Abstract
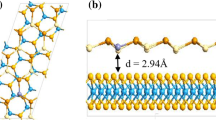
Devising the two-dimensional (2D) structures of low-cost and non-toxic semiconductors for nanoscale technological applications has attracted substantial interest since the past decade. In this work, we design two types of ZnO monolayers derived from polar 0001-plane and nonpolar \(11\overline{2}0\)-plane of the wurtzite structure, and explore their physical properties using the first-principles approach. Both ZnO\(\left( {11\overline{2}0} \right)\) and ZnO(0001) monolayers exhibited cohesive and formation energies comparable to that of the stable wurtzite-structured ZnO. However, both monolayers exhibited substantially different electronic structures of band gaps 1.56 eV for single-layered ZnO\(\left( {11\overline{2}0} \right)\) and 0.71 eV for ZnO(0001) monolayer. The edges of the valence and conduction bands of ZnO\(\left( {11\overline{2}0} \right)\) monolayer are formed by parabolic bands, whereas almost flat band gap edges have been seen for ZnO(0001) surface. As a result, charge carriers associated with ZnO\(\left( {11\overline{2}0} \right)\) monolayer exhibited relatively lighter effective mass than ZnO(0001) monolayer. The ZnO(0001) monolayer exhibited symmetrical bond lengths and subsequently isotropic optical spectra, whereas asymmetrical bond lengths and anisotropic subsequent optical spectra have been recorded for ZnO\(\left( {11\overline{2}0} \right)\) monolayer. The optical absorption recorded for the designed monolayers has been found higher than their bulk counterpart. The refraction spectra indicated these monolayers of transparent behavior over a significant range of the electromagnetic spectrum. These fascinating features of ZnO\(\left( {11\overline{2}0} \right)\) and ZnO(0001) monolayers suggest them suitable for applications in electronic and optoelectronic devices.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors' comment: The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.]
References
S. Zhang, M. Xie, F. Li, Z. Yan et al., Semiconducting group 15 monolayers: a broad range of band gaps and high carrier mobilities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55(5), 1666–1669 (2016)
V. Sorkin, Y. Cai, Z. Ong, G. Zhang et al., Recent advances in the study of phosphorene and its nanostructures. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 42(1), 1–82 (2017)
S.C. Dhanabalan, J.S. Ponraj, H. Zhang, Q. Bao, Present perspectives of broadband photodetectors based on nanobelts, nanoribbons, nanosheets and the emerging 2D materials. Nanoscale 8(12), 6410–6434 (2016)
K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, D. Jiang et al., Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306(5696), 666–669 (2004)
D. Tyagi, H. Wang, W. Huang, L. Hu et al., Recent advances in two-dimensional materials based sensing technology towards health and environmental applications. Nanoscale 5, 67 (2020)
C.E.N.E.R. Rao, A.E.K. Sood, K.E.S. Subrahmanyam, A. Govindaraj, Graphene: the new two-dimensional nanomaterial. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48(42), 7752–7777 (2009)
L.C. Gomes, A. Carvalho, A.C. Neto, Vacancies and oxidation of two-dimensional group-IV monochalcogenides. Phys. Rev. B 94(5), 054103 (2016)
H. Zheng, X.-B. Li, N.-K. Chen, S.-Y. Xie et al., Monolayer II-VI semiconductors: A first-principles prediction. Phys. Rev. B 92(11), 115307 (2015)
H. Liu, A.T. Neal, Z. Zhu, Z. Luo et al., Phosphorene: an unexplored 2D semiconductor with a high hole mobility. ACS Nano 8(4), 4033–4041 (2014)
L. Li, Y. Yu, G.J. Ye, Q. Ge et al., Black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9(5), 372–377 (2014)
Q. Guo, A. Pospischil, M. Bhuiyan, H. Jiang et al., Black phosphorus mid-infrared photodetectors with high gain. Nano Lett. 16(7), 4648–4655 (2016)
C. Jin, F. Lin, K. Suenaga, S. Iijima, Fabrication of a freestanding boron nitride single layer and its defect assignments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102(19), 195505 (2009)
L. Wang, B. Wu, J. Chen, H. Liu et al., Monolayer hexagonal boron nitride films with large domain size and clean interface for enhancing the mobility of graphene-based field-effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 26(10), 1559–1564 (2014)
Y. Lin, T.V. Williams, J.W. Connell, Soluble, exfoliated hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1(1), 277–283 (2010)
Q.H. Wang, K. Kalantar-Zadeh, A. Kis, J.N. Coleman et al., Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7(11), 699–712 (2012)
D.J. Late, Y.-K. Huang, B. Liu, J. Acharya et al., Sensing behavior of atomically thin-layered MoS2 transistors. ACS Nano 7(6), 4879–4891 (2013)
C.N.R. Rao, Transition metal oxides. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 40(1), 291–326 (1989)
K. Kalantar-zadeh, J.Z. Ou, T. Daeneke, A. Mitchell et al., Two dimensional and layered transition metal oxides. Appl. Mater. Today 5, 73–89 (2016)
Z. Tu, X. Hu, Elasticity and piezoelectricity of zinc oxide crystals, single layers, and possible single-walled nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 74(3), 035434 (2006)
Z. Tu, First-principles study on physical properties of a single ZnO monolayer with graphene-like structure. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 7(6), 1182–1186 (2010)
F. Claeyssens, C.L. Freeman, N.L. Allan, Y. Sun et al., Growth of ZnO thin films—experiment and theory. J. Mater. Chem. 15(1), 139–148 (2005)
H.-K. Hong, J. Jo, D. Hwang, J. Lee et al., Atomic scale study on growth and heteroepitaxy of ZnO monolayer on graphene. Nano Lett. 17(1), 120–127 (2017)
L. Chen, S. Li, Y. Cui, Z. Xiong et al., Manipulating the electronic and magnetic properties of ZnO monolayer by noble metal adsorption: a first-principles calculations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 479, 440–448 (2019)
C. Tusche, H. Meyerheim, J. Kirschner, Observation of depolarized ZnO (0001) monolayers: formation of unreconstructed planar sheets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99(2), 026102 (2007)
G. Weirum, G. Barcaro, A. Fortunelli, F. Weber et al., Growth and surface structure of zinc oxide layers on a Pd (111) surface. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(36), 15432–15439 (2010)
N. Marana, V. Longo, E. Longo, J. Martins et al., Electronic and structural properties of the (1010) and (1120) ZnO surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. A 112(38), 8958–8963 (2008)
J.-T. Luo, A.-J. Quan, Z.-H. Zheng, G.-X. Liang et al., Study on the growth of Al-doped ZnO thin films with (112 [combining macron] 0) and (0002) preferential orientations and their thermoelectric characteristics. RSC Adv. 8(11), 6063–6068 (2018)
O. Dulub, L.A. Boatner, U. Diebold, STM study of the geometric and electronic structure of ZnO (0001)-Zn, (0001)-O, (1010), and (1120) surfaces. Surf. Sci. 519(3), 201–217 (2002)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, T. Alshahrani, R. Ahmed et al., Exploring optoelectronic properties of ZnO monolayers originated from NaCl-and GeP-like polymorphs: a first-principles study. Results Phys. 19, 103367 (2020)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, T. Alshahrani, R. Ahmed et al., Investigations of thermoelectric properties of ZnO monolayers from the first-principles approach. Physica E 126, 114444 (2021)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, T. Alshahrani, R. Ahmed et al., Devising square-and hexagonal-shaped monolayers of ZnO for nanoscale electronic and optoelectronic applications. Sol. Energy 211, 920–927 (2020)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, T. Al-shahrani, S. Al-Qaisi et al., First-principles investigations of ZnO monolayers derived from zinc-blende and 5–5 phases for advanced thermoelectric applications. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 149, 109780 (2020)
M. Wu, D. Sun, C. Tan, X. Tian et al., Al-doped ZnO monolayer as a promising transparent electrode material: a first-principles study. Materials 10(4), 359 (2017)
A. Es-Smairi, N. Fazouan, E.H. Atmani, Enhanced optical and thermoelectric properties of ZnS monolayer and stacked bilayer compared with bulk. Mater. Res. Express 6(12), 125047 (2019)
S. Xu, Z.L. Wang, One-dimensional ZnO nanostructures: solution growth and functional properties. Nano Res. 4(11), 1013–1098 (2011)
W. Sun, Y. Li, J.K. Jha, N.D. Shepherd et al., Effect of surface adsorption and non-stoichiometry on the workfunction of ZnO surfaces: a first principles study. J. Appl. Phys. 117(16), 165304 (2015)
C. Qin, Y. Gu, X. Sun, X. Wang et al., Structural dependence of piezoelectric size effects and macroscopic polarization in ZnO nanowires: a first-principles study. Nano Res. 8(6), 2073–2081 (2015)
J. Wang, X. Chen, S. Wu, D. Bai et al., Stability and band offsets of nonpolar ZnO on (001) LaAlO3. Vacuum 150, 29–34 (2018)
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(18), 3865 (1996)
Blaha, P., K. Schwarz, G. Madsen, D. Kvasnicka, et al.: wien2k. An augmented plane wave+ local orbitals program for calculating crystal properties, 2001.
B.U. Haq, R. Ahmed, A. Shaari, F.E.H. Hassan et al., Study of wurtzite and zincblende GaN/InN based solar cells alloys: first-principles investigation within the improved modified Becke-Johnson potential. Sol. Energy 107, 543–552 (2014)
B.U. Haq, A. Afaq, G. Abdellatif, R. Ahmed et al., First principles study of scandium nitride and yttrium nitride alloy system: prospective material for optoelectronics. Superlattices Microstruct. 85, 24–33 (2015)
B.U. Haq, M.B. Kanoun, R. Ahmed, M. Bououdina et al., Hybrid functional calculations of potential hydrogen storage material: complex dimagnesium iron hydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 39(18), 9709–9717 (2014)
B. Ul Haq, R. Ahmed, S. Goumri-Said, A. Shaari et al., Electronic structure engineering of ZnO with the modified Becke-Johnson exchange versus the classical correlation potential approaches. Phase Trans. 86(12), 1167–1177 (2013)
B.U. Haq, R. Ahmed, S. Goumri-Said, DFT characterization of cadmium doped zinc oxide for photovoltaic and solar cell applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 130, 6–14 (2014)
B.U. Haq, R. Ahmed, J.Y. Rhee, A. Shaari et al., Composition-induced influence on the electronic band structure, optical and thermoelectric coefficients of the highly mismatched GaNSb alloy over the entire range: a DFT analysis. J. Alloy. Compd. 693, 1020–1027 (2017)
B.U. Haq, R. Ahmed, M. Mohamad, A. Shaari et al., Engineering of highly mismatched alloy with semiconductor and semi-metallic substituent’s for photovoltaic applications. Curr. Appl. Phys. 17(2), 162–168 (2017)
D. Koller, F. Tran, P. Blaha, Merits and limits of the modified Becke-Johnson exchange potential. Phys. Rev. B 83(19), 195134 (2011)
D. Koller, F. Tran, P. Blaha, Improving the modified Becke-Johnson exchange potential. Phys. Rev. B 85(15), 155109 (2012)
F. Tran, P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, Band gap calculations with Becke-Johnson exchange potential. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 19(19), 196208 (2007)
F.-B. Zheng, C.-W. Zhang, P.-J. Wang, H.-X. Luan, First-principles prediction of the electronic and magnetic properties of nitrogen-doped ZnO nanosheets. Solid State Commun. 152(14), 1199–1202 (2012)
D. Fang, A. Rosa, R. Zhang, T. Frauenheim, Theoretical exploration of the structural, electronic, and magnetic properties of ZnO nanotubes with vacancies, antisites, and nitrogen substitutional defects. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(13), 5760–5766 (2010)
M. Topsakal, S. Cahangirov, E. Bekaroglu, S. Ciraci, First-principles study of zinc oxide honeycomb structures. Phys. Rev. B 80(23), 235119 (2009)
U.H. Bakhtiar, R. Ahmed, R. Khenata, M. Ahmed et al., A first-principles comparative study of exchange and correlation potentials for ZnO. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16(4), 1162–1169 (2013)
J.E. Jaffe, J.A. Snyder, Z. Lin, A.C. Hess, LDA and GGA calculations for high-pressure phase transitions in ZnO and MgO. Phys. Rev. B 62(3), 1660 (2000)
C. Li, W. Guo, Y. Kong, H. Gao, First-principles study of the dependence of ground-state structural properties on the dimensionality and size of ZnO nanostructures. Phys. Rev. B 76(3), 035322 (2007)
R. Ramprasad, H. Zhu, P. Rinke, M. Scheffler, New perspective on formation energies and energy levels of point defects in nonmetals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(6), 066404 (2012)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, A. Laref, R. Ahmed et al., Dimensionality reduction of germanium selenide for high-efficiency thermoelectric applications. Ceram. Int. 45(12), 15122–15127 (2019)
B. Ul Haq, S. AlFaify, A. Laref, Exploring novel flat-band polymorphs of single-layered germanium sulfide for high-efficiency thermoelectric applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 123(30), 18124–18131 (2019)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, A. Laref, R. Ahmed et al., Optoelectronic properties of new direct bandgap polymorphs of single-layered Germanium sulfide. Ceram. Int. 45(14), 18073–18078 (2019)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, A. Laref, Investigations of the optoelectronic properties of novel polymorphs of single-layered Tin-Sulfide for nanoscale optoelectronic and photovoltaic applications. Sol. Energy 186, 29–36 (2019)
Z.-Y. Hu, K.-Y. Li, Y. Lu, Y. Huang et al., High thermoelectric performances of monolayer SnSe allotropes. Nanoscale 9(41), 16093–16100 (2017)
H. Guo, Y. Zhao, N. Lu, E. Kan et al., Tunable magnetism in a nonmetal-substituted ZnO monolayer: a first-principles study. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(20), 11336–11342 (2012)
J. Ren, H. Zhang, X. Cheng, Electronic and magnetic properties of all 3d transition-metal-doped ZnO monolayers. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 113(19), 2243–2250 (2013)
L. Chen, A. Wang, Z. Xiong, S. Shi et al., Effect of hole doping and strain modulations on electronic structure and magnetic properties in ZnO monolayer. Appl. Surf. Sci. 467, 22–29 (2019)
X. Jia, Q. Hou, Z. Xu, L. Qu, Effect of Ce doping on the magnetic and optical properties of ZnO by the first principle. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 465, 128–135 (2018)
R. Chowdhury, S. Adhikari, P. Rees, Optical properties of silicon doped ZnO. Phys. B 405(23), 4763–4767 (2010)
F.-G. Kuang, X.-Y. Kuang, S.-Y. Kang, M.-M. Zhong et al., Ab initio study on physical properties of wurtzite, zincblende, and rocksalt structures of zinc oxide using revised functionals. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 31, 700–708 (2015)
L. Xu, M. Yang, S.J. Wang, Y.P. Feng, Electronic and optical properties of the monolayer group-IV monochalcogenides M X (M= Ge, Sn; X= S, Se, Te). Phys. Rev. B 95(23), 235434 (2017)
F. Wooten, Optical Properties of Solids (Academic Press, New York, 2013).
S. Shabbir, A. Shaari, B.U. Haq, R. Ahmed et al., Investigations of novel polymorphs of ZnO for optoelectronic applications. Optik 206, 164285 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through the General Research Program under Grant No. G.R.P/67/42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ul Haq, B., AlFaify, S. & Ahmed, R. First-principles investigations of optoelectronic properties of ZnO\(\left( {11\overline{2}0} \right)\) and ZnO(0001) monolayers. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136, 251 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01197-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01197-2