Abstract.
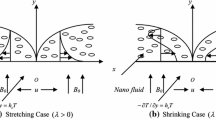
The present study is dedicated to analyze the dual-nature solutions of the axisymmetric flow of a magneto-hydrodynamics (MHD) nanofluid over a permeable shrinking sheet. In those phenomena where the fluid flow is due to the shrinking surface, some reverse behaviors of the flow arise because of vorticity effects. Despite of heat transfer analysis, the main purpose of the present study is to attain the solutions of the complex nature problem that appear in reverse flow phenomena. Thermophysical properties of both base fluid (water) and nanoparticles (copper) are also taken into account. By means of similarity transformation, partial differential equations are converted into a system of coupled nonlinear ordinary differential equations and then solved via the Runge-Kutta method. These results are divided separately into two cases: the first one is the unidirectional shrinking along the surface (m = 1) and the other one is for axisymmetric shrinking phenomena (m = 2) . To enhance the thermal conductivity of base fluid, nanoparticle volume fractions (\(0\le \phi\le 0.2\)) are incorporated within the base fluid. The numerical investigation explores the condition of existence, non-existence and the duality of similarity solution depends upon the range of suction parameter (S) and Hartmann number (M). The reduced skin friction coefficient and local Nusselt number are plotted to analyze the fluid flow and heat transfer at the surface of the shrinking sheet. Streamlines and isotherms are also plotted against the engineering control parameters to analyze the flow behavior and heat transfer within the whole domain. Throughout this analysis it is found that both nanoparticle volume fraction and Hartmann number are increasing functions of both skin friction coefficient and Nusselt number.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.U.S. Choi, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, in International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, San Francisco, USA, ASME, FED 231/MD, Vol. 66 (1995) pp. 99--105
L. Cheng, Recent Patents Engin. 3, 1 (2009)
J. Buongiorno, ASME J. Heat Transfer 128, 240 (2006)
M. Miklavcic, C.Y. Wang, Q. Appl. Math. 64, 283 (2006)
C.Y. Wang, Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 43, 377 (2008)
Y.Y. Lok, A. Ishak, I. Pop, Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 21, 61 (2011)
K. Bhattacharyya, S. Mukhopadhyay, G.C. Layek, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 54, 302 (2011)
K. Bhattacharyya, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 38, 917 (2011)
N.C. Rosca, T. Grason, I. Pop, Sains Malaysiana 41, 1271 (2012)
D.A. Nield, A.V. Kuznetsov, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 52, 5792 (2009)
A.V. Kuznetsov, D.A. Nield, Int. J. Thermal Sci. 50, 712 (2011)
W.A. Khan, I. Pop, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 53, 2477 (2010)
N. Bachok, A. Ishak, I. Pop, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 55, 2101 (2012)
A.M. Rohni, S. Ahmad, A.I. Ismail, I. Pop, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 43, 75 (2013)
S.K. Nandy, T.R. Mahapatra, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 64, 1091 (2013)
Rizwan Ul Haq, Zakia Hammouch, Waqar Ahmed Khan, Thermal Science, DOI:10.2298/TSCI141102148H (2015)
N.F.M. Noor, Rizwan Ul Haq, S. Nadeem, I. Hashim, Meccanica 50, 2007 (2015)
Wubshet Ibrahim, Rizwan Ul Haq, J. Brazil. Soc. Mech. Sci. Engin., DOI:10.1007/s40430-015-0347-z (2015)
W.A. Khan, Z.H. Khan, Rizwan Ul Haq, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 86 (2015)
Rizwan Ul Haq, S. Nadeem, Z.H. Khan, N.F.M. Noor, Physica E 73, 45 (2015)
B.K. Dutta, P. Roy, A.S. Gupta, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 12, 89 (1985)
T. Ray Mahapatra, A.S. Gupta, Heat Mass Transfer 38, 517 (2002)
N.F.M. Noor, S.A. Kechil, I. Hashim, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 15, 144 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ul Haq, R., Rajotia, D. & Noor, N.F.M. Thermophysical effects of water driven copper nanoparticles on MHD axisymmetric permeable shrinking sheet: Dual-nature study. Eur. Phys. J. E 39, 33 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2016-16033-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2016-16033-6