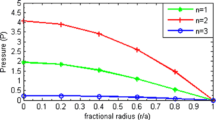
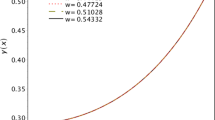
Abstract
Static spherically symmetric solutions of the Einstein’s field equations in isotropic coordinates representing perfect fluid matter distributions from Newtonian potential–density pairs are investigated. The approach is illustrated with three simple examples based on the potential–density pairs corresponding to a harmonic oscillator (homogeneous sphere), the well-known Plummer model and a massive spherical dark matter halo model with a logarithmic potential. Moreover, the geodesic circular motion of test particles around such structures is studied. The stability of the orbits against radial perturbations is also analyzed using an extension of the Rayleigh criteria of stability of a fluid in rest in a gravitational field. The models considered satisfy all the energy conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.I. Wilkinson, J. Kleyna, N.W. Evans, G. Gilmore, MNRAS 330, 778 (2002)
A.T. Bajkova, V.V. Bobylev, Astron. Lett. 42(9), 567 (2016)
V.V. Bobylev, A.T. Bajkova, A.O. Gromov, Astron. Lett. 43(4), 241 (2017)
W. Dehnen, MNRAS 265, 250 (1993)
S. Tremaine et al., Astron. J. 107, 634 (1994)
H.C. Plummer, MNRAS 71, 460 (1911)
L. Hernquist, Astrophys. J. 356, 359 (1990)
J.F. Navarro, C.S. Frenk, S.D.M. White, Astrophys. J. 462, 563 (1996)
M.S.R. Delgaty, K. Lake, Comput. Phys. Commun. 115, 395 (1998)
H. Stephani, D. Kramer, M. McCallum, C. Hoenselaers, E. Herlt, Exact Solutions of Einsteins’s Field Equations (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2003)
D. Vogt, P.S. Letelier, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 402, 1313 (2010)
D. Vogt, P.S. Letelier, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 406, 2689 (2010)
P.H. Nguyen, M. Lingam, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 436(3), 2014 (2013)
G. García-Reyes, Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 49(3), 1–13 (2017)
G. García-Reyes, K.A. Hernández-Gómez, Int. J. Mod. Phys. 27(07), 1850068-1 (2018)
R.C. Tolman, Relativity, Thermodynamics, and Cosmology (Oxford University Press, London, 1934)
YaB Zeldovich, J.D. Novikov, Relativistic Astrophysics, vol. I: Stars and Relativity (University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1971)
T. Matos, D. Núñez, R.A. Sussman, Class. Quant. Gravity 21(22), 5275 (2004)
L.D. Landau, E.M. Lifshitz, Classical Theory of Fields (Pergamon, Oxford, 1976)
L.D. Landau, E.M. Lifshitz, Fluid Mechanics (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1989)
A.H. Taub, Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 10, 301 (1978)
J.L. Synge, Relativity: The General Theory (NorthHolland, Amsterdam, 1966)
C.W. Misner, K.S. Thorne, J.A. Wheeler, Gravitation (Freeman, San Francisco, 1973)
S.W. Hawking, G.F.R. Ellis, The Large-Scale Structure of Space-Time (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1973)
B. Schutz, A First Course in General Relativity, 2nd edn. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2009)
P. Kustaanheimo, B. Qvist, Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 30(4), 663 (1998)
Lord Rayleigh, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 93, 148 (1917)
P.S. Letelier, Phys. Rev. D 68, 104002 (2003)
G. Darmois, Mémorial des Sciences Mathématiques (Gauthier-Villars, Paris, 1927). Fasc. 25
W.B. Bonnor, P.A. Vickers, Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 13(1), 29 (1981)
M. Miyamoto, R. Nagai, Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 27, 533 (1975)
R. Nagai, M. Miyamoto, Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 28, 1 (1976)
H.A. Buchdahl, Astrophys. J. 140, 1512 (1964)
J. Binney, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 196, 455 (1981)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Reyes, G. Poisson type relativistic perfect fluid spheres. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 931 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00948-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00948-x