Abstract.
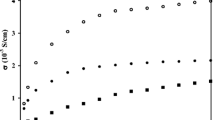
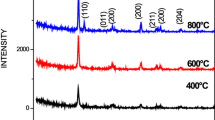
In the present work, we developed a new kind of electrorheological (ER) materials, metal cations modified amorphous TiO2 gels. The static yield stress of Sn4+ modified amorphous TiO2 gel based ER fluid with a volume fraction Φ = 38% reaches 26.2 kPa at E = 3.5 kV/mm. The result shows that metal cations can significantly enhance the ER activity of amorphous TiO2 gels. We then proposed a novel ER effect mechanism (metal cations enhanced polarization mechanism) to clarify the experimental results. We believe that it is the metal cations that enhanced the polarization of the polar groups (-OH) which results in the corresponding enhancement of the interfacial polarization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Block, J.P. Kelly, J. Phys. D 21, 1661 (1988).
S.P. Couter, K.D. Weiss, J.D. Carlson, J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 4, 248 (1993).
T. Hao, Adv. Mater. 13, 1847 (2001).
Y. Tian, Y.G. Meng, S.Z. Wen, J. Appl. Phys. 90, 493 (2001).
Y.L. Zhang, K.Q. Lu, G.H. Rao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 888 (2002).
X.P. Zhao, X. Duan, Mater. Lett. 54, 348 (2002).
T.C. Halsey, Science 258, 761 (1992).
M. Parthasarathy, D. Klingenberg, J. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 17, 57 (1996).
T. Hao, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 206, 240 (1998).
W.J. Wen, X.X. Huang, S.H. Yang, K.Q. Lu, P. Sheng, Nature Mater. 2, 727 (2003).
S. Ahuja, T.R.N. Kutty, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 97, 99 (1996).
T.R.N. Kutty, P. Padmini, Mat. Res. Bull. 27, 945 (1992).
S.M. Huang, R.G. Green, A. Plaskowski, IEEE Trans. 37, 368 (1988).
Ni, Ershan, Dielectric Measurement (Scientific Press, Beijing, 1981) p. 63 (in Chinese).
K. Negita, Y. Osawa, Phys. Rev. E. 52, 1934 (1995).
C. Boissy, C.W. Wu, Y. Fahmy, H. Conrad, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 14-16, 1775 (1999).
F.A. Cotton, G. Wilkinson, Basic Inorganic Chemistry (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1976).
Y.K. Wen, J. Shao, Chin. Sci. Bull. 3, 39 (1997).
F.Q. Sun, G.Y. Jiang, Z.Z. Lian, J. Teach. Coll. Univ. 23, 42 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Q., Yuan Zhao, B., Fang, C. et al. An enhanced polarization mechanism for the metal cations modified amorphous TiO2 based electrorheological materials. Eur. Phys. J. E 17, 63–67 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2004-10108-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2004-10108-y