Abstract
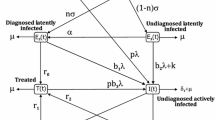
This study investigates a novel tuberculosis (TB) model by integrating key factors that contribute to the spread of TB, such as endogenous reactivation, reinfection of recovered individuals, slow-fast progression of TB via non-monotonic information-induced incidence term, saturation in treatment function, and exogenous reinfection. The mathematical analysis of the model is carried out, and both transcritical and backward bifurcation are obtained conditionally, which infers that \({\mathcal {R}}_0<1\) is not sufficient for TB eradication. The combined impact of reinfections and treatment saturation on backward bifurcation is illustrated, along with the presence of exogenous reinfection. Further analysis shows that the model system exhibits interesting rich and complex nonlinear dynamics, such as bistability, multistability, Hopf bifurcation, and Hopf–Hopf bifurcation (stability switches). Analytical results are further explored and supplemented with numerical findings. The model system is fitted with real-time data of India and Turkey. It is observed that our model fits well and is reasonably accurate for short-term prediction.























Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
Our Manuscript has no associated data.
References
B.R. Bloom, Tuberculosis: pathogenesis, protection, and control (ASM Press, Washington, 1994)
S. Saha, A. Kumar, K. Saurabh, S.H. Shankar, A. Kashyap, N. Nischal, A. Biswas, N. Wig et al., Current status of treatment of latent tuberculosis infection in India. Indian J. Med. Sci. 71(2), 54–59 (2020)
Who, global tuberculosis report 2021 (2021). https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/global-tuberculosis-report-2021
T. Lillebaek, A. Dirksen, I. Baess, B. Strunge, V.Ø. Thomsen, Å.B. Andersen, Molecular evidence of endogenous reactivation of mycobacterium tuberculosis after 33 years of latent infection. J. Infect. Dis. 185(3), 401–404 (2002)
V. Deepak, S.R. Bhoi, R. Asmita, Latent tuberculosis in India: an overview. Cureus 15(3), 1–7 (2023)
Z. Feng, C. Castillo-Chavez, A.F. Capurro, A model for tuberculosis with exogenous reinfection. Theor. Popul. Biol. 57(3), 235–247 (2000)
S. Khajanchi, D.K. Das, T.K. Kar, Dynamics of tuberculosis transmission with exogenous reinfections and endogenous reactivation. Physica A 497, 52–71 (2018)
I.M. Wangari, L. Stone, Backward bifurcation and hysteresis in models of recurrent tuberculosis. PloS One 13(3), e0194256 (2018)
D.K. Das, S. Khajanchi, T.K. Kar, Transmission dynamics of tuberculosis with multiple re-infections. Chaos Solitons Fractals 130, 109450 (2020)
M. Zignol, A. Wright, E. Jaramillo, P. Nunn, M.C. Raviglione, Patients with previously treated tuberculosis no longer neglected. Clin. Infect. Dis. 44(1), 61–64 (2007)
R.E. Chaisson, G.J. Churchyard, Recurrent tuberculosis: relapse, reinfection, and HIV. J Infect Dis. 201(5), 653–655 (2010)
S. Verver, R.M. Warren, N. Beyers, M. Richardson, G.D. Van Der Spuy, M.W. Borgdorff, D.A. Enarson, M.A. Behr, P.D. Van Helden, Rate of reinfection tuberculosis after successful treatment is higher than rate of new tuberculosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 171(12), 1430–1435 (2005)
M.-L. Lambert, E. Hasker, A. Van Deun, D. Roberfroid, M. Boelaert, P. Van der Stuyft, Recurrence in tuberculosis: relapse or reinfection? Lancet Infect. Dis 3(5), 282–287 (2003)
H.M. Yang, S.M. Raimundo, Assessing the effects of multiple infections and long latency in the dynamics of tuberculosis. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 7, 1–37 (2010)
M.G.M. Gomes, A.O. Franco, M.C. Gomes, G.F. Medley, The reinfection threshold promotes variability in tuberculosis epidemiology and vaccine efficacy. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 271(1539), 617–623 (2004)
M. Herrera, P. Bosch, M. Nájera, X. Aguilera et al., Modeling the spread of tuberculosis in semiclosed communities. Comput. Math. Methods Med. (2013)
B.I. Omede, O.J. Peter, W. Atokolo, B. Bolaji, T.A. Ayoola, A mathematical analysis of the two-strain tuberculosis model dynamics with exogenous re-infection. Healthc. Anal. 4, 100266 (2023)
I.A. Baba, R.A. Abdulkadir, P. Esmaili, Analysis of tuberculosis model with saturated incidence rate and optimal control. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 540, 123237 (2020)
V. Capasso, G. Serio, A generalization of the Kermack–McKendrick deterministic epidemic model. Math. Biosci. 42(1–2), 43–61 (1978)
W. Liu, S.A. Levin, Y. Iwasa, Influence of nonlinear incidence rates upon the behavior of sirs epidemiological models. J. Math. Biol. 23(2), 187–204 (1986)
S. Ruan, W. Wang, Dynamical behavior of an epidemic model with a nonlinear incidence rate. J. Differ. Equ. 188(1), 135–163 (2003)
D. Xiao, S. Ruan, Global analysis of an epidemic model with nonmonotone incidence rate. Math. Biosci. 208(2), 419–429 (2007)
A. Srivastava, P.K. Srivastava et al., Nonlinear dynamics of a SIRI model incorporating the impact of information and saturated treatment with optimal control. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137(9), 1–25 (2022)
I.A. Baba, E. Hincal, Global stability analysis of two-strain epidemic model with bilinear and non-monotone incidence rates. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132, 1–10 (2017)
A. Meskaf, O. Khyar, J. Danane, K. Allali, Global stability analysis of a two-strain epidemic model with non-monotone incidence rates. Chaos Solitons Fractals 133, 109647 (2020)
World Health Organization et al., TB/HIV: A Clinical Manual. Number WHO/HTM/TB/2004.329. World Health Organization (2004)
W. Wang, Backward bifurcation of an epidemic model with treatment. Math. Biosci. 201(1–2), 58–71 (2006)
X. Zhang, X. Liu, Backward bifurcation of an epidemic model with saturated treatment function. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 348(1), 433–443 (2008)
G.-H. Li, Y.-X. Zhang, Dynamic behaviors of a modified sir model in epidemic diseases using nonlinear incidence and recovery rates. PLoS ONE 12(4), e0175789 (2017)
J.K. Ghosh, U. Ghosh, M.H.A. Biswas, S. Sarkar, Qualitative analysis and optimal control strategy of an sir model with saturated incidence and treatment. Differ. Equ. Dyn. Syst. 31(1), 1–15 (2019)
A. Yadav, P.K. Srivastava, The impact of information and saturated treatment with time delay in an infectious disease model. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 66(1), 277–305 (2021)
F. Sulayman, F.A. Abdullah, Analysis of a tuberculosis infection model considering the influence of saturated recovery (treatment). Complexity 2021, 1805651 (2021)
L. Xuejuan, S. Wang, S. Liu, J. Li, An sei infection model incorporating media impact. Math. Biosci. Eng. 14(5 &6), 1317 (2017)
P. Van den Driessche, J. Watmough, Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 180(1–2), 29–48 (2002)
N. Chitnis, J.M. Hyman, J.M. Cushing, Determining important parameters in the spread of malaria through the sensitivity analysis of a mathematical model. Bull. Math. Biol. 70(5), 1272–1296 (2008)
C. Castillo-Chavez, Z. Feng, W. Huang et al., On the computation of r0 and its role in global stability. IMA Vol. Math. Its Appl. 125, 229–250 (2002)
M.Y. Li, J.S. Muldowney, A geometric approach to global-stability problems. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 27(4), 1070–1083 (1996)
W.A. Coppel, Stability and asymptotic behavior of differential equations. Heath (1965)
J.S. Muldowney, Compound matrices and ordinary differential equations. Rocky Mt. J. Math. 20(4), 857–872 (1990)
H.I. Freedman, S. Ruan, M. Tang, Uniform persistence and flows near a closed positively invariant set. J. Dyn. Differ. Equ. 6(4), 583–600 (1994)
C. Castillo-Chavez, B. Song, Dynamical models of tuberculosis and their applications. Math. Biosci. Eng. 1(2), 361 (2004)
W.-M. Liu, Criterion of hopf bifurcations without using eigenvalues. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 182(1), 250–256 (1994)
T.K. Kar, P.K. Mondal, Global dynamics of a tuberculosis epidemic model and the influence of backward bifurcation. J. Math. Model. Algorithms 11, 433–459 (2012)
Y. Ucakan, S. Gulen, K. Koklu, Analysing of tuberculosis in Turkey through SIR, SEIR and BSEIR mathematical models. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst. 27(1), 179–202 (2021)
Macrotrends, Turkey life expectancy 1950–2023. https://www.macrotrends.net/countries/TUR/turkey/life-expectancy
Nikshay, National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme. https://reports.nikshay.in/Reports/TBNotification
Macrotrends, Agra (India) population 1950-2023. https://www.macrotrends.net/cities/21151/agra/population
Macrotrends, India life expectancy 1950–2023. https://www.macrotrends.net/countries/IND/india/life-expectancy
Macrotrends, Lucknow (India) population 1950–2023. https://www.macrotrends.net/cities/21318/lucknow/population
Ayodhya (India), population. https://www.census2011.co.in/census/district/548-faizabad.html (2021)
Acknowledgements
AS acknowledges financial support from the Indian Institute of Technology Patna.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, A., Srivastava, P.K. A tuberculosis model incorporating the impact of information, saturated treatment and multiple reinfections. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 1156 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04754-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04754-z