Abstract
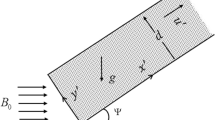
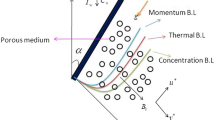
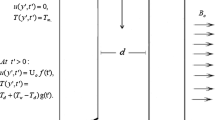
Jeffrey fluid flow was found to have extensive applications in many fields of engineering. There are numerous applications of Jeffrey fluid in polymer industries and industrial fluids like paints, paper, toothpaste, ketchup, etc. The present work explains the entropy generation of Jeffrey fluid on natural convection Navier-slip flow through a vertical channel having an inclined magnetic field. The governing equations are converted into dimensionless equations by using suitable transformation. To solve dimensionless governing equations, the spectral quasi-linearization method is used. The findings are shown graphically and quantitatively for active parameters that appear in mathematical formulations. The results demonstrate that as the magnetic parameter, angle of inclination, and Soret parameter values increase, the entropy generation number also increases.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No Data associated in the manuscript.
References
A. Bar-Cohen, W. Rohsenow, Thermally optimum spacing of vertical, natural convection cooled, parallel plates. (1984)
D. Pedersen, J. Tessier, J. Heineman, Experimental and Analytical Studies of Passive Shutdown Heat Removal Systems (Tech. Rep, Argonne National Lab, 1987)
A.R.H. Al-Azzawi, Natural convection in a vertical channel related to passive solar systems (1987)
D. Sohn, A Numerical Study of Turbulent Natural Convection in a Vertical Parallel-Plate Channel with Symmetric and Asymmetric Heating (The Pennsylvania State University, 1989)
T. Yilmaz, An experimental and Numerical Invetigation of Laminar and Turbulent Natural Convection in Vertical Parallel-Plate Channels (1997)
F. Zulkifee, A. Mohammed, S. Shafi, Radiation effect on unsteady free convection and mass transfer flow between two vertical parallel plates with newtonian heating. ASM Sci. J. 13, 1–7 (2020)
N.C. Roy, I. Pop, Analytical investigation of transient free convection and heat transfer of a hybrid nanofluid between two vertical parallel plates. Phys. Fluids 34, 072005 (2022)
N.A. Shah, A. Ebaid, T. Oreyeni, S.-J. Yook, MHD and porous effects on free convection flow of viscous fluid between vertical parallel plates: advance thermal analysis. Waves Random Complex Med. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2023.2186717
A. Kitagawa, R. Kobayashi, P. Denissenko, Y. Murai, Natural convection heat transfer enhancement using bubble injection between vertical parallel plates. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 202, 123658 (2023)
H.M. Elshehabey, F. Hady, S.E. Ahmed, R. Mohamed, Numerical investigation for natural convection of a nanofluid in an inclined l-shaped cavity in the presence of an inclined magnetic field. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 57, 228–238 (2014)
A. Dogonchi, M. Sheremet, D. Ganji, I. Pop, Free convection of copper-water nanofluid in a porous gap between hot rectangular cylinder and cold circular cylinder under the effect of inclined magnetic field. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 135, 1171–1184 (2019)
T. Hymavathi, J. Mathews, R. Kiran Kumar, Heat transfer and inclined magnetic field effects on unsteady free convection flow of mos2 and mgo-water based nanofluids over a porous stretching sheet. Int. J. Ambient Energy 43, 5855–5863 (2022)
M. Goswami, K.G. Singha, B.K. Dutta, A. Goswami, The unsteady magnetohydrodynamtc flow and heat transfer between two non-conducting infinite vertical parallel plates with inclined magnetic field. Math. Stat. Eng. Appl. 72, 413–431 (2023)
K.K. Asogwa et al., Inclined relative magnetic field analysis of brinkman type dusty fluid through fluctuating upright parallel plates. Heliyon 9, e14770 (2023)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, I. Pop, Exact analytical solutions for the flow and heat transfer near the stagnation point on a stretching/shrinking sheet in a jeffrey fluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 57, 82–88 (2013)
T. Hayat, Z. Iqbal, M. Mustafa, A. Alsaedi, Unsteady flow and heat transfer of Jeffrey fluid over a stretching sheet. Therm. Sci. 18, 1069–1078 (2014)
P.S. Narayana, D.H. Babu, Numerical study of MHD heat and mass transfer of a Jeffrey fluid over a stretching sheet with chemical reaction and thermal radiation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 59, 18–25 (2016)
O. Ojjela, A. Raju, P.K. Kambhatla, Influence of thermophoresis and induced magnetic field on chemically reacting mixed convective flow of Jeffrey fluid between porous parallel plates. J. Mol. Liq. 232, 195–206 (2017)
K. Ramesh, V. Joshi, Numerical solutions for unsteady flows of a magnetohydrodynamic Jeffrey fluid between parallel plates through a porous medium. Int. J. Comput. Methods Eng. Sci. Mech. 20, 1–13 (2019)
M. Aleem, M.I. Asjad, A. Ahmadian, M. Salimi, M. Ferrara, Heat transfer analysis of channel flow of MHD Jeffrey fluid subject to generalized boundary conditions. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 26 (2020)
D. Khan et al., A generalized two-phase free convection flow of dusty Jeffrey fluid between infinite vertical parallel plates with heat transfer. J. Math. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8470139
A. Abd-Alla, S. Abo-Dahab, E.N. Thabet, F. Bayones, M. Abdelhafez, Heat and mass transfer in a peristaltic rotating frame Jeffrey fluid via porous medium with chemical reaction and wall properties. Alex. Eng. J. 66, 405–420 (2023)
E. Omokhuale, M. Dange, Heat absorption effect on magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow of Jeffery fluid in an infinite vertical plate. FUDMA J. Sci. 7, 45–51 (2023)
T.A. Ameel, X. Wang, R.F. Barron, R.O. Warrington, Laminar forced convection in a circular tube with constant heat flux and slip flow. Microsc. Thermophys. Eng. 1, 303–320 (1997)
A. Raisi, B. Ghasemi, S. Aminossadati, A numerical study on the forced convection of laminar nanofluid in a microchannel with both slip and no-slip conditions. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A: Appl. 59, 114–129 (2011)
J.H. Merkin, A.M. Rohni, S. Ahmad, I. Pop, On the temperature slip boundary condition in a mixed convection boundary-layer flow in a porous medium. Transp. Porous Med. 94, 133–147 (2012)
N. Loussif, J. Orfi, A. Omri, Slip flow effect on laminar convection inside micro-tubes with permeable walls. Desalination Water Treat. 51, 1973–1979 (2013)
G.-M. Gie, J. Whitehead, Boundary layer analysis for Navier-slip Rayleigh-bénard convection: the non-existence of an ultimate state. J. Math. Fluid Mech. 21, 1–25 (2019)
E.O. Fatunmbi, S.O. Salawu, Analysis of hydromagnetic micropolar nanofluid flow past a nonlinear stretchable sheet and entropy generation with navier slips. Int. J. Model. Simul. 42, 359–369 (2022)
R. Zhang, Q. He, The least-square/fictitious domain method based on Navier slip boundary condition for simulation of flow-particle interaction. Appl. Math. Comput. 415, 126687 (2022)
A.J. Badday, A.J. Harfash, The effects of the soret and slip boundary conditions on thermosolutal convection with a Navier–Stokes–Voigt fluid. Phys. Fluids 35, 014101 (2023)
K.D. Housiadas, C. Tsangaris, Channel flow with variable geometry and Navier slip at the walls using high-order lubrication theory. Eur. J. Mech.-B/Fluids 98, 194–207 (2023)
M. Othman, K. Lotfy, S. Said, O.A. Bég, Wave propagation in a fiber-reinforced micropolar thermoelastic medium with voids using three models. Int. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 8, 52–69 (2012)
P.K. Yadav, A. Kumar, An inclined magnetic field effect on entropy production of non-miscible Newtonian and micropolar fluid in a rectangular conduit. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 124, 105266 (2021)
P. Mondal, D.K. Maiti, G. Shit, G. Ibáñez, Heat transfer and entropy generation in a MHD Couette–Poiseuille flow through a microchannel with slip, suction-injection and radiation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 147, 4253–4273 (2022)
P.K. Yadav, A. Kumar, A. Filippov, Analysis of entropy production of immiscible micropolar and Newtonian fluids flow through a channel: Effect of thermal radiation and magnetic field. Colloid J. 85(1), 95–113 (2023)
F. Selimefendigil, H. Chouikhi, H.F. Oztop, Natural convection and entropy generation of hybrid nanofluid in double annulus separated by a thin rotating partition under magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 582, 170974 (2023)
R. Bellman, H. Kagiwada, R. Kalaba, Quasilinearization, system identification and prediction. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 327–334 (1965)
P. Williams, Application of pseudospectral methods for receding horizon control. J. Guidance Control Dyn. 27, 310–314 (2004)
V. Mandelzweig, Quasilinearization method: nonperturbative approach to physical problems. Phys. Atom. Nuclei 68, 1227–1258 (2005)
S. Motsa, V. Magagula, P. Sibanda, A bivariate chebyshev spectral collocation quasilinearization method for nonlinear evolution parabolic equations. Sci. World J. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/581987
D. Srinivasacharya, S.S. Motsa, O. Surender, Numerical study of free convection in a doubly stratified non-darcy porous medium using spectral quasilinearization method. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 16, 173–183 (2015)
K. Kaladhar, K. Madhusudhan Reddy, D. Srinivasacharya, Inclined magnetic field, thermal radiation, and hall current effects on mixed convection flow between vertical parallel plates. J. Heat Transf. 141, 102501 (2019)
K. Gangadhar, D. Vijayakumar, A.J. Chamkha, T. Kannan, G. Sakthivel, Effects of Newtonian heating and thermal radiation on micropolar ferrofluid flow past a stretching surface: spectral quasi-linearization method. Heat Transf. 49, 838–857 (2020)
O.P. Meena, Mixed convection flow over a vertical cone with double dispersion and chemical reaction effects. Heat Transf. 50, 4516–4534 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaladhar, K., Mahla, R. Entropy analysis of natural convection Jeffrey fluid flow through a vertical channel with an inclined magnetic field effect under Navier-slip conditions. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 739 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04357-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04357-8