Abstract
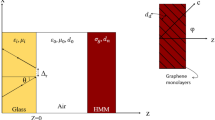
In this paper, we have studied electrically tunable Goos–Hänchen shift (GHS) for TM/p polarized light wave incident on a multilayered epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) structure containing graphene. Transfer matrix method has been used to obtain GHS for the multilayered structure composed of three slabs. We have studied the impact of changing Fermi energy, incident angle and graphene layer position on the obtained GHS. We observed that by adjusting the Fermi energy, the direction of GHS in the multilayered structure can be changed. Moreover, the imaginary part of graphene conductivity affects the magnitude and sign of GHS while real part of conductivity is closely linked with Brewster angle position. Besides, we have discussed the effect of changing permittivity of slabs and number of graphene layers on the obtained GHS. Published results for single epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) slab were recovered by using equal slab permittivity and zero conductivity for graphene. The results presented in this work will help in designing optical sensors using multilayered ENZ medium.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Author’s comment: This is a theoretical study and there are no experimental data available].
References
F. Goos, H. Hänchen, A new and fundamental experiment on total reflection. Ann. Phys. (Leipz.) 1(7–8), 333–346 (1947)
K. Artmann, Berechnung der seitenversetzung des totalreflektierten strahles. Ann. Phys. 437(1–2), 87–102 (1948)
W.I. Waseer, Q.A. Naqvi, M.J. Mughal, Goos–hänchen shift at the planar interface of NID dielectric and topological insulator. Optik 227, 166023 (2021)
K. Ali, A.A. Syed, W.I. Waseer, Q.A. Naqvi, Goos–Hanchen-effect for near-zero-index metamaterials excited by fractional dual fields. Optik 243, 167501 (2021)
W.I. Waseer, R. Parveen, Q.A. Naqvi, M.J. Mughal, Observing the Goos–Hänchen shift for a planar interface of dielectric and orthorhombic anisotropic medium. JOSA B 37(8), 2366–2371 (2020)
W.I. Waseer, Q.A. Naqvi, M.J. Mughal, Analysis of the Goos Hanchen shift for a planar interface of NID dielectric and general medium. Optik 218, 165140 (2020)
A. Othman, The general treatment of giant Goos–Hänchen shift in a slab cavity. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 14(1), 1147–1155 (2020)
A. Razaque, Q. Minhas, Q.A. Naqvi, W.I. Waseer, Analysis of the Goos–Hänchen shift for a planar dielectric-chiral interface excited by fractional dual fields. Optik 216, 164659 (2020)
I.Z.U. Haq, A.A. Syed, Q.A. Naqvi, Observing the Goos–Hänchen shift in non-integer dimensional medium. Optik 206, 164071 (2020)
Y. Guo, N.M. Singh, C.M. Das, Q. Ouyang, L. Kang, K. Li, P. Coquet, K.-T. Yong, Two-dimensional PtSe2 theoretically enhanced Goos–Hänchen shift sensitive plasmonic biosensors. Plasmonics 15, 1815–1826 (2020)
M. Gao, D. Deng, Spatial Goos–Hänchen and Imbert-Fedorov shifts of rotational 2-D finite energy airy beams. Opt. Express 28(7), 10531–10541 (2020)
D. Xu, S. He, J. Zhou, S. Chen, S. Wen, H. Luo, Goos–Hänchen effect enabled optical differential operation and image edge detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 116(21), 211103 (2020)
Y. Ding, D. Deng, X. Zhou, W. Zhen, M. Gao, Y. Zhang, Barcode encryption based on negative and positive Goos–Hänchen shifts in a graphene-ITO/TIO2/ITO sandwich structure. Opt. Express 29(25), 41164–41175 (2021)
J. Wang, H. Huang, C. Chen, H. He, Y. Dong, H. Qi, Goos–Hänchen lateral displacements at the interface between isotropic and gyroelectric media. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2013 (2013)
Y.-L. Chuang, S. Qamar, R.-K. Lee et al., Goos–Hänchen shift of partially coherent light fields in epsilon-near-zero metamaterials. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 1–6 (2016)
A.K. Geim, Graphene: status and prospects. Science 324(5934), 1530–1534 (2009)
Y. Zhang, Y.-W. Tan, H.L. Stormer, P. Kim, Experimental observation of the quantum hall effect and berry’s phase in graphene. Nature 438(7065), 201–204 (2005)
Y. Fan, N.-H. Shen, F. Zhang, Q. Zhao, H. Wu, Q. Fu, Z. Wei, H. Li, C.M. Soukoulis, Graphene plasmonics: a platform for 2D optics. Adv. Opt. Mater. 7(3), 1800537 (2019)
F.H. Koppens, D.E. Chang, F.J. García de Abajo, Graphene plasmonics: a platform for strong light-matter interactions. Nano Lett. 11(8), 3370–3377 (2011)
A.C. Neto, F. Guinea, N.M. Peres, K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, The electronic properties of graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81(1), 109 (2009)
V. Ginis, P. Tassin, T. Koschny, C.M. Soukoulis, Tunable terahertz frequency comb generation using time-dependent graphene sheets. Phys. Rev. B 91(16), 161403 (2015)
D. Abergel, V.I. Fal’ko, Optical and magneto-optical far-infrared properties of bilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. B 75(15), 155430 (2007)
L. Jiang, Q. Wang, Y. Xiang, X. Dai, S. Wen, Electrically tunable Goos–Hänchen shift of light beam reflected from a graphene-on-dielectric surface. IEEE Photonics J. 5(3), 6500108–6500108 (2013)
X. Li, P. Wang, F. Xing, X.-D. Chen, Z.-B. Liu, J.-G. Tian, Experimental observation of a giant Goos–Hänchen shift in graphene using a beam splitter scanning method. Opt. Lett. 39(19), 5574–5577 (2014)
S. Grosche, M. Ornigotti, A. Szameit, Goos–Hänchen and Imbert-Fedorov shifts for gaussian beams impinging on graphene-coated surfaces. Opt. Express 23(23), 30195–30203 (2015)
G. Xu, M. Cao, C. Liu, J. Sun, T. Pan, Tunable lateral and angular shifts of a reflected beam from a graphene-based structure. Optik 127(5), 2521–2524 (2016)
Y. Fan, N.-H. Shen, F. Zhang, Z. Wei, H. Li, Q. Zhao, Q. Fu, P. Zhang, T. Koschny, C.M. Soukoulis, Electrically tunable Goos–Hänchen effect with graphene in the terahertz regime. Adv. Opt. Mater. 4(11), 1824–1828 (2016)
C. Wang, F. Wang, R. Liang, Z. Wei, H. Meng, H. Dong, H. Cen, N. Lin, Electrically tunable Goos–Hänchen shifts in weakly absorbing epsilon-near-zero slab. Opt. Mater. Express 8(4), 718–726 (2018)
R. Peng, Z. Xiao, Q. Zhao, F. Zhang, Y. Meng, B. Li, J. Zhou, Y. Fan, P. Zhang, N.-H. Shen et al., Temperature-controlled chameleonlike cloak. Phys. Rev. X 7(1), 011033 (2017)
K.J. Manzoor, W.I. Waseer, Q.A. Naqvi, M.J. Mughal, Goos–Hänchen shift observed from stratified medium. Eur. Phys. J. D 76(5), 1–11 (2022)
N.A.F. Zambale, J.L.B. Sagisi, N.P. Hermosa, Goos-h\(\backslash \)” anchen shifts due to 2D materials with complex conductivity. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.08223 (2018)
Q. Yue, W. Zhen, Y. Ding, X. Zhou, D. Deng, Giant Goos–Hänchen shifts controlled by exceptional points in a pt-symmetric periodic multilayered structure coated with graphene. Opt. Mater. Express 11(12), 3954–3965 (2021)
W. Lin, Z. Xiao, W. Zhou, M. Ren, Z. Zheng, Graphene-assisted Goos–Hänchen shift in a planar multilayer configuration in the visible light range. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2020 (2020)
X. Zhou, S. Liu, Y. Ding, L. Min, Z. Luo, Precise control of positive and negative Goos–Hänchen shifts in graphene. Carbon 149, 604–608 (2019)
C. How Gan, Analysis of surface plasmon excitation at terahertz frequencies with highly doped graphene sheets via attenuated total reflection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101(11), 111609 (2012)
H. Tian, Y. Yang, J. Tang, L. Jiang, Y. Xiang, Graphene Tamm plasmon-induced enhanced and tunable photonic spin hall effect of reflected light in terahertz band. Results Phys. 25, 104300 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed substantially and equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Manzoor, K.J., Naqvi, Q.A. & Mughal, M.J. Electrically tunable Goos–Hänchen shift from epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) structure with graphene. Eur. Phys. J. D 76, 239 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-022-00570-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-022-00570-9