic attractors are discussed. Finally, a microcontroller-based hardware experiment was also conducted, in order to further verify the correctness of the numerical simulation. This study provides a theoretical basis for the implementation of MCHNN in human brain dynamics.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
B. Bao, A. Hu, H. Bao et al., Three-dimensional memristive Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model with hidden coexisting asymmetric behaviors. Complexity 2018, 1–11 (2018)
M. Ma, Y. Lu, Z. Li et al., Multistability and phase synchronization of Rulkov neurons coupled with a locally active discrete memristor. Fractal Fractional. 7(1), 82 (2023)
M. Ma, K. Xiong, Z. Li et al., Dynamic Behavior analysis and synchronization of memristor-coupled heterogeneous discrete neural networks. Mathematics. 11(2), 375 (2023)
B. Bao, Q. Yang, D. Zhu et al., Initial-induced coexisting and synchronous firing activities in memristor synapse-coupled Morris–Lecar bi-neuron network. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(3), 2339–2354 (2019)
G.S. Bortolotto, R.V. Stenzinger, M.H. Tragtenberg, Electromagnetic induction on a map-based action potential model. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(1), 433–444 (2018)
Chialvo, D.R., Girardi Schappo, M., Bortolotto, G.S., et al.: Phase diagrams and dynamics of a computationally efficient map-based neuron model. Plos One. 12(3) (2017)
M. Courbage, V. Nekorkin, L. Vdovin, Chaotic oscillations in a map-based model of neural activity. Chaos: Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 17(4), 043109 (2007)
M. Courbage, V.I. Nekorkin, Map based models in neurodynamics. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos. 20(06), 1631–1651 (2010)
I.S. Doubla, Z.T. Njitacke, S. Ekonde et al., Multistability and circuit implementation of tabu learning two-neuron model: application to secure biomedical images in IoMT. Neural Comput. Appl. 33(21), 14945–14973 (2021)
Z.H. Guo, Z.J. Li, M.J. Wang et al., Hopf bifurcation and phase synchronization in memristor-coupled Hindmarsh–Rose and FitzHugh–Nagumo neurons with two time delays. Chin. Phys. B 32(3), 038701 (2023)
L. Hou, H. Bao, Q. Xu et al., Coexisting infinitely many nonchaotic attractors in a memristive weight-based Tabu learning neuron. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos. 31(12), 2150189 (2021)
Z. Huang, C. Yang, X. Zhou et al., Brain-inspired STA for parameter estimation of fractional-order memristor-based chaotic systems. Appl. Intell. 53, 1–13 (2023)
B. Ibarz, J.M. Casado, M.A. Sanjuán, Map-based models in neuronal dynamics. Phys. Rep. 501(1–2), 1–74 (2011)
Q. Lai, C. Lai, Design and implementation of a new hyperchaotic memristive map. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 69(4), 2331–2335 (2022)
Q. Lai, L. Yang, Discrete memristor applied to construct neural networks with homogeneous and heterogeneous coexisting attractors. Chaos Solitons Fractals 174, 113807 (2023)
C. Li, Y. Yang, X. Yang et al., Application of discrete memristors in logistic map and Hindmarsh–Rose neuron. Eur. Phys. J. Special Top. 231(16), 3209–3224 (2022)
K.X. Li, B.C. Bao, J. Ma et al., Synchronization transitions in a discrete memristor-coupled bi-neuron model. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 165, 112861 (2022)
R. Li, Z. Wang, E. Dong, A new locally active memristive synapse-coupled neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(4), 4459–4475 (2021)
T. Liu, J. Mou, L. Xiong et al., Hyperchaotic maps of a discrete memristor coupled to trigonometric function. Phys. Scr. 96(12), 125242 (2021)
Y. Lu, C. Wang, Q. Deng, Rulkov neural network coupled with discrete memristors. Netw. Comput. Neural Syst. 33(3–4), 214–232 (2022)
J. Ma, L. Mi, P. Zhou et al., Phase synchronization between two neurons induced by coupling of electromagnetic field. Appl. Math. Comput. 307, 321–328 (2017)
F.F. Yang, G.D. Ren, J. Tang, Dynamics in a memristive neuron under an electromagnetic field. Nonlinear Dyn. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08969-8
M.L. Ma, X.H. Xie, Y. Yang et al., Synchronization coexistence in a Rulkov neural network based on locally active discrete memristor. Chin. Phys. B 32(5), 058701 (2023)
T. Ma, J. Mou, B. Li et al., Study on the complex dynamical behavior of the fractional-order hopfield neural network system and its implementation. Fractal Fractional. 6(11), 637 (2022)
T. Ma, J. Mou, A.-B.A. Abdullah et al., Hidden dynamics of memristor-coupled neurons with multi-stability and multi-transient hyperchaotic behavior. Phys. Scr. 98(10), 105202 (2023)
M. Ma, K. Xiong, Z. Li et al., Dynamical behavior of memristor-coupled heterogeneous discrete neural networks with synaptic crosstalk. Chin. Phys. B 98(10), 105202 (2023)
Z.T. Njitacke, B.N. Koumetio, B. Ramakrishnan et al., Hamiltonian energy and coexistence of hidden firing patterns from bidirectional coupling between two different neurons. Cognit. Neurodyn. 16(4), 899–916 (2021)
Q. Xu, T. Liu, S. Ding et al., Extreme multistability and phase synchronization in a heterogeneous bi-neuron Rulkov network with memristive electromagnetic induction. Cognit. Neurodyn. 17(3), 755–766 (2023)
M. Chen, D. Guo, T. Wang et al., Bidirectional control of absence seizures by the basal ganglia: a computational evidence. PLoS Comput. Biol. 10(3), 1003495 (2014)
S.S. Muni, K. Rajagopal, A. Karthikeyan et al., Discrete hybrid Izhikevich neuron model: nodal and network behaviours considering electromagnetic flux coupling. Chaos Solitons Fractals 155, 111759 (2022)
Y. Peng, K. Sun, S. He, A discrete memristor model and its application in Hénon map. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 137, 109873 (2020)
R. Qiu, Y. Dong, X. Jiang et al., Two-neuron based memristive hopfield neural network with synaptic crosstalk. Electronics 11(19), 3034 (2022)
L. Ren, J. Mou, S. Banerjee et al., A hyperchaotic map with a new discrete memristor model: design, dynamical analysis, implementation and application. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 167, 113024 (2023)
N.F. Rulkov, Modeling of spiking-bursting neural behavior using two-dimensional map. Phys. Rev. E 65(4), 041922 (2002)
T. Ma, J. Mou, H. Yan et al., A new class of Hopfield neural network with double memristive synapses and its DSP implementation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 137(10), 1–19 (2022)
S. Majhi, M. Perc, D. Ghosh, Chimera states in uncoupled neurons induced by a multilayer structure. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 39033 (2016)
S.S. Muni, Mode-locked orbits, doubling of invariant curves in discrete Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model. Physica Scripta. 98(8) (2023)
F.F. Yang, Q. Guo, J. Ma, A neuron model with nonlinear membranes. Cognit. Neurodyn. 1–12 (2023)
H. Lin, C. Wang F. Yu, et al., A triple-memristor hopfield neural network with space multi-structure attractors and space initial-offset behaviors. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. (2023)
S. Zhang, J. Zheng, X. Wang et al., Initial offset boosting coexisting attractors in memristive multi-double-scroll Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 102(4), 2821–2841 (2020)
H. Lin, C. Wang, J. Sun et al., Memristor-coupled asymmetric neural networks: bionic modeling, chaotic dynamics analysis and encryption application. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 166, 112905 (2023)
M. Ma, Y. Yang, Z. Qiu et al., A locally active discrete memristor model and its application in a hyperchaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 107(3), 2935–2949 (2022)
L. Zhang, Y. Wang, X. Leng et al., Analysis of neural network connections based on memristors and their multiple offset phenomena. Phys. Scr. 98(11), 2023 (2023)
Acknowledgements
National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 62061014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Miao Wang designed and carried out experiments, data analyzed and manuscript wrote. Jun Mou and Hadi Jahanshahi made the theoretical guidance for this paper. Lei Qin improved the algorithm. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interests about the publication by all authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Mou, J., Qin, L. et al. A memristor-coupled heterogeneous discrete neural networks with infinite multi-structure hyperchaotic attractors. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 1137 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04772-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04772-x