Abstract.
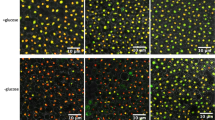
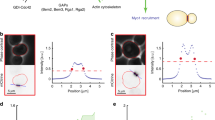
Regulation of organelle size and shape is a poorly understood but fascinating subject. Several theoretical studies were reported on Golgi size regulation, but a combination of experimental and theoretical approaches is rare. In combination with the quantitative microscopy and a coarse-grained simulation model, we have developed a technique to gain insights into the functions of potential regulators of Golgi size in budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. To validate our method, we tested wild-type and arf1\(\Delta\) strain harboring early and late Golgi cisternae labeled with green and red fluorescent fusions. Our concentration-dependent maturation model prediction concurs with most of the experimental results for both wild-type and arf1\(\Delta\) strains. Decisive match of simulation and experimental data provide insight into such specific factor's function in regulating the Golgi size. Details of the complex multifactorial network of Golgi size regulation can be deciphered in the future using a similar combination of quantitative microscopy and in silico model.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Dmitrieff, M. Rao, P. Sens, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 15692 (2013)
Q. Vagne, P. Sens, Biophys. J. 114, 947 (2018)
E. Losev et al., Nature 441, 1002 (2006)
K. Matsuura-Tokita et al., Nature 441, 1007 (2006)
M. Bhave et al., J. Cell Sci. 127, 250 (2014)
J. Kuhnle et al., Biophys. J. 98, 2839 (2010)
Y. Suda, A. Nakano, Traffic 13, 505 (2012)
S. Wooding, H.R. Pelham, Mol. Biol. Cell 9, 2667 (1998)
J. Bigay et al., Nature 426, 563 (2003)
R. Beck et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 11731 (2008)
J.B. Moseley, B.L. Goode, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 70, 605 (2006)
J.G. Donaldson, Biochem. J. 414, (2008)
E.C. Gaynor et al., Mol. Biol. Cell 9, 653 (1998)
Y. Kondo et al., Cell Struct. Funct. 37, 141 (2012)
M. Krauss et al., J. Biol. Chem. 283, 27717 (2008)
R. Lundmark et al., Biochem. J. 414, 189 (2008)
W. Nakai et al., Mol. Biol. Cell 24, 2570 (2013)
R.A. Kahn et al., Biochem. Soc. Trans. 33, 1269 (2005)
A. Wach et al., Yeast 10, 1793 (1994)
J. Kunz et al., Cell 73, 585 (1993)
R.D. Gietz, R.A. Woods, Methods Enzymol. 350, 87 (2002)
A.T. Hammond, B.S. Glick, Traffic 1, 935 (2000)
B.J. Bevis et al., Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 750 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
The EPJ Publishers remain neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iyer, P., Sutradhar, S., Paul, R. et al. A novel combinatorial approach of quantitative microscopy and in silico modeling deciphers Arf1-dependent Golgi size regulation. Eur. Phys. J. E 42, 154 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2019-11920-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2019-11920-x