Abstract
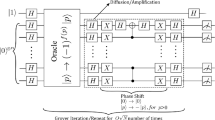
A quantum search algorithm with phase shift of π/18 is proposed to find a multiplicative inverse of an equation in an unsorted database. The unitary operator \(Q{\text{ }}\) (\(Q{\text{ = }}I_{t} U^{{ - 1}} I_{0} U\)) is operated repeatedly on the initial state with \(\left\lfloor {9\sqrt {{N \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {N M}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} M}} } \right\rfloor\) times to find a marked item successfully. At least 99.81% of the probability of success could be achieved by this proposed quantum search algorithm with time complexity \(O\left( {\sqrt {{N \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {N M}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} M}} } \right)\). Compared with four typical algorithms, the proposed search algorithm has better performance to find out a match in terms of success probability with the same time complexity \(O\left( {\sqrt {{N \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {N M}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} M}} } \right)\).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Nielsen, I.L. Chuang, Quantum Computation and Quantum Information (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000)
V.E. Korepin, Y. Xu, Quantum search algorithms. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 31, 5727–5758 (2009)
A. Pathak, Elements of Quantum Computation and Quantum Communication (CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, New York, 2013)
P.W. Shor, Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM Rev. 41, 303–332 (1999)
P.W. Shor, Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring, in Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Santa Fe, 20–22 Nov., pp 124–134 (1994)
L.K. Grover, A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search, in Proceedings of the 28th Annual ACM Symposium on the Theory of Computing, New York, pp 212–219 (1996)
L.K. Grover, Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 325–328 (1997)
C.H. Bennett, E. Bernstein, G. Brassard, U. Vazirani, Strengths and weaknesses of quantum computing. Siam J. Comput. 26, 1510–1523 (1997)
M. Boyer, G. Brassard, P. Høyer, A. Tapp, Tight bounds on quantum searching. Fortsch. Phys. Prog. Phys. 46, 493–505 (1998)
C. Zalka, Grover’s quantum searching algorithm is optimal. Phys. Rev. A 60, 2746–2751 (1999)
L.K. Grover, Quantum computers can search rapidly by using almost any transformation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4329–4332 (1998)
G.L. Long, Y.S. Li, W.L. Zhang, C.C. Tu, Dominant gate imperfection in Grover’s quantum search algorithm. Phys. Rev. A 61, 042305 (2000)
D. Biron, O. Biham, E. Biham, M. Grassl, D.A. Lidar, Generalized Grover search algorithm for arbitrary initial amplitude distribution. Phys. Rev. A 60, 2742–2745 (1999)
D. Reitzner, D. Nagaj, V. Bužek, Quantum walks. Acta Phys. Slovaca 61, 603–725 (2011)
T. Tulsi, L.K. Grover, A. Patel, A new algorithm for fixed point quantum search. Quant. Inform. Comput. 6, 483–494 (2006)
A. Younes, J. Rowe, J. Miller, Quantum search algorithm with more reliable behaviour using partial diffusion. Quant. Commun. 734, 171–174 (2006)
L.K. Grover, Fixed-point quantum search. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 150501 (2005)
H.F. Wang, S. Zhang, Y.F. Zhao, Phase matching in fixed-point quantum search algorithm. Int. J. Quant. Inform. 6, 1269–1275 (2009)
P.C. Li, S.Y. Li, Phase matching in Grover’s algorithm. Phys. Lett. A 366, 42–46 (2007)
G.L. Long, Y.S. Li, W.L. Zhang, L. Niu, Phase matching in quantum searching. Phys. Lett. A 262, 27–34 (1999)
E. Biham, O. Biham, D. Biron, M. Grassl, D.A. Lidar, D. Shapira, Analysis of generalized Grover’s quantum search algorithms using recursion equations. Phys. Rev. A 63, 5348–5353 (2000)
A.W. Harrow, A. Hassidim, S. Lloyd, Quantum algorithm for linear systems of equations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 150502 (2009)
K. Srinivasan, B.K. Behera, P.K. Panigrahi, Solving linear systems of equations by gaussian elimination method using Grover's search algorithm: an IBM quantum experience (2017)
X. Tao, S.J. Wei, J.L. Cui, J.X. Xiao, I. Arrazola, L. Lamata, X.Y. Kong, D.W. Lu, E. Solano, G.L. Long, Quantum algorithm for solving linear differential equations: theory and experiment. Phys. Rev. A 101, 032307 (2020)
K. Chakraborty, S. Maitra, Application of Grover’s algorithm to check non-resiliency of a Boolean function. Cryptogr. Commun. 8, 401–413 (2016)
H.Y. Tseng, C.W. Tsai, T. Hwang, Controlled deterministic secure quantum communication based on quantum search algorithm. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51, 2447–2454 (2012)
R.H. Shi, M. Zhang, Privacy-preserving quantum sealed-bid auction based on Grover’s search algorithm. Sci. Rep. 9, 7626 (2019)
A.Y. Wei, P. Naik, A.W. Harrow, J. Thaler, Quantum algorithms for jet clustering. Phys. Rev. D 101, 094015 (2020)
S. Yamashita, How to utilize a Grover search in general programming. Laser Phys. 16, 730–734 (2006)
H.F. Wang, S. Zhang, Y.F. Zhao, K.H. Yeon, Quantum mechanical algorithm for solving quadratic residue equation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 48, 3262–3267 (2009)
D. Reitzner, M. Ziman, Two notes on Grover’s search: programming and discriminating. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 129, 128 (2014)
B. Broda, Quantum search of a real unstructured database. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 131, 38 (2016)
F. Morikoshi, Problem-solution symmetry in Grover’s quantum search algorithm. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50, 1858–1867 (2011)
N. Bhattacharya, H.B. van Linden van den Heuvell, R.J.C. Spreeuw, Implementation of quantum search algorithm using classical Fourier optics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, (2002)
J. Böhm, M. Bellec, F. Mortessagne, U. Kuhl, S. Barkhofen, S. Gehler, H.J. Stockmann, I. Foulger, S. Cnutzmann, G. Tanner, Microwave experiments simulating quantum search and directed transport in artificial grapheme. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 110501 (2015)
I.L. Chuang, N. Gershenfeld, M. Kubinec, Experimental implementation of fast quantum searching. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 3408 (1997)
J.A. Jones, M. Mosca, R.H. Hansen, Implementation of a quantum search algorithm on a quantum computer. Nature 393, 344–346 (1998)
J.P. Home, D. Hanneke, J.D. Jost, J.M. Amini, D. Leibfried, D.J. Wineland, Complete methods set for scalable ion trap quantum information processing. Science 325, 1227–1230 (2009)
C. Figgatt, D. Maslov, K.A. Landsman, N.M. Linke, S. Debnath, C. Monroe, Complete 3-qubit Grover search on a programmable quantum computer. Nat. Commun. 8, 1918 (2017)
W.X. Zhang, K.Y. Cheng, C. Wu, Y. Wang, H.Q. Li, X.D. Zhang, Implementing quantum search algorithm with metamaterials. Adv. Mater. 30, 1703986 (2018)
H. Sakhouf, M. Daoud, R.A. Laamara, Implementation of Grover’s search algorithm in the QED circuit for two superconducting qubits. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 3436–3448 (2020)
C. Cafaro, S. Mancini, On Grover’s search algorithm from a quantum information geometry viewpoint. Phys. A 391, 1610–1625 (2012)
C. Cafaro, Geometric algebra and information geometry for quantum computational software. Phys. A 470, 154 (2017)
G. Hardy, E. Wright, An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers, 6th edn. (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2008)
X. Li, P.C. Li, A fixed-phase quantum search algorithm with more flexible behavior. J. Quant. Inform. Sci. 2, 28–34 (2012)
Z. Pawlak, Rough sets. Int. J. Comput. Inform. Sci. 11, 341–356 (1982)
S.J. Hong, Data mining. Fut. Gener. Comput. Syst. 13, 95–97 (1997)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61462061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix A
In this appendix, Eq. (12) can be deduced. The required number of iterations can be calculated as follows,
where \({\text{CI}}(x)\) represents the integer closest to x.
Let \(\sin ^{2} \theta = {M \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {M N}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} N} = \lambda\), Eq. (24) becomes
Equation (24) implies that \({\text{R}} \le \left\lfloor {{\pi \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\pi {4\theta }}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {4\theta }}} \right\rfloor\)(26), and assume that \(M \le {N \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {N 2}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} 2}\) for the moment, the following condition would be obtained.
Combining Eq. (26) with Eq. (27), the upper bound on the number of iteration required is
In conclusion, according to Eqs. (25) and (28), (12)\(R = {\text{CI}}\left( {\frac{{\arccos \sqrt \lambda }}{{2\arcsin \sqrt \lambda }}} \right){\text{ = }}\left\lfloor {\frac{\pi }{4}\sqrt {\frac{N}{M}} } \right\rfloor\) in Sect. 2.1 can be taken.
Appendix B
In this appendix, a derivation is given to Eq. (17) in Sec. 3. By observing that \(M \ll N\), we have \(\sin \theta = \sqrt {{M \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {M N}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} N}} \approx \theta\), and \(\arcsin (\sin ({\phi \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\phi 2}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} 2})\sin \theta ) \approx \sin ({\phi \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\phi 2}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} 2})\sin \theta\), so the following form can be taken,
when \(\phi = {\pi \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\pi {18}}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {18}}\), Eq. (29) becomes
So Eq. (17) can be deduced.
Appendix C
In this appendix, calculation expressions about the success probability and the number of iterations of five algorithmic schemes are shown as follows (Table
2).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, YF., Duan, LZ., Qiu, TR. et al. Multiplicative inverse with quantum search algorithm under π/18 phase rotation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136, 734 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01704-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01704-5