Abstract
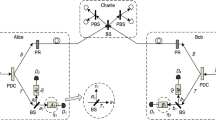
The performance degradation of reference-frame-independent measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution (RFI-MDI-QKD) protocol caused by the finite key size effect impedes its practical implementation. The protocol utilizes the double-scanning method, which makes it possible to precisely estimate both the counts of single-photon pairs and the phase-flip error. This method effectively counteracts the statistical fluctuation brought on by the finite key size effect. Based on this method, we propose a scheme in this work that substitutes heralded single-photon sources (HSPS) for weak coherent sources (WCS), and we compare the performance of the two schemes by calculating the key rate. The RFI-MDI-QKD using HSPS, according to the results of the simulation, has a lower key rate than the RFI-MDI-QKD using WCS, but it also has a longer transmission distance and a more noticeable improvement in transmission distance at larger rotation angles. Thus, we demonstrate that the RFI-MDI-QKD protocol, based on the double-scanning method and using HSPS, has promising future application potential.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Author’s comment: The datasets generated during and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.]
References
H. Lo, H. Chau, Unconditional security of quantum key distribution over arbitrarily long distances. Science 283(5410), 2050–2056 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.283.5410.2050
P. Shor, J. Preskill, Simple proof of security of the bb84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(2), 441–444 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.441
D. Mayers, Unconditional security in quantum cryptography. J. ACM 48(3), 351–406 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1145/382780.382781
R. Renner, Security of quantum key distribution. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 6(1), 1–127 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219749908003256
C.H. Bennett, G. Brassard, in Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing (IEEE, Bangalore, India, 1984), pp. 175–179
S. Wang, W. Chen, J.-F. Guo, Z.-Q. Yin, H.-W. Li, Z. Zhou, G.-C. Guo, Z.-F. Han, 2 GHz clock quantum key distribution over 260 km of standard telecom fiber. Opt. Lett. 37, 1008–1010 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.37.001008
T. Sasaki, Y. Yamamoto, M. Koashi, Practical quantum key distribution protocol without monitoring signal disturbance. Nature 509, 475 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13303
M. Lucamarini, Z.L. Yuan, J.F. Dynes, A.J. Shields, Overcoming the rate-distance limit of quantum key distribution without quantum repeaters. Nature (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0066-6
N. Lutkenhaus, M. Jahma, Quantum key distribution with realistic states: photon-number statistics in the photon-number splitting attack. New J. Phys. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/4/1/344
X. Wang, Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.230503
H. Lo, X. Ma, K. Chen, Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.230504
H.-K. Lo, M. Curty, B. Qi, Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.130503
S.L. Braunstein, S. Pirandola, Side-channel-free quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.130502
Z.-W. Yu, Y.-H. Zhou, X.-B. Wang, Statistical fluctuation analysis for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with three-intensity decoy-state method. Phys. Rev. A (2015). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.91.032318
Y.-H. Zhou, Z.-W. Yu, X.-B. Wang, Making the decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution practically useful. Phys. Rev. A (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.93.042324
H.-L. Yin, T.-Y. Chen, Z.-W. Yu, H. Liu, L.-X. You, Y.-H. Zhou, S.-J. Chen, Y. Mao, M.-Q. Huang, W.-J. Zhang, H. Chen, M.J. Li, D. Nolan, F. Zhou, X. Jiang, Z. Wang, Q. Zhang, X.-B. Wang, J.-W. Pan, Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution over a 404 km optical fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.190501
C.-H. Zhang, C.-M. Zhang, G.-C. Guo, Q. Wang, Biased three-intensity decoy-state scheme on the measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution using heralded single-photon sources. Opt. Express 26(4), 4219–4229 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.26.004219
Y. Cao, Y.-H. Li, K.-X. Yang, Y.-F. Jiang, S.-L. Li, X.-L. Hu, M. Abulizi, C.-L. Li, W. Zhang, Q.-C. Sun, W.-Y. Liu, X. Jiang, S.-K. Liao, J.-G. Ren, H. Li, L. You, Z. Wang, J. Yin, C.-Y. Lu, X.-B. Wang, Q. Zhang, C.-Z. Peng, J.-W. Pan, Long-distance free-space measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 260503 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.125.260503
X.-Y. Zhou, H.-J. Ding, C.-H. Zhang, J. Li, C.-M. Zhang, Q. Wang, Experimental three-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with uncharacterized sources. Opt. Lett. 45(15), 4176–4179 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.398993
H.-J. Ding, J.-Y. Liu, X.-Y. Zhou, C.-H. Zhang, J. Li, Q. Wang, Improved finite-key security analysis of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution against a trojan-horse attack. Phys. Rev. Appl. 19, 044022 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.19.044022
Y. Li, Z.-Q. Sun, P.-Y. Li, Z.-H. Li, J.-P. Wang, L. Zhou, H.-Q. Ma, Polarization and orbital angular momentum coupling for high-dimensional measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution protocol. Quantum Inf. Process. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03886-6
A. Laing, V. Scarani, J.G. Rarity, J.L. O’Brien, Reference-frame-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.82.012304
Z.-Q. Yin, S. Wang, W. Chen, H.-W. Li, G.-C. Guo, Z.-F. Han, Reference-free-independent quantum key distribution immune to detector side channel attacks. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(5), 1237–1244 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0726-2
C. Wang, X.-T. Song, Z.-Q. Yin, S. Wang, W. Chen, C.-M. Zhang, G.-C. Guo, Z.-F. Han, Phase-reference-free experiment of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.160502
H. Liu, J. Wang, H. Ma, S. Sun, Polarization-multiplexing-based measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution without phase reference calibration. Optica 5(8), 902–909 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/OPTICA.5.000902
Z. Li, H. Liu, J. Wang, S. Yang, T. Dou, W. Qu, F. Zhou, Y. Huang, Z. Sun, Y. Han, G. Miao, H. Ma, Reference-frame-independent measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with mismatched-basis statistics. Opt. Lett. 45(22), 6334–6337 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.403481
F.-Y. Lu, Z.-Q. Yin, G.-J. Fan-Yuan, R. Wang, H. Liu, S. Wang, W. Chen, D.-Y. He, W. Huang, B.-J. Xu, G.-C. Guo, Z.-F. Han, Efficient decoy states for the reference-frame-independent measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 101, 052318 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.101.052318
J.-R. Zhu, C.-M. Zhang, Q. Wang, Reference-frame-independent measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with imperfect sources. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 54(14), 145501 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6455/ac0c05
M. Curty, F. Xu, W. Cui, C.C.W. Lim, K. Tamaki, H.-K. Lo, Finite-key analysis for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4732
L. Sheridan, T.P. Le, V. Scarani, Finite-key security against coherent attacks in quantum key distribution. New J. Phys. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/12/12/123019
C. Wang, Z.-Q. Yin, S. Wang, W. Chen, G.-C. Guo, Z.-F. Han, Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution robust against environmental disturbances. Optica 4(9), 1016–1023 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/OPTICA.4.001016
C. Jiang, Z.-W. Yu, X.-L. Hu, X.-B. Wang, Higher key rate of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution through joint data processing. Phys. Rev. A (2021). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.103.012402
D.C. Burnham, D.L. Weinberg, Observation of simultaneity in parametric production of optical photon pairs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 25, 84–87 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.25.84
Q. Wang, X.-B. Wang, G.-C. Guo, Practical decoy-state method in quantum key distribution with a heralded single-photon source. Phys. Rev. A (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.75.012312
Q. Wang, A. Karlsson, Performance enhancement of a decoy-state quantum key distribution using a conditionally prepared down-conversion source in the poisson distribution. Phys. Rev. A (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.76.014309
F. Xu, H. Xu, H.-K. Lo, Protocol choice and parameter optimization in decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.89.052333
Q. Wang, X.-B. Wang, Efficient implementation of the decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with heralded single-photon sources. Phys. Rev. A (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.88.052332
Q. Wang, X.-B. Wang, Simulating of the measurement-device independent quantum key distribution with phase randomized general sources. Sci. Rep. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04612
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude for financial support from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities No. 2019XD-A02, and the State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications) No. IPOC2021ZT10.
Funding
This study was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities No. 2019XD-A02, and the State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications) No. IPOC2021ZT10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LZ performed the data analyses and wrote the manuscript; ZL contributed significantly to the analysis and manuscript preparation; JW and ZS contributed to the conception of the study; YL helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions; HM approved the final submission of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Li, Z., Wang, J. et al. Improve the performance of reference-frame-independent measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with heralded single-photon sources. Eur. Phys. J. D 77, 156 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00737-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00737-y